By Shantanu Kaushik
Content is data and information presented in a way that retains value for a specific set of users, depending on their requirements and considerations. In the age where everything runs via the Internet, content delivery networks (CDNs) are the basis of productive on-set services that help businesses yield maximum value from their practice.
Delivering content securely, promptly, and constantly without interruptions is the basic responsibility of a content delivery network (CDN). The second most comprehensive responsibility is reaching the masses. A content delivery network (CDN) is a globally distributed network. There are multiple presence points useful for providing seamless content delivery irrespective of the physical or geographic location of the user.
In this article, we will discuss the importance of content delivery and how a content delivery network functions in practical applications.
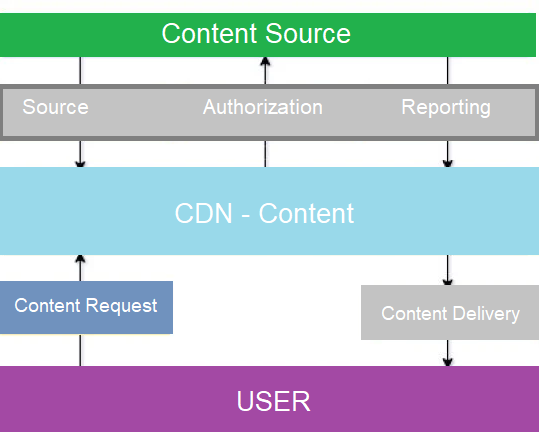
Content delivery is not just a service that entails sending and receiving content from one point to another. The content source matters a lot, and delivering data properly requires data security at rest and in transit. The authentication of the source and the destination is all a part of content delivery.
The destination or user authentication and authorization depend on the type of data. Alibaba Cloud Sensitive Data Discovery and Protection is a specialized product that enables sensitive data detection, classification, grading, and de-identification. We will discuss this further in a separate article.
Different organizations conduct their business using different websites and portals, such as e-commerce and video sharing. There are many services used as standardized platforms for content sharing, and these services have mass followings of people that produce content using blogs. These are standard content delivery networks that enable written and video content.
The scale of these content delivery networks encompasses individual to large enterprise-level CDN solutions. For the scope of this article, we will be referencing Alibaba Cloud CDN.
There are four types of content delivered to the user:
1. Static Content
Typically, static content is images, scripts, or data that does not frequently change. This type of content is locally stored and cached by the websites, so the data does not need to be transmitted on the next load. This saves time and bandwidth.
2. Dynamic Content
This content changes continually, and most of the data is updated on the website. Dynamic content includes a blog where a writer creates new content or machine learning submissions where real-time data is updated on the servers.
3. Mixed Content
In today's digital sphere, mixed content is sorted using metadata. This type of content can be classified as micro-content. It changes sometimes but not regularly. Mixed content can also be mixed with other content types, including a small video tutorial within a video or text tutorial that clarifies a concept.
4. Streaming Content
Streaming content refers to audio or video streaming. Streaming content requires a strong CDN for seamless Internet playback.
Alibaba Cloud Content Delivery Network (CDN) is a distributed network built over a seasoned transport network. This network contains edge nodes deployed in different regions to facilitate a seamless and uninterrupted content delivery experience for users.
Alibaba Cloud CDN distributes the network traffic to free the origin servers. This enables a no-congestion network and a highly available CDN platform for deployment. Alibaba Cloud CDN provisions the resources from the origin servers and uses ultra-fast caching technology to store the data resources on CDN nodes (edge nodes) deployed in nearly 3000 regions.
When the user requests are received, it does not get redirected to the origin servers. Alibaba Cloud CDN automatically locates the cached version of content on the edge nodes closest to the user's geographical location and provides the user with the requested content. The chart below shows the Alibaba Cloud CDN architecture:
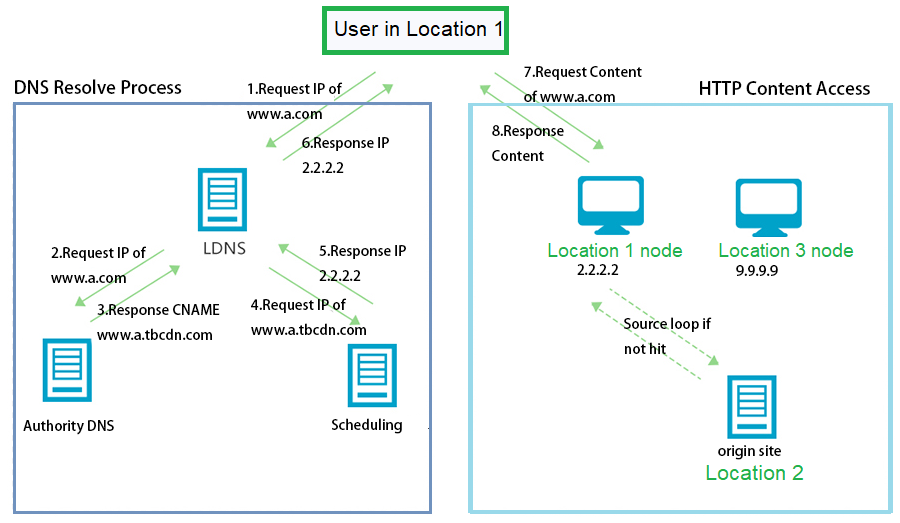
Alibaba Cloud Content Delivery Network (CDN) accelerates website content delivery in different regions and different scenarios using multiple Alibaba Cloud services.
The whole process works with a user in one location sending out a request to retrieve some content on the website. Alibaba Cloud CDN resolves the IP address and matches it with a local DNS server to ping a CDN node in the same geographical location. This initiates the whole content retrieval process. If the local node is not responsive, the same request will be handled by the next closest CDN node.
You can use the Server Load Balancer (SLB) and Alibaba Cloud CDN as a content origin to balance the bandwidth requirement for retrieving the user's requested content. Similarly, an Elastic Compute Service (ECS) improves website availability and protects the content origin information.
You can integrate Object Storage Service (OSS) with Alibaba Cloud CDN to accelerate the overall access time required to retrieve content and reduced the time to transmit it to the user. You can access the content directly from the edge nodes when using Alibaba Cloud OSS with CDN.
In this article, we introduced and explained how a content delivery network (CDN) functions. We also introduced the Alibaba Cloud CDN and explained the service interactions and architectural flow of this solution. In Part 2 of this series, we will discuss the benefits and features of Alibaba Cloud CDN.

2,593 posts | 793 followers
FollowAlibaba Clouder - March 30, 2021
Alibaba Clouder - November 10, 2020
Alibaba Clouder - February 26, 2019
Alibaba Clouder - June 23, 2020
Alibaba Cloud Community - July 26, 2024
Alibaba Clouder - July 29, 2020

2,593 posts | 793 followers
Follow Server Load Balancer
Server Load Balancer
Respond to sudden traffic spikes and minimize response time with Server Load Balancer
Learn More Secure Content Delivery Solution
Secure Content Delivery Solution
Accelerate static and dynamic web content in a fast, reliable, and safe way using Secure DCDN (Dynamic Route for CDN)
Learn More Content Delivery Solution
Content Delivery Solution
Save egress traffic cost. Eliminate all complexity in managing storage cost.
Learn More Media Solution
Media Solution
An array of powerful multimedia services providing massive cloud storage and efficient content delivery for a smooth and rich user experience.
Learn MoreMore Posts by Alibaba Clouder