By DNS Team
Today, let's talk about DNS hijacking. Let's review the concept of DNS hijacking first. DNS hijacking refers to fiddling with the mapping relationship between a correct domain name and IP address through technical means, so the domain name is mapped to a wrong IP address. Therefore, DNS hijacking can be considered a DNS redirection attack. DNS hijacking can be used for domain name fraud (displaying irrelevant information to earn income when users visit web pages) and phishing (displaying fake websites visited by users and then illegally stealing users' personal information).
Before introducing the principle of DNS hijacking, you need to understand the typical DNS resolution process.
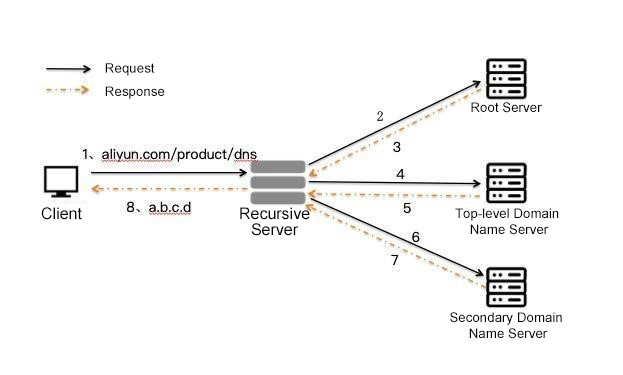
A client initiates a recursive DNS request. Local recursive DNS (carrier DNS in most cases) or public DNS requests multiple-level authoritative DNS servers through iterative queries and returns the query results to the client. You can see a complete DNS query below:
We will divide DNS hijacking into three categories: client-side, recursive DNS server, and authoritative DNS server.
DNS hijacking on the client side is named local DNS hijack. Local DNS hijack refers to:
DNS hijacking that occurs during DNS resolution when the client communicates with the DNS server online is classified as DNS resolution path hijacking. After dividing the hijacking paths of DNS resolution packets in the query phase, DNS resolution path hijacking can be divided into the following three categories:
Redirect DNS traffic to other DNS servers through technical means (middle box, software, etc.).
Case:
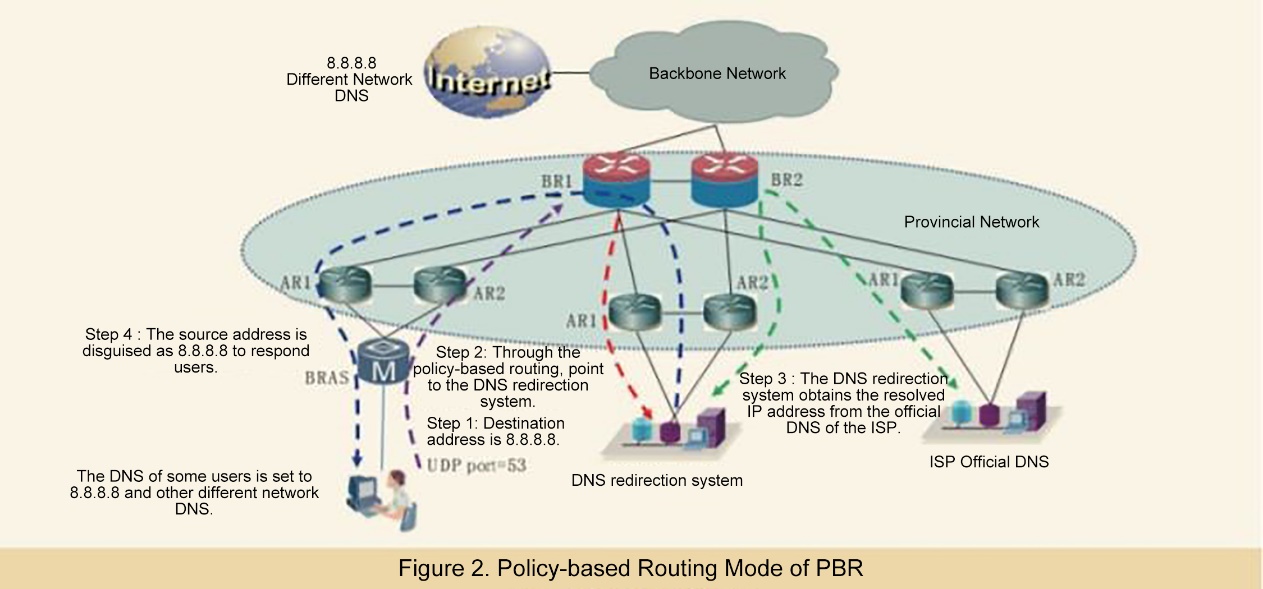
The picture above is from Wu Junfeng, Shen Han. DNS Control Practice of Different Networks Based on Bypass Response Mechanism. Telecommunications Technology [J]
The DNS query is copied to the network device with the optical splitter, and the DNS hijacking result is returned before the normal response.
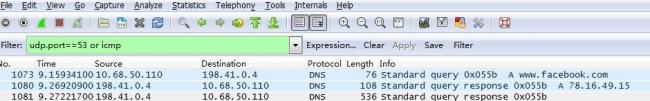
Case: One packet capture of the DNS query returns two different responses.
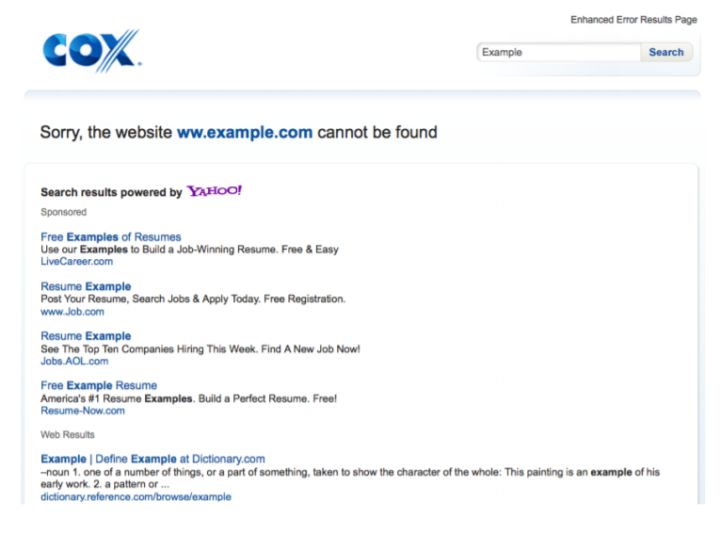
Network device or software directly replaces the DNS server to answer DNS queries.
Case: Some DNS servers implement the functions of SERVFAIL rewrite and NXDOMAIN rewrite.
Fiddling with DNS authoritative records refers to hackers illegally invading the DNS authoritative record administrator account and then directly modifying DNS records.
Case: Hackers hack into the administrator account of the domain name, fiddle with the authoritative DNS records, and redirect users to their malicious servers to implement DNS hijacking.
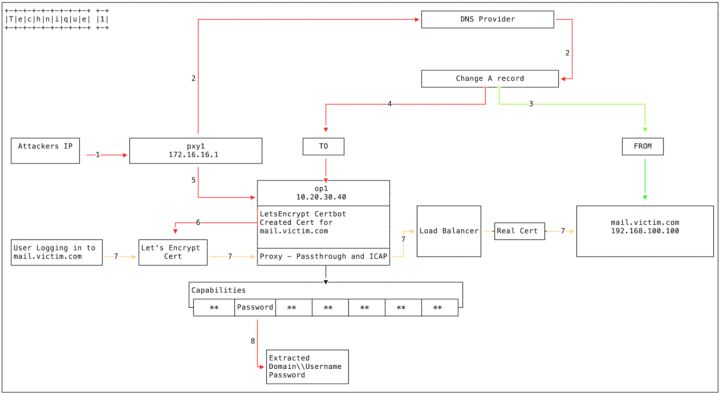
Hackers hack into the administrator account of the upper-level domain name registry, fiddle with the NS authorization records of the domain name, and authorize the domain name to a malicious DNS server (built by hackers) to implement DNS hijacking.
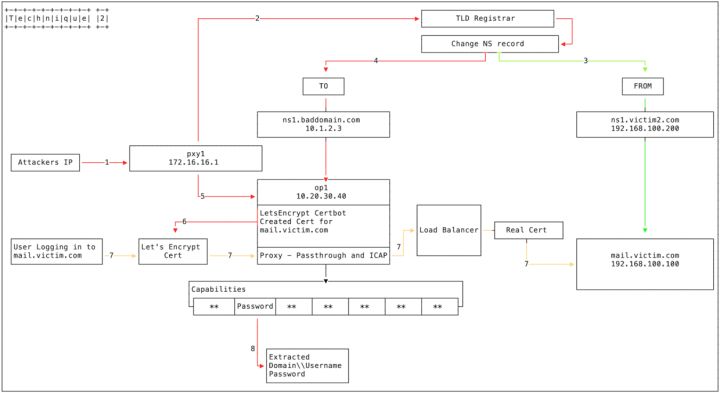
Hackers hack into the administrator account of the upper-level domain name registry, fiddle with the NS authorization records of the domain name, and authorize the domain name to a malicious DNS server (built by hackers) to implement DNS hijacking. (Please see the FireEye blog for more information.)
DNS hijacking seems to have become a common occurrence on the Internet, but how can we deal with various DNS hijackings? If you suspect that you are experiencing DNS hijacking, the first thing to do is confirm the problem.
Check whether the router DNS configuration has been fiddled with or altered
View the DNS server that replies to the DNS response with tools and check whether the DNS resolution is redirected
Some DNS-related test tools can be installed on the mobile terminal for troubleshooting:
Related product: https://www.alibabacloud.com/product/emas/httpdns
Alibaba Rolls Out Deeper Immersive Luxury Shopping Experience In The Metaverse

1,345 posts | 472 followers
FollowAlibaba Cloud Community - September 30, 2022
Dikky Ryan Pratama - May 8, 2023
Alibaba Cloud Community - October 17, 2022
Alibaba Cloud New Products - June 3, 2020
Alibaba Clouder - March 8, 2021
Alibaba Cloud Native Community - January 8, 2026

1,345 posts | 472 followers
Follow HTTPDNS
HTTPDNS
HTTPDNS is a domain name resolution service for mobile clients. It features anti-hijacking, high accuracy, and low latency.
Learn More EMAS HTTPDNS
EMAS HTTPDNS
EMAS HTTPDNS is a domain name resolution service for mobile clients. It features anti-hijacking, high accuracy, and low latency.
Learn More DNS
DNS
Alibaba Cloud DNS is an authoritative high-availability and secure domain name resolution and management service.
Learn More Global Traffic Manager
Global Traffic Manager
Allows you to access the nearest node based on the Domain Name System (DNS) architecture.
Learn MoreMore Posts by Alibaba Cloud Community