Network issues are frequently reported by users of Alibaba Cloud Data Transmission Service (DTS), mostly because of the complex nature of the DTS connections. Failures or quality issues at any point in the network, from the source database to DTS and then from DTS to the target database, can result in DTS task interruptions or delays.
Among all types of network disruptions, the majority are caused by Express Connect circuit/VPN gateway/intelligent gateway or Cloud Enterprise Network (CEN) connections to data sources. Firstly, customers who utilize these connections often link to a remote network environment via VBR in combination with an Express Connect circuit or a VPN Gateway. The network quality is hard to ensure due to the long distances and potential unpredictability of the network links. Secondly, the destination network environment might be outside Alibaba Cloud's control, like a private network IDC or another cloud's VPC, and its routing conditions and database versions may not meet standard requirements. Consequently, Alibaba Cloud cannot directly address these problems and must rely on users to troubleshoot cross-network domain issues, which can significantly decrease efficiency.
Therefore, this article aims to present the troubleshooting methods for DTS network connection failures in the simplest way possible, offering straightforward verification ideas and methods. Knowing the correct troubleshooting direction can greatly facilitate the resolution of network issues.
Firstly, let’s discuss how to establish a smooth network channel from the perspective of the TCP/IP protocol, avoiding the kind of frustrating errors shown below.
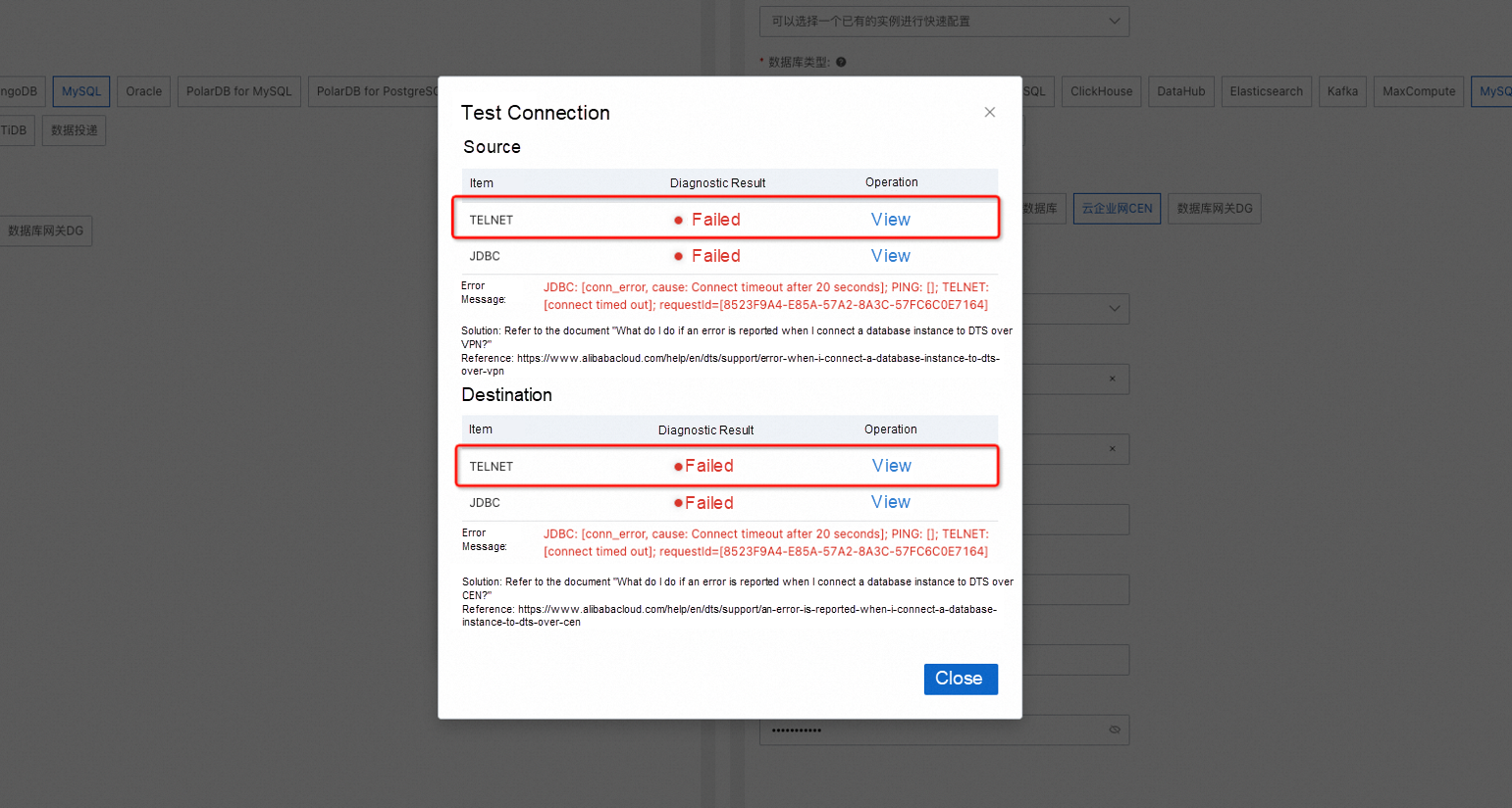
Error of network connection failure during task configuration
First of all, what is the TCP/IP protocol? How to ensure that the TCP/IP protocol is unblocked?
The answer to this question is quite lengthy and not directly relevant to the actual business scenario. Instead, we can provide a minimal model and a more simplified definition:
A network is unblocked when the traffic of DTS can reach the user database in the correct direction of Arrow 1 and the back-to-source traffic of the user database can reach DTS in the correct direction of Arrow 2.
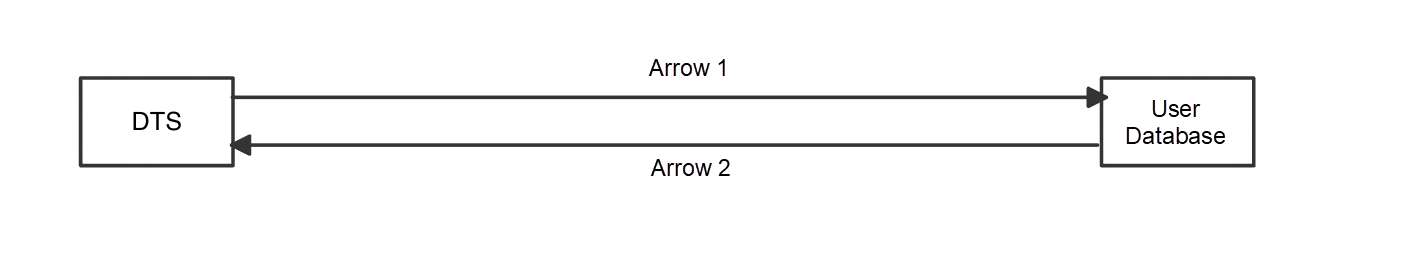
Minimal network communication between DTS and the user database
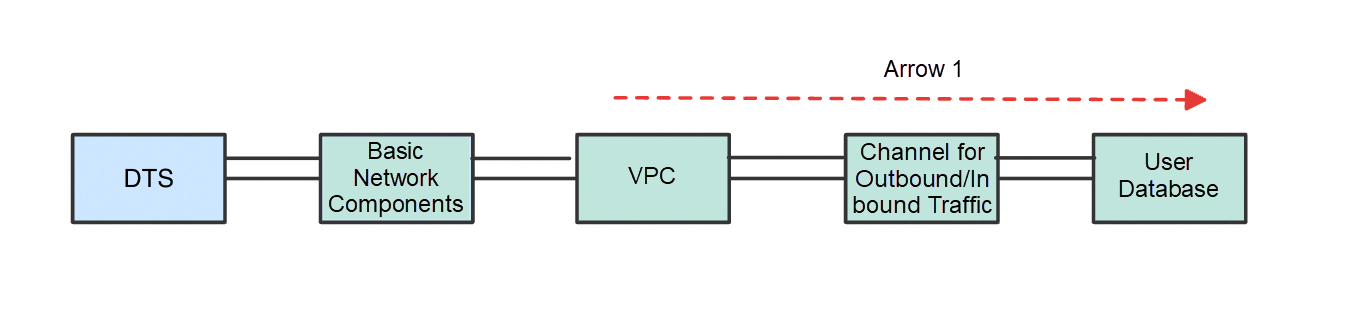
Then, by elaborating on the previous figure, we arrive at a more complete communication topology. In this topology, the traffic from DTS to the user database must travel through basic network components, the Virtual Private Cloud (VPC), and the channels for migrating data to and from the cloud (the outbound/inbound channels, typically an Express Connect circuit or VPN).
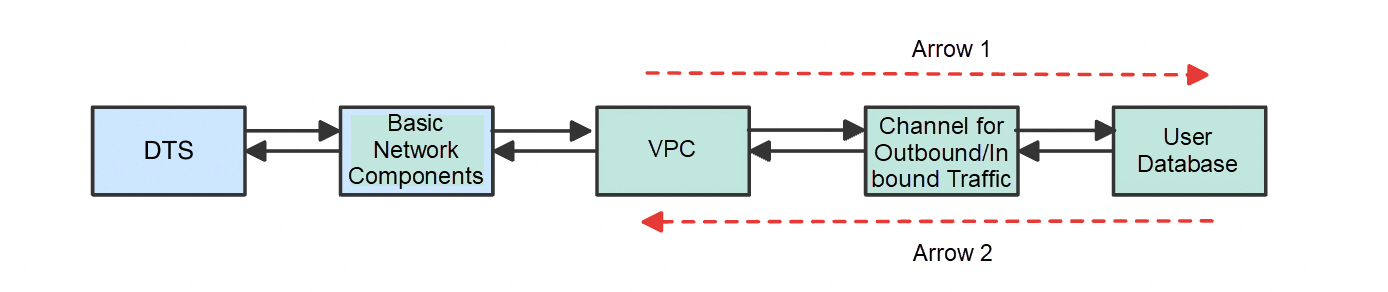
Complete network communication between DTS and the user database
However, the DTS and basic network components on the left are not visible to users, while the three components on the right (VPC, the outbound/inbound channels, and the user database) are visible. Consequently, I redefine the previously mentioned simplified definition as follows:
A network is unblocked when the traffic from DTS that is injected into the VPC can correctly reach the user database in the direction of Arrow 1, and the return traffic from the user database can correctly reach the VPC in the direction of Arrow 2.
We have now outlined the essential conditions for an unobstructed network, but we haven't specified which VPC it is: The answer is the VPC connected to the source database, which the user selects when setting up the DTS task. (The same applies to the destination.)
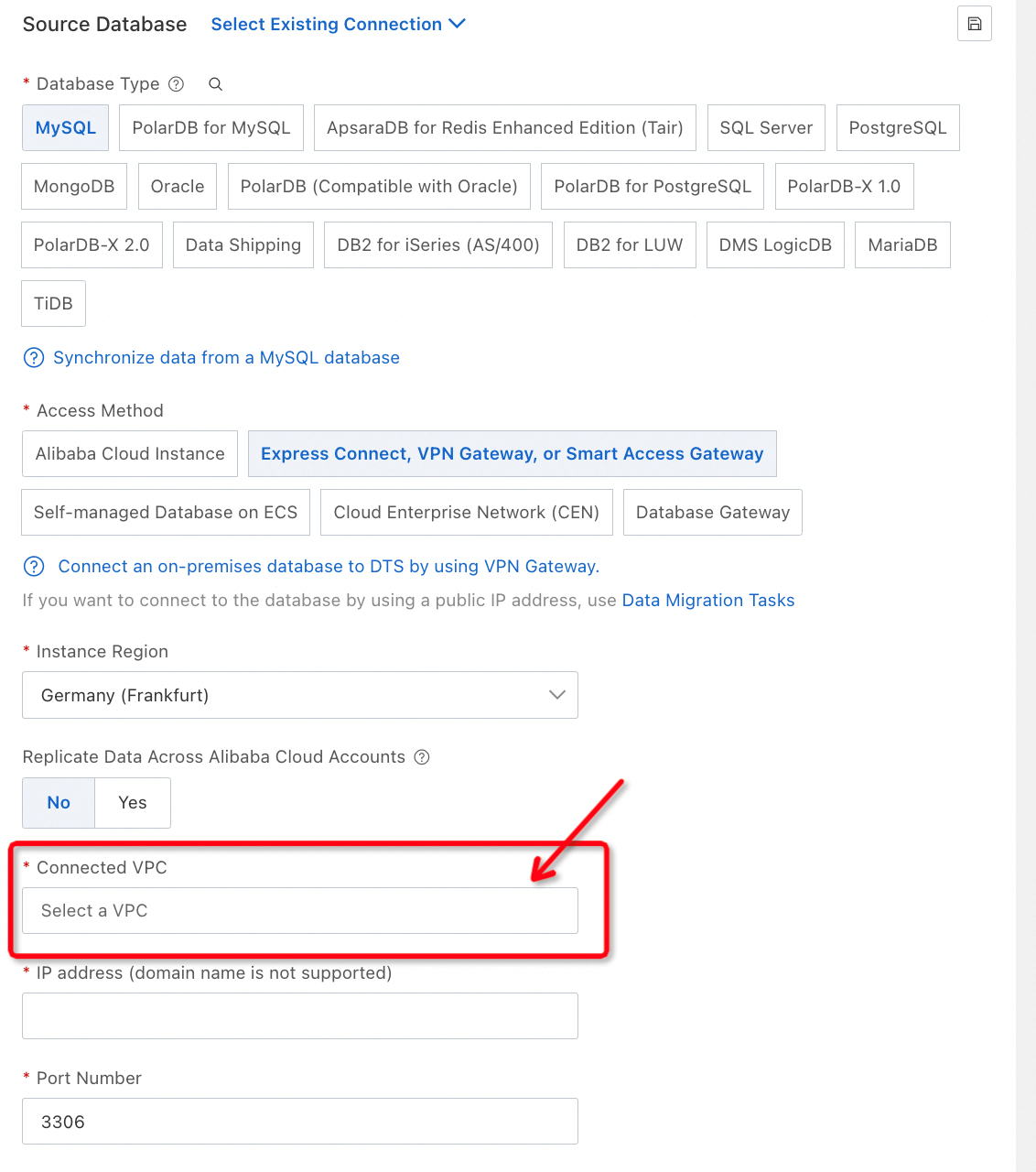
At this point, we need to update the definition as follows:
A network is unblocked when the traffic of DTS injected into the VPC selected by the user when configuring the task can reach the user database in the correct direction of Arrow 1, and the back-to-source traffic of the user database can reach the VPC selected by the user when configuring the task in the correct direction of Arrow 2.
Finally, we have answered and defined how to construct an unblocked network channel. But how can we confirm that the network we construct meets the requirements of an unblocked network?
Next, let's discuss the troubleshooting and verification ideas in the following two parts:
The following figure illustrates our minimal model and gives a minimal definition of an unblocked network for outbound traffic:
The traffic of DTS injected into the VPC selected by the user when configuring the task can reach the user database in the correct direction of Arrow 1.
Minimal model
Before we confirm that the outbound traffic arrives in the correct direction, we must know what the traffic looks like, otherwise, the analysis is impossible.
The following is a notification model: The source IP, referred to as the cloud service IP, consists of CIDR blocks starting with 100.104. The destination IP is the user's database IP. The traffic of DTS injected into the VPC will flow in this form in the user's network and flow all the way to the user's database along with the user's various vSwitch route tables.
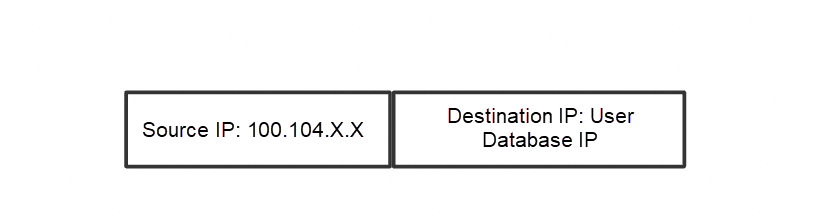
Outbound traffic notification model
Then how to confirm the CIDR block of this source IP?
We can refer to the CIDR block whitelist of DTS for confirmation. The CIDR blocks of cloud service IP vary in different regions and the number of CIDR blocks also varies.
If the configuration is correct, how to confirm that the channel for outbound traffic is unblocked?
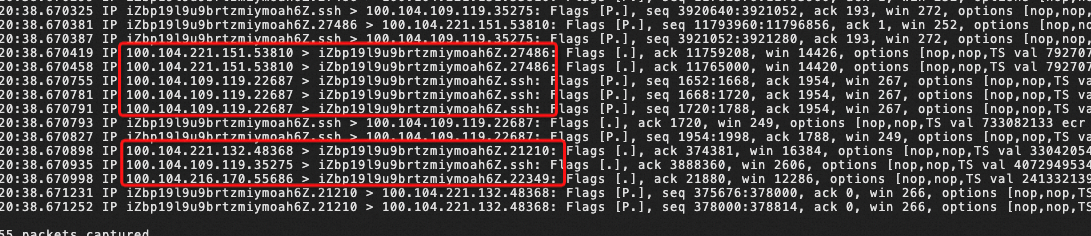
We can run the packet capture command of tcpdump to capture packets and view them on the user database.
sudo tcpdump net 100.104If the notification from the 100.104 CIDR block shown in the shell output is constantly updated, it means that the database machine has received the inbound traffic from the CIDR block of the cloud service IP.
Again, the following figure illustrates our minimal model and gives a minimal definition of an unblocked network for inbound traffic:
The back-to-source traffic of the user database can reach the VPC selected by the user when configuring the task in the correct direction of Arrow 2.
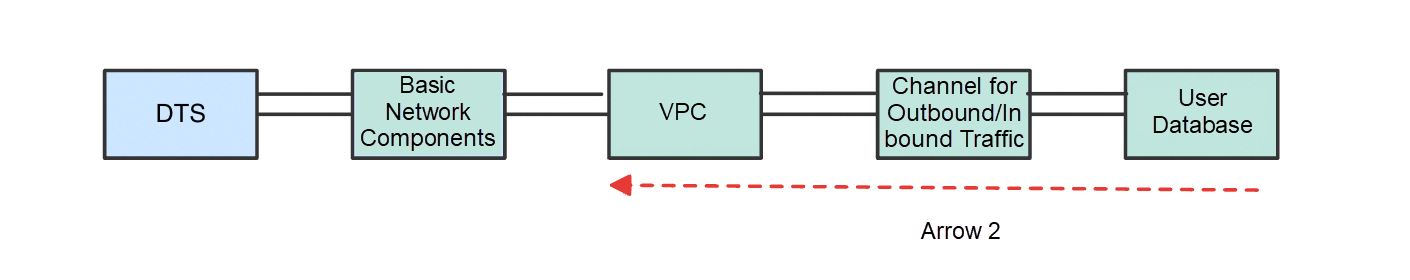
Minimal model
We have received the outbound traffic, then the database will return a packet to the cloud. The destination IP of this packet is the source IP of the outbound traffic, thus the inbound traffic notification model:
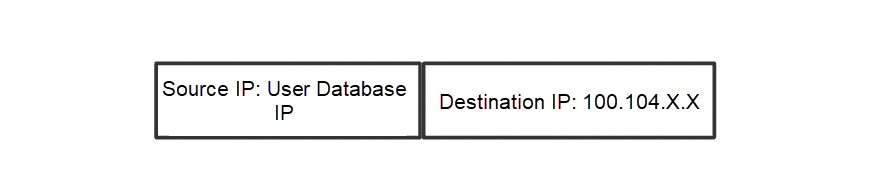
Inbound traffic notification model
Then we need to confirm whether the notification has returned to the cloud. We can execute the following command:
MTR 100.104.X.XBut what is the MTR address?
To confirm the specific address of 100.104.X.X, you can use the sudo tcpdump net 100.104 method to see what the source IP is.

The method of confirming the IP of 100.104
After the MTR is completed, we can know from the path points whether the packets sent from the database have returned to Alibaba Cloud. Due to the lack of a ready-made dedicated line test environment, we will not demonstrate it here.
In most cases, the reason for connection failures during migration to the cloud is that the notification does not leave the non-Alibaba Cloud environment at all and still remains within this network domain. This is mostly due to some routing configuration errors that cause the back-to-source route to not point to the VBR's peer IP addresses or to point to the VPN gateway for the outbound traffic. Of course, the specific situation requires the user's network worker to troubleshoot.
This article proposes a simplified definition of an unblocked network from the perspective of DTS and discusses a set of simple troubleshooting ideas for network connection failures. It is a qualitative analysis that mainly answers the following two questions: Is the data moved out of the cloud and Is the data migrated to the cloud. With these ideas, users can troubleshoot by themselves before aftermarket service is provided. However, this article does not cover more complex scenarios that require quantitative analysis. For example, there are other more extreme cases where the notification is confirmed to have migrated to the cloud, but it has not returned to the VPC specified by the user, or where the notification has moved from the cloud, but the user database has not received it. These complex network problems require more comprehensive knowledge analysis and are beyond the scope of this article.
Network problems are very comprehensive, involving multiple departments and covering a wide range, so the troubleshooting lasts long and is difficult. From our experience, if a network problem occurs during operation, you may start with the change, which is probably the cause of the problem. If a network problem occurs during configuration, it is mostly due to the planning of the CIDR block of the cloud service IP that is missing from the user's network planning.
[Infographic] Highlights | Database New Feature in Feburary 2024
ApsaraDB - December 5, 2025
ApsaraDB - March 19, 2025
Alibaba Clouder - March 12, 2020
ApsaraDB - October 30, 2025
Alibaba Clouder - August 25, 2020
Alibaba Cloud Product Launch - January 22, 2019
 Data Transmission Service
Data Transmission Service
Supports data migration and data synchronization between data engines, such as relational database, NoSQL and OLAP
Learn More Time Series Database (TSDB)
Time Series Database (TSDB)
TSDB is a stable, reliable, and cost-effective online high-performance time series database service.
Learn More Big Data Consulting for Data Technology Solution
Big Data Consulting for Data Technology Solution
Alibaba Cloud provides big data consulting services to help enterprises leverage advanced data technology.
Learn More Cloud Migration Solution
Cloud Migration Solution
Secure and easy solutions for moving you workloads to the cloud
Learn MoreMore Posts by ApsaraDB