With the Web Application Firewall (WAF) Protection Configuration module, you can combine various security features—such as Core Protection Rule, HTTP Flood Protection, and Bot Management—to effectively defend against a range of web attacks including SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), HTTP flood attacks, and malicious bots.
How it works
Protected objects and protected object groups: When you onboard a domain name or a cloud service instance to WAF, the system automatically creates a protected object for it. You can group multiple protected objects into a protected object group for centralized management.
Protection modules: WAF provides various protection modules, such as Core Protection Rule, API Security, and Bot Management. You enable a module by creating protection templates. Select modules based on your needs.
Protection templates: A protection template defines the specific rule content and inspection scope. It consists of three parts: template type, protection rules, and effective objects.
Template type: Some protection modules offer two template types: default protection template and custom protection template. A default protection template applies to all current and future protected objects without manual assignment.
Protection rules: Define specific detection logic and response actions.
Effective objects: Specify the target of the protection template. You use this setting to apply protection rules to specific protected objects or protected object groups.
Configuration process

WAF automatically creates protected objects for onboarded resources. View them on the page.
Select protection modules based on business needs. For example, to use the Custom Rule module, you must create a new protection template. For more information, see Create a protection template.
After you create a template, add protection rules to it. For more information, see Add protection rules to a protection template.
Finally, select protected objects to apply the protection template. For more information, see Configure effective objects for a protection template.
Supported protection modules
Supported protection modules vary by WAF edition. For example, the Subscription Basic edition does not support Peak Traffic Throttling. For more information, see Edition comparison.
Core Web Protection - Common
Protection module | Use cases and recommendations | Initial status |
Leverages Alibaba Cloud's built-in rule sets to defend against common web application attacks, such as SQL injection, XSS, code execution, WebShell uploads, and command injection. Keep default settings; adjust only to resolve false positives. | Includes an initial default protection template, which is enabled by default and uses the block action. Resources onboarded to WAF are protected by this module by default, automatically blocking attack requests. | |
Protection Rule Group (Legacy WAF only) Note This module has been upgraded to the engine configuration feature. For details, see Announcement. | Rule groups referenced by Web Application Protection Rules. Keep the default settings. | Includes medium, strict, and loose rule groups. The medium rule group is enabled by default. If false positives or false negatives occur, manually switch the enabled rule group. |
If you identify frequent malicious requests from specific IP addresses, add them to the IP Blacklist. | No initial protection template. | |
To precisely protect against specific attacks (such as malicious calls, malicious requests, or high-frequency scanning), you can use Custom Rules to build personalized protection policies with flexible matching conditions and rule actions. | ||
Block all IP addresses from specific regions with a single click—ideal for locations with no legitimate business traffic. | ||
Identifies scanning behavior and scanner signatures to block large-scale scanning attempts against your site, mitigating intrusion risks and reducing unwanted traffic. | Only Subscription Advanced, Enterprise, and Ultimate editions have an initial default protection template enabled by default. Other editions do not have an initial protection template. | |
Mitigates HTTP flood attacks using built-in algorithms. Combine this with Custom Rules for better protection results. |
Core Web Protection - Others
Protection module | Use cases and recommendations | Initial status |
Allows you to customize the style and content of the block page returned by WAF to the client when a request is blocked. | No initial protection template. | |
Locks protected pages to prevent malicious tampering. When a locked page receives a request, WAF returns the cached page. | ||
Masks sensitive information (such as ID card numbers and bank card numbers) in server responses (error pages or keywords). | ||
Limits QPS or sets throttling ratios based on URL and region. Suitable for traffic surges during major events to ensure origin server availability. |
Whitelist
Use cases and recommendations: Unlike other protection modules, the Whitelist module is used to allow requests with specific characteristics. When enabled, matching requests bypass detection by all or specific protection modules. Add known trusted requests (such as O&M IP addresses) to the whitelist.
Initial status: This module has an initial default template (no rules defined) and is enabled by default.
Advanced protection
Protection module | Use cases and recommendations | Initial status |
Enable API Security to protect APIs (such as mobile apps) from unauthorized access and data leaks. It automatically discovers API assets, identifies risks, and provides remediation suggestions and compliance references. | N/A | |
Automated tools often cause issues such as data scraping, fraud, spam registration, scalping, coupon abuse, and SMS interface abuse. After enabling Bot Management, you can create precise protection policies based on traffic analysis to protect core data assets and reduce server load. | No initial protection template. | |
Supports security assurance for critical events during specific time periods, providing more precise and customized defense modes. | ||
If your AI application is exposed to the internet and needs protection against prompt injection and non-compliant content generation, enable AI Application Protection. It automatically identifies high-risk requests and blocks attacks to ensure secure and compliant model output. |
Disable WAF protection
To temporarily bypass WAF, turn off the WAF Protection Status switch in the upper-right corner of the Protected Objects page in the WAF console.

When the switch is turned off, traffic to your website temporarily bypasses the WAF protection engine and is no longer logged. After you complete operations that require temporary WAF suspension (such as emergency testing), turn this switch back on as soon as possible to reduce the risk of asset exposure.
Billing: For Pay-as-you-go WAF instances, turning off this switch still incurs feature fees, base request fees, and API security traffic fees (if API security is enabled).
API Security: The detection process of the API Security module is not affected by this switch.
Unsupported features: This feature is not supported for Microservices Engine (MSE) and Function Compute (FC) instances onboarded via cloud native mode. For hybrid cloud access, a specific version is required. For more information, contact your account manager.
Flexibly manage multiple protection templates with template types
Define multiple Protection Templates within a module to apply independent rules to different objects. To manage these templates efficiently, understand the two template types: default protection template and custom protection template.
Template type | Description | Use cases |
Default protection template |
| Deploy general protection rules that need to be enforced globally. |
Custom protection template | Applies only to manually specified protected objects or groups. | Deploy fine-grained protection rules for specific business scenarios (such as login or payment interfaces). |
If a protected object is not in any template (set as Ineffective in all templates), it is not protected by WAF.
The default protection template is marked with
Default. Templates without this mark are custom protection templates.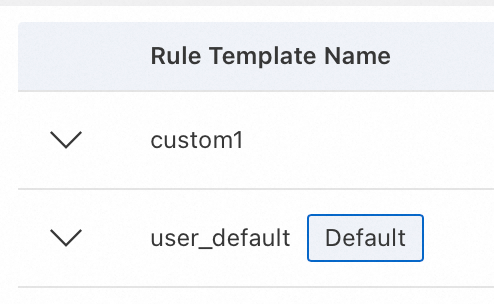
Modules that support default protection templates: Core Protection Rule, Whitelist, IP Blacklist, Custom Rules, HTTP Flood Protection, Custom Response, Scanning Protection, Geo-blocking, and Peak Traffic Throttling.
Modules that do not support default protection templates: All templates created are custom templates. You must manually specify effective objects.
Applying multiple templates to a single protection object
The following protection modules support associating multiple protection templates with a single protection object or group:
Whitelist, IP Blacklist, Custom Rules, Bot Management, and Prompt Injection Protection.
For the modules listed above that support multiple templates: Associating a protection object with a custom template does not remove it from the scope of the default template. The object will be protected by both the default template and all associated custom templates simultaneously.
For modules that do not support multiple templates (such as Core Protection Rule): A protection object can only be associated with one template at a time. When you associate an object with a custom template, it is automatically removed from the scope of the default template.
Example 1: Using different protection modes (monitor/block) for new and existing objects
Taking the Core Protection Rule module as an example, it includes an initial default template whose default rule action is Block and is automatically applied to all newly onboarded protection objects.
Scenario:
You want to apply Monitor mode (log attacks without blocking) to newly onboarded objects, while maintaining Block mode for existing objects.
Steps:
Set the Action of the default protection template to Monitor.
Create a Core Protection Rule template (custom protection template), set its Action to Block, and set Apply To to all currently protected objects.
Example 2: Configuring an additional whitelist rule for a specific object
Taking the Whitelist module as an example, it includes an initial default template (with no rules defined) that is enabled for all objects by default.
Scenario:
You want to allow IP1 for all protection objects, but also need to allow IP2 for one specific object.
Steps:
In the default template, add a rule to allow
IP1. All protected objects/groups are selected by default.Create a Whitelist template (custom protection template) to allow
IP2, and set Apply To to the specific protected object.
FAQ
When must I manually configure protected objects?
You must manually configure protected objects in the following cases:
If you use cloud native mode and multiple domains resolve to the same cloud instance, but you want to configure different protection rules for these domains, you must manually add each domain as a protected object. For more information, see Manually add protected objects.
If you need to modify advanced functions such as WAF cookie issuance, WAF decoding, or account extraction, you must manually configure protected objects. For more information, see Configure advanced protection behavior for protected objects.
How do I verify that protection is effective? (View active protection modules)
Go to the Protected Object page, find the target object, and click View Protection Rule in the Actions column. On the Core Web Protection page, view the object's protection rules. If no template appears on the Core Web Protection page, the configuration is inactive. Check the effective objects setting of the protection template.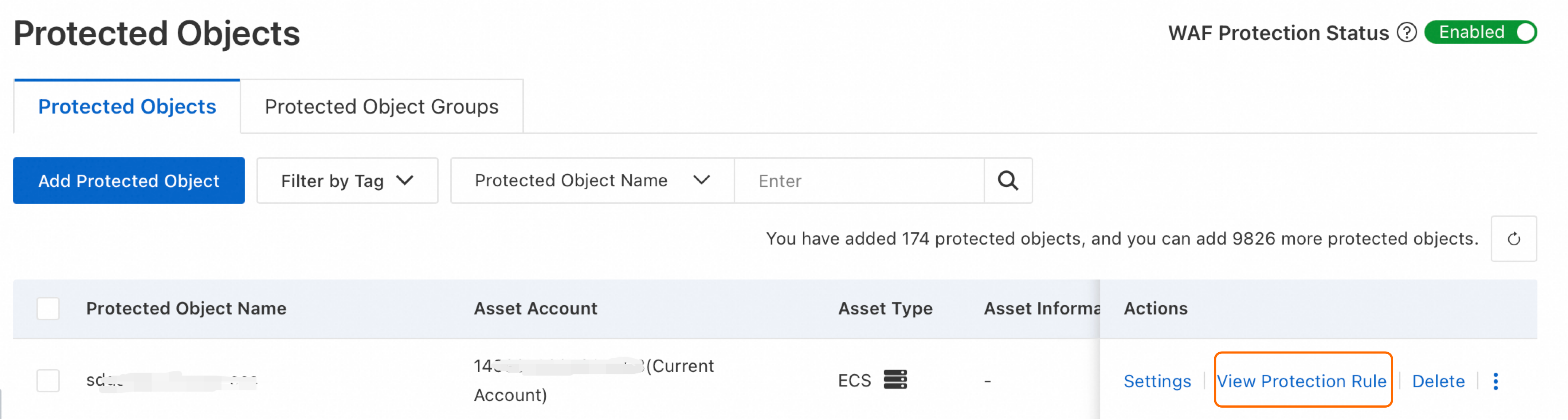
What if legitimate business requests are blocked?
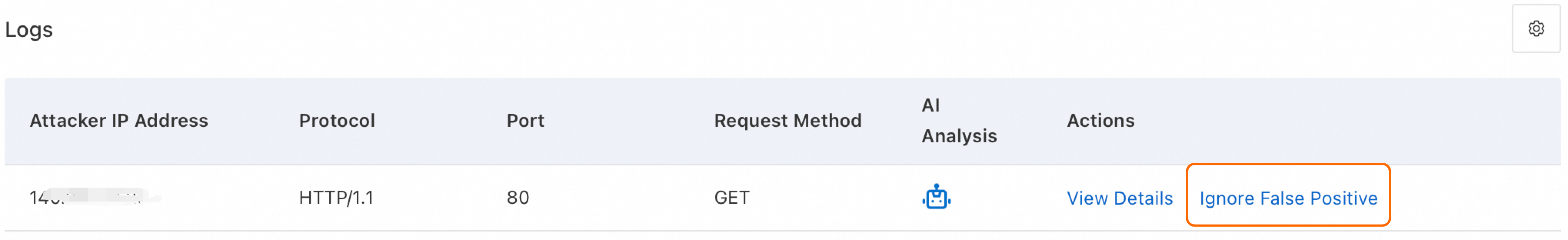
Go to the page. Search and analyze requests based on time, client IP, or URL to identify the protection module and rule that triggered the block.
To resolve a false positive, locate the request in the Logs and click Ignore False Positive in the Actions column to create a whitelist rule.