Certificate Management Service provides automated SSL certificate deployment for cloud servers. This feature enables one-click deployment to Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instances and automatic updates for ECS and Simple Application Server, so you can deploy certificates through the console instead of manually configuring certificate files on each server.
Two deployment methods are available:
| Feature | Method 1: One-click deployment | Method 2: Manual deployment |
|---|---|---|
| Best for | Initial deployment on eligible trusted ECS instances | Updating an existing certificate on any cloud server |
| Mechanism | Fully automated. The private key never leaves the instance and communicates with the trusted module through a PKCS#11 interface. | Semi-automated. Uploads the certificate file to a specified path on the server to overwrite the old file. |
| Supported servers | 7th/8th generation x86-based trusted ECS instances only. Simple Application Server is not supported. | All ECS and Simple Application Server instances. |
| Operating systems | Alibaba Cloud Linux 3.x, Ubuntu 22.04 UEFI images | All major Linux and Windows Server distributions |
| Web servers | Specific versions of Nginx installed from yum or apt sources only | All web servers (Nginx, Apache, Tomcat) |
| Certificate requirements | Single-domain SSL certificates using the RSA algorithm | All types of SSL certificates |
| Automatic renewal | Yes, for multi-year certificates | Not applicable |
If neither method meets your needs, see SSL certificate deployment solution selection to choose a different deployment solution.
Method 1: One-click deployment (trusted ECS instance)
This method integrates with the trusted module of an ECS trusted instance for fully automated certificate and private key deployment. If you purchase a multi-year certificate, the system automatically updates it after each renewal.
Prerequisites
Before you begin, ensure that you have:
A 7th or 8th generation x86-based trusted ECS instance. For more information, see Create a trusted instance
Alibaba Cloud Linux 3.x or Ubuntu 22.04 UEFI image installed on the instance
Nginx installed from
yumoraptsources:Alibaba Cloud Linux 3.x: Nginx version from 1.18.0-2.1.al8 to 1.20.1-1.0.5.al8 (exclusive)
Ubuntu 22.04: Nginx installed using
apt
A single-domain SSL certificate using the RSA algorithm with status Issued
A
rootaccount or an account withsudoprivileges on the instanceThe domain DNS record configured and resolving to the server's public IP address
Step 1: Verify the Cloud Assistant status
Cloud Assistant must be installed and running on your ECS instance. Otherwise, the one-click deployment feature is unavailable.
Select the resource group and region where your instance is located.
On the ECS Instances tab, locate your ECS instance and check the Cloud Assistant Status column.
If Cloud Assistant is not installed or its status is abnormal, see Check Cloud Assistant status and troubleshoot abnormal statuses.
Step 2: Configure Nginx for the PKCS#11 interface
For an initial deployment, modify the Nginx configuration to allow it to call the private key from the trusted module through the PKCS#11 interface. This step is not required for subsequent updates.
Alibaba Cloud Linux 3.x
This section uses Nginx 1.20.1 as an example. The default installation directory for Nginx installed viayumis/etc/nginx/. If you changed this directory, adjust the configurations accordingly.
Confirm your Nginx version. Only Nginx versions from 1.18.0-2.1.al8 to 1.20.1-1.0.5.al8 (exclusive) are supported.
ImportantIf Nginx is already installed on your ECS instance, check its version before using the one-click deployment feature. If the version is not supported, downgrade to a supported version or reinstall it.
Open
/etc/nginx/nginx.confand addssl_engine pkcs11;afterpid /run/nginx.pid;to specify the PKCS#11 encryption library.user nginx; worker_processes auto; error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log; pid /run/nginx.pid; # Specify the use of the PKCS#11 encryption library. ssl_engine pkcs11;In the same
/etc/nginx/nginx.conffile, uncomment the Settings for a TLS enabled server section and addinclude "/etc/acm/ssl/nginx-acm.conf";to reference the SSL key configuration. Complete server block example:server { listen 443 ssl http2; listen [::]:443 ssl http2; # Specify the hostname or Common Name (CN). server_name example.com; root /usr/share/nginx/html; ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m; ssl_session_timeout 10m; ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on; # Reference the SSL key configuration. include "/etc/acm/ssl/nginx-acm.conf"; # Load configuration files for the default server block. include /etc/nginx/default.d/*.conf; error_page 404 /404.html; location = /40x.html { } error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; location = /50x.html { } }Open
/usr/lib/systemd/system/nginx.serviceand add the following environment variables to configure communication with the SSL key service. Content to add: Complete service file example:If you do not know the path to the Nginx systemd service configuration file, run
sudo find / -name "nginx.service"to find it.Environment="P11_KIT_SERVER_ADDRESS=unix:path=/etc/acm/ssl/acm-p11-kit.sock" Environment="OPENSSL_CONF=/etc/acm/ssl/openssl-acm.cnf"[Unit] Description=A high performance web server and a reverse proxy server Documentation=man:nginx(8) After=network.target nss-lookup.target [Service] Type=forking PIDFile=/run/nginx.pid ExecStartPre=/usr/sbin/nginx -t -q -g 'daemon on; master_process on;' ExecStart=/usr/sbin/nginx -g 'daemon on; master_process on;' ExecReload=/usr/sbin/nginx -g 'daemon on; master_process on;' -s reload ExecStop=-/sbin/start-stop-daemon --quiet --stop --retry QUIT/5 --pidfile /run/nginx.pid TimeoutStopSec=5 KillMode=mixed # Configure communication with the SSL key service. Environment="P11_KIT_SERVER_ADDRESS=unix:path=/etc/acm/ssl/acm-p11-kit.sock" Environment="OPENSSL_CONF=/etc/acm/ssl/openssl-acm.cnf" [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.targetReload the Nginx systemd service configuration.
systemctl daemon-reload
Ubuntu 22.04
This section uses Nginx 1.18.0 as an example. The default installation directory for Nginx installed viaaptis/etc/nginx/. If you changed this directory or installed Nginx using a different method, adjust the paths accordingly.
Open
/etc/nginx/nginx.confand addssl_engine pkcs11;afterpid /run/nginx.pid;to specify the PKCS#11 encryption library.user www-data; worker_processes auto; pid /run/nginx.pid; # Specify the use of the PKCS#11 encryption library. ssl_engine pkcs11; include /etc/nginx/modules-enabled/*.conf;Open
/etc/nginx/sites-enabled/defaultand create a new server block withinclude "/etc/acm/ssl/nginx-acm.conf";. Complete server block example:server { listen 443 ssl; # Specify the hostname or Common Name (CN). server_name example.com; root /var/www/html; index index.html index.htm; access_log /var/log/nginx/access_6equj5.log; error_log /var/log/nginx/error_6equj5.log; ssl on; # Reference the SSL key configuration. include "/etc/acm/ssl/nginx-acm.conf"; location / { try_files $uri $uri/ =404; } }Open
/usr/lib/systemd/system/nginx.serviceand add the following environment variables to configure communication with the SSL key service. Content to add: Complete service file example:If you do not know the path to the Nginx systemd service configuration file, run
sudo find / -name "nginx.service"to find it.Environment="P11_KIT_SERVER_ADDRESS=unix:path=/etc/acm/ssl/acm-p11-kit.sock" Environment="OPENSSL_CONF=/etc/acm/ssl/openssl-acm.cnf"[Unit] Description=A high performance web server and a reverse proxy server Documentation=man:nginx(8) After=network.target nss-lookup.target [Service] Type=forking PIDFile=/run/nginx.pid ExecStartPre=/usr/sbin/nginx -t -q -g 'daemon on; master_process on;' ExecStart=/usr/sbin/nginx -g 'daemon on; master_process on;' ExecReload=/usr/sbin/nginx -g 'daemon on; master_process on;' -s reload ExecStop=-/sbin/start-stop-daemon --quiet --stop --retry QUIT/5 --pidfile /run/nginx.pid TimeoutStopSec=5 KillMode=mixed # Configure communication with the SSL key service. Environment="P11_KIT_SERVER_ADDRESS=unix:path=/etc/acm/ssl/acm-p11-kit.sock" Environment="OPENSSL_CONF=/etc/acm/ssl/openssl-acm.cnf" [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.targetReload the Nginx systemd service configuration.
systemctl daemon-reload
Step 3: Deploy the certificate from the console
Log on to the Certificate Management Service console.
In the left navigation pane, choose Deployment and Resource Management > Deployment to Cloud Servers.
On the Deployment to Cloud Servers page, click Create Task.
On the Configure Basic Information page, enter a custom task name and click Next.
On the Select Certificate page, select the certificate type and the SSL certificate associated with the cloud server, and click Next. Each deployment task can deploy only one certificate. To deploy multiple certificates, create multiple tasks.
On the Select Resource page, select an ECS instance that supports one-click deployment and click Next.

The system automatically detects and retrieves all eligible ECS instances under your Alibaba Cloud account. If no resources are displayed, click Synchronize Cloud Resources in the Total Resources area in the upper-left corner. The synchronization time varies based on the number of your cloud resources.
To filter instances, select Quick Deployment/Manual Deployment from the All Types drop-down list.
On the Quick Deployment tab, confirm that the deployment environment requirements are met. Select Confirm that the preceding operations are complete. and click Continue to Deploy.
In the dialog box that appears, click OK. After the deployment task completes:
Manually restart Nginx:
systemctl restart nginx.serviceTest the Nginx SSL connection using curl:
curl -v https://<your_domain_name>
WarningRestarting the web server affects your business. Perform the deployment during off-peak hours.

Step 4: Verify the deployment
On the Deployment to Cloud Servers page, find the task you created. If the Task Status is Deployed, the certificate has been deployed to the cloud server.

A successful deployment task does not guarantee that the certificate is working correctly. Verify by accessing your domain over HTTPS:
Open
https://yourdomainin a browser. Replaceyourdomainwith your actual domain.If a lock icon appears in the address bar, the certificate is working. If you encounter access errors or the lock icon does not appear, clear your browser cache or try again in incognito (privacy) mode. Starting from version 117, the
 icon in the Chrome address bar has been replaced with a new
icon in the Chrome address bar has been replaced with a new  icon. Click this icon to view the lock information.
icon. Click this icon to view the lock information.
Method 2: Manual deployment (certificate update)
This method updates certificates on cloud servers (ECS or Simple Application Server) where a certificate is already configured. It overwrites old certificate files to simplify renewals and replacements. It is not suitable for initial deployment.
Prerequisites
Before you begin, ensure that you have:
An Alibaba Cloud server (Simple Application Server or Elastic Compute Service (ECS))
A web server that directly references PEM or CRT format certificates (such as Nginx or Apache). IIS is not supported
A
rootaccount or an account withsudoprivileges on the server
Step 1: Deploy the SSL certificate
Log on to the Certificate Management Service console.
In the left navigation pane, choose Deployment and Resource Management > Deployment to Cloud Servers.
On the Deployment to Cloud Servers page, click Create Task.
On the Configure Basic Information page, enter a Task Name and click Next.
On the Select Certificate page, select a Certificate Type, select the Associated Certificates, and click Next. Certificates issued by the Private CA service are synchronized to the Manage Uploaded Certificates tab.
On the Select Resource page, select a cloud server type, select the target instance, and click Next. The system automatically detects and retrieves all eligible cloud server instances under your Alibaba Cloud account that have a web application deployed.
NoteIf no resources are displayed, click Synchronize Cloud Resources in the Total Resources area to manually synchronize them. The synchronization time varies depending on the number of cloud product resources.

On the Deployment Configuration page, configure the following parameters and click OK.
ImportantThe Certificate Path and Private Key Path must match the paths configured in your web server. Otherwise, the certificate does not take effect.
The following figure shows the certificate file configuration path for Nginx on a cloud server. The path is for reference only.

Parameter Description Example (use your actual paths) Certificate Path The absolute path where the certificate file is stored on the cloud server. Linux: /ssl/cert.pemWindows: c:\ssl\cert.pemPrivate Key Path The absolute path where the private key file is stored on the cloud server. Linux: /ssl/cert.keyWindows: c:\ssl\cert.keyCertificate Chain Path The absolute path where the certificate chain file is stored on the cloud server. Only required if a certificate chain file is configured in the web server. Linux: /ssl/cert.cerWindows: c:\ssl\cert.cerReload Command A command to restart the web server or reload its configuration after certificate deployment. If the web server fails to restart, log on to the server to troubleshoot. Nginx: sudo nginx -s reloadApache: sudo systemctl restart httpdIn the dialog box that appears, click OK.
If you did not configure a reload command, a prompt appears asking you to manually restart the web server. Click OK, then log on to the server and restart the web service to make the certificate take effect.
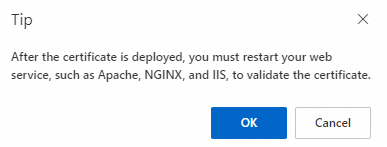
If you configured a reload command, a prompt appears to confirm the risks. Click OK. The reload command runs after the deployment task finishes to make the certificate take effect.

Step 2: Verify the deployment
On the Deployment to Cloud Servers page, find the task you created. If the Task Status is Deployed, the certificate has been updated on the cloud server.

Access your domain over HTTPS to confirm the certificate is working:
Open
https://yourdomainin a browser. Replaceyourdomainwith your actual domain.If a lock icon appears in the address bar, the certificate is deployed. If you encounter access errors or the lock icon does not appear, clear your browser cache or try again in incognito (privacy) mode. Starting from version 117, the
 icon in the Chrome address bar has been replaced with a new
icon in the Chrome address bar has been replaced with a new  icon. Click this icon to view the lock information.
icon. Click this icon to view the lock information.
If the issue persists, see the FAQ section below for troubleshooting.
Quotas and limits
| Item | Details |
|---|---|
| Official certificates | Free. Does not consume deployment quotas. |
| Self-uploaded certificates | Consumes deployment quota. Purchase a deployment package at USD 5 per deployment. If a deployment fails, the quota is refunded. |
| Task scope | Each deployment task deploys one certificate to one cloud server instance. To deploy to multiple instances, create multiple tasks. |
Production deployment considerations
Service interruption: Both deployment methods may require restarting the web server (such as Nginx or Apache), which causes a brief service interruption. Perform deployment during off-peak hours.
Graceful reload: For web servers that support graceful reloads (such as Nginx), use
nginx -s reloadorsystemctl reload nginxinstead ofrestartin the Reload Command of Method 2 to minimize the impact on existing connections.Certificate monitoring: After deploying the certificate, enable domain monitoring. Alibaba Cloud automatically checks the certificate's validity and sends reminders before expiration, helping you renew in time to avoid service interruptions. For details, see Purchase and enable public domain name monitoring.
FAQ
Why is my SSL certificate not working or HTTPS inaccessible after deployment?
Check the following common causes:
Port 443 is not open: Make sure port 443 is open in both your server's security group rules and any host-based firewalls (such as
firewalldor Windows Firewall).Domain mismatch: Verify that the domain you are accessing over HTTPS is listed as a Common Name (CN) or Subject Alternative Name (SAN) in the certificate details. A mismatch between the URL and the certificate's domain causes browsers to reject the connection.
Deployment task failed: Go to the task details page and check the Task Status. Click View Failure Cause to diagnose the problem, correct your configuration, and run the task again.
For further troubleshooting, see Resolve certificate deployment issues based on browser error messages and SSL certificate deployment troubleshooting guide.
What do I do if I get the error "the cloud Assistant not install or run" during deployment?

Cloud Assistant is not installed on the ECS instance, or its status is abnormal. To fix this:
Find the target server and check the Cloud Assistant status.
If it is not installed, click Install to install it automatically.
If the status is abnormal, see Troubleshoot abnormal Cloud Assistant statuses for solutions.
After the Cloud Assistant status returns to normal, create a cloud server deployment task again in the Certificate Management Service console.
Alternatively, bypass the console deployment and manually install the certificate on the server. See Install an SSL certificate on an Nginx or Tengine server (Linux).