Websites that use only the HTTP protocol transmit data in plaintext, making it vulnerable to eavesdropping and tampering. Modern web browsers also flag these sites as "Not Secure." To enable HTTPS encrypted communication, install an SSL certificate on a website hosted on a Windows Internet Information Services (IIS) server. This secures data transmission, protects user privacy, and enhances trust. This topic shows you how to install an SSL certificate on an IIS server and verify its installation.
Usage notes
Before you begin, make sure that you meet the following requirements:
Certificate status: You have an SSL certificate issued by a trusted certificate authority. If the certificate is about to expire or has expired, you must first renew the SSL certificate.
Domain name matching: Make sure that the certificate matches all domain names that you want to secure. To add or modify domain names, you can Purchase a commercial certificate or Append and replace domain names.
Exact-match domain name: Applies only to the specified domain.
example.comprotects onlyexample.com.www.example.comprotects onlywww.example.com.
Wildcard domain name: Applies only to its first-level subdomains.
*.example.comapplies to first-level subdomains such aswww.example.comanda.example.com.*.example.comdoes not protect the root domainexample.comor multi-level subdomains such asa.b.example.com.
NoteTo match multi-level subdomains, the Bound Domains field must contain the exact domain, such as
a.b.example.com, or a corresponding wildcard domain, such as*.b.example.com.Server permissions: You must use the
Administratoraccount or an account with administrator permissions.Domain name resolution: The domain's DNS record is configured and resolves to the server's public IP address.
Environment requirements: This guide uses Windows Server 2008 R2 and Windows Server 2012 R2 as examples, but the instructions apply to all versions from Windows Server 2008 R2 onward.
NoteThe UI may vary between operating system versions. Adjust the steps as needed.
Procedure
Step 1: Prepare the SSL certificate
Go to the SSL Certificate Service page. In the Actions column for the target certificate, click Download Certificate. On the Download tab, download the certificate for the Server Type IIS.
Extract the downloaded certificate package:
If the package contains both a certificate file (in .pfx format) and a password file (in .txt format), save both files securely. You will need them during deployment.
ImportantThe system generates a new password with each download. This password is valid only for the accompanying certificate file.
If the package contains only a certificate file (in .pem format), you must use a certificate tool to convert the certificate file and your certificate password or private key file into the .pfx format. For detailed instructions, see Convert the format of a certificate.
NoteIf you used a tool such as OpenSSL or Keytool to generate the Certificate Signing Request (CSR) file when you requested the certificate, the private key file is saved locally and is not included in the downloaded certificate package. If you lose the private key, you cannot use the certificate. You will need to Purchase a commercial certificate and generate a new CSR and private key.
Upload the exacted certificate file to the server.
NoteThese steps use an Alibaba Cloud Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance as an example. For other types of servers, refer to their official documentation.
Go to ECS console - Instances. In the top navigation bar, select the target region and resource group.
Locate the target instance. Click Connect and select Sign in now. Log on to the server desktop as prompted.
Press Win+E to open File Explorer.
Under Redirected drives and folders, double-click workbench on ***. Drag the certificate file from your local machine into this directory, and then right-click the folder and select Refresh.
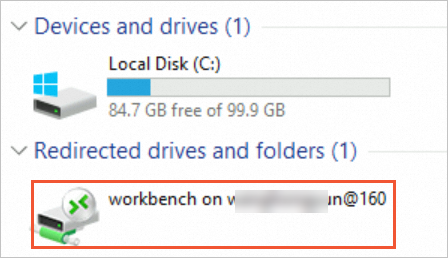
Drag the certificate file from this directory to the
C:drive or another drive for storage.ImportantWhen you reconnect to or exit the instance, workbench automatically clears all uploaded files from the Redirected drives and folders directory to save space. This directory is for file transfer only. Do not save your files here.
Step 2: Configure the system and network environment
Open port 443 in the security group.
ImportantIf your server is deployed on a cloud platform, ensure that its security group allows inbound access on port 443 (TCP). Otherwise, the service cannot be accessed from the Internet. The following steps use Alibaba Cloud ECS as an example. For other cloud platforms, see their official documentation.
Log on to the ECS console. In the upper-left corner of the page, select the region where the target ECS instance is located. On the Instances page, find the target ECS instance.
Click the name of the target instance to open the instance details page. Click and ensure that a rule exists with the following settings: Action is set to Allow, Protocol Type is TCP, Destination Port Range is HTTPS (443), and Authorization Object is set to All IPv4 Addresses.
If this rule does not exist, refer to Add a security group rule to add the rule.
Open port 443 in the server firewall.
Log on to the Windows server, click the Start menu in the lower-left corner, and open the Control Panel.
Click .
If the firewall is off, as shown in the following figure, no further action is needed. Go directly to Step 3: Import the SSL certificate in MMC.
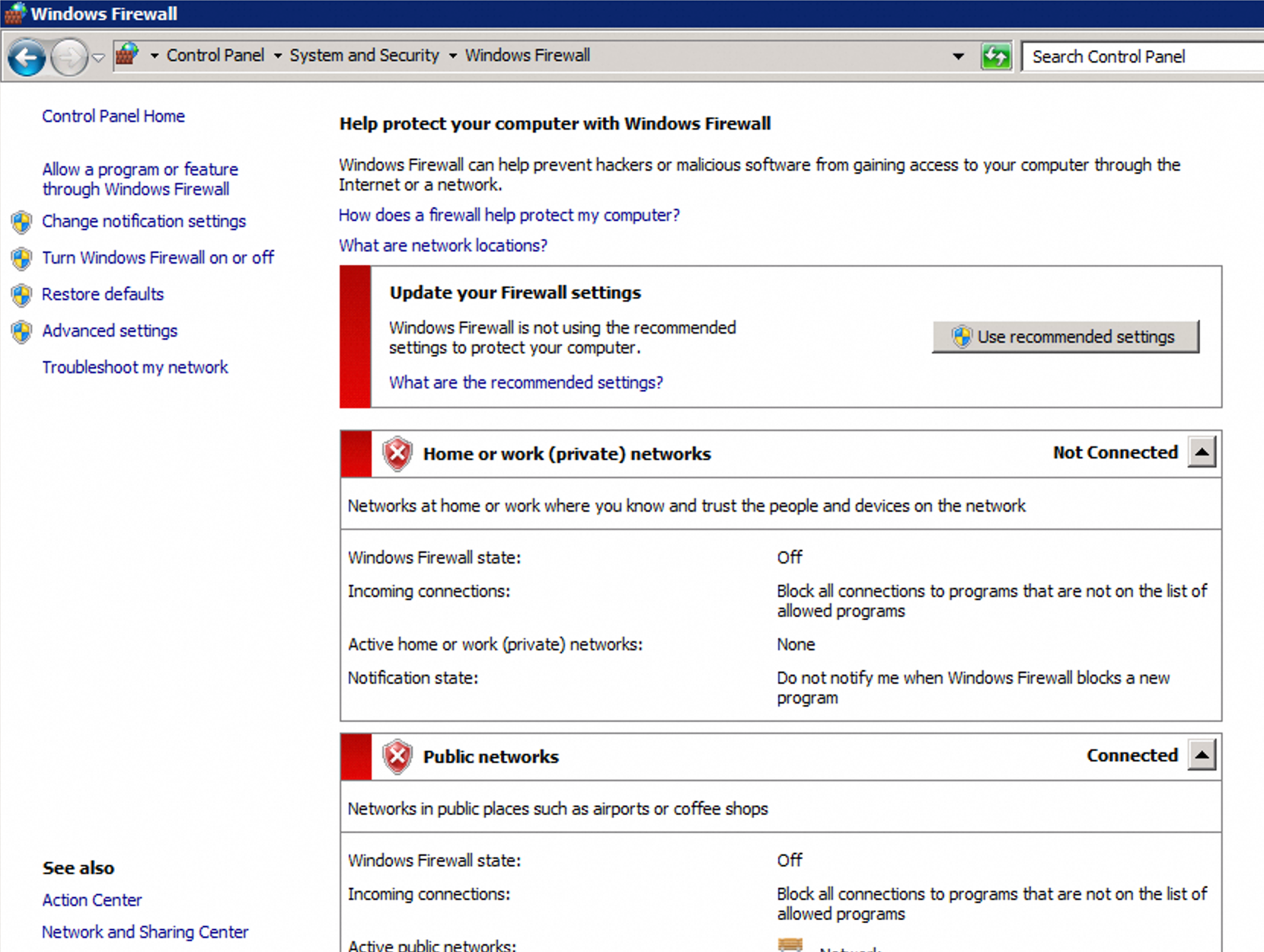
If the firewall is on, allow the HTTPS rule.
Step 3: Import the SSL certificate in MMC
In the lower-left corner, click the Start menu. Search for and open the Run dialog box. Enter
mmcand click OK.In the MMC console, add the Certificates snap-in.
In the menu bar at the top of the console, choose .
In the Add or Remove Snap-ins dialog box, select Certificates from the Available Snap-ins list on the left, and click Add.
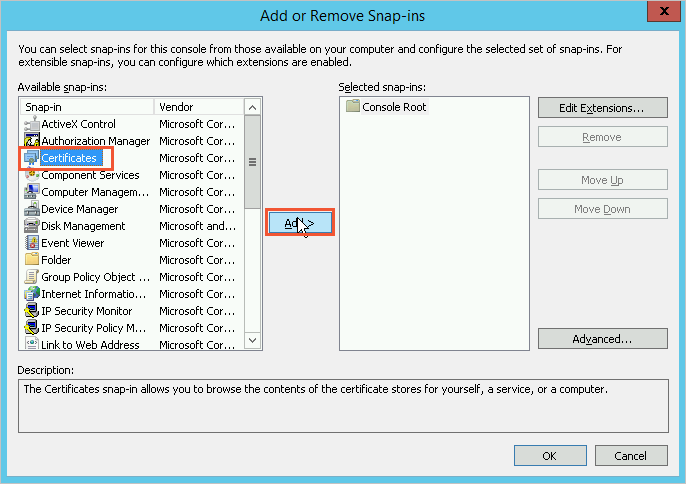
In the Certificates snap-in dialog box, select Computer Account and click Next.
In the Select Computer dialog box, select Local computer (the computer this console is running on) and click Finish.
Click OK.
In the left navigation pane of the console, expand . Right-click Personal and choose .
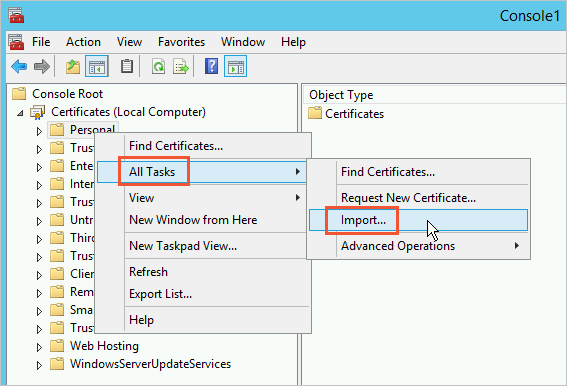
Follow the prompts in the Certificate Import Wizard.
Welcome to the Certificate Import Wizard: Click Next.
File to Import dialog box: Click Browse, open the PFX certificate file, set the file type to All Files (*), and click Open. Then, click Next.
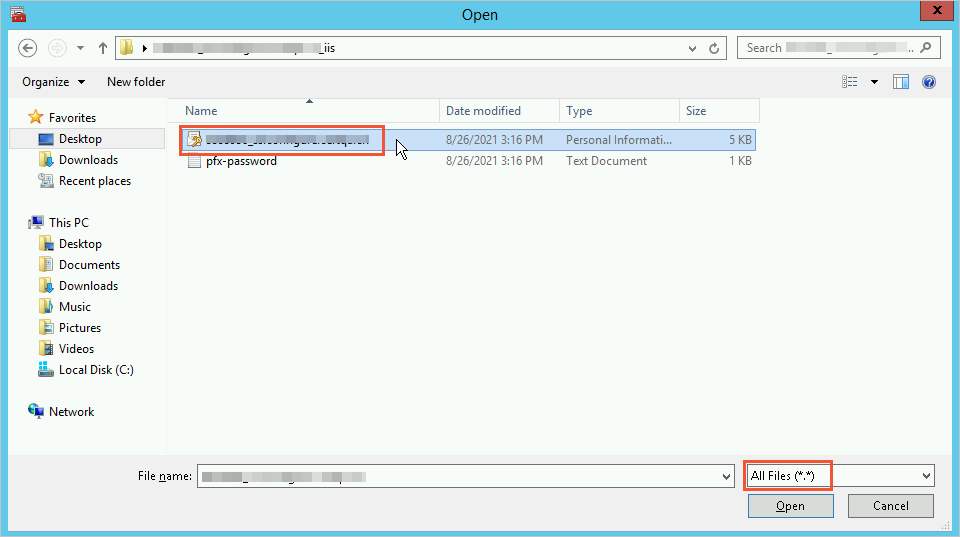
Type the password for the private key: Open the TXT private key file, copy its content, and paste it into the Password text box. Click Next.
Certificate Store: Select Automatically select the certificate store based on the type of certificate and click Next.
Completing the Certificate Import Wizard: Click Finish.
After the The Import Was Successful message appears, click OK.
Step 4: Bind the SSL certificate to the website in IIS Manager
Add a site binding. Follow the steps for your operating system version.
Windows Server 2012 R2 and later
Click the
 Start icon, and then click .
Start icon, and then click .In the Connections pane on the left, expand the server, click Sites, and then click the target website in the list. In the Actions pane on the right, click Bindings.
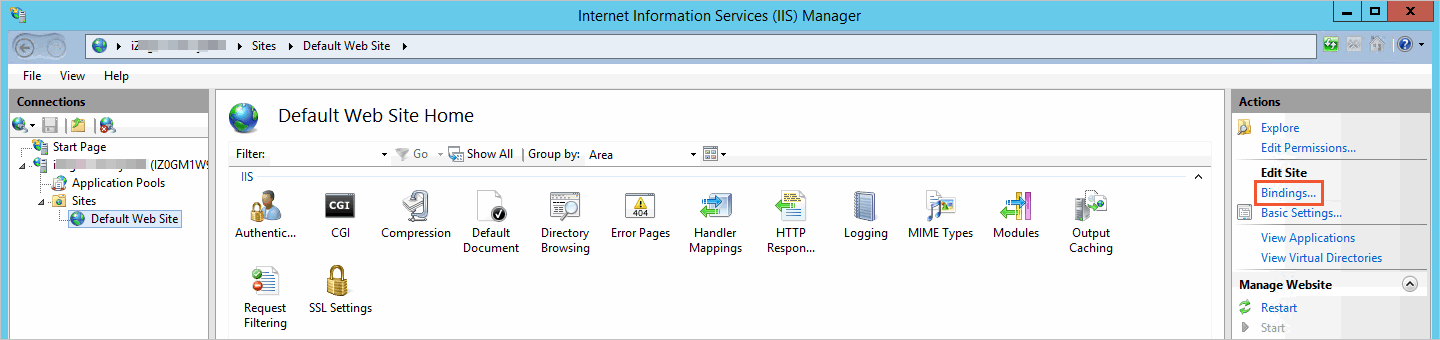
In the Site Bindings dialog box, click Add.
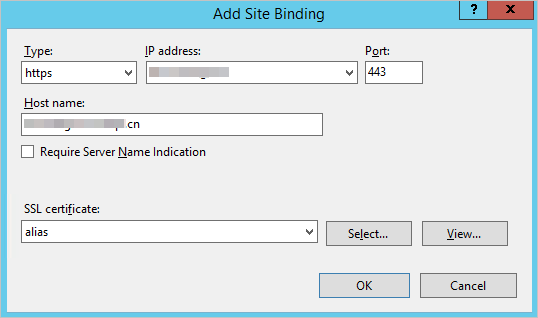
In the Add Site Binding dialog box, configure the website parameters and click OK. Your configuration depends on one of two scenarios.
Configure a certificate for one or multiple websites
Configure certificates for multiple websites
Type: Select https.
IP address: Select the server's IP address. If the server only has one IP address, leave this as All Unassigned.
Port: Keep the default value of 443.
NoteWe recommend using port 443. If you set a non-standard port, users must include the port number in the URL when accessing the website (such as
https://domain.com:8443).Host name: Enter the domain name for which you want to enable HTTPS, such as
domain.com.Require Server Name Indication: Do not select this checkbox for a single-site configuration.
NoteSelecting this option triggers a warning: The default SSL site has not been created. To support browsers that do not support SNI, it is recommended to create a default SSL site. Resolving this requires additional steps. For details, see Configure certificates for multiple websites.
SSL certificate: Select the imported certificate.
Type: Select https.
IP address: Select the server's IP address. If the website is deployed on this server and the server only have one IP addresses, keep the default setting All Unassigned.
Port: Keep the default value of 443.
Host name: For each website, enter its corresponding domain name, such as
example1.comandexample2.com.Require Server Name Indication: Select this checkbox.
SSL certificate: For each website, select its corresponding imported certificate.
The default SSL site handles requests from non-SNI-compliant browsers. It can be a blank page or a redirect page. Configure it as needed.
If you are certain your users do not use legacy browsers, ignore this warning.
In the IIS Manager, in the Connections pane on the left, expand the server and click Sites. In the website list, select the Default Web Site or add a new website. In the Actions pane on the right, click Bindings.
In the Site Bindings dialog box, click Add. In the Add Site Binding dialog box, complete the following configuration and click OK.

Type: Select https.
IP address: Select the server's IP address.
Port: Keep the default 443.
Host name: Leave this blank.
Require Server Name Indication: Do not select this checkbox.
SSL certificate: Select any imported certificate.
Create a secondary Elastic Network Interface (ENI) and attach it to the ECS instance that hosts the IIS server. For details, see Create and use an ENI.
Create elastic IP addresses (EIPs) and associate them with the secondary ENI. The mapping between public IP addresses and private IP addresses is as follows.

At your DNS provider, modify the DNS records to point each website's domain to its corresponding public IP address. For example, point
example1.comandexample2.comto106.xx.xx.198and101.xx.xx.50, respectively.In IIS Manager, configure each website as follows:
IIS website
SSL certificate
IP address (Private)
Public IP address of the ECS instance
Web01
Certificate for
example1.com192.168.1.211106.xx.xx.198Web02
Certificate for
example2.com192.168.1.212101.xx.xx.50

Type: Select https.
IP address: For each website, enter its corresponding private IP address on the server. For example,
192.168.1.211for web01 and192.168.1.212for web02.Port: Keep the default value of 443.
SSL certificate: For each website, select its corresponding imported certificate.
In the Site Bindings dialog box, click Close.
(Optional) Set the TLS policy.
Download the IIS Crypto tool to the server and select IIS Crypto GUI: https://www.nartac.com/Products/IISCrypto/Download
On the server, double-click the downloaded file to run it. On the Schannel homepage, click Best Practices. In the dialog box that opens, click OK and then click Apply. Restart the server instance.
Configure a certificate for one or multiple websites
Configure certificates for multiple websites
(Recommended) Use SNI to configure certificates for multiple websites
Server Name Indication (SNI) lets you host multiple SSL-enabled websites on a single IP address and port.
In the example below, two websites,
web01andweb02, are deployed on the same IIS server and share the same IP address and port (443). You must select the Require Server Name Indication checkbox for each site binding. Otherwise, IIS will show an error "At least one other site is using the same HTTPS binding.".

After configuration, a warning may appear
The default SSL site has not been created...This means that some older browsers that do not support SNI (such as Internet Explorer on Windows XP) will encounter errors when accessing your website. To support these browsers, configure a default SSL site as a fallback.NoteUse multiple IP addresses to configure certificates for multiple websites
ImportantIf multiple websites share an IP address and port, such as port 80. This method requires you to modify DNS records. The entry IP address for website access changes from a single IP to multiple IPs. This change might affect your services. Fully assess the business impact before proceeding.
Windows Server 2008 R2
Click the Start menu, and then click .
In the Connections pane, expand the server node, expand Sites, and click the target website. In the Actions pane, click Bindings.

In the Site Bindings dialog box, click Add.
In the Add Site Binding dialog box, configure the website settings, and then click OK. Your options depend on your scenario.
Configure a certificate for a single website: Select this to configure a certificate for one website or to use the same certificate for multiple websites.
Configure certificates for multiple websites: Select this to configure a different certificate for each of the multiple websites on the IIS server.
Type: Select https.
IP address: Select the server's IP address. If the website is deployed on this server and the server only have one IP address, keep the default value of All Unassigned.
Port: Keep the default value of 443.
NoteSet the port to 443. If you set it to a port other than 443, you must add the port number after the domain name when you access the website from a browser. For example:
https://domain.com:8443.SSL certificate: Select the imported certificate.
Create a secondary Elastic Network Interface (ENI) and attach it to the ECS instance that hosts the IIS server. For details, see Create and use an ENI.
Create elastic IP addresses (EIPs) and associate them with the secondary ENI. The mapping between public IP addresses and private IP addresses is as follows.

At your DNS provider, modify the DNS records to point each website's domain to its corresponding public IP address. For example, point
example1.comandexample2.comto106.xx.xx.198and101.xx.xx.50, respectively.In IIS Manager, configure each website as follows:
IIS website
SSL certificate
IP address (Private)
Public IP address of the ECS instance
Web01
Certificate for
example1.com192.168.1.211106.xx.xx.198Web02
Certificate for
example2.com192.168.1.212101.xx.xx.50

Type: Select https.
IP address: For each website, enter its corresponding private IP address on the server. For example,
192.168.1.211for web01 and192.168.1.212for web02.Port: Keep the default value of 443.
SSL certificate: For each website, select its corresponding imported certificate.
After you complete the configuration, you can view the added https site binding in the Site Bindings list.
NoteSome Windows Server 2008 systems might report the error
One or more intermediate certificates in the certificate chain are missing. For a solution, see FAQ.In the Site Bindings dialog box, click Close.
Set the TLS policy.
For Windows Server 2008, the default TLS configuration might not be trusted by modern browsers, apps, or miniapps. If you receive errors such as
ERR_SSL_VERSION_OR_CIPHER_MISMATCHorUnsupported protocolwhen you access the website after configuration, set the TLS policy as follows:Download the IIS Crypto tool to the server. Select IIS Crypto GUI from: https://www.nartac.com/Products/IISCrypto/Deprecated
On the server, double-click the downloaded file to run it. On the Schannel tab, click Best Practices, click OK in the pop-up, then click Apply. Restart the server instance when prompted.
Configure a certificate for a single website

Configure certificates for multiple websites
Windows Server 2008 does not support Server Name Indication (SNI). To host multiple HTTPS-enabled websites, each site must be bound to a unique IP address, and each IP address must have a unique certificate.
ImportantIf multiple websites share an IP address and port, such as port 80. This method requires you to modify DNS records. The entry IP address for website access changes from a single IP to multiple IPs. This change might affect your services. Fully assess the business impact before proceeding.
(Optional) Set up automatic HTTP to HTTPS redirection.
In IIS Manager, in the Connections pane on the left, expand the server, click Sites, and select the site you want to configure. In the site's home view, check if the URL Rewrite module is present. If it does not exist, go to https://www.iis.net/downloads/microsoft/url-rewrite. download the appropriate version for your system, and install it. Close and reopen IIS Manager for the change to take effect.


Double-click URL Rewrite. In the Actions pane on the right, click Add Rule(s).
In the Add Rule(s) dialog box, select Inbound Rules > Blank Rule, and then click OK.
In the Edit Inbound Rule dialog box, complete the configuration as follows. Keep the default values for any parameters not mentioned.
Parameter
Configuration
Name
Enter a descriptive name (such as HTTP to HTTPS Redirect).
Match URL
Requested URL
Select Matches the Pattern.
Using
Select Regular Expressions.
Pattern
Enter
(.*).Ignore case
Select the checkbox.
Conditions
Logical grouping
Select Match All.
Condition to add
Condition input
Enter
{HTTPS}.Check if input string
Select Matches the Pattern.
Pattern
Enter
^OFF$.Ignore case
Select the checkbox.
Action
Action type
Select Redirect.
Redirect URL
Enter
https://{HTTP_HOST}/{R:1}.Append query string
Select the checkbox.
Redirect type
Select Found (302) or Permanent (301).

In the Actions pane on the right, click Apply.
Return to IIS Manager. In the Connections pane on the left, click the server and then click Restart. After configuration, verify that HTTP requests automatically redirect to HTTPS.

Step 5: Verify the deployment result
Access your domain over HTTPS in a web browser. For example,
https://yourdomain. Replaceyourdomainwith your actual domain.If a lock icon appears in the browser's address bar, the certificate is deployed successfully. If you encounter access errors or the lock icon does not appear, clear your browser cache or try again in incognito (privacy) mode.

Starting from version 117, the
 icon in the Chrome address bar has been replaced with a new
icon in the Chrome address bar has been replaced with a new  icon. Click this icon to view the lock information.
icon. Click this icon to view the lock information.
If the issue persists, refer to the FAQ for troubleshooting.
Going live
When you deploy to a production environment, follow these best practices to enhance security, stability, and maintainability:
Run as a non-administrator user:
Create a dedicated, low-privilege system user for the application. Never run the application with an account that has administrator privileges.
NoteA recommended approach is to configure SSL at the gateway layer. This involves deploying the certificate on a Server Load Balancer (SLB) or a reverse proxy such as Nginx. The gateway terminates the HTTPS traffic and forwards the decrypted HTTP traffic to the backend application.
Externalize credential management:
Never hard-code passwords or other sensitive information in your code or configuration files. Use environment variables, Vault, or a cloud provider's key management service to inject credentials.
Enforce HTTP to HTTPS redirection:
Redirect all HTTP traffic to HTTPS to prevent man-in-the-middle attacks.
Configure modern TLS protocols:
Disable old and insecure protocols (such as SSLv3, TLSv1.0, and TLSv1.1) in your server configuration. Enable only TLSv1.2 and TLSv1.3.
Monitor certificates and automate renewal:
After you deploy the certificate, enable domain monitoring. Alibaba Cloud automatically checks the certificate validity period and sends renewal reminders before expiration to help you renew in a timely manner and avoid service interruption. For detailed instructions, see Purchase and enable public domain name monitoring.
FAQ
Why is my website not accessible via HTTPS after installing an SSL certificate on IIS?
This issue is often caused by one of the following configuration problems. Check them in order:
Port 443 blocked: The server's security group or firewall does not have port 443 open. See Configure the system and network environment.
Domain mismatch: The domain you are accessing is not listed in the certificate's Bound Domains. See Domain name match.
Incorrect certificate configuration: The certificate was not replaced correctly. Check whether the certificate file you are using is the latest and valid one.
Missing certificate on other services: If your domain uses services such as a Content Delivery Network (CDN), Server Load Balancer (SLB), or Web Application Firewall (WAF), the certificate must also be installed on those services. See Certificate deployment locations when traffic passes through multiple Alibaba Cloud services to complete the setup.
Incomplete deployment on multiple servers: If your domain's DNS resolves to multiple servers, the certificate must be installed on all of them.
For further troubleshooting, see Resolve certificate deployment issues based on browser error messages and SSL certificate deployment troubleshooting guide.
How can I fix the "One or more intermediate certificates in the certificate chain are missing" error on Windows Server 2008 R2?
To fix this, you must manually install the missing root or intermediate certificate into the server's Trusted Root Certification Authorities store. This error occurs because the certificate store on older operating systems such as Windows Server 2008 R2 may not contain the modern root certificates required to validate your certificate's chain.
Identify the correct root certificate:
Log on to the Digital Certificate Management Service console. In the left navigation pane, choose . Navigate to your certificate's details page.
In the Certificate Chain Information section, check the certificate issuer and issuance date. This determines which root certificate you need. For example, if the certificate was issued after December 1, 2024, download Digicert_Global_Root_G2_DV_OV (New - Cross-signed Root). If it was issued before December 1, 2024, download DigiCert_Global_Root_G2_DV_OV (Old - Transitional). For details on selecting the correct DigiCert root, see [Announcement] Replacement of DigiCert root certificates.


Download the certificate: Go to Download a root certificate and download the file you identified in the previous step.
Install the certificate:
Upload the root certificate file to your server.
Double-click the file to open the Certificate Import Wizard.
Follow the prompts to install the certificate, ensuring you place it in the Trusted Root Certification Authorities store for the Local Computer.
What is the correct way to update an existing SSL certificate in IIS?
To update an SSL certificate, import the new certificate and then edit the existing HTTPS site binding to select the new one.
Import the new certificate: Follow the instructions in Step 3: Import the SSL certificate in MMC to import your new
.pfxfile into the server'sLocal Computer>Personalstore.Update the site binding:
In IIS Manager, navigate to your site and open its Bindings, as shown in Step 4: Bind the SSL certificate to the website in IIS Manager.
Select the
httpsbinding and click Edit.From the SSL certificate dropdown menu, choose your newly imported certificate. Click OK.
Verify the update: Open your website in a new private/incognito browser window to avoid cache issues. Click the browser's security icon to inspect the certificate and confirm its details (such as expiration date) are correct.
|
|
|
Why is my .pfx certificate file not visible in the MMC Certificate Import Wizard?
You must change the file type filter in the file browser window. By default, the wizard filters for files with extensions like .cer. To see your .pfx file, you must change the filter in the bottom-right corner from "X.509 Certificate" to "All Files (*.*)".
How can I recover the password for my .pfx file if I've lost it?
You cannot recover a lost .pfx password. You must download the certificate again.
A new, unique password is generated with each certificate download. If you have lost the password, follow the actions in Step 1: Prepare the SSL certificate to download the certificate package again. This will provide you with a new .pfx file and its matching password file.
How do I determine if my Windows Server is 32-bit (x86) or 64-bit (x64)?
You can use one of the following methods:
Method 1: Via Command Prompt
Open Command Prompt by searching for
cmdin the Start menu.Run the following command:
wmic os get osarchitecture.The output will show
64-bit(for x64) or32-bit(for x86).
Method 2: Via the ECS console
If your server is an Alibaba Cloud ECS instance, you can find the architecture listed on the instance's details page in the ECS console.



