You can use the syslog-ng utility to collect logs to Simple Log Service by using a syslog protocol. This topic describes how to upload logs to Simple Log Service by using a syslog protocol.
Limits
Syslogs must be stored based on the RFC 5424 protocol. You can also use other syslog protocols. For more information, see Collect Linux syslogs.
The maximum size of each log is 64 KB.
Transport Layer Security (TLS) 1.2 must be used to ensure the security of data transmission.
Configuration method
In most cases, you cannot use the TLS or RFC 5424 protocol to collect logs from devices such as on-premises VPNs and routers. We recommend that you use the syslog plug-in of Logtail to collect logs from these devices. For more information, see Collect Linux syslogs.
If you upload logs by using a syslog protocol, you must specify the endpoint to which you want to upload the logs in the Project name.Simple Log Service endpoint:Syslog protocol port number format. Example: test-project-1.cn-hangzhou-intranet.log.aliyuncs.com:10009. We recommend that you specify an endpoint based on the region where your Simple Log Service project resides. For more information, see Endpoints. The syslog port is 10009. You must also specify a Simple Log Service project, a Logstore, and an AccessKey pair in the STRUCTURED-DATA field. The following table describes the parameters.
Parameter | Description | Example |
STRUCTURED-DATA | The value is fixed as logservice. | logservice |
Project | The name of the Simple Log Service project. Before you can collect logs, you must create a project. For more information, see Create a project. | test-project-1 |
Logstore | The name of the Simple Log Service Logstore. Before you can collect logs, you must create a Logstore. For more information, see Create a Logstore. | test-logstore-1 |
access-key-id | The AccessKey ID. We recommend that you use the AccessKey pair of a Resource Access Management (RAM) user. For more information, see Grant permissions to the RAM user. | yourAccessKeyID |
access-key-secret | The AccessKey secret. We recommend that you use the AccessKey pair of a RAM user. For more information, see Grant permissions to the RAM user. | yourAccessKeySecret |
Example 1: Use syslog-ng to collect logs
Syslog-ng is a syslog protocol-based open source utility that runs on UNIX and UNIX-like systems. You can run the sudo yum install syslog-ng or sudo apt-get install syslog-ng command to install the syslog-ng utility.
The rsyslog utility is pre-installed on Linux servers. The rsyslog utility is incompatible with the syslog-ng utility. Before you use the syslog-ng utility, you must uninstall the rsyslog utility.
Open the syslog-ng configuration file.
The default path of the syslog-ng configuration file is /etc/syslog-ng/syslog-ng.conf.
Configure the following settings and append the settings to the syslog-ng configuration file.
### Syslog-ng Logging Config for LogService ### template LogServiceFormat { template("<${PRI}>1 ${ISODATE} ${HOST:--} ${PROGRAM:--} ${PID:--} ${MSGID:--} [logservice project=\"test-project-1\" logstore=\"test-logstore-1\" access-key-id=\"<yourAccessKeyId>\" access-key-secret=\"<yourAccessKeySecret>\"] $MSG\n"); template_escape(no); }; destination d_logservice{ tcp("test-project-1.cn-hangzhou.log.aliyuncs.com" port(10009) tls(peer-verify(required-untrusted)) template(LogServiceFormat)); }; log { source(s_sys); # default use s_sys destination(d_logservice); }; ### END Syslog-ng Logging Config for LogService ###Restart the syslog-ng utility.
Run the sudo /etc/init.d/syslog-ng restart, sudo service syslog-ng restart, or sudo systemctl restart syslog-ng command to restart the syslog-ng utility.
Run the logger command to generate test logs.
For example, you can run the logger hello world! command to generate logs.
Sample logs
After you upload logs to Simple Log Service, you must create indexes for the logs before you can view the logs in the Simple Log Service console. For more information, see Create indexes.
For more information about log fields, see RFC 5424.
By default, Simple Log Service deletes the Logservice field to ensure that your AccessKey pair is not leaked.
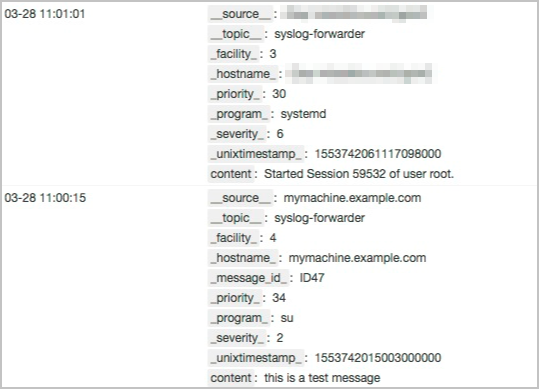
Field | Description |
__source__ | The hostname in the raw log. |
__topic__ | The value is fixed as syslog-forwarder. |
__facility__ | The facility information, such as the information about a device or module. |
__program__ | The process name. |
__serverity__ | The severity level of the log. |
__priority__ | The priority of the log. |
__unixtimestamp__ | The UNIX timestamp of the raw log. Unit: nanoseconds. |
content | The msg field in the raw log. |
FAQ and troubleshooting
How do I simulate log upload?
You can use Netcat to simulate log upload to check whether the network is connected and whether the AccessKey pair has the upload permissions.
Log on to the server on which you want to simulate log upload.
Run the following command to install Netcat:
sudo yum install nmap-ncatRun the following command to connect to Simple Log Service:
ncat --ssl <yourProject>.<yourEndpoint> 10009Example command:
ncat --ssl test-project-1.cn-hangzhou.log.aliyuncs.com 10009Netcat does not automatically detect whether the network connection is interrupted. After you run a ncat command, enter the log that you want to upload and press the Enter key within 30 seconds.
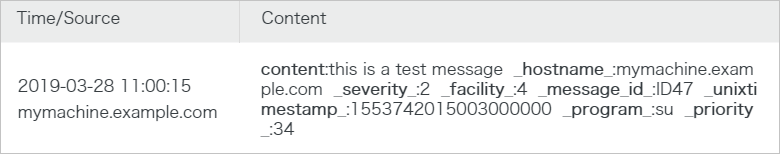
<34>1 2019-03-28T03:00:15.003Z mymachine.example.com su - ID47 [logservice project="<yourProject>" logstore="<yourLogstore>" access-key-id="<yourAccessKeyID>" access-key-secret="<yourAccessKeySecret>"] this is a test messageExample command:
<34>1 2019-03-28T03:00:15.003Z mymachine.example.com su - ID47 [logservice project="trace-doc-test" logstore="doc-test-001-logs" access-key-id="<yourAccessKeyID>" access-key-secret="<yourAccessKeySecret>"] this is a test messagePreview the log in the Simple Log Service console to check whether the log is uploaded.
For more information, see Preview logs.
What do I do if logs fail to be uploaded?
If logs fail to be uploaded, you can troubleshoot the failure based on the error message. For more information, see How do I view Logtail collection errors?