Import log files from Amazon S3 to Simple Log Service (SLS) for querying, analysis, and processing. SLS supports the import of individual S3 objects up to 5 GB, with this limit applying to the file size after decompression for compressed files.
Prerequisites
Log files are uploaded to Amazon S3.
A project and logstore are created. For more information, see Manage a project and Create a logstore.
Custom permissions:
Create a custom policy that grants permissions to manage S3 resources, as shown in the example that follows. For more information, see Create custom permissions on AWS.
NoteYou must configure custom permissions for S3 to import objects into SLS.
{ "Version": "1", "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "s3:GetObject", "s3:ListBucket" ], "Resource": [ "arn:aws:s3:::your_bucket_name", "arn:aws:s3:::your_bucket_name/*" ] } ] }Create a custom policy that grants permissions to manage Amazon Simple Queue Service (SQS) resources. For more information, see Create custom permissions on AWS.
NoteThis is required only if you enable SQS.
{ "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "sqs:ReceiveMessage", "sqs:DeleteMessage", "sqs:GetQueueAttributes", "kms:Decrypt" ], "Resource": "*" }
Create a data import configuration
Log on to the Simple Log Service console.
On the Data Import tab in the Import Data area, select S3 - Data Import.
Select the target project and logstore, then click Next.
Configure import settings.
In the Import Configuration step, set the following parameters.
Parameter
Description
Job Name
The unique name of the SLS task.
S3 Region
The region where the bucket that stores the objects to import is located.
AWS AccessKey ID
The AccessKey ID used to access AWS.
ImportantMake sure your AccessKey has permissions to access the corresponding AWS resources.
AWS Secret AccessKey
The Secret AccessKey used to access AWS.
SQS Queue URL
The identifier of the SQS queue. For more information, see Queue and message identifiers.
ImportantThis feature takes effect only after you enable SQS.
File Path Prefix Filter
Filter S3 objects by file path prefix to locate the objects to import. For example, if all objects to import are in the `csv/` directory, set the prefix to `csv/`.
If you do not set this parameter, the entire S3 bucket is traversed.
NoteSet this parameter. If the bucket contains many objects, traversing the entire bucket is inefficient.
File Path Regex Filter
Filter S3 objects by a regular expression on the file path to locate the objects to import. Only objects whose names, including their paths, match the regular expression are imported. By default, this parameter is empty, which means no filtering is performed.
For example, if an S3 object is named
testdata/csv/bill.csv, set the regular expression to(testdata/csv/)(.*).For more information about how to debug a regular expression, see Debug a regular expression.
File Modification Time Filter
Filter S3 objects by their modification time to locate the objects to import.
All: To import all S3 objects that meet specified conditions, select this option.
From Specific Time: To import files modified after a point in time, select this option.
Specific Time Range: If you want to import files modified within a specific time range, select this option.
Data Format
The parsing format of the objects. The options are described as follows.
CSV: A delimited text file. Specify the first line as field names or manually specify field names. All lines except the first line are parsed as the values of log fields.
Single-line JSON: An S3 file is read line by line. Each line is parsed as a JSON object. The fields in JSON objects are log fields.
Single-line Text Log: Each line in an S3 file is parsed as a log.
Multi-line Text Logs: Multiple lines in an S3 object are parsed as a log. Specify a regular expression to match the first line or the last line of a log.
Compression Format
The compression format of the S3 objects to import. SLS decompresses the objects and reads the data based on the specified format.
Encoding Format
The encoding format of the S3 objects to import. Only UTF-8 and GBK are supported.
New File Check Cycle
If new objects are constantly generated in the specified directory of S3 objects, configure New File Check Cycle as needed. After you configure this parameter, the data import job is continuously running in the background, and new objects are automatically detected and read at regular intervals. The system ensures that data in an S3 object is not repeatedly written to SLS.
If new objects are no longer generated in the target S3 path, set the option to Never Check. The import job will then automatically exit after reading all objects that meet the specified conditions.
Log Time Configuration
Time Field
When you set Data Format to CSV or Single-line JSON, set a time field. This field is the name of the column in the file that represents time and is used to specify the timestamp for logs when they are imported to SLS.
Regular Expression To Extract Time
Use a regular expression to extract the time from a log.
For example, if a sample log is 127.0.0.1 - - [10/Sep/2018:12:36:49 0800] "GET /index.html HTTP/1.1", set Regular Expression To Extract Time to
[0-9]{0,2}\/[0-9a-zA-Z]+\/[0-9:,]+.NoteFor other data formats, you can also use a regular expression to extract only part of the time field.
Time Field Format
Specify the time format to parse the value of the time field.
Specify a time format that follows the Java SimpleDateFormat syntax. For example:
yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss. For more information about the syntax, see Class SimpleDateFormat. For more information about common time formats, see Time formats.Epoch formats are supported, including epoch, epochMillis, epochMicro, and epochNano.
Time Zone
Select the time zone for the time field. When the time field format is an epoch type, you do not need to set a time zone.
If daylight saving time needs to be considered when parsing log time, select a UTC format. Otherwise, select a GMT format.
NoteThe default time zone is UTC+8.
If you set Data Format to CSV, you must configure the additional parameters described in the following table.
CSV-specific parameters
Parameter
Description
Delimiter
Set the delimiter for logs. The default value is a comma (,).
Quote
The quote character used for a CSV string.
Escape Character
Configure the escape character for logs. The default value is a backslash (\).
Maximum Lines
If you turn on First Line As Field Name, the first line in a CSV file is used as the field name.
Custom Fields
If you turn off First Line As Field Name, you can specify custom field names. Separate multiple field names with commas (,).
Lines To Skip
Specify the number of log lines to skip. For example, if you set this to 1, log collection starts from the second line of the CSV file.
Multi-line text log-specific parameters
Parameter
Description
Position to Match Regular Expression
Set the position for the regular expression to match. The options are described as follows:
Regular Expression To Match First Line: If you select this option, the regular expression that you specify is used to match the first line of a log entry. The unmatched lines are collected as a part of the log entry until the maximum number of lines that you specify is reached.
Regular Expression To Match Last Line: Uses a regular expression to match the last line of a log entry. Unmatched lines are considered part of the next log entry until the maximum number of lines is reached.
Regular Expression
Set the correct regular expression based on the log content.
For more information about how to debug a regular expression, see Debug a regular expression.
Maximum Lines
The maximum number of lines for a single log entry.
Click Preview to view the import result.
After confirming the information, click Next.
Preview data, configure indexes, and click Next.
By default, full-text indexing is enabled in SLS. You can also manually create field indexes based on collected logs, or click Automatic Index Generation to have SLS generate them automatically. For more information, see Create indexes.
ImportantTo query and analyze logs, you must enable either full-text indexing or field indexing. If both are enabled, field indexes take precedence.
View the import configuration
After you create an import configuration, view the configuration and its statistical reports in the console.
In the Project list, click the target project.
In , find the target logstore, select , and click the configuration name.
View basic information and statistical reports for the data import configuration.
You can also modify the configurations, start or stop the import, and delete the configuration.
WarningThe delete operation is irreversible. Proceed with caution.
Billing
The import feature in SLS is free of charge. However, this feature requires access to service provider APIs and will incur traffic and request fees. The pricing model is as follows, and the final fees are determined by the bill from the service provider.
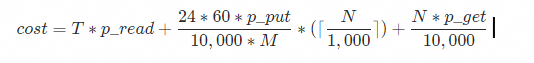
Field | Description |
| Total daily data import volume in GB. |
| Fee per GB of outbound internet traffic. |
| Fee per 10,000 Put requests. |
| Fee per 10,000 Get requests. |
| New file check interval in minutes. You can set New File Check Cycle when you create a data import configuration. |
| Number of listable files in the bucket based on the prefix. |
FAQ
Problem | Possible cause | Solution |
No data is displayed in the preview. | There are no objects in S3, the objects contain no data, or no objects meet the filter conditions. |
|
Garbled text appears in the data. | The data format, compression format, or encoding format is configured incorrectly. | Check the format of the S3 objects, and then modify the Data Format, Compression Format, or Encoding Format settings as needed. To fix existing garbled data, you must create a new logstore and a new import configuration. |
The log time in SLS is inconsistent with the actual time in the data. | When the import configuration was created, the log time field was not specified, or the time format or time zone was configured incorrectly. | Specify the log time field and set the correct time format and time zone. For more information, see Log Time Configuration. |
Data cannot be queried or analyzed after it is imported. |
|
|
The number of imported log entries is less than expected. | Some objects contain single lines of data larger than 3 MB, which are discarded during import. For more information, see Collection limits. | When writing data to S3 objects, make sure that a single line of data does not exceed 3 MB. |
The number of objects and the total data volume are large, but the import speed is slower than the expected speed of up to 80 MB/s. | The number of shards in the logstore is too small. For more information, see Performance limits. | If the number of shards in the logstore is small, increase the number of shards to 10 or more and then check the latency. For more information, see Manage shards. |
Some objects are not imported. | The filter conditions are set incorrectly, or some individual objects exceed 5 GB in size. For more information, see Collection limits. |
|
Multi-line text logs are parsed incorrectly. | The first line regular expression or last line regular expression is set incorrectly. | Verify the correctness of the first line regular expression or the last line regular expression. |
High latency occurs when importing new objects. | There are too many existing objects. This means that too many objects match the file path prefix filter. | If the number of objects that match the file path prefix filter is too large (for example, more than 1 million), we recommend that you set a more specific prefix and create multiple data import tasks. Otherwise, the efficiency of discovering new files is significantly reduced. |
Error handling
Error | Description |
File read failure | When reading a file, if an incomplete file error occurs due to a network exception or file corruption, the import task automatically retries. If the read fails after three retries, the file is skipped. The retry interval is the same as the new file check interval. If the new file check interval is set to Never Check, the retry interval is 5 minutes. |
Compression format parsing error | When decompressing a file, if an invalid compression format error occurs, the import task skips the file. |
Data format parsing error | If data fails to be parsed, the data import job stores the original text content in the content field of logs. |
S3 bucket does not exist | The import task retries periodically. After the bucket is recreated, the import task automatically resumes. |
Permission error | If a permission error occurs when reading data from an S3 bucket or writing data to an SLS logstore, the import task retries periodically. After the permission issue is fixed, the import task automatically resumes. When a permission error occurs, the import task does not skip any files. Therefore, after the permission issue is fixed, the import task automatically imports data from the unprocessed objects in the bucket to the SLS logstore. |