Answers to frequently asked questions about health checks for Classic Load Balancer (CLB).
Quick navigation:
Category | Links |
Principles and configuration | |
Error handling | |
Logging issues |
How do health checks work?
Health checks send periodic requests to backend servers to verify availability and status.
CLB instances run in clusters. Cluster nodes forward traffic and perform health checks. If any node detects a failed health check, all nodes stop routing requests to that backend server.
CLB health checks use the CIDR block 100.64.0.0/10. This CIDR block is reserved by Alibaba Cloud and cannot be blocked by backend servers. IP addresses within this CIDR block are not allocated to users, so allowing access from this CIDR block does not increase security risks. You don't need to configure a security group rule to allow access from 100.64.0.0/10 unless you've configured security rules such as iptables.

For more information, see CLB health checks.
What are the recommended settings for health checks?
Refer to the following table:
Parameter | For TCP, HTTP, and HTTPS listeners | For UDP listeners |
Health Check Response Timeout | 5 Seconds | 10 Seconds |
Health Check Interval | 2 Seconds | 5 Seconds |
Healthy Threshold | 3 Times | 3 Times |
Unhealthy Threshold | 3 Times | 3 Times |
CLB declares a backend server healthy or unhealthy only after the backend server passes or fails health checks consecutively for the specified number of times within the specified time window. For more details, see Configure and manage CLB health checks.
We recommend that you use these settings to ensure that your service recovers immediately after a backend server fails health checks. You can specify a shorter response timeout period as needed. However, you must ensure that the specified timeout period is longer than the normal response time of your backend server.
Can I disable the health check feature?
Yes, you can. For more information, see Disable health checks.
If you disable the health check feature, requests may be distributed to unhealthy backend servers. This can cause service interruptions.
If your business is highly sensitive to traffic fluctuations, frequent health checks may affect the availability of your business. To reduce the impacts of health checks on your business, you can reduce the health check frequency, increase the health check interval, or change Layer 7 health checks to Layer 4 health checks. To ensure business continuity, we recommend that you enable the health check feature.
How do TCP listeners perform health checks?
TCP listeners support both HTTP and TCP health checks:
TCP health checks: Verify backend port availability by sending SYN packets.
HTTP health checks: Verify backend server availability by sending HEAD or GET requests (similar to browser requests).
TCP health checks consume fewer server resources. Use TCP health checks when you only need to verify that backend ports are open. Use HTTP health checks when you need more precise health verification.
What happens if I set the weight of an ECS instance to zero?
Setting an ECS instance's weight to zero stops traffic forwarding to that instance, but does not affect health check results.
Use case: Set weight to zero when you need to restart or reconfigure an ECS instance without affecting health check status.
What method does an HTTP listener use to perform health checks on backend ECS instances?
HTTP listeners perform health checks by sending HEAD requests.
ECS instances that do not support HEAD requests will fail health checks. Run the following command to verify HEAD request support:
curl -v -0 -I -H "Host:" -X HEAD http://IP:portWhat is the IP address that HTTP listeners use to perform health checks on ECS instances?
CLB uses the CIDR block 100.64.0.0/10 for health checks. Ensure your ECS instances allow requests from this CIDR block.
You don't need to configure a security group rule for this CIDR block unless you've set up additional security rules (such as iptables). This CIDR block is reserved by Alibaba Cloud and IP addresses within it are not allocated to users, so allowing access poses no security risk.
When do CLB health checks start?
Once health checks are configured for a CLB instance, the health check process begins immediately. The CLB instance will then periodically send health check requests according to the configured health check interval.
How do I handle a health check failure caused by a faulty backend database?
Problem
The static website
www.example.comand the dynamic websitealiyundoc.comare deployed on an ECS instance. CLB is used to provide load balancing services for the websites. The backend database is down. As a result, the HTTP 502 error occurs whenwww.example.comis accessed.Possible causes
The health check domain name is set to
aliyundoc.com. When the ApsaraDB RDS instance or self-managed database is down, access toaliyundoc.comfails, which causes the health check failure.Solutions
Change the health check domain name to
www.example.com.
Why does the log data indicate connection failure to a backend port even though the backend port has passed TCP health checks?
Problem
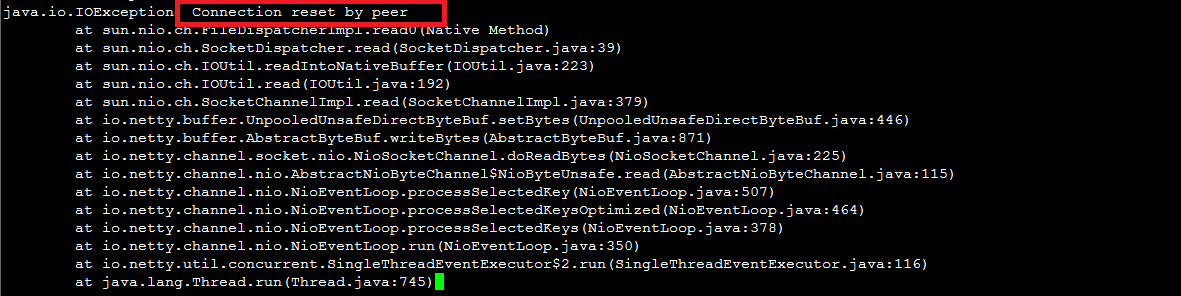
The log data shown in the following figure indicates frequent connection failures to a backend port of a TCP listener. A packet capture tool is used to identify the source of the connection requests. The result shows that the connection requests are sent by CLB. The packet capture tool has also captured RST packets sent by CLB.
Possible causes
The issue is related to the health check mechanism.
In a TCP health check on a backend port, CLB establishes a connection with the backend port, completes a three-way handshake, and sends an RST packet to close the connection. The process is as follows:
CLB sends an SYN packet.
The backend port returns an SYN-ACK packet.
After CLB receives the response, CLB considers the backend port to be reachable. In this case, the health check succeeds.
Then, CLB sends an RST packet to close the connection instead of sending service requests through the connection.
After CLB completes the health check, the TCP connection is closed. The status of the TCP connection is not updated to the connection pool of services at the application layer, for example, Java connection pools. Therefore, the
Connection reset by peererror occurs.Solutions
Configure CLB to perform HTTP health checks instead of TCP health checks.
In addition, screen out the log entries that record requests from the CIDR block of CLB and ignore the related error messages.
Why does a backend server that works as expected fail a health check?
Problem
The HTTP health check always fails, but when you run the
curl -Icommand, the status code returned is normal.Possible causes
If the status code returned is not specified in the health check configuration in the console, the backend server fails the health check. For example, if you specified the HTTP 2xx status code in the console and another status code is returned, the backend server fails the health check.
When you run the
curlcommand on Tengine or NGINX, the result shows that the destination is reachable. However, when you run theechocommand to access the test file test.html, you are directed to the default website and the HTTP 404 error code is returned.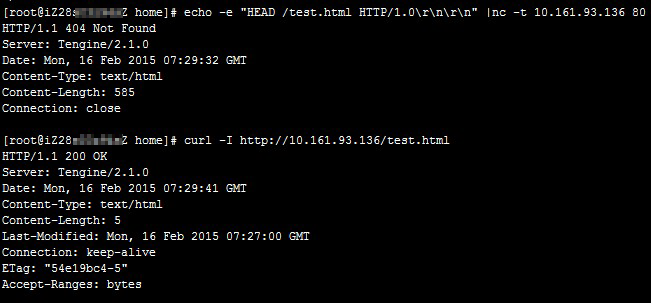
Diagnosis
Run the following command to verify health check response:
curl -v -H "Host: your-health-check-domain" http://backend-ip:port/health-check-pathSolutions
Modify the main configuration file and comment out the default site.
Add the domain name that is used for health checks to the health check configuration.
Why are the health check rates recorded in web logs different from the health check configurations in the console?
Health checks are performed by groups of servers to prevent single points of failure. CLB is deployed across multiple servers. Each server performs health checks independently, which increases the total number of health checks that are actually performed. Therefore, the health check rates recorded in logs are different from the configurations in the console.
How can I effectively differentiate between health check logs and business logs in my backend service?
Problem
In the backend service's logs, requests from the CLB instance's health checks are mixed in with regular business traffic logs. This causes the log files to become large and makes it difficult to filter and analyze actual user activity.
Cause
Health checks work by sending periodic HTTP, TCP, or UDP requests to the backend service to test its availability. The backend service's web server or application logs these health check probes as standard requests, mixing them with logs from your actual application traffic.
Solutions
Reduce the health check frequency: You can reduce the volume of health check logs by increasing the health check interval, thereby lowering the check frequency.
Adjust the health check path (recommended for HTTP/HTTPS): Configure the health check to target a dedicated, non-business endpoint (e.g.,
/healthor/status). This allows you to easily filter out health check logs by looking for that specific path in your log entries.Disable health checks (not recommended): If you are certain that health checks are not required for your use case, you can disable them entirely to stop the generation of health check logs. This is generally not advised as it removes a critical high-availability feature.
Filter by source IP: Configure your logging to exclude requests from the CLB health check CIDR block (
100.64.0.0/10).
Why can't I see any CLB health check failure records in the log console?
Health check logs are generated hourly and, by default, are only retained for 3 days.
However, a new log entry is created only when the health status of a CLB listener changes (e.g., from healthy to unhealthy, or vice-versa).
Therefore, if a listener's health status has not changed within the last 3 days (for example, it has been consistently healthy), no new health check logs will be generated for it.
For longer retention periods, you can configure your health check logs to be stored in Object Storage Service (OSS).