This topic describes how to use tools such as Task Manager, Resource Monitor, or Wireshark to troubleshoot and resolve high bandwidth usage on a Windows server.
Symptoms
When you use a Simple Application Server that runs Windows, you may experience the following symptoms.
Services have long response times or experience access timeouts.
You receive an alert that network bandwidth usage has exceeded the set threshold.
Causes
The preceding issue may occur due to the following reasons:
Frequent access to services causes high bandwidth consumption.
Network traffic is triggered by viruses or Trojans.
NoteThird-party malicious programs disguise themselves as svchost.exe or tcpsvcs.exe in the operating system, causing high bandwidth usage for these processes.
Windows built-in services, such as Windows Update services, generate high network traffic.
Troubleshooting steps
Use Resource Monitor to view network metrics
You can use various tools to identify the high bandwidth utilization issue on Windows instances, including Task Manager, Resource Monitor, Performance Monitor, and Process Explorer. You can also use Wireshark to capture network packets for further analysis.
On Windows Server 2008 R2 and later, you can use the built-in Resource Monitor to monitor bandwidth.
On the taskbar, click Search, enter Resource Monitor, and press Enter.
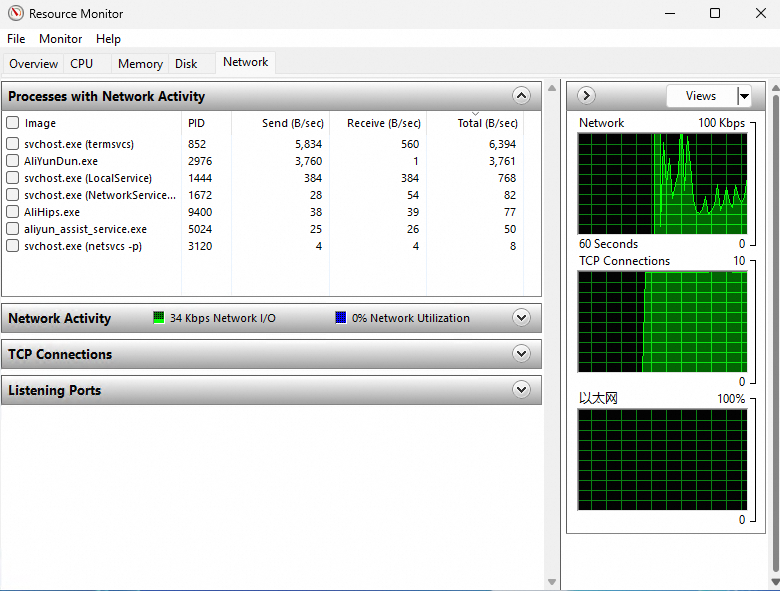
In the Resource Monitor dialog box, view the processes that have high bandwidth utilization on the Network tab.
 Note
NoteTo view detailed information about a process, use Task Manager. On the Processes tab of Task Manager, find the abnormal process that you identified in Resource Monitor. Right-click the process name, select Properties, Go to details, or Open file location, and then view process information to determine whether the process belongs to a malicious program.
(Optional) Use TCPView to view network connection information
If you do not find processes with high bandwidth utilization in Resource Monitor but the instance bandwidth utilization remains high, external services may access the instance. In this case, use Microsoft TCPView for further analysis. This tool displays a detailed list of all TCP and UDP network connections on the instance, including local and remote IP addresses and the status of TCP connections.
Download and decompress the TCPView tool.
Download the TCPView tool from the Microsoft website and decompress the downloaded package.
Double-click to open TCPView and view the network bandwidth details.
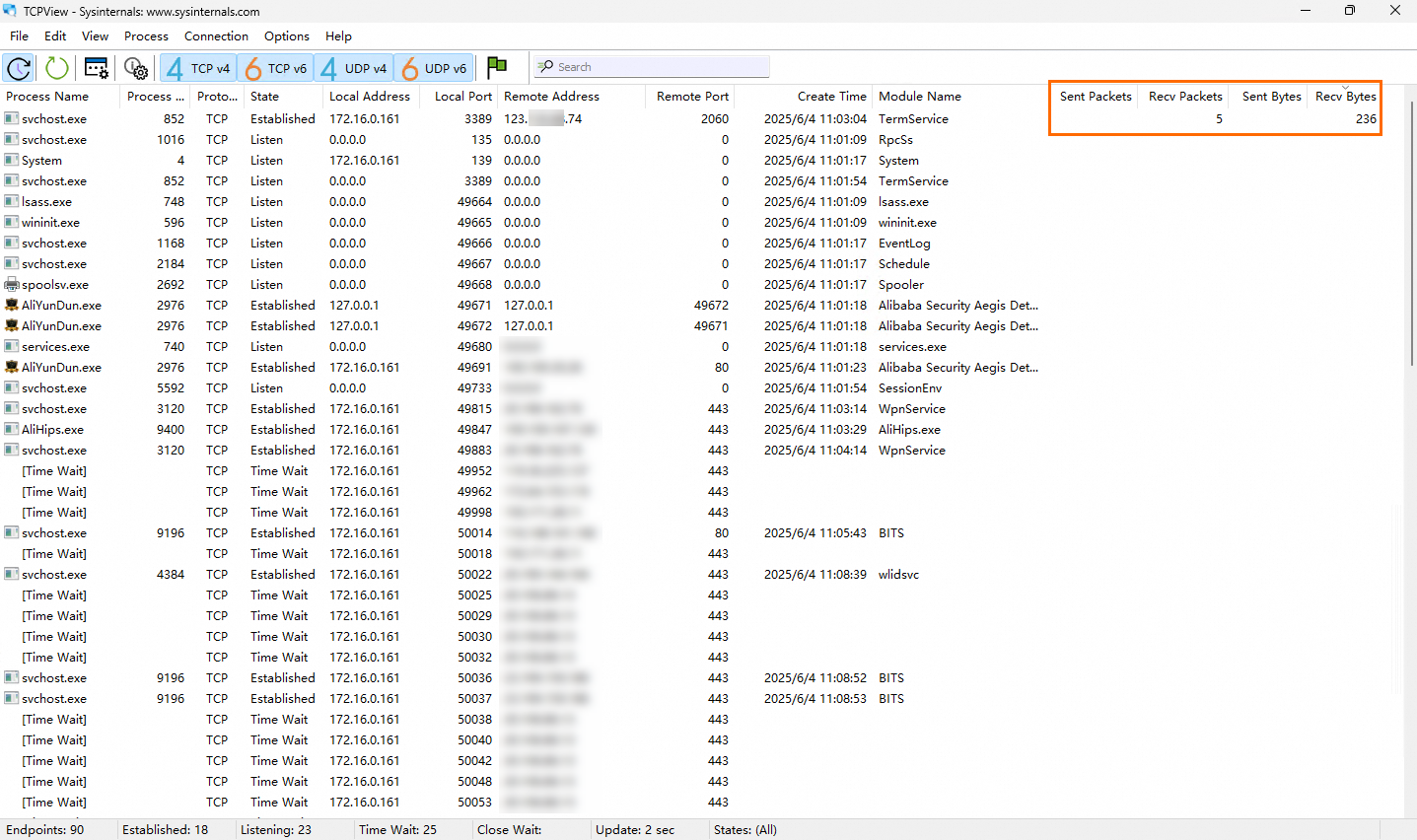
As shown in the preceding figure, the remote IP address 123.xxx.xxx.74 transmits data to the instance and occupies excessive network bandwidth resources.
(Optional) Use Wireshark to analyze traffic
To perform in-depth analysis of traffic data packets, use Wireshark to capture and analyze data packets.
Install and start the Wireshark tool.
Visit the Wireshark official website, obtain the Wireshark installation package, and then install the Wireshark tool.
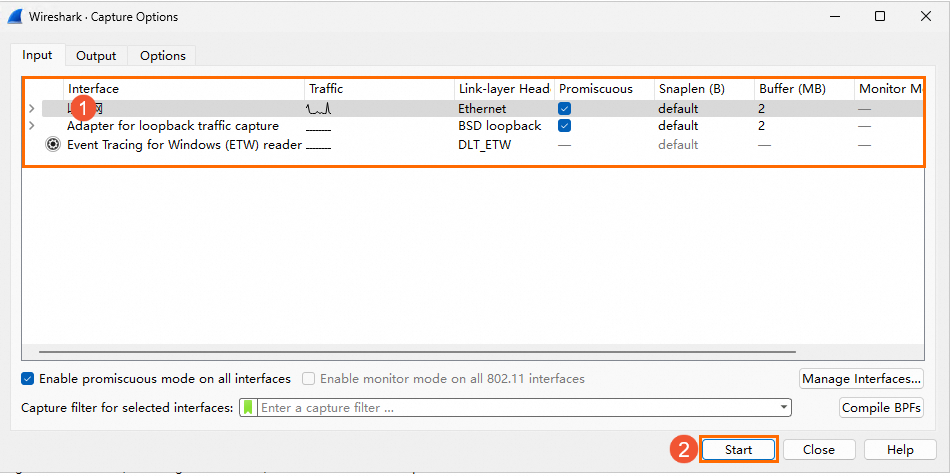
Choose Capture> Options.
On the Wireshark Capture Options page, select a network interface for packet capture based on the interface name or IP address and click Start.
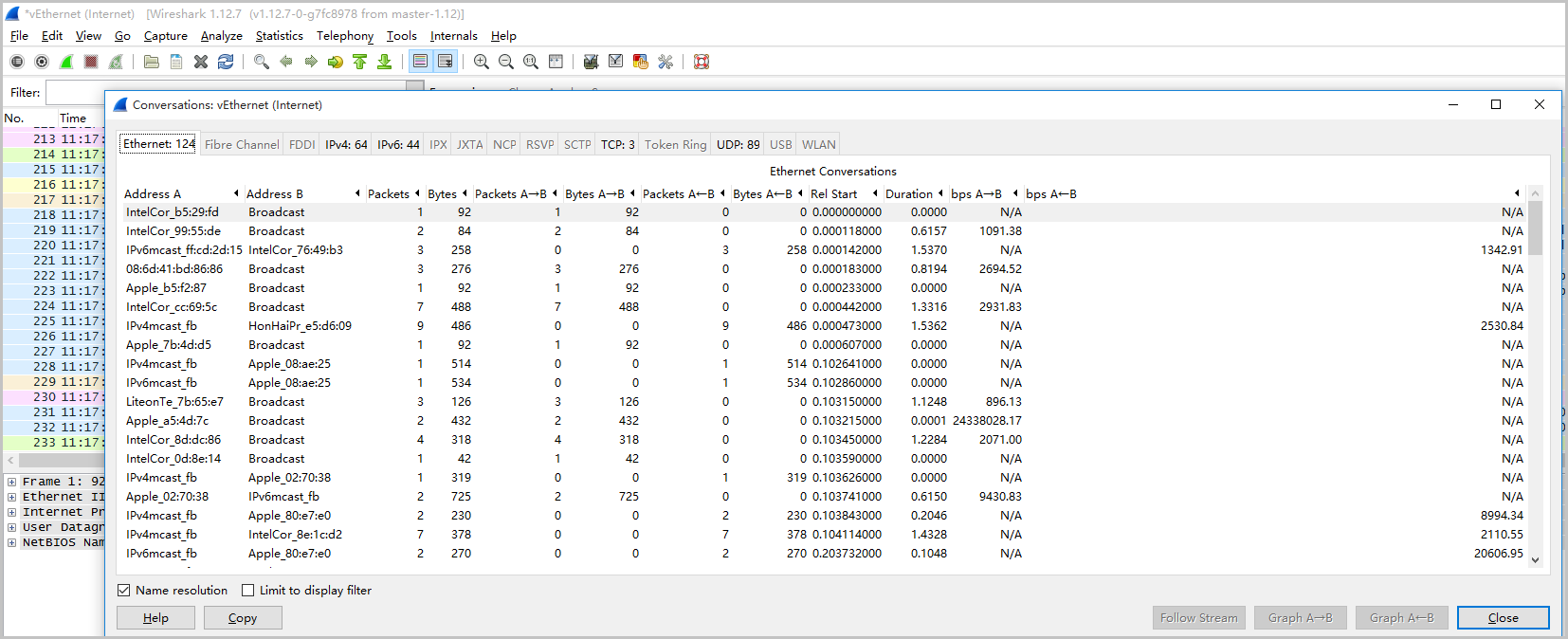
In the Wireshark toolbar, choose Statistics > Conversations.
On the Conversations page, view all network communication information. The traffic details and communication between the two endpoints are provided from the data link layer, IP layer, and TCP layer. By capturing network packets for a period of time, you can analyze which connections and ports have high traffic.
You can further analyze network packets by capturing packets. For more information, see Use the Wireshark tool in Windows instances.
Resolve high network bandwidth usage
The following table describes common causes of high network bandwidth usage and their solutions.
Symptom | Cause | Solution |
An abnormal user program or process consumes a large amount of network resources for a long time, or an illegal IP address maliciously accesses the service, which results in a high network load. | The program is an abnormal program or process that consumes excessive network resources at runtime. |
|
A normal user program or process consumes a large amount of network resources for a long time, or a specific IP address accesses the service, which results in a high network load. | The program is a normal business program or process that consumes excessive network resources during runtime. | Frequent access to services or internal Windows services, such as the update service, can consume high network traffic and CPU resources. If the instance experiences performance bottlenecks, select a solution based on your needs.
|
A single business program or process occasionally consumes high network resources, but for a short duration and at a low frequency. | The business application requires optimization to resolve high network resource consumption that is triggered by specific scenarios, such as large file uploads or downloads. | Optimize the business application. You can consider optimizing the application code and adjusting application configuration parameters, such as the number of connections, cache settings, and web and database configuration parameters. |