Threats are constantly changing and attack behavior may not always be identified. To reinforce system security, you must take note of the status of anti-ransomware policies and handle security alerts and vulnerabilities on your system at the earliest opportunity. This topic describes how to use the anti-ransomware feature to prevent ransomware attacks and reduce potential ransomware risks.
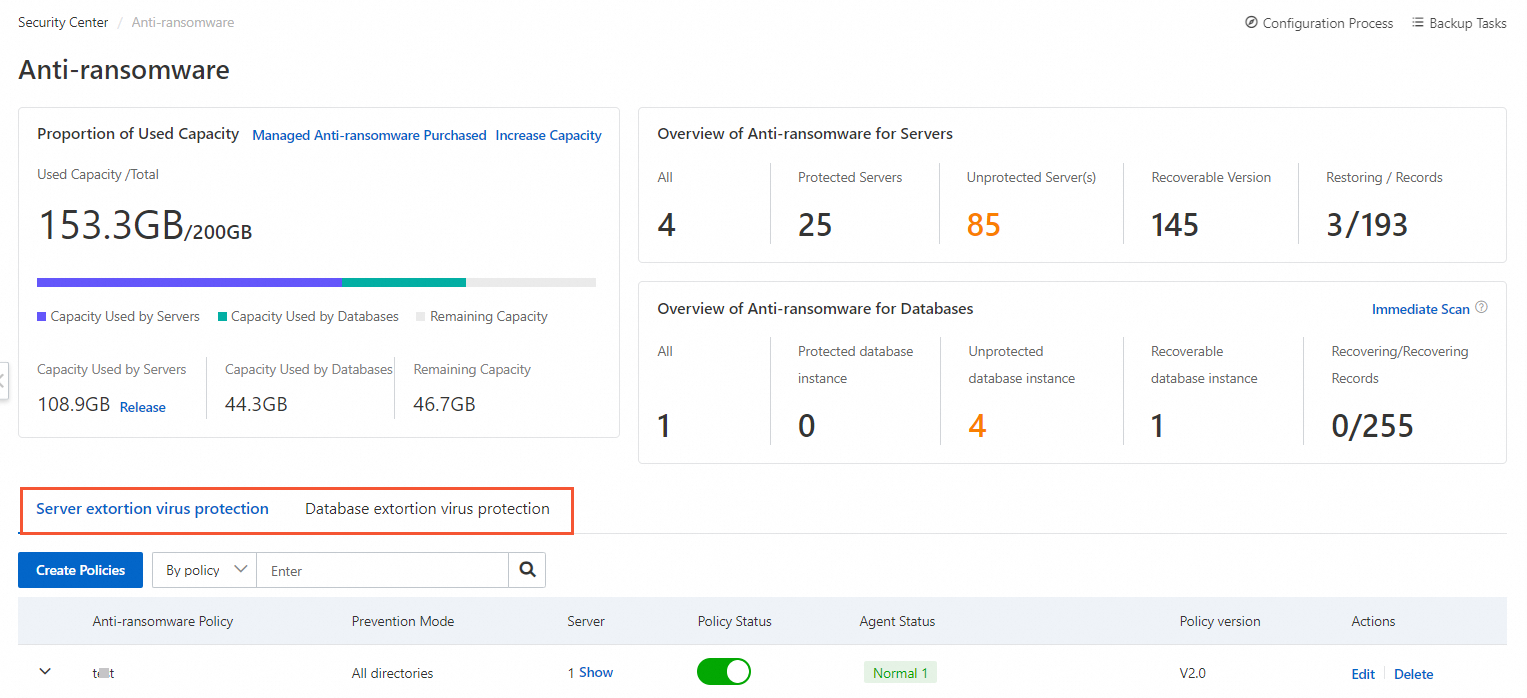
Step 1: Create an anti-ransomware policy
Purchase the anti-ransomware capacity based on the size of the files or databases that you want to protect. For more information, see Enable anti-ransomware.
Create an anti-ransomware policy for core data or files.
To protect files on a database, create an anti-ransomware policy on the Anti-ransomware for Databases tab of the Anti-ransomware page. For more information, see Create an anti-ransomware policy.
To protect files in specific directories of a server, create an anti-ransomware policy on the Anti-ransomware for Servers tab of the Anti-ransomware page. For more information, see Create an anti-ransomware policy.
The anti-ransomware agent is automatically installed on a server after you create an anti-ransomware policy for the server. You must manually check whether the agent is successfully installed and whether the status of the agent is normal. This helps ensure that backup tasks run as expected.
 Important
ImportantThe first time you use an anti-ransomware policy to back up data, the system backs up all data in the protected directories that you specify. Therefore, the first backup process requires a long period of time to complete. Subsequent backup tasks are periodically performed to back up only incremental data.
You can use anti-ransomware for servers and anti-ransomware for databases at the same time.
You cannot specify a non-local path as the protected directory when you create an anti-ransomware policy. This prevents additional fees from being generated when the system accesses data from the path. A non-local path refers to a mount path, such as a directory in an ECS instance to which an Object Storage Service (OSS) object or File Storage NAS (NAS) file system is attached. If you want to back up files from a mount path, we recommend that you use Cloud Backup. For more information, see Get started with OSS backup and Get started with on-premises NAS backup.
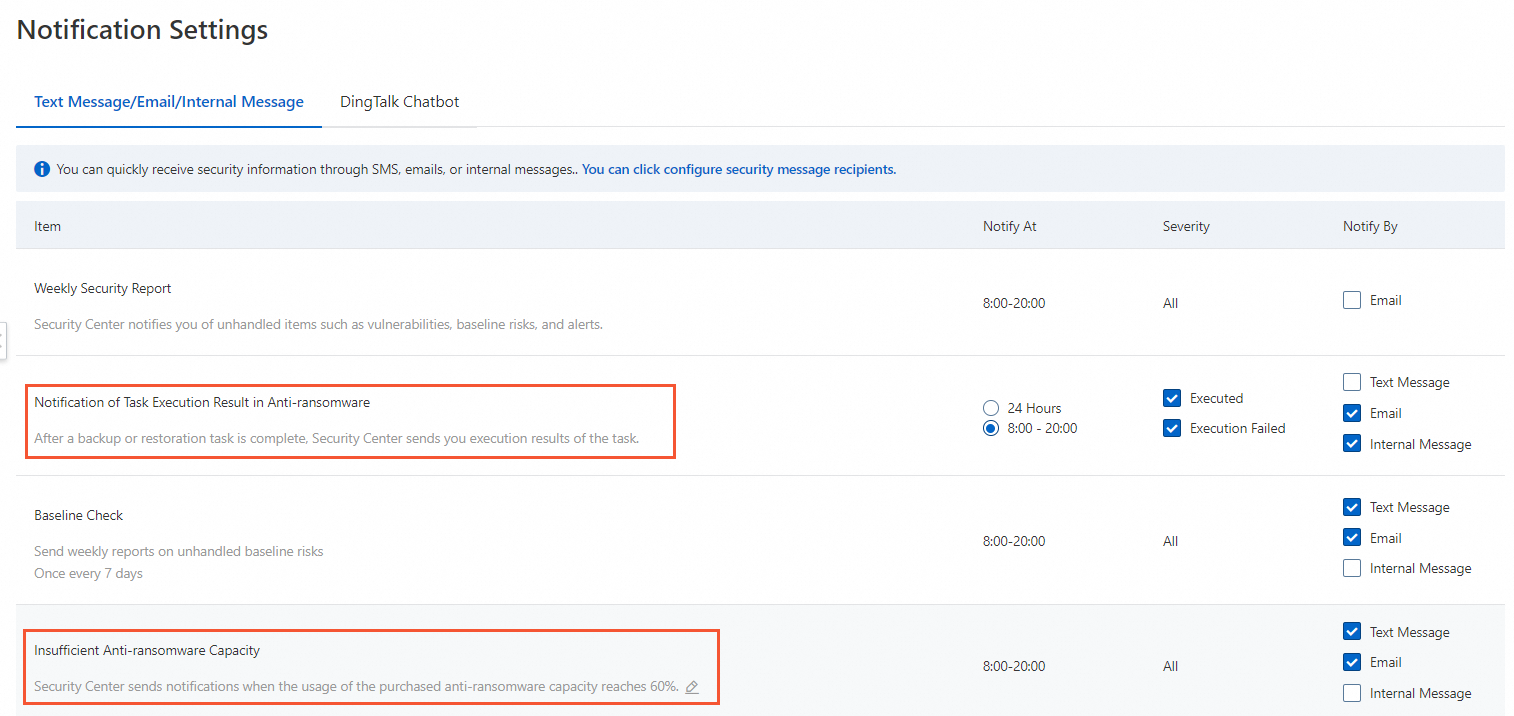
Step 2: Configure anti-ransomware notifications
After you create an anti-ransomware policy, you must configure anti-ransomware notifications to be informed of events related to anti-ransomware policies and backup tasks. To configure the notifications, configure the Anti-ransomware Task Results and Insufficient Anti-ransomware Capacity parameters on the Notification Settings page. For more information, see Configure notification settings.
Step 3: Perform routine inspection
After you create an anti-ransomware policy and configure notification settings, you must perform routine inspection to ensure that the anti-ransomware feature runs as expected and to improve your server security. To perform routine inspection, perform the following steps:
Check whether backup tasks run as expected on a regular basis.
We recommend that you go to the Anti-ransomware page in the Security Center console every day or based on the backup retention period that you specified. You can check whether the status of the anti-ransomware agent is normal, whether the anti-ransomware capacity is sufficient, whether backup tasks run as expected, and whether the status of backup data is normal. If an exception occurs, we recommend that you troubleshoot the issue at the earliest opportunity. For more information, see Troubleshoot the issues that cause the abnormal status of the anti-ransomware agent and backup tasks and Troubleshoot the issues causing the abnormal status of an anti-ransomware policy for a database.
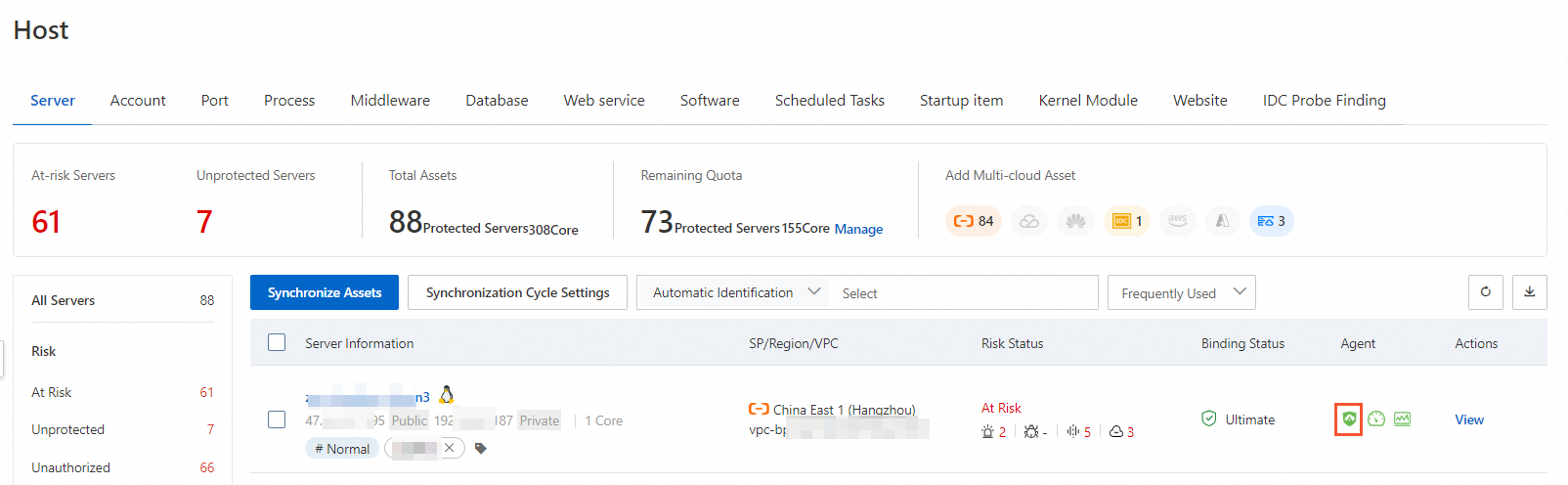
Check whether the Security Center agent installed on your server is online on a regular basis.
The Security Center agent is a software component that can be installed on servers to collect and analyze logs and data, and monitor and detect threats on the servers. We recommend that you regularly check whether the Security Center agent is online. If the Security Center agent is offline on a server, the server is not protected. You can view the status of the Security Center agent on the Host page. For more information, see Troubleshoot why the Security Center agent is offline.
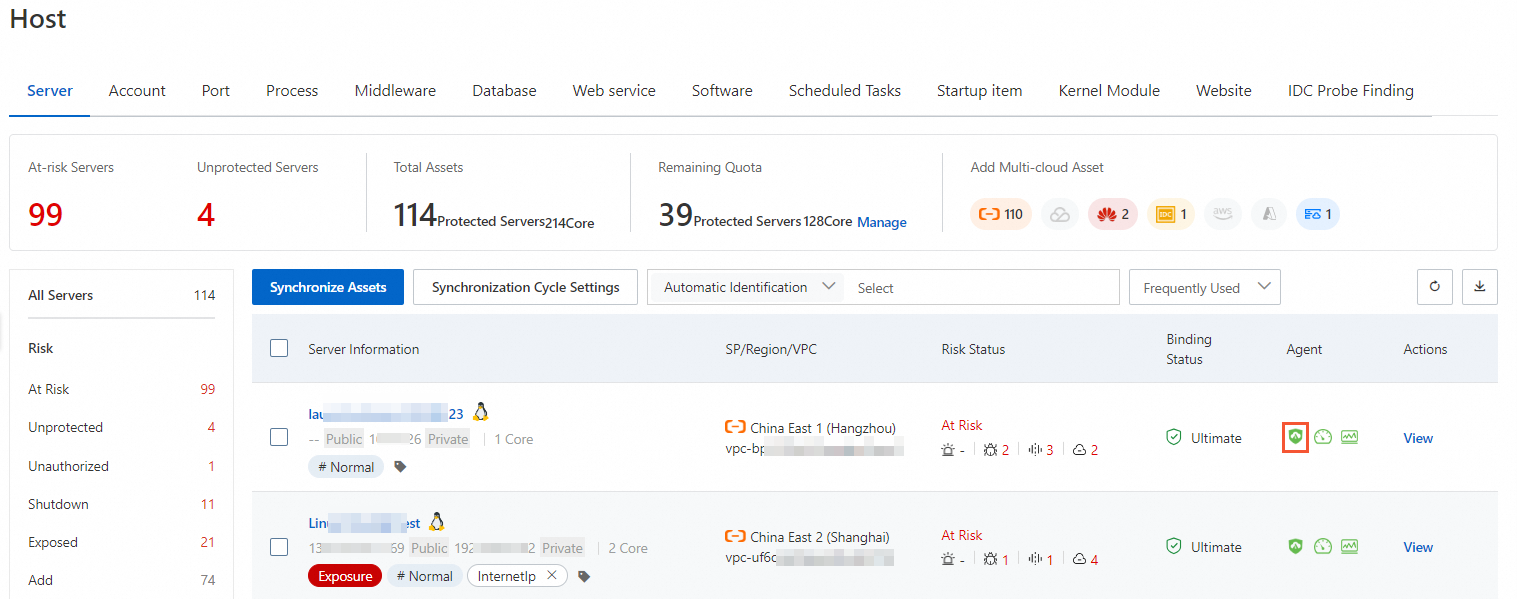
Take note of alerts that are generated for your server and handle the alerts at the earliest opportunity.
You can check whether your server is attacked based on the alerts that are generated for the server. Security Center detects threats and generates alerts in real time. Different types of alerts are supported, including Web Tamper Proofing, Suspicious Process Behavior, Webshell, Unusual Logon, and Malicious Process. You can go to the details page of a server from the Host page to view all alerts of the server. For more information, see View and handle alerts.
Configure vulnerability detection and fix vulnerabilities at the earliest opportunity.
Vulnerabilities in a system provide an opportunity for attackers to intrude into the system. You can fix the vulnerabilities at the earliest opportunity to reduce potential security risks. We recommend that you configure periodic vulnerability detection and handle the detected vulnerabilities at the earliest opportunity. After you perform vulnerability detection on a server, you can go to the server details page from the Host page to view all vulnerabilities that are detected on the server. For more information, see Scan for vulnerabilities and View and handle vulnerabilities.
Configure baseline check policies and fix baseline risks at the earliest opportunity.
Viruses and attackers can exploit the defects in the security configurations of a server to intrude into the server and steal data or insert webshells. We recommend that you use the baseline check feature to detect and fix the configuration risks of your server operating systems, databases, software, and containers. This helps reinforce system security, reduce intrusion risks, and meet security compliance requirements. For more information, see Baseline check.
Check whether your core service runs as expected on a regular basis.
We recommend that you configure periodic inspection tasks or manually check whether your core service can be accessed on a regular basis. Ransomware can encrypt your server data or delete data from your databases, which causes your service to be inaccessible. To ensure the security of your core service, we recommend that you perform periodic inspection tasks to detect and handle ransomware attacks at the earliest opportunity.
Usage notes
When a backup task is running on a server, do not restart the server. If you restart the server, the backup task fails. If the backup task fails, the system does not back up data until the next cycle.
If a ransomware attack occurs, we recommend that you do not delete anti-ransomware policies or the attacked servers for which anti-ransomware policies are created. If you delete the anti-ransomware policies or the attacked servers, backup data is deleted and cannot be restored.
We recommend that you use anti-ransomware together with other methods to protect important files and database data.