Security Center's Agentic SOC feature uses the standard Kafka protocol to ingest logs from Azure Event Hubs. This enables unified security management and threat detection in multicloud environments.
How it works
This solution takes advantage of the compatibility between Azure Event Hubs and the Apache Kafka protocol, which allows an Event Hub to function as a Kafka service. Security Center acts as a Kafka client that uses a specified endpoint, topic, and credentials to retrieve log data from the Event Hub. The retrieved data is then used for unified normalization, parsing, and threat detection. The configuration process is as follows:

Prepare an Event Hub in Azure
For more information, see the official Azure document Create an event hub using the Azure portal.
Step 1: Create a resource group
Log on to the Azure portal.
In the left navigation pane, select Resource groups, and then click Add.
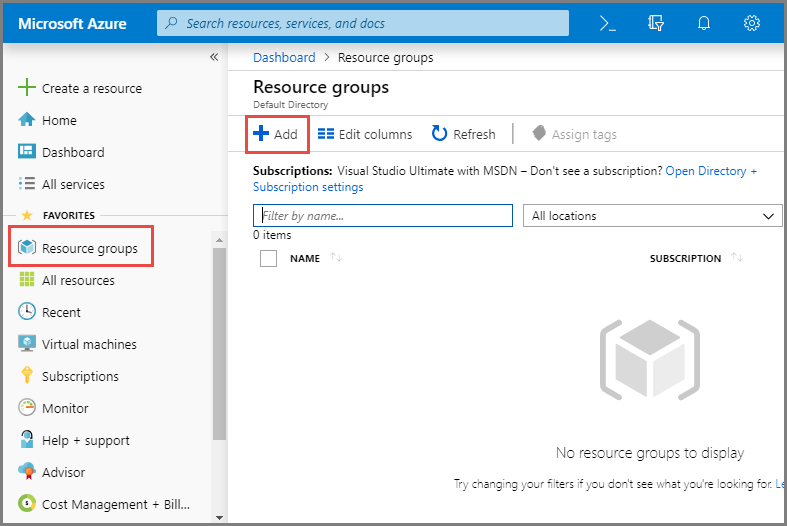
On the Create a resource group page, specify the configuration, and then click Review + create.
Subscription: Select the Azure subscription that will contain the resource group.
Resource group name: A unique name for the resource group.
Region: Select the region that contains the resource group.
After confirming the information, click Add.
Step 2: Create an Event Hubs namespace
In the left navigation pane, click All services. In the Analytics service area, click Event Hubs.
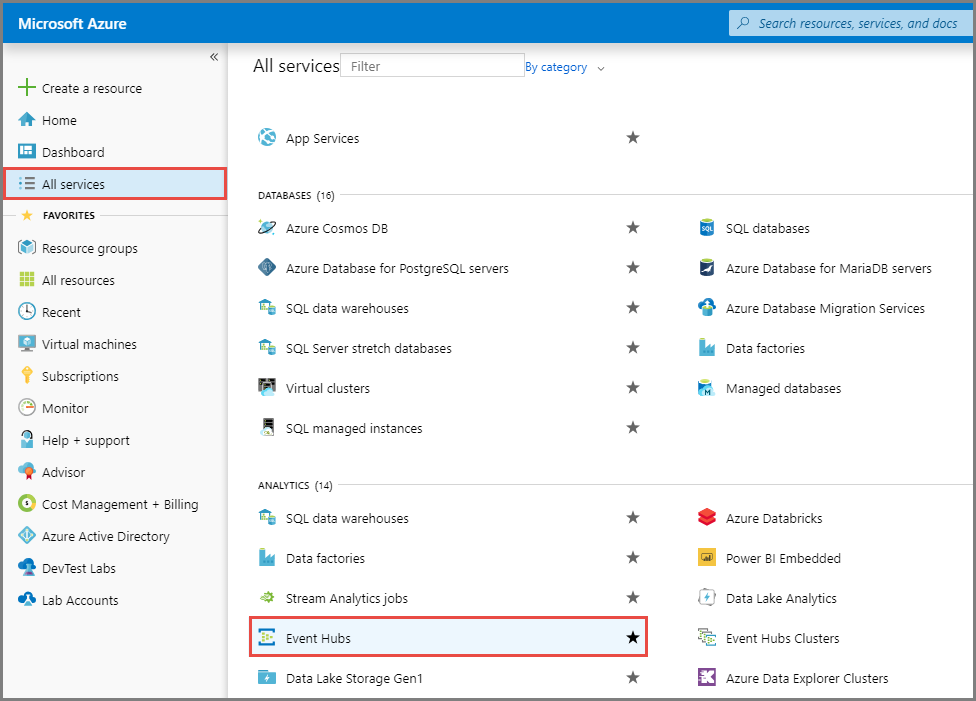
On the Event Hubs page, click Create and configure the parameters as described below.
Subscription: Select the Subscription name that you specified in Step 1.
Resource group: Select the Resource group created in Step 1.
Namespace name: Enter a name for the namespace. The corresponding endpoint is displayed below the text box.
ImportantThe namespace name determines the endpoint for the Kafka broker.

Region: Select the region that contains the Resource group you created in Step 1.
Pricing tier: Select a pricing tier based on your business needs. The default value is Basic.
NoteFor more information about the differences between tiers, see Quotas and limits, Event Hubs Premium, and Event Hubs Dedicated.
Throughput units / Processing units (Premium tier): Keep the default configurations.
NoteFor more information about throughput units or processing units, see Scalability of Event Hubs.
Enable Auto-inflate: You can enable this feature based on your business needs.
Enter the configuration settings and click Review + create at the bottom of the page.
After you confirm the configuration, click Create and wait for the deployment to complete.
On the Your deployment is complete page, click Go to resource to view the namespace details page.
NoteOn the Event Hubs home page, click a namespace name in the list to open its details page.
Step 3: Create an event hub
On the details page of the namespace created in Step 2, click + Event Hub.
On the creation page, enter the information and click Review + create.
Name: Enter a name for the Event Hub.
ImportantThe Event Hub name corresponds to the topic when you configure Kafka. Use a descriptive and easily understandable name.
Other configurations: Keep the default settings.
On the confirmation page, click Create. Wait for the task to complete.
Return to the namespace home page. The new data appears in the Event Hubs section.
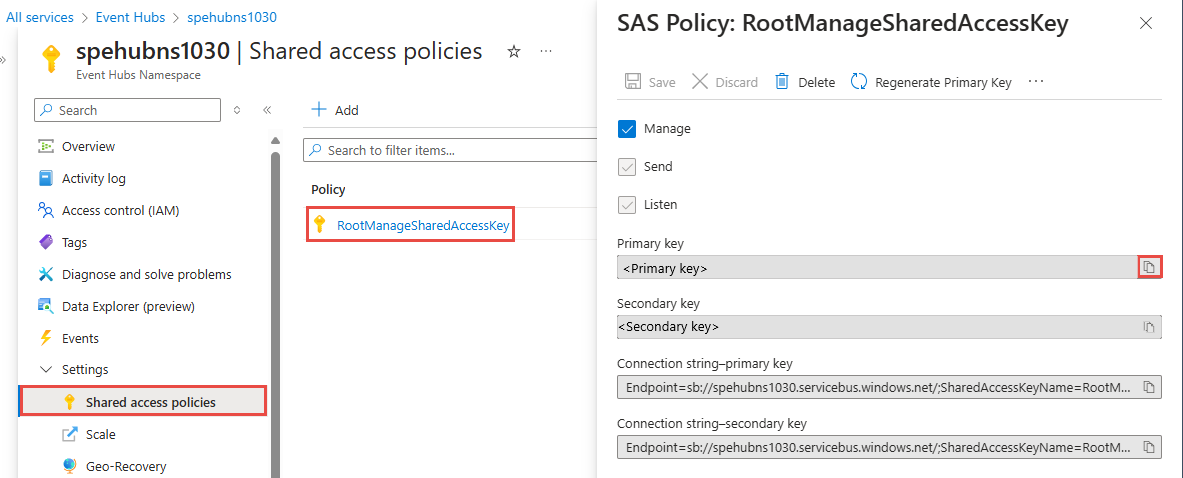
Step 4: Get the primary connection string
On the namespace page, in the left navigation pane, under Settings, click Shared access policies.
Click the primary policy,
RootManageSharedAccessKey. In the policy details pane, copy the Connection string-primary key.ImportantThe Connection string-primary key is the credential (password) for the Kafka import.
Step 5: Write data to the event hub
Follow the instructions in the official Azure documentation to write the data that you want to analyze to the event hub that you created in Step 3. You can refer to the following documents:
Configure data import in Security Center
Step 1: Authorize Security Center to access the Event Hub
Go to the Security Center console > Agentic SOC > Integration Center. In the upper-left corner of the page, select the region where your assets are located: Chinese Mainland or Outside Chinese Mainland.
On the Multi-cloud Configuration Management tab, click Multi-cloud Assets. Then, click Grant Permission and select IDC from the drop-down list. In the panel that appears, configure the following parameters:
Service Provider: Select Apache.
Connection Type: Select Kafka.
Endpoint:
<YOUR-NAMESPACE>.servicebus.windows.net:9093.NoteReplace
<YOUR-NAMESPACE>with the Event Hubs namespace name.Username: This is fixed to
$ConnectionStringand cannot be changed.Password: The primary connection string of the Event Hub.
Communication Protocol:
sasl_ssl.SASL Authentication Mechanism:
plain.
Configure a synchronization policy
AK Service Status Check: This parameter is not applicable. You can skip this step.
Step 2: Create a data import task
Create a data source
Create a data source for the Azure log data. If you have already created one, skip this step.
Log on to the Security Center console and navigate to Agentic SOC > Integration Center. In the upper-left corner of the page, select the region where your assets are located: Chinese Mainland or Outside Chinese Mainland.
On the Data Source tab, create a data source to receive logs. For more information, see Create a data source for Simple Log Service (SLS).
Source Data Source Type: Select Agentic SOC Dedicated Collection Channel (Recommended) or User Log Service.
Add Instances: We recommend that you create a new Logstore to isolate data.
On the Data Import tab, click Add Data. In the panel that appears, configure the following parameters:
Data Source Type: Kafka.
Endpoint:
<YOUR-NAMESPACE>.servicebus.windows.net:9093.Topics: The name of the Event Hub that you set when you created the event hub.
Value Type: json.
Configure the destination data source
Data Source Name: Select the data source that you created in the Create a data source step of this section.
Destination Logstore: Select the Logstore that you set in the Create a data source step of this section.
Click OK to save the configuration. After the import is configured, Security Center automatically retrieves logs from Azure Event Hubs.
Analyze imported data
After the data is successfully ingested, you must configure parsing and detection rules to allow Security Center to analyze the logs.
Create a new integration policy
For more information, see Product integration. Create a new integration policy and configure the following parameters:
Data Source: Select the target data source configured in the data import task.
Standardized Rule: Agentic SOC provides built-in standardized rules for some cloud products that you can use directly.
Standardization Method: When converting access logs into alert logs, only the "Real-time Consumption" method is supported.
Configure threat detection rules
Based on your security needs, enable or create log detection rules in rule management to analyze logs, generate alerts, and create security events. For more information, see Rule management.
Expenses and costs
This solution involves costs for the following services. Before you proceed, review the billing documentation for each product to estimate your costs.
Azure side: Event Hubs pricing.
On the Alibaba Cloud side: Costs depend on the data storage method you choose.
NoteFor information about Agentic SOC billing, see Billing details and Pay-as-you-go billing for Threat Analysis and Response.
For information about Simple Log Service (SLS) billing, see SLS billing overview.
Data source type
Agentic SOC billable items
SLS billable items
Notes
Agentic SOC Dedicated Collection Channel
Log ingestion fee.
Log storage and write fees.
NoteBoth items consume Log Ingestion Traffic.
Fees for items other than log storage and writes (such as public network traffic).
Agentic SOC creates and manages the SLS resources. Therefore, fees for Logstore storage and writes are billed through Agentic SOC.
User Log Service
Log ingestion fee, which consumes Log Ingestion Traffic.
All log-related fees (including storage, writes, public network traffic, etc.).
All log resources are managed by Simple Log Service (SLS). Therefore, all log-related fees are billed through SLS.