If you want to upgrade an application that contains multiple instances, you can upgrade the application instances to different versions using the canary release or phased release method. This topic describes the canary release method. It also describes how to perform a canary release for an application and how to roll back an application.
Prerequisites
The number of instances in the target application is greater than 1.
Background
Canary release is a deployment method used to test the performance of a new version when the original deployment version remains available. A canary release helps you ensure system stability and allows you to identify and fix errors at the earliest opportunity.
To ensure the stability of an application, the number of application instances in a canary release cannot exceed 50% of the total number of application instances. The remaining application instances are released in specific batches. After the first batch of application instances are released, you can specify whether to release the next batch. Before you manually release the next batch, you can collect business data of the new version to decide whether to release the next batch.
The following types of canary releases are supported:
Canary release by traffic ratio: For example, you can forward 20% traffic to the new version and 80% traffic to the current version.
Canary release by request content: For example, you can forward traffic that is generated by the requests sent by specific user IDs to the new version, and other traffic to the current version.
The canary release method provides more fine-grained traffic control than the phased release method. For more information about the phased release method, see Perform a phased release for an application.
Scenario
For example, an application contains 10 instances of V1, and you want to upgrade the instances to V2. In this example, a canary release is performed for two instances, and the remaining eight instances are released in three batches. The following figure shows the canary release process.

Procedure
After you redeploy an application, the application is restarted. To prevent unpredictable errors such as business interruptions, we recommend that you deploy applications during off-peak hours.
On the SAE Application List page, select a region and namespace at the top, and click the ID of the target application to open the application details page.
On the Basic Information page of the target application, click Deploy Application.
Configure deployment parameters.
NoteThe deployment method of an application is based on the deployment method that you selected for the application for the first time. Configure the parameters based on the selected method.
Deployment with WAR Packages: Upload another WAR package or enter the path of a newly deployed WAR package, and configure the runtime environment and other settings.
Deployment with JAR Packages: Upload another JAR package or enter the path of a newly deployed JAR package, and configure the runtime environment and other settings.
Deployment with ZIP Packages: Upload another ZIP package or enter the path of a newly deployed ZIP package, and configure the runtime environment and other settings.
Image: In the Configure Image section, click Modify Image. In the Modify Image panel, select another image repository or image version.
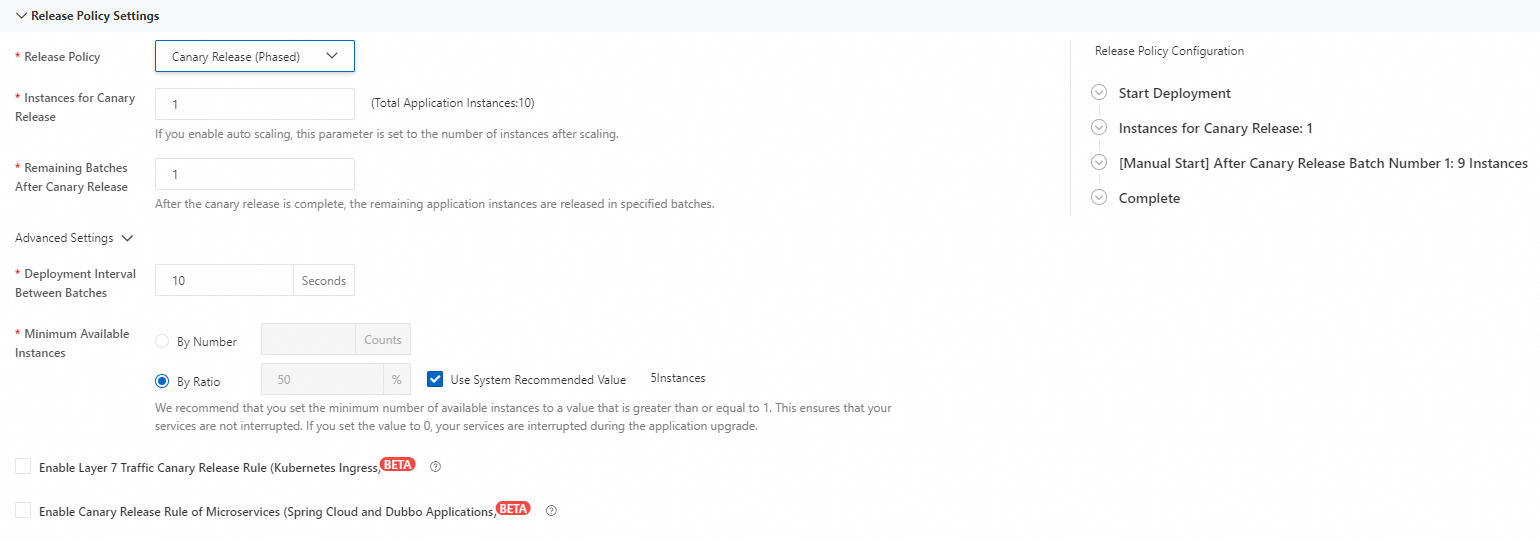
In the Release Policy Settings section, configure the canary release.
Configuration item
Description
Release Policy
Select Canary Release (Phased).
Instances for Canary Release
The number of instances for which you want to perform the canary release.
Remaining Batches After Canary
The number of batches in which you want to release the remaining instances after the canary release.
Minimum Available Instances
The minimum number of available instances per rolling upgrade.
By Number: Enter the minimum number of available instances. If you select Use System Recommended Value, the minimum number of available instances is set to 25% of the number of existing instances.
By Ratio: Enter a percentage.
NoteMake sure that at least one instance is available during application deployment and rollback. This ensures business continuity. If you set the value to 0, business interruptions occur when the application is upgraded.
If you specify a percentage, the minimum number of available instances is rounded up to the nearest integer. For example, five instances are available and you specify 25%. In this case, the minimum number of available instances is 2.
Enable Layer 7 Traffic Canary Release Rule (Kubernetes Ingress)
This feature takes effect only after you create a canary release of layer 7 traffic (Kubernetes Ingress).
Enable Canary Release Rule of Microservices (Spring Cloud and Dubbo Applications)
This feature takes effect only after you create a canary release of microservices traffic.
After the configurations are complete, click OK.
Use one of the following methods to check whether the configurations have taken effect:
Method 1: On the Change Records page, view the change details and release status of the application. If all batches are executed, the application is upgraded.
Method 2: On the Basic Information page, click the Instances tab to view the status of the instances. If Running is displayed in the Status column, the application is deployed.
Roll back application
If one or more instances have not been upgraded when you use the canary release or phased release method to upgrade the instances of an application, the upgrade status of the application is Executing.
If no response is returned for the first release batch of application instances due to an exception, click Roll Back Now on the Change Details page to roll back the upgraded instances to the previous version and restore the application configurations to the original configurations before the upgrade.
If an application fails to be upgraded because an exception occurs (for example, a deployment package is unavailable or a health check fails) during an application change process, SAE stops the application and rolls back the application.
The application upgrade process in SAE requires approximately 30 minutes to complete. If an upgrade times out, SAE reports a timeout exception and stops the change process. In this case, you must manually terminate the release process and roll back the application on the Change Details page.
Reference
The following table describes the operations that you can perform on an application after you deploy the application on SAE.
Operation | References |
Lifecycle management operations, such as updating, starting, stopping, and deleting an application, and scaling in or scaling out the instances for an application | |
Performance optimization operations, such as configuring auto scaling policies for an application, binding Server Load Balancer (SLB) instances to an application, and starting or stopping applications in batches | |
Application status-based operations, such as managing logs, configuring monitoring settings, viewing application events, and viewing change records |