You can use the data backup files and log backup files of an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance to restore the data of the RDS instance to a new RDS instance. This method is suitable for the analysis of historical data and the restoration of data on which unintended operations are performed.
Prerequisites
The original RDS instance meets the following requirements:
The RDS instance is in the Running state and is not locked.
No ongoing migration tasks exist.
A backup is completed. ApsaraDB RDS provides the automatic backup feature. For more information about backup methods, see Overview of backup methods.
The log backup feature is enabled. This requirement must be met if you want to restore data to a specific point in time. For more information about how to enable the feature, see Use the log backup feature for an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance.
At least one physical backup is completed. This requirement must be met if you want to restore data from backup sets. For more information, see Automatic backup.
Feature description

Item | Description |
Restoration range | The entire RDS instance is restored. |
Specifications of the new RDS instance | The new RDS instance uses the same whitelist configurations, backup configurations, and parameter configurations as the original RDS instance. |
Account information about the new RDS instance | Account information that is stored at the point of time for data restoration is included in the new RDS instance. Account information in data backup files that you select for data restoration is also included in the new RDS instance. |
Data on the new RDS instance | The data on the new RDS instance is the same as the data in the specified backup file of the original RDS instance. |
Point in time for data restoration |
Note
|
Time required for data restoration | The period of time that is required for data restoration varies based on various factors. For example, if you restore 200 GB of data, approximately 3 hours are required. For more information, see the "FAQ" section of this topic. |
Billing rules
You are charged for the new RDS instance that is used to restore data. You can view the price of the new RDS instance when you create the instance.
If you want to temporarily use an RDS instance, you can create a pay-as-you-go or serverless RDS instance. After data is restored to the new RDS instance, you can migrate the data to the original RDS instance and then release the new RDS instance. For more information, see Migrate data between ApsaraDB RDS instances and Release or unsubscribe from an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance.
You are immediately charged for the new RDS instance after the instance is created.
Enable the full data restoration feature
You do not need to manually enable the full data restoration feature. After an RDS instance is created, the system automatically performs periodic backups on the RDS instance. You can use the data backup files and log backup files that are generated to restore full data of the RDS instance.
Procedure
You can use the backup data of the original RDS instance to create another RDS instance for data restoration. This method does not affect the performance of the original RDS instance.
Go to the Instances page. In the top navigation bar, select the region in which the RDS instance resides. Then, find the RDS instance and click the ID of the instance.
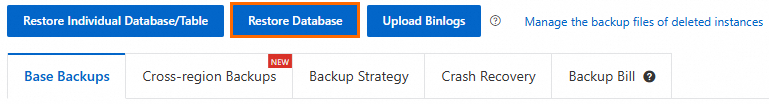
In the left-side navigation pane, click Backup and Restoration.
On the page that appears, click Restore Database.
 Note
NoteYou can also click Restore Instance in the Instance Distribution section of the Basic Information page.

On the Restore Instance page, select a point in time to which you want to restore data or select a backup set from which you want to restore data. Then, configure other parameters.
Parameter
Description
Billing Method
Subscription: A subscription RDS instance is an instance for which you pay an upfront fee. This method is suitable for long-term use. You are offered lower prices for longer subscription durations.
Pay-as-you-go: A pay-as-you-go RDS instance is billed per hour based on your actual resource usage. This method is suitable for short-term use. If you no longer require an pay-as-you-go RDS instance, you can release it.
Restoration Mode
By Backup Set: This method allows you to restore data from a specified backup set. Logical backup files are not supported.
By Point in Time: This method allows you to restore data to a point in time within the log backup retention period. This option is available only if the log backup feature is enabled.
Product Type
If you set the Edition parameter to Basic Edition, this parameter is not displayed.
If you set the Edition parameter to High-availability Edition, the product type that you can select depends on the storage type of your RDS instance.
If you set the Storage Type parameter to ESSD or Premium ESSD, the Standard and YiTian product types are available. For more information, see Product types.
If you set the Storage Type parameter to PremiumLocal SSD, only the Standard product type is available.
If you set the Edition parameter to Cluster Edition, the Standard and YiTian product types are available.
Zone of Primary Node and Zone of Secondary Node
You can select the Single-zone Deployment or Multi-zone Development method.
Single-zone Deployment: If you select this deployment method, the primary and secondary RDS instances are deployed in the same zone.
Multi-zone Development: If you select this deployment method, the primary and secondary RDS instances are deployed across zones to implement zone-disaster recovery. We recommend that you select this deployment method.
NoteAfter the RDS instance is created, you can view information about the new RDS instance and its secondary RDS instance on the Service Availability page.
If you select RDS Basic Edition, the database system supports only the single-zone deployment method.
Instance Type
General-purpose Instance Types: A general-purpose RDS instance exclusively occupies the memory and I/O resources. However, this type of instance shares CPU and storage resources with other general-purpose instances that are deployed on the same host.
Dedicated Instance Types: A dedicated RDS instance exclusively occupies the CPU, memory, storage, and I/O resources that are allocated. The dedicated host instance family is the highest configuration of the dedicated instance family. A dedicated host RDS instance exclusively occupies all the CPU, memory, storage, and I/O resources on the host on which the instance is deployed.
NoteEach instance type supports a specific number of cores, memory capacity, maximum number of connections, and maximum IOPS. For more information, see Primary ApsaraDB RDS instance types.
Storage Capacity
The maximum amount of storage that is provisioned to store data files, system files, binary log files, and transaction files in the RDS instance.
You can adjust the storage capacity at a step size of 5 GB.
Click Next: Instance Configuration to configure the network type and resource group of the RDS instance.
Parameter
Description
Network Type
Classic Network: the traditional type of network.
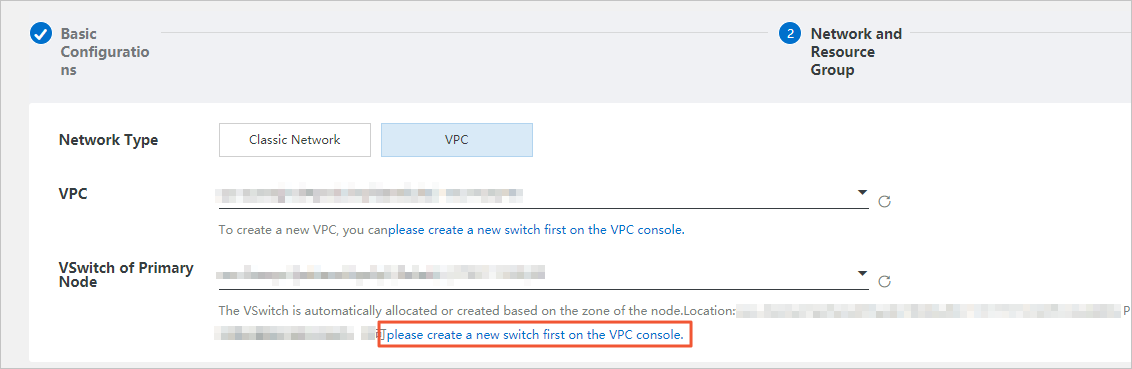
VPC: the recommended type of network. A virtual private cloud (VPC) is an isolated virtual network that provides higher security and higher performance than the classic network. If you select the VPC network type, you must configure the VPC and vSwitch of Primary Node parameters. If you set the Deployment Method parameter to Multi-zone deployment in the previous step, you must also configure the vSwitch of Secondary Node parameter.
NoteThe network type of the new RDS instance must be the same as the network type of the Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance that you want to connect. If the new RDS instance and the ECS instance reside in VPCs, make sure that the instances reside in the same VPC. If the new RDS instance and the ECS instance reside in different VPCs, these instances cannot communicate over an internal network.
Resource Group
You can use resource groups to categorize the resources of your Alibaba Cloud account. Resource groups help you simplify the management of resources and permissions in your Alibaba Cloud account. You can select an existing resource group or create a resource group. If you do not need to group resources, select Default Resource Group.
Click Next: Confirm Order.
Confirm the settings in the Parameter Configuration section, configure the Quantity and Subscription Duration parameters, click Confirm Order, and then complete the payment. You must configure the Duration parameter only when you select the subscription billing method for the RDS instance.
NoteIf you select the subscription billing method for the new RDS instance, we recommend that you select Auto-renew below the Duration parameter. This way, you do not need to renew the new RDS instance on a regular basis. This also helps prevent interruptions on your workloads on the new RDS instance if a payment becomes overdue.
Optional. Log on to the new RDS instance and verify the data.
Correct the online data on the new RDS instance
After you restore the data of the original RDS instance to the new RDS instance, you can use Data Transmission Service (DTS) to migrate some or all data of the required databases and tables to the original RDS instance to correct the online data of the original RDS instance. For more information, see Migrate data between ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instances.
When you create a task, use the new RDS instance as the source database and the original RDS instance as the destination database, and set the Access Method parameter for both the source and destination databases to Alibaba Cloud Instance.
References
This topic is suitable for full data restoration. For more information about how to restore individual databases and tables, see Restore individual databases and tables of an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance. For more information, see Overview of data restoration methods.
If you want to restore data to the original RDS instance, an existing RDS instance, or a self-managed instance, you can use multiple methods. The following table describes the methods.
ImportantYou cannot restore downloaded backup files to an existing RDS for MySQL instance. To achieve this goal, you can restore the backup files to a new instance, verify the data on the new instance, and then migrate data from the new instance to an existing instance.
Restoration destination
Restoration method
Original RDS instance
Method 1: Restore the data of the original RDS instance to a new RDS instance, verify the data on the new RDS instance, and then migrate some or all data of the required databases and tables to the original RDS instance.
Method 2: Use the restoration feature for databases and tables to restore full data to the original RDS instance.
Method 3: Use Database Backup (DBS) to create a logical backup. Then, restore data to the original RDS instance by using the logical backup file. For more information, see Restore a MySQL database from a logical backup.
Another existing RDS instance
Method 1: Restore the data of the original RDS instance to a new RDS instance, verify the data on the new RDS instance, and then migrate the data to another existing RDS instance.
Method 2: Use DBS to create a logical backup. Then, restore data to another existing RDS instance by using the logical backup file. For more information, see Restore a MySQL database from a logical backup.
Self-managed database
Method 1: Restore the data of the original RDS instance to a new RDS instance, verify the data on the new RDS instance, and then migrate the data to a self-managed database.
Method 2: Use DBS to create a logical backup. Then, restore data to the self-managed database by using the logical backup file. For more information, see Restore a MySQL database from a logical backup.
Method 3: Download a backup file. Then, restore data to the self-managed database from the backup file. For more information, see Restore the data of an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance from a physical backup file to a self-managed MySQL database, Restore the data of an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance from a logical backup file to a self-managed MySQL instance, or Restore the data of an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance to a self-managed MySQL instance by using snapshot backup files.
For more information about how to restore the data of an RDS instance that runs a different database engine, see the following topics: