When a MySQL table contains a large amount of data, using the DELETE statement to clean up data does not directly release disk space, it only marks database records or data pages as reusable. To actually reclaim tablespace and reduce disk usage, you can use OPTIMIZE TABLE.
Prerequisites
Only InnoDB and MyISAM engines support the
OPTIMIZE TABLEstatement.The remaining disk space of the instance must be greater than or equal to the space of the table to be released.
NoteIf the remaining disk space of the instance is insufficient, you must first scale up the disk space. After the operation is complete, you can scale down the disk space as needed, and the system will refund the price difference.
Considerations
You must delete a large amount of data first: If you do not first delete a large amount of data using
DELETE, directly executingOPTIMIZE TABLEwill not effectively reduce tablespace usage.Temporary increase in disk space usage: When executing
OPTIMIZE TABLE, MySQL creates a temporary table to store the reorganized data, which causes disk space to increase temporarily. After the operation is complete, the temporary table is deleted, and disk space usage returns to normal.Performance impact and peak period risks: In RDS MySQL 5.7 and 8.0,
OPTIMIZE TABLEis executed using Online DDL, which supports concurrent DML operations. However, performing this operation on large tables may cause sudden IO and Buffer resource consumption, with risks of table locking or resource contention. During business peak periods, it may even cause the instance to become unavailable or monitoring to be interrupted. Therefore, it is recommended to perform this operation during business off-peak hours to avoid affecting normal business operations.
Use the CLI to release a tablespace
Use the
DELETEstatement to clean up unwanted data as needed.Execute the
OPTIMIZE TABLEcommand to release tablespace.OPTIMIZE TABLE <$Database1>.<Table1>,<$Database2>.<Table2>;Note<$Database1> and <$Database2> are database names, <Table1> and <Table2> are table names.
When executing the
OPTIMIZE TABLEstatement on an InnoDB engine, you will see the following message. This is a normal execution result that you can ignore. Just confirm that it returns "ok". For more information, see OPTIMIZE TABLE Statement.Table does not support optimize, doing recreate + analyze instead
Use DMS to release a tablespace
In the left-side panel, select the instance ID of the target instance, then double-click the target database, right-click any table name, and select Batch Operations.
Select the tables for which you want to release space, and then select .
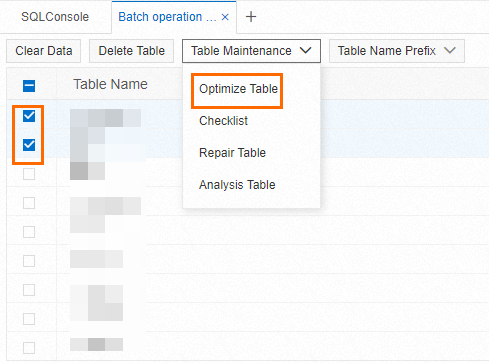
In the dialog box that appears, confirm that the change information is correct, and then click Confirm.