The detail table is a core tool for table-type components in Quick BI. It displays the detailed distribution and ranking of metrics across dimensions. Visual configuration lets you perform deep data analysis and support decision-making. It supports complex calculations and interactive features.
Chart Overview
Scenarios
You can use this chart to analyze detailed data across dimensions. Analyze and make decisions based on distribution, ranking order, and other perspectives.
Key Benefits
Calculation power: You can configure advanced calculations with one click, such as period-over-period (PoP) and year-over-year (YoY) comparisons, cumulative totals, and subtotals.
Visual effects: You can customize table themes, freeze rows or columns, wrap text, and adjust column width.
Annotation support: You can add custom text or metric annotations and footnotes. You can also define external link paths to enable interaction between your data and other systems.
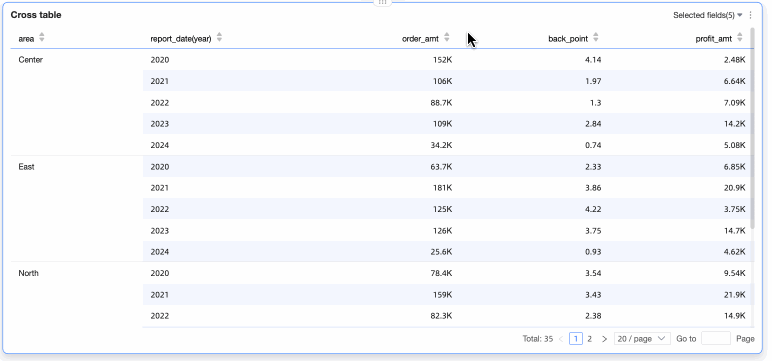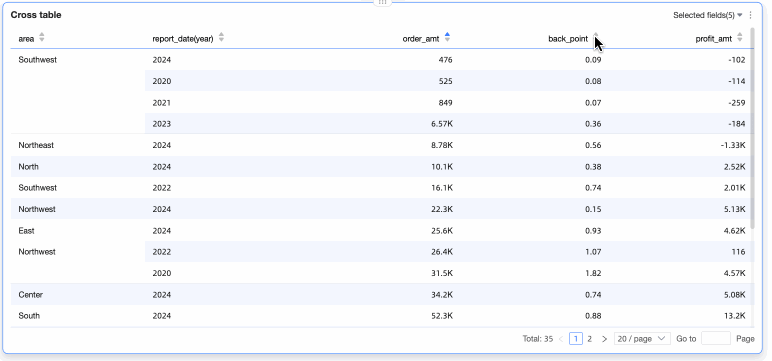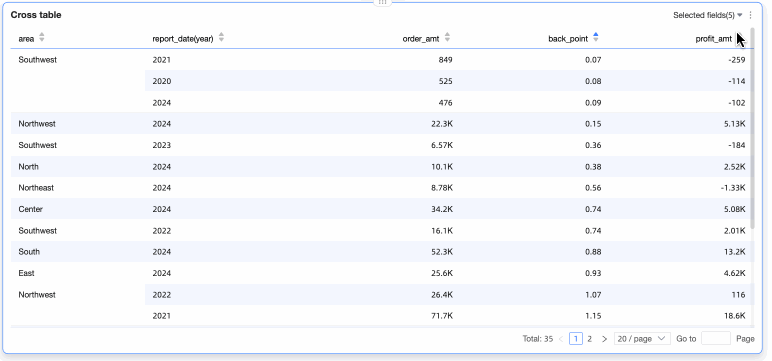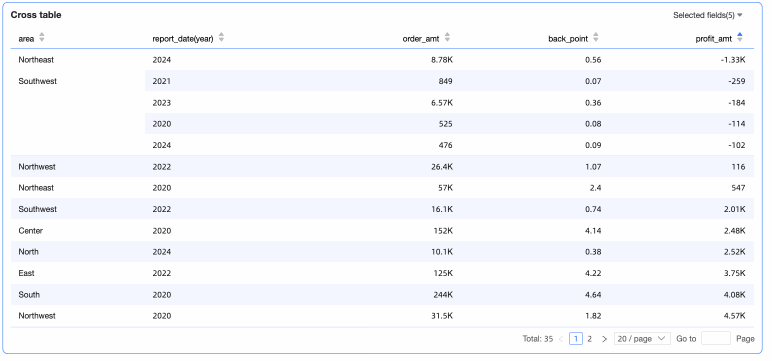
Example Visualization
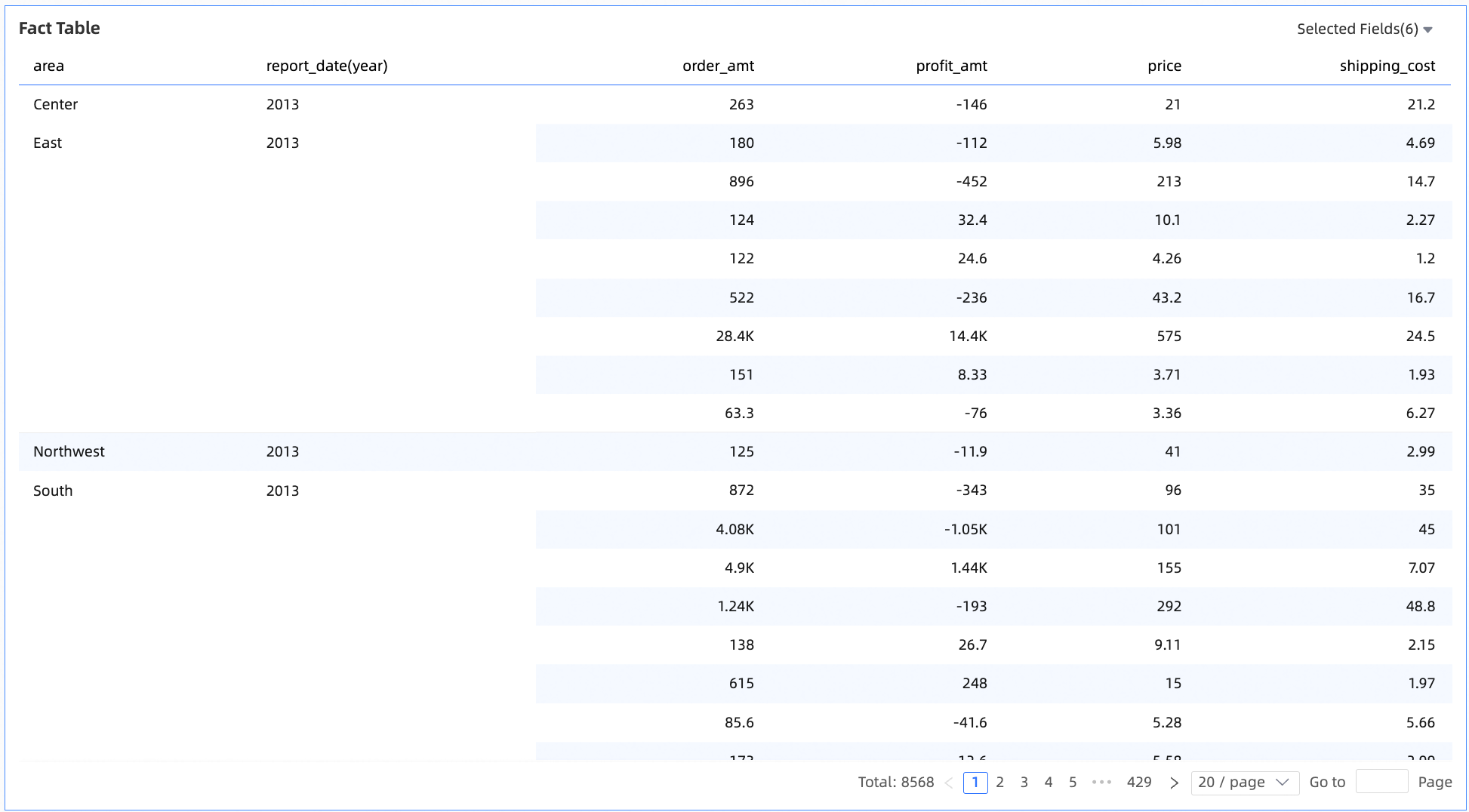
Limits
Prerequisites: You have created a dashboard. For details, see Create a Dashboard.
To ensure the correct configuration and effective display of the detail table, observe these field and data volume limits:
A detail table contains only numeric columns, dimensions, or measures. You can add dimension fields and measure fields.
Chart Data Configuration
A detail table contains only numeric columns, dimensions, or measures. You can add dimension fields and measure fields.
In the Data tab, select the dimension and measure fields you need.
In the Dimensions list, locate Region and Order Date (Year). Double-click each or drag them into the Numeric Columns/Dimensions or Measures area.
In the Measures list, locate Order Amount, Unit Price, Shipping Cost, and Profit Amount. Double-click each or drag them into the Numeric Columns/Dimensions or Measures area.
NoteWhen the field type is image, you can set its display size. On mobile devices, the image width and height default to half the values set for PC.

Click Update. The system updates the chart automatically.
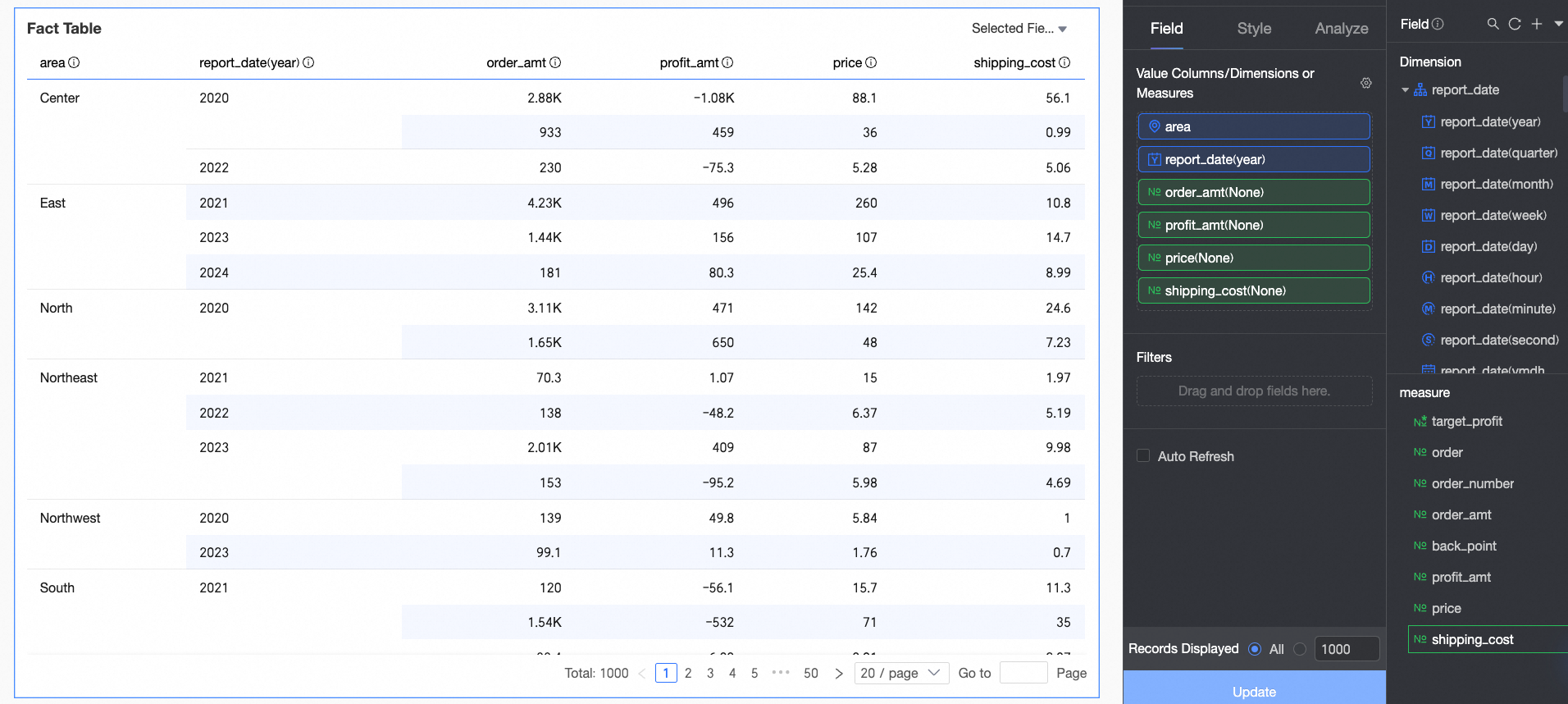
Chart Style Configuration
This section explains how to configure chart styles. For general chart style settings, see Configure the Chart Title.
You can enter keywords in the Search Box at the top of the configuration panel to quickly find and configure configuration items. Click the ![]() icon on the right to expand or collapse all categories. You can use the same icon to switch between the new and old detail table versions.
icon on the right to expand or collapse all categories. You can use the same icon to switch between the new and old detail table versions.
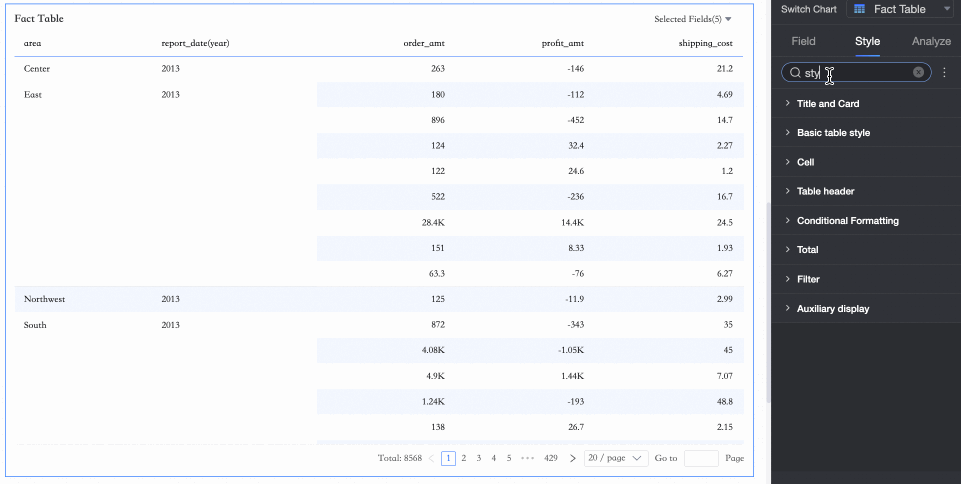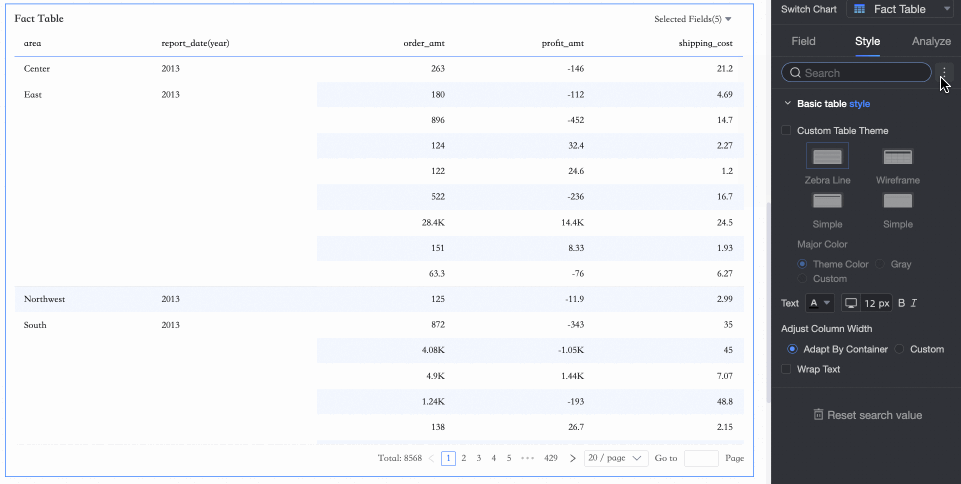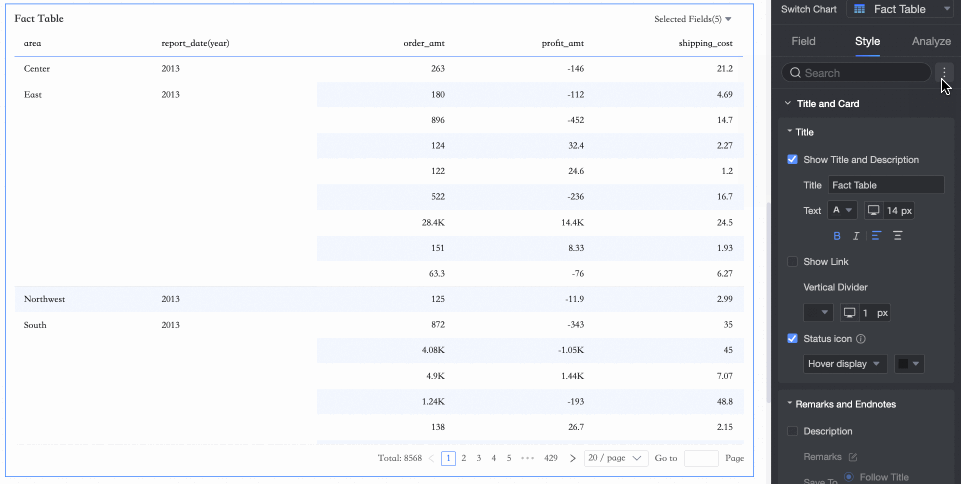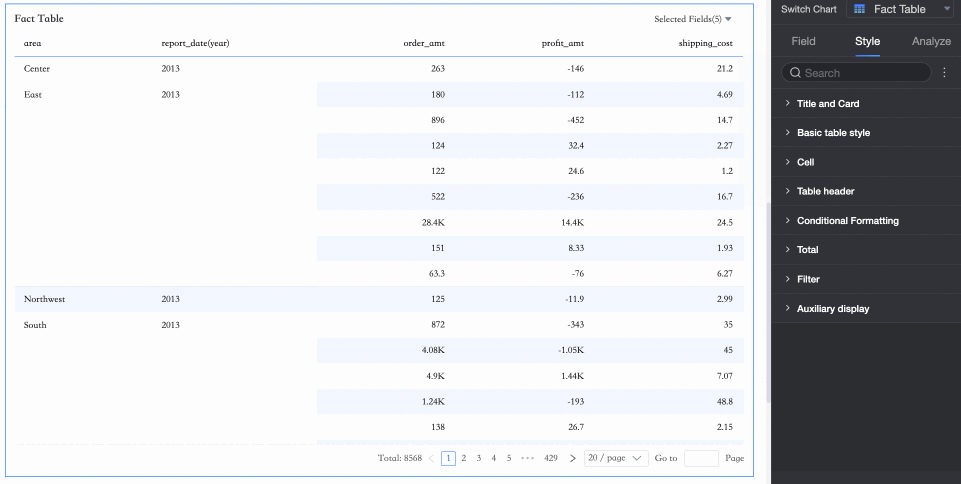
In Basic Table Styles, you can configure the appearance of the detail table.
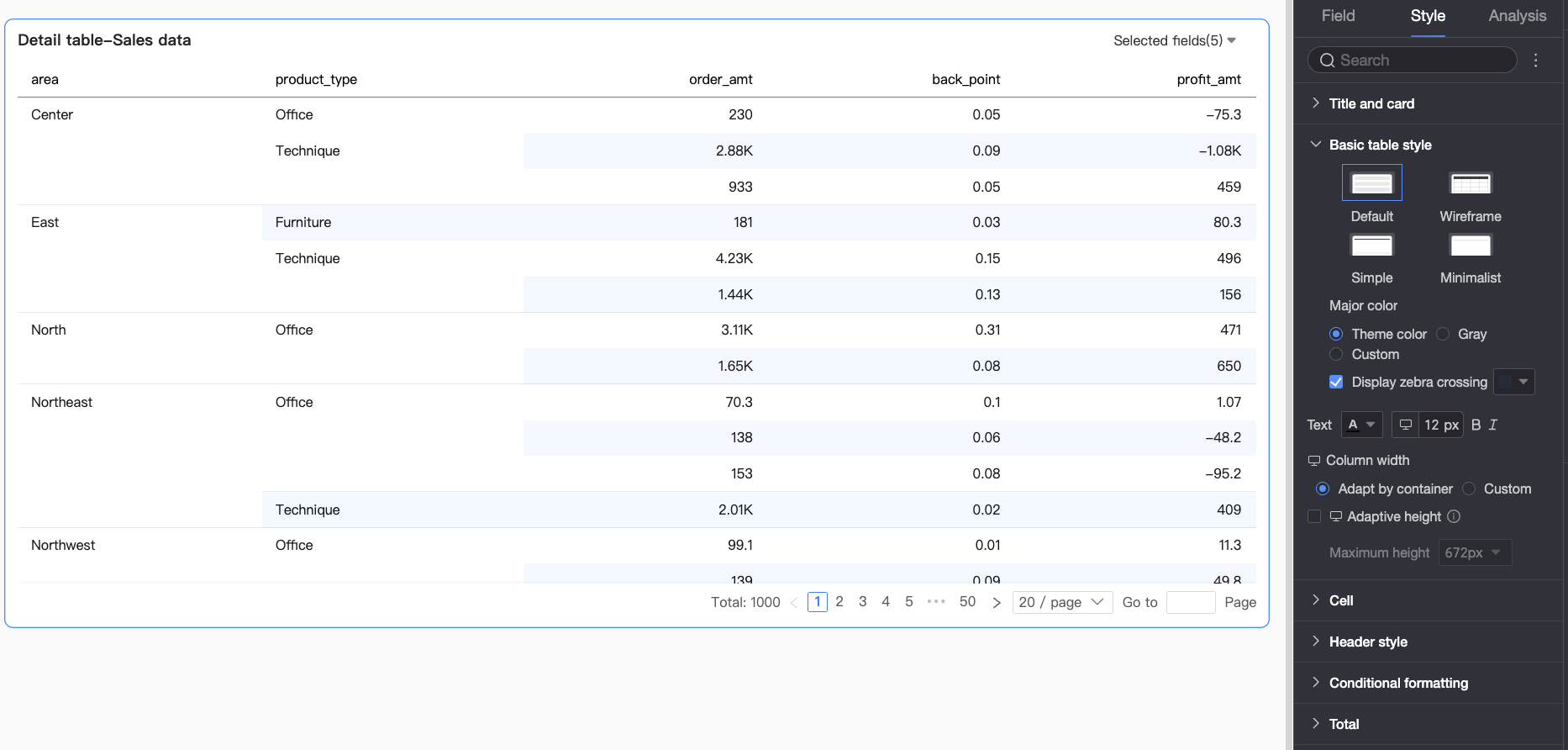
Chart Configuration Item
Description
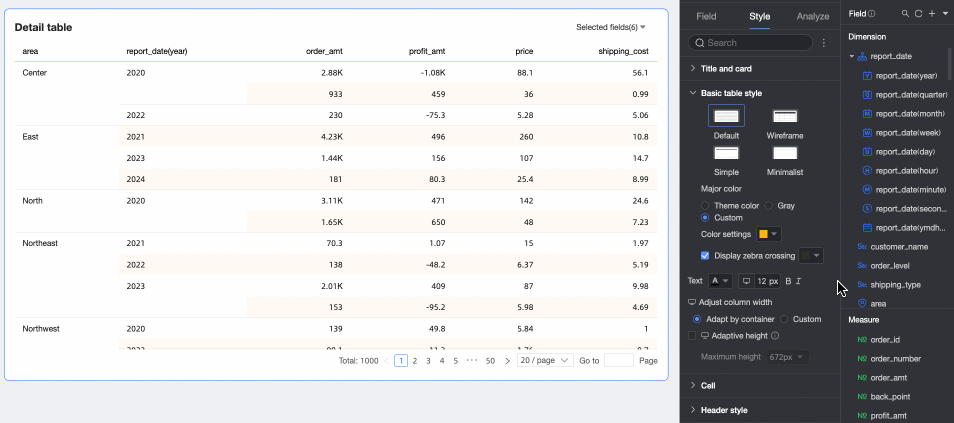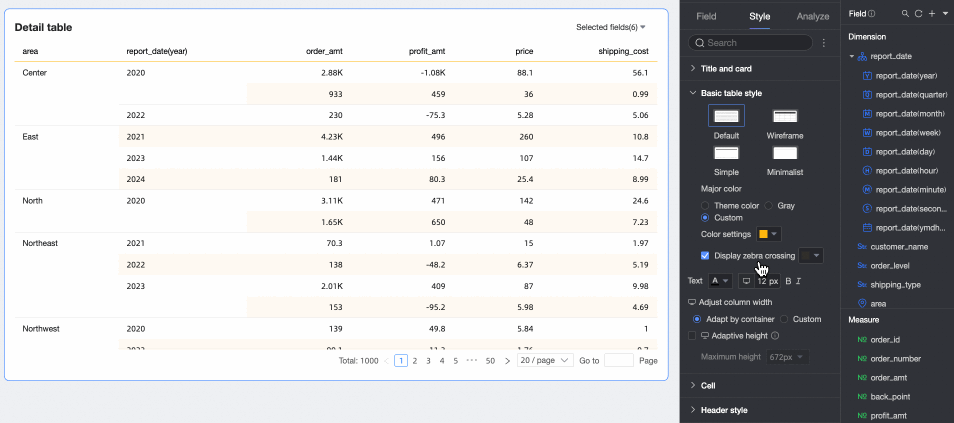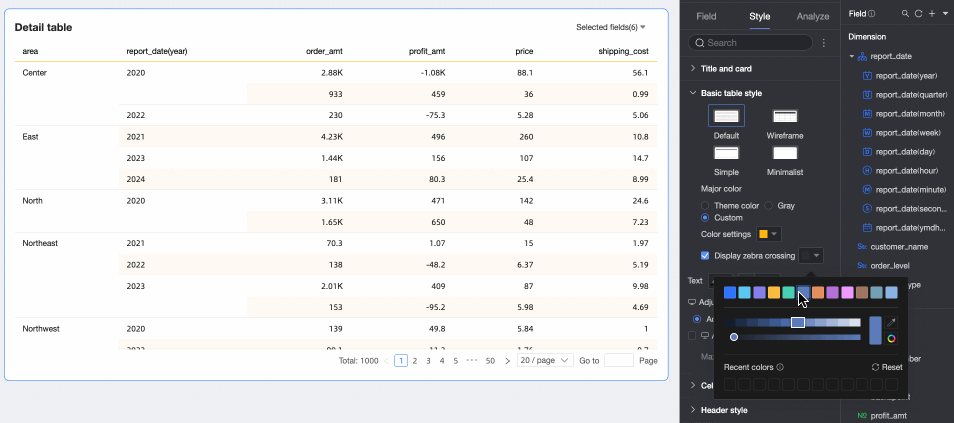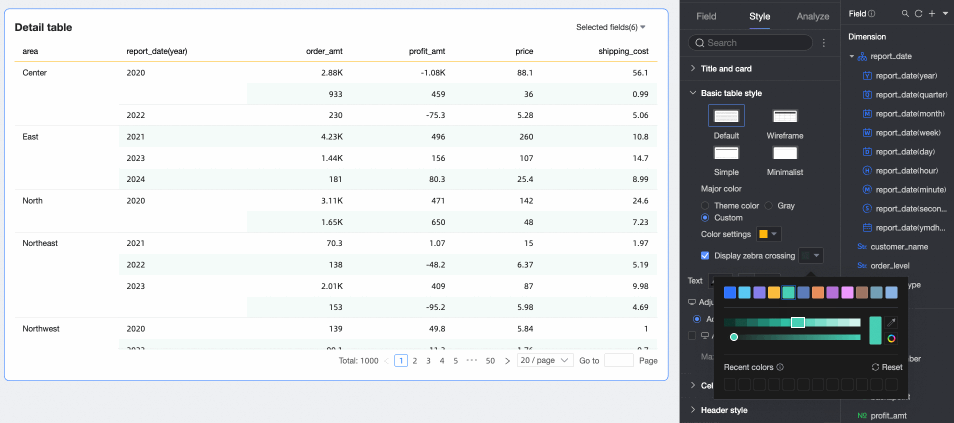
Custom Table Theme
Set the appearance of the detail table.
Theme Style: Choose from Default, Outline, Simple, or Minimal.
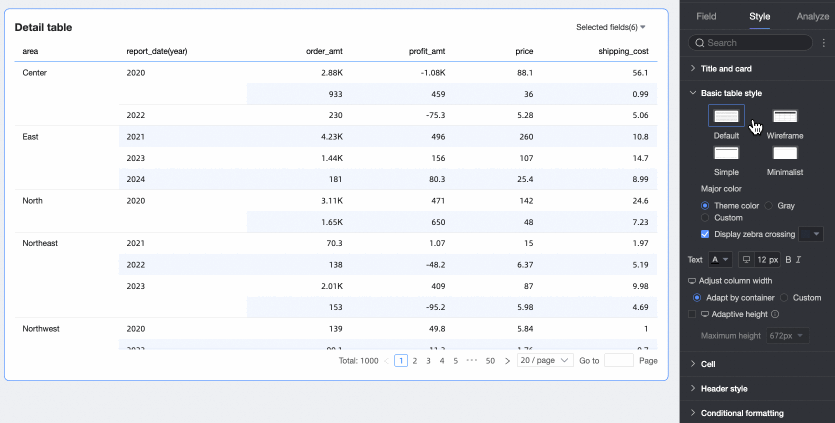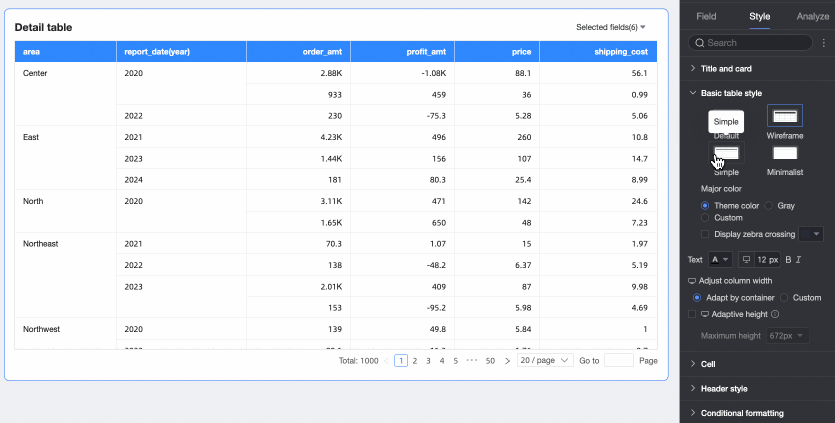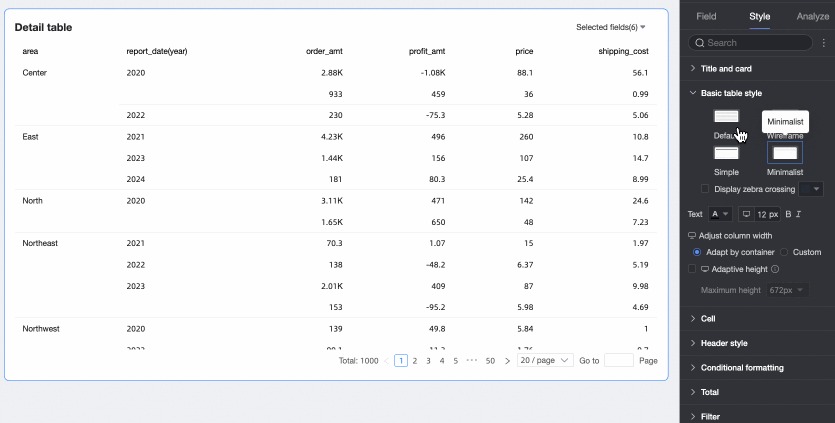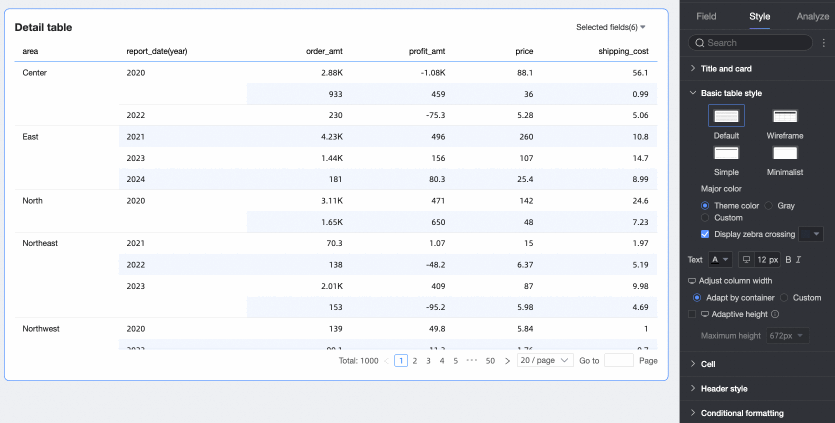
Primary Color Scheme: When the theme style is Default, Outline, or Simple, choose the primary color scheme. Options are Theme Color, Gray, or Custom.
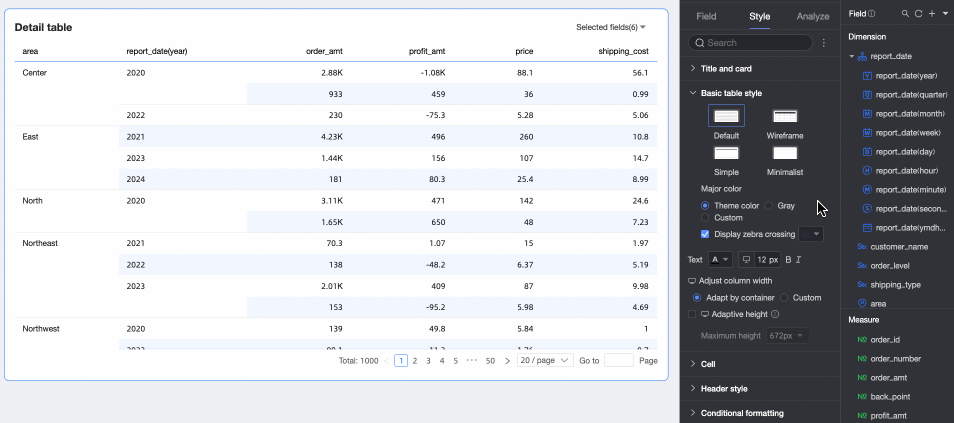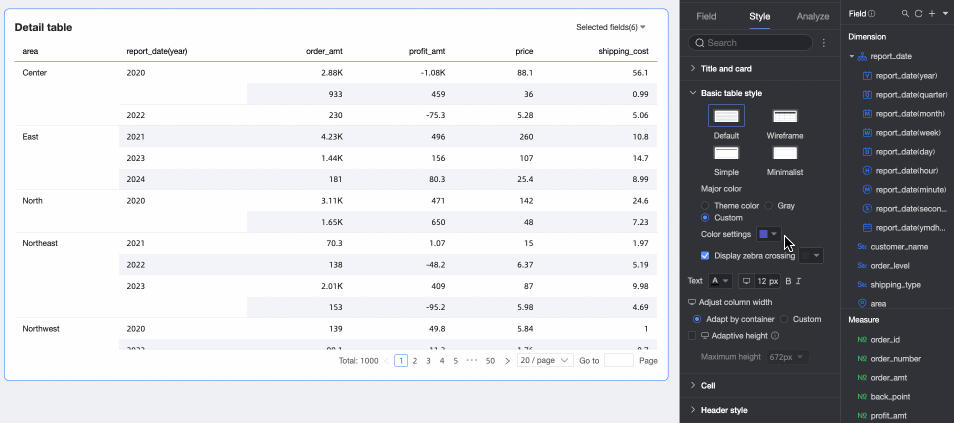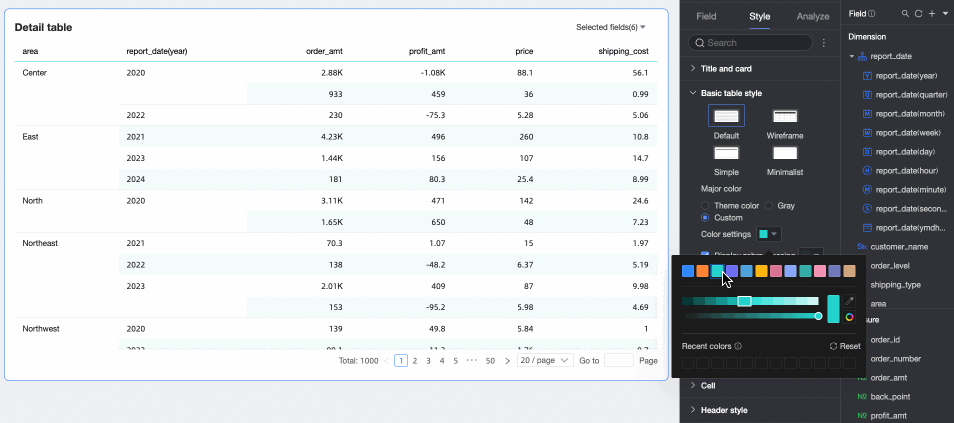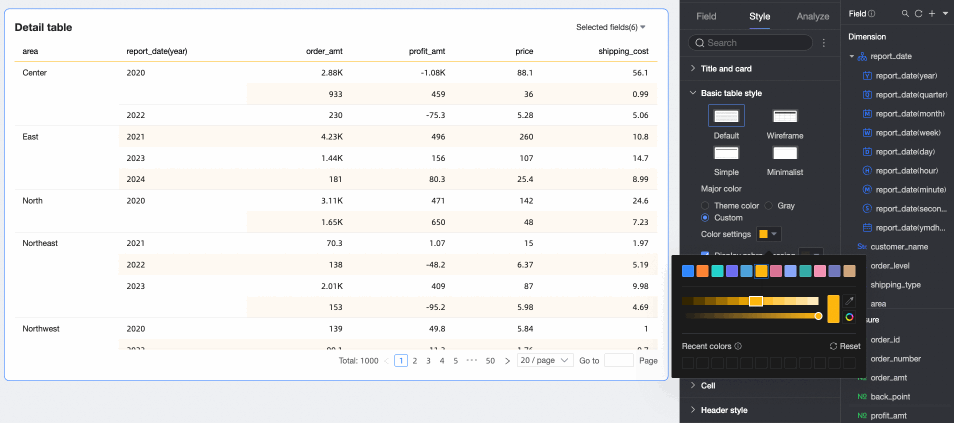
Show Zebra Stripes: Choose whether to show zebra stripes and their color.
Text
Set the text style for the detail table.
Column Width and Row Height
Set the column width and row height. Choose between Auto-fit and Custom.
Auto-fit: The system allocates column width based on available space in the chart container. It sets row height based on the amount of text in each cell. This ensures efficient use of chart space and full visibility of all text. Use this option when you need flexible, multi-device layout and automatic sizing.
Custom: Enter specific values for column width and row height. Use this option when precise table layout matters. After selecting Custom mode, row height and column width default to Auto. Clear Auto to enter exact pixel values.
If you do not know the ideal row height value, drag the row border to preview and confirm the best display effect visually.
You can drag the header row height and data row height separately. Dragging adjusts all rows in that section uniformly. The new height value appears automatically in the corresponding setting box.
NoteColumn width and row height settings for PC and mobile are independent. Set them separately as needed.
Auto Wrap
Select to enable automatic line breaks in table content.
NoteThe detail table recognizes line feed characters in fields. You can also use line feed characters to customize line breaks.
Dynamic Table Height and Maximum Height
Choose between fixed height and dynamic height.
Fixed Height: By default, the table uses fixed height. Drag the bottom border of the chart container to set the height manually.
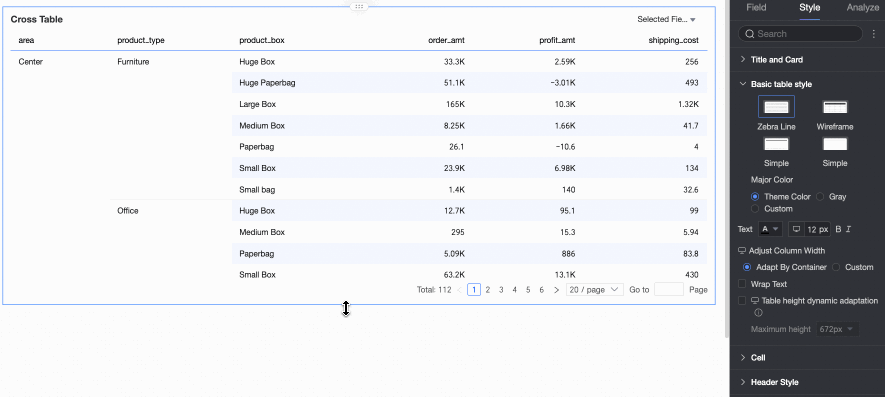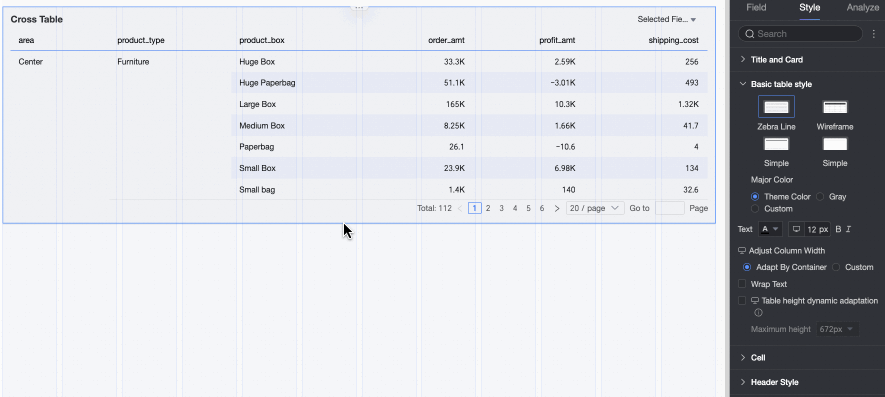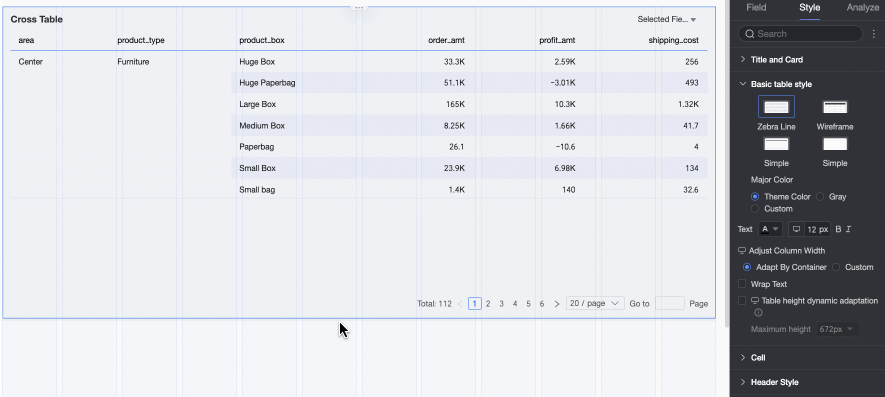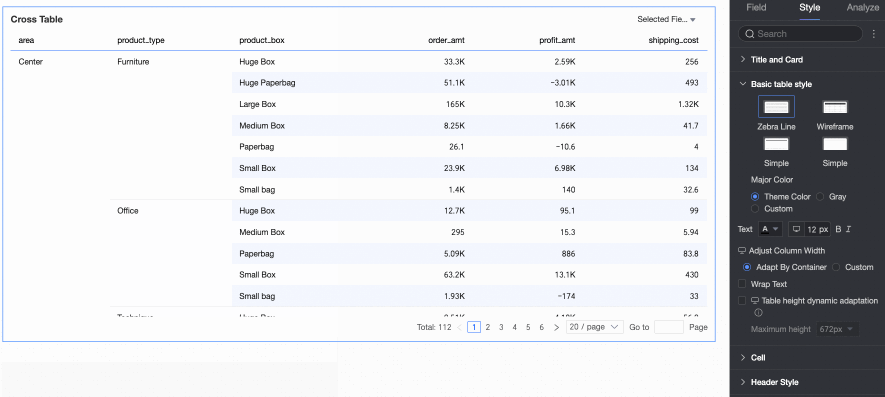
Dynamic Height: Enable dynamic height to let the table container resize automatically based on content. You can also set a maximum height—the combined height of the header and data rows. When dynamic height is enabled, the table will not exceed this value.
Available maximum heights: 192 px (about 5 rows), 352 px (about 10 rows), 672 px (about 20 rows), 1632 px (about 50 rows), or Custom.
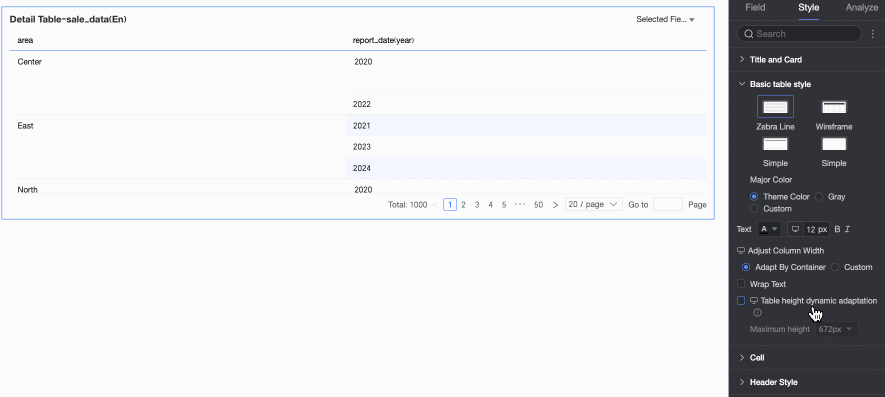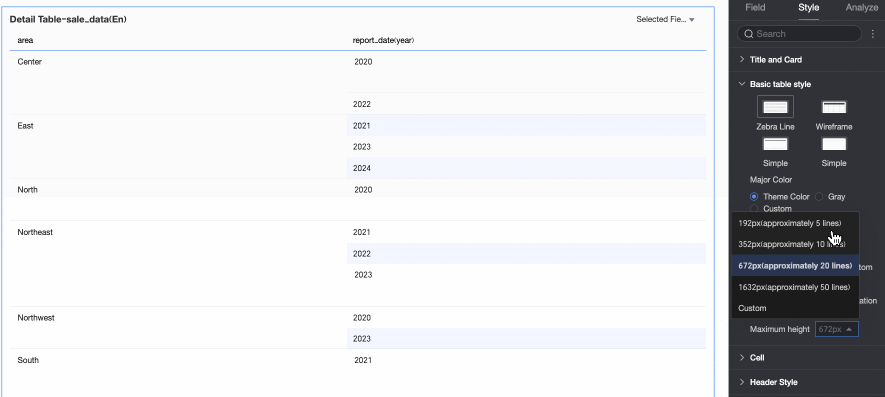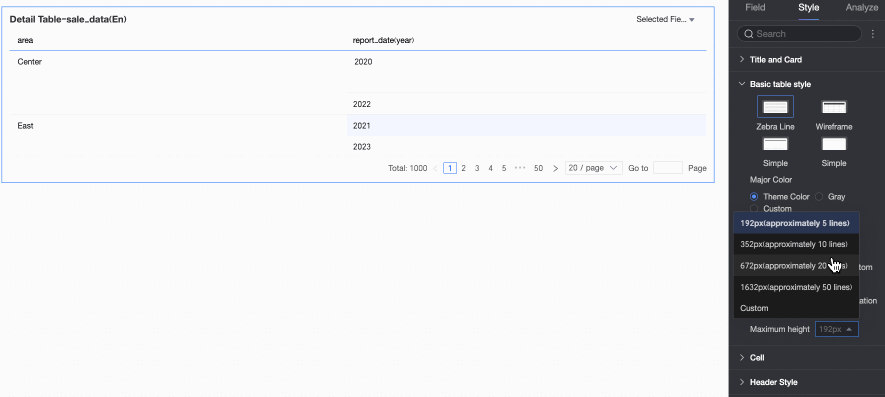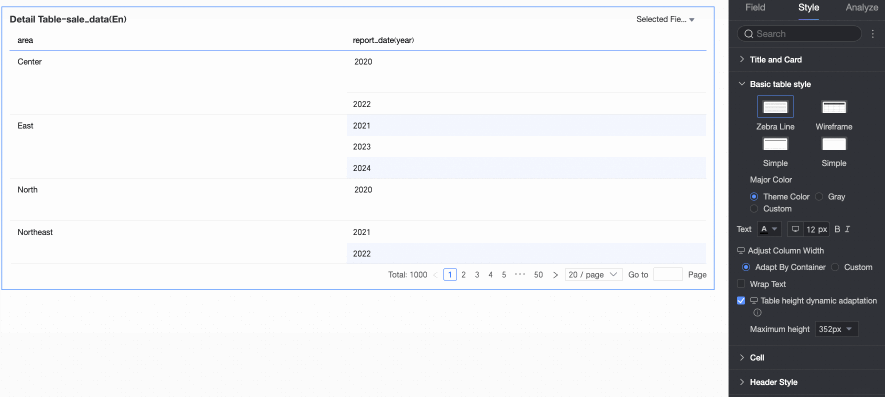
NoteWhen row height is set to Custom, only Custom is available for dynamic height. Set the maximum height to match your desired table effect.
Click the
 icon at the top of the page to configure dynamic height separately for PC and mobile.
icon at the top of the page to configure dynamic height separately for PC and mobile.Mobile devices enable dynamic height by default. You can only adjust the maximum height value.
This feature may affect overall report layout. Enable it only if needed.
In Cell, you can configure cell display and sorting options.

Chart Configuration Item
Description
Freeze
Choose whether to freeze the header or columns.
Measure Grouping
Enable measure grouping. When Mixed Dimensions and Measures is turned on, dimension fields can also be grouped. Groups support field descriptions.
Sorting Mode
Set the sorting mode for the detail table.

All Options: A dropdown shows all sorting options. Select and switch the sort order for any column from the list.

Global Sort Only: Choose this option to sort any field globally by clicking its column header. After selecting, click the
 icon on the right side of the column header to choose ascending or descending order. Global sort works for multiple columns or a single column.
icon on the right side of the column header to choose ascending or descending order. Global sort works for multiple columns or a single column.With Multiple Columns, the system sorts first by the first selected column. If values are equal, it sorts by the second column—and so on.

With Single Column, the chart sorts only by that column. All rows reorder based on that column’s values. Only one column can have active sorting logic. For example, if you sort column A, then sort column B, the sort on column A clears automatically.
No Sorting: Sorting is disabled. Report viewers cannot sort any column.
Merge Identical Cells
Choose whether to merge identical cells.
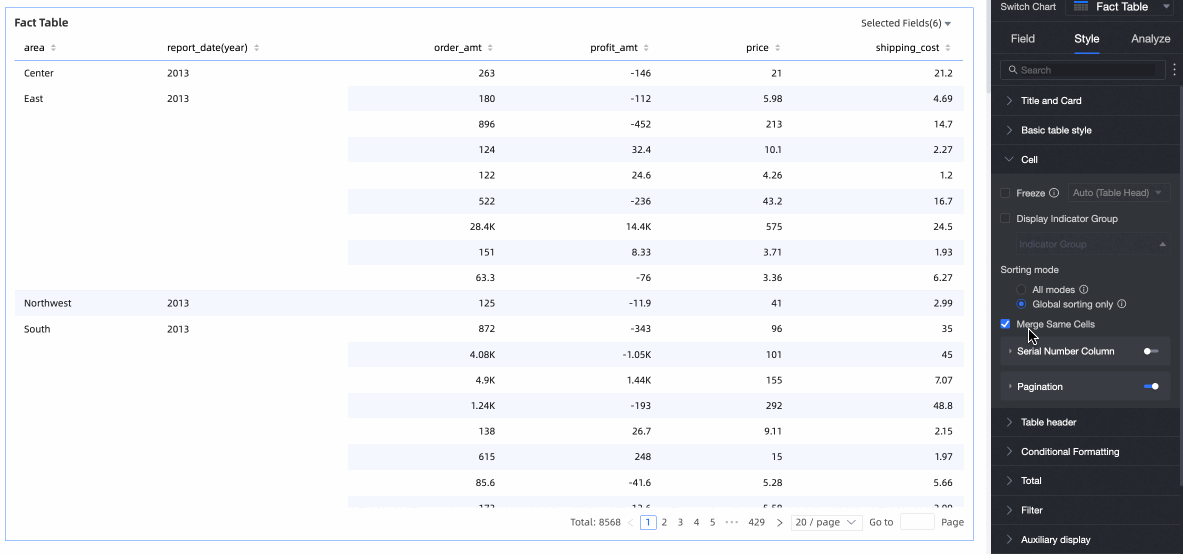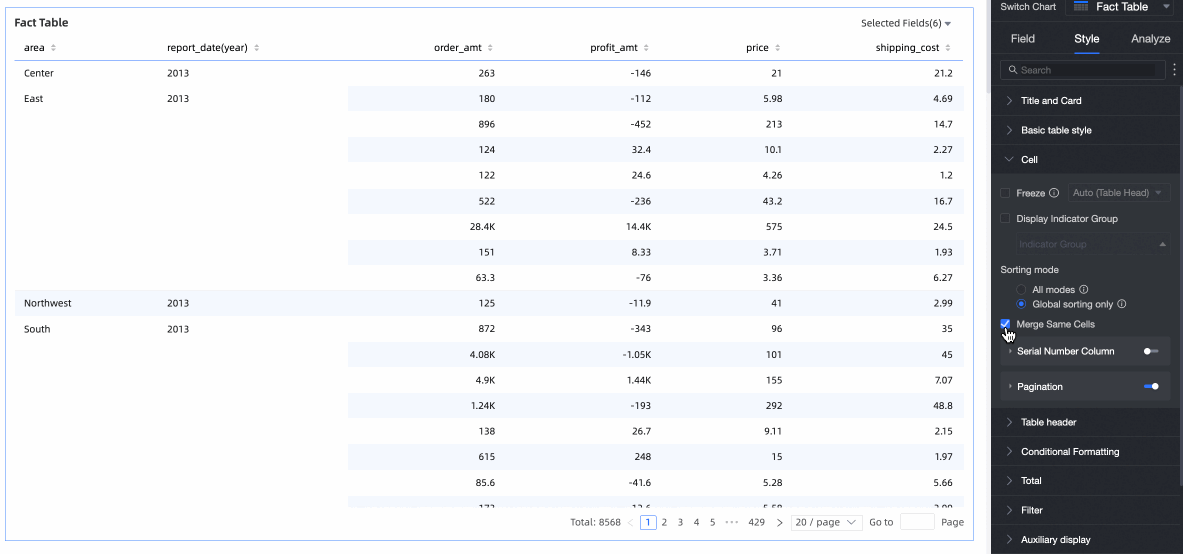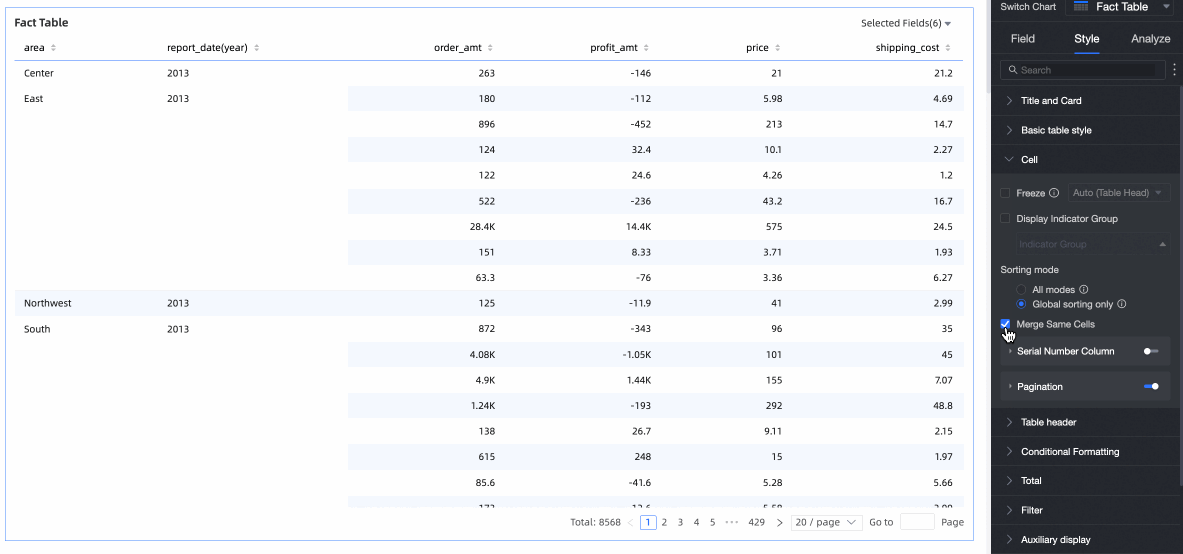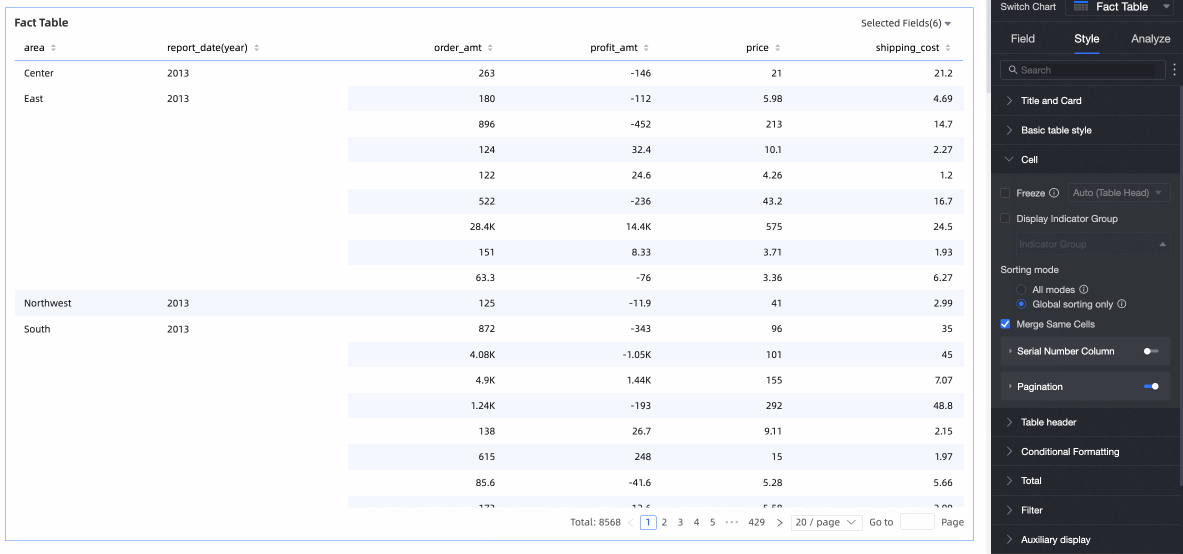
Auto Wrap
Select to enable automatic line breaks in table content.
NoteThe detail table recognizes line feed characters in fields. You can also use line feed characters to customize line breaks.
Image Field Display
When the chart includes an image field, set how images display. Options: scale to fit while preserving aspect ratio, crop to fit, or stretch to fill.
NoteYou can use Image Field only if your dataset contains an image field of type
 .
.Row Number Column
Select to show row numbers in the column header.
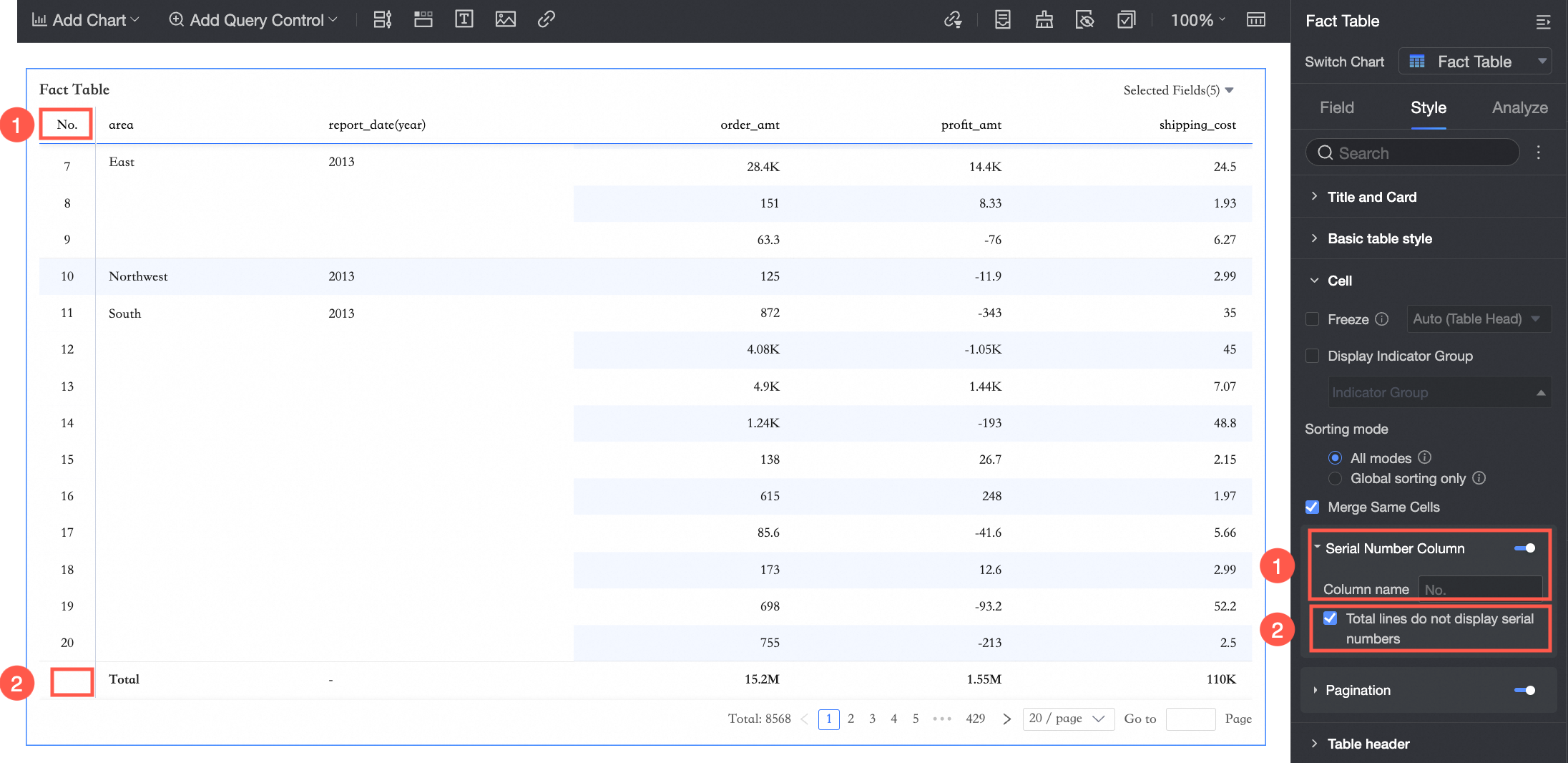
① Set the row number column name.
② Select Hide Row Numbers in Total Rows.
NoteYou can select Hide Row Numbers in Total Rows only if the detail table has column totals enabled.
Paginator
Choose whether to show the paginator. When your chart displays large volumes of data, use the paginator to avoid confusion, help users locate information, and improve loading speed. Click the paginator toggle icon (
 ) to enable it.
) to enable it.After enabling, the paginator editor opens. Configure the following:
The default paginator mode is Regular. If the data volume is too large, select Simple mode. This mode does not calculate the total number of entries.
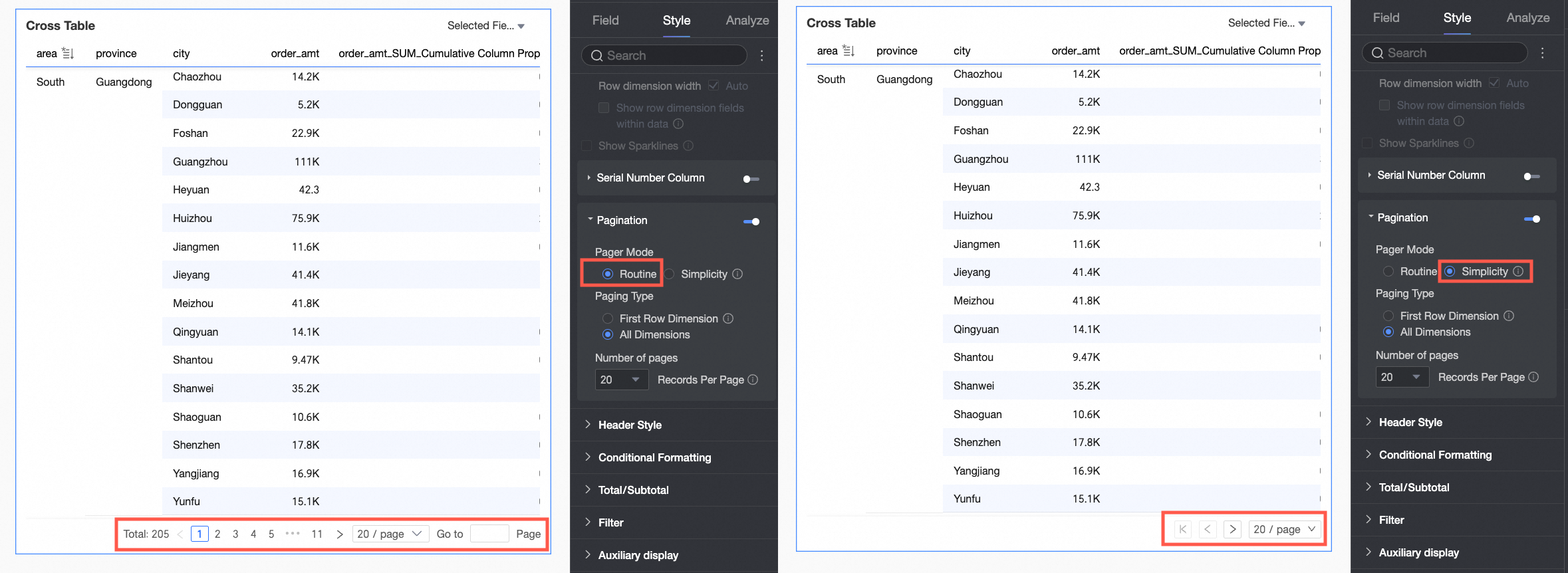
Supported page sizes are 10, 20, 30, 50, 80, 100, 200, and 500 items per page.
In Header, you can configure the style of row and column headers.
Configuration Item
Description
Hide Header
Select to hide the header.
Background Fill
Set the background fill color for the header.
Text
Set the text style for the header.
Alignment
Set header alignment: left, center, or right.
In Conditional Formatting, you can configure conditional formatting for data.
Chart configuration items
Configuration item descriptions
Select fields
Select the fields for which you want to configure conditional formatting. You can select any field added to the data panel area.
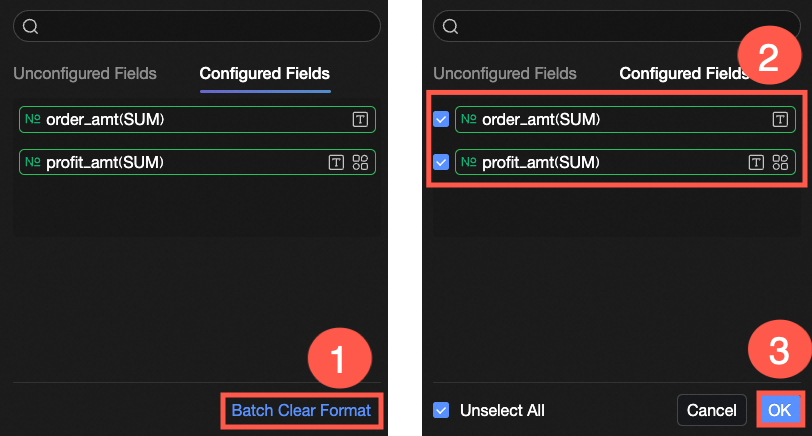
After configuring styles, if you no longer need some of the configured conditional formats, you can also click the Batch Purge Formats operation in the lower-right corner of the field panel. Then, select the conditional formats to purge from the list and click OK to complete the format purge.
Quick styles
Set the mark icon or font display color for the current field from the styles provided by the system. You can only configure quick styles for measure fields, not for dimension fields.
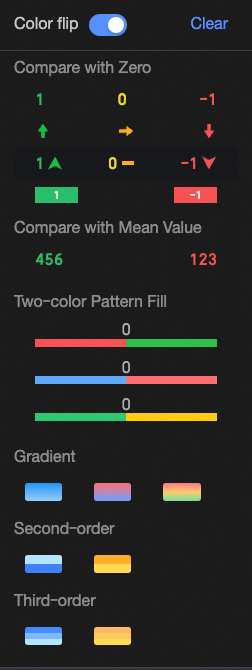
Comparison: Select Compare with 0 or Compare with mean.
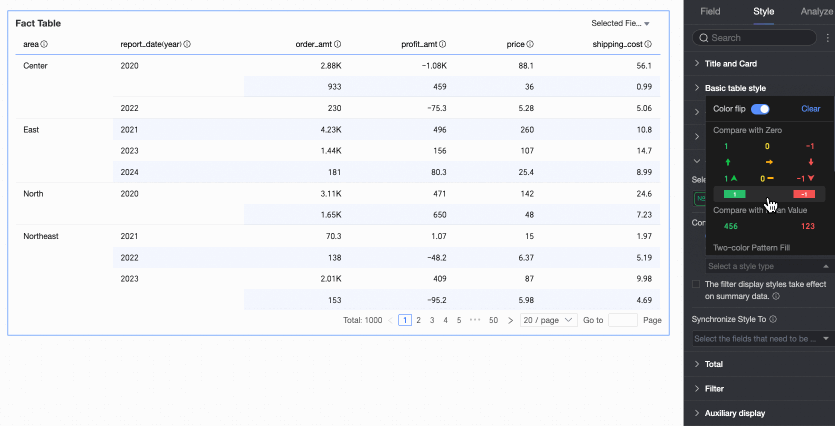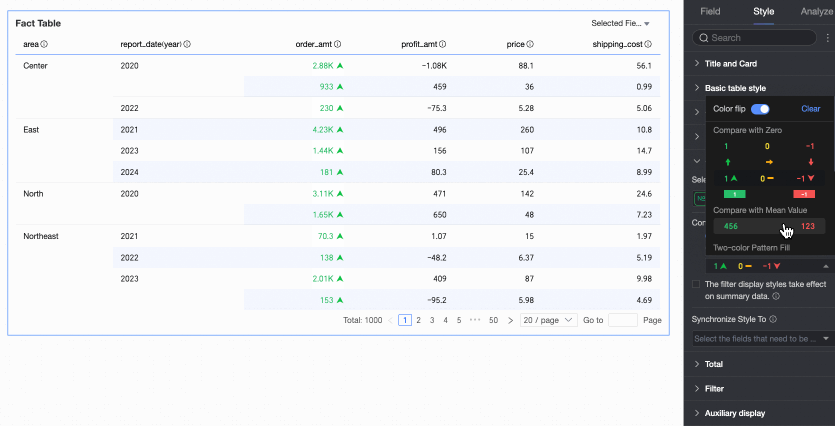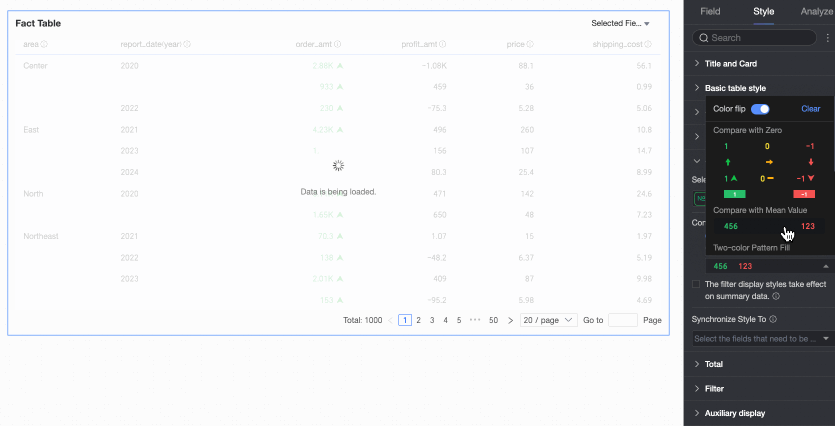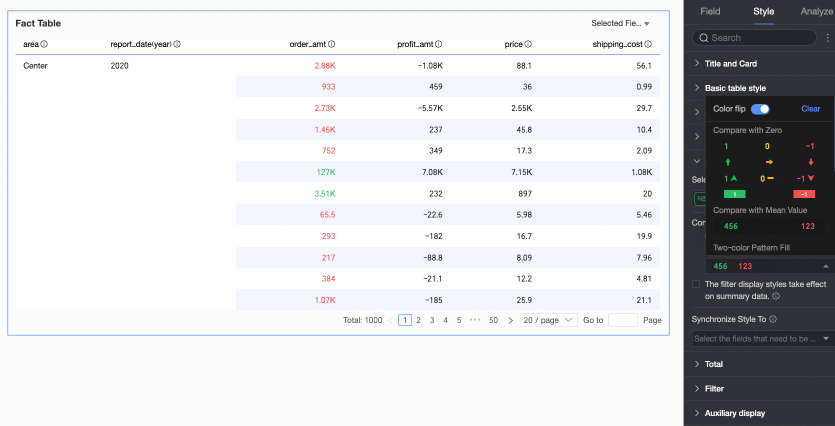
Two-color fill: Select the data bar color.
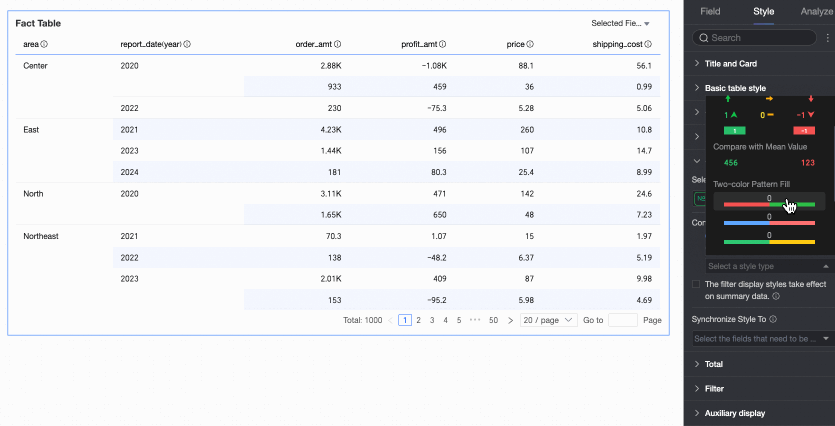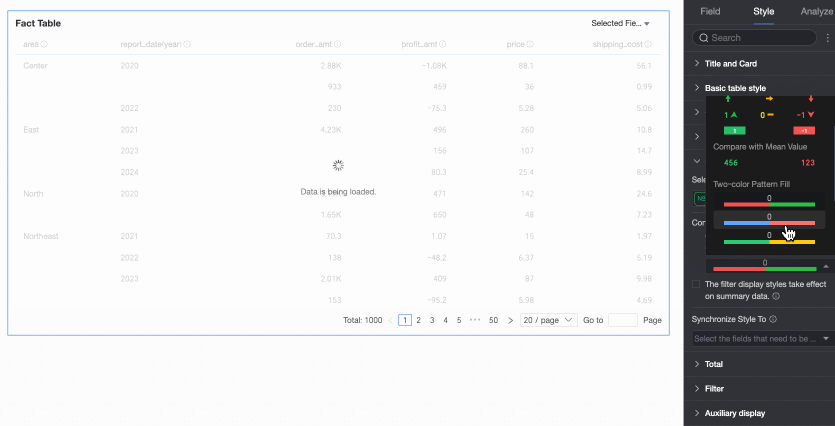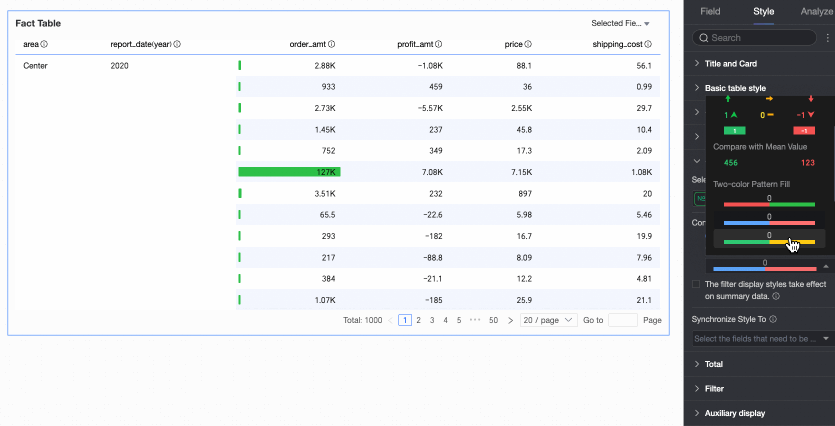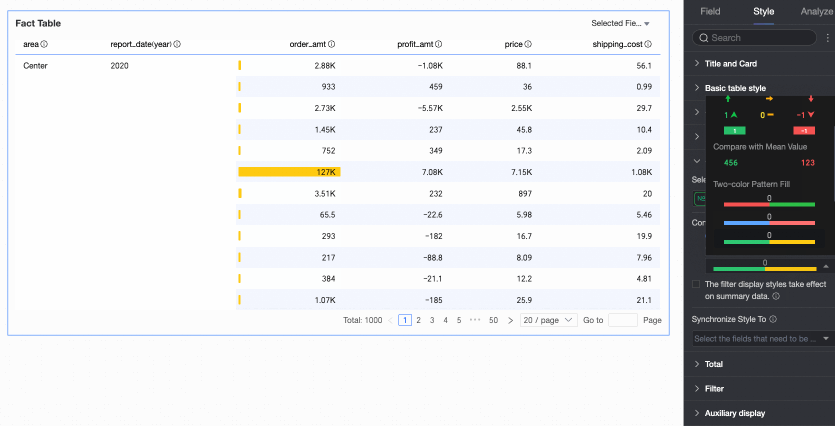 Note
NoteData bar length calculation: If the maximum and minimum values have opposite signs, the denominator is the maximum absolute value of the positive and negative values. If the maximum and minimum values have the same sign (both negative or both positive), the denominator is the difference between their absolute values.
Color scale: Select Gradient, Two-step, or Three-step.
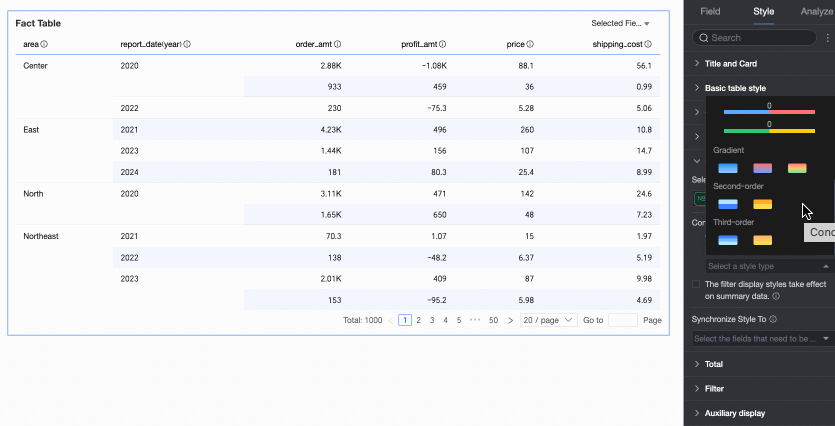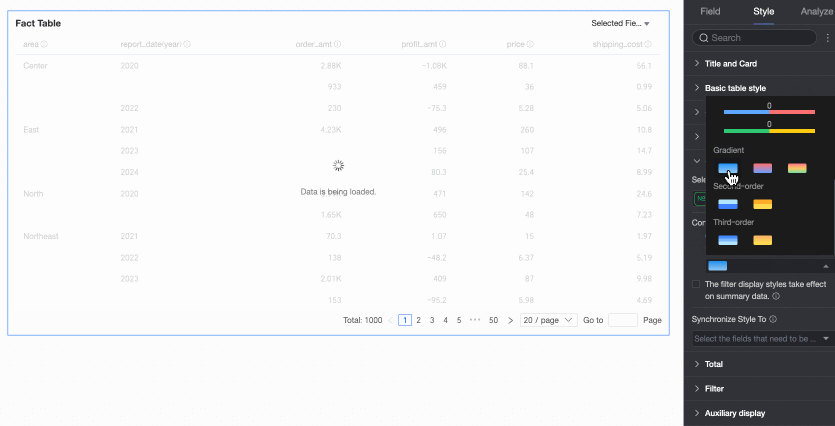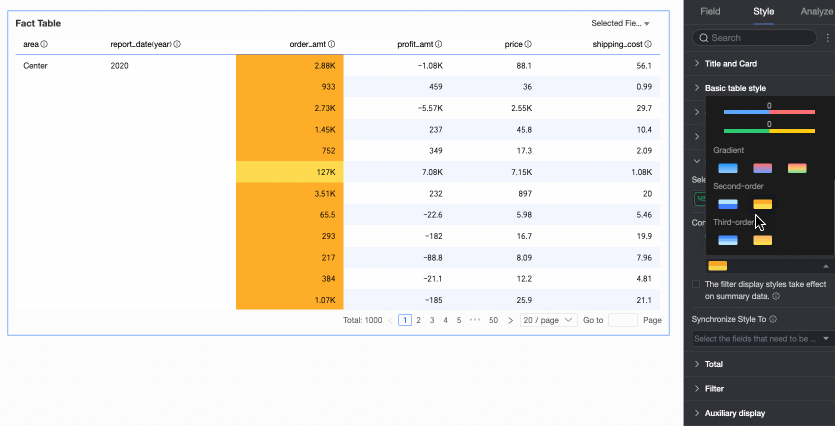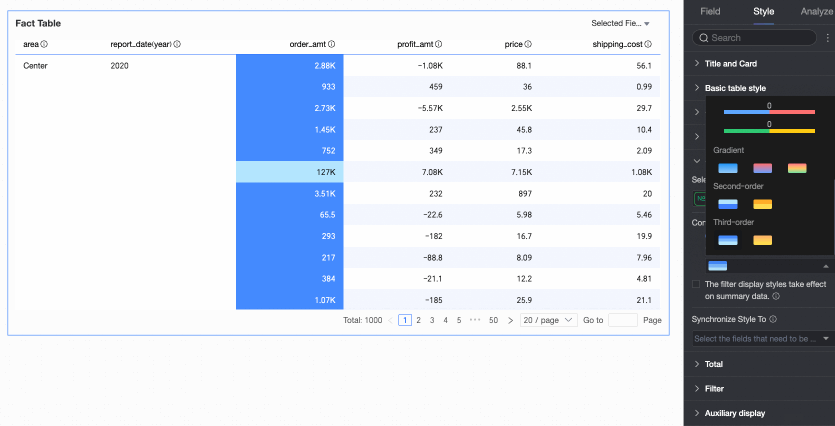
Flip colors
For example, in a comparison, values less than 0 are red, and values greater than 0 are green. After flipping, values less than 0 become green, and values greater than 0 become red.
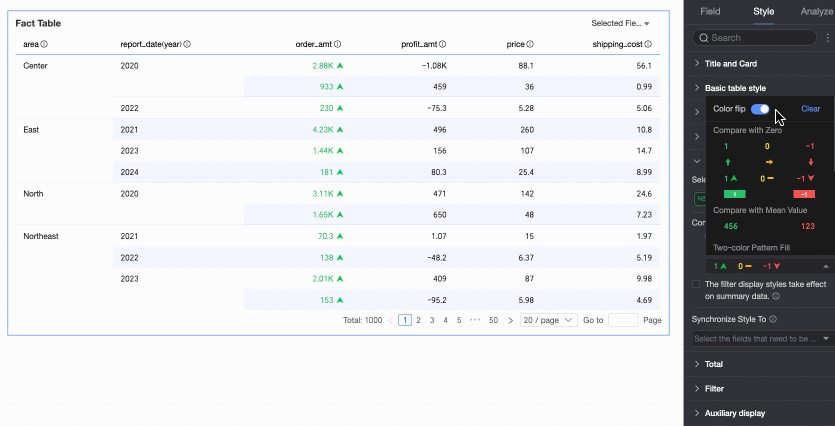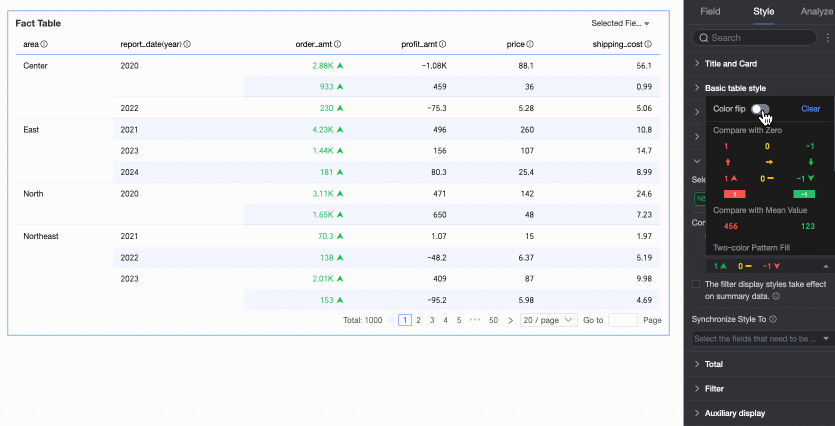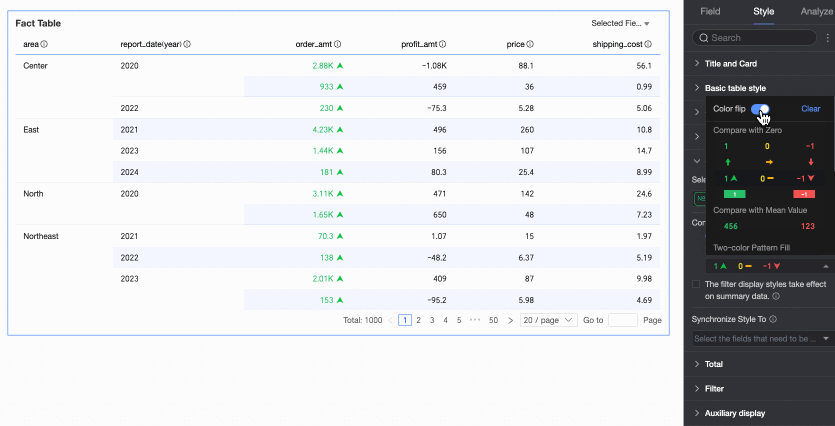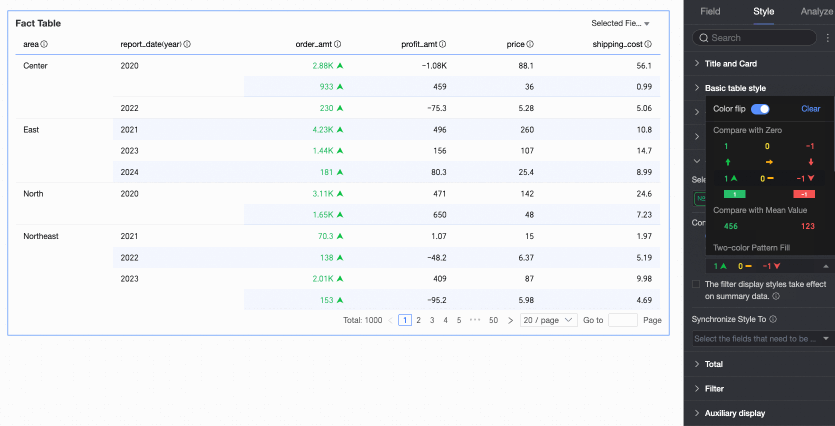
Delete: If you no longer need a quick style you have set, click Delete to remove it.
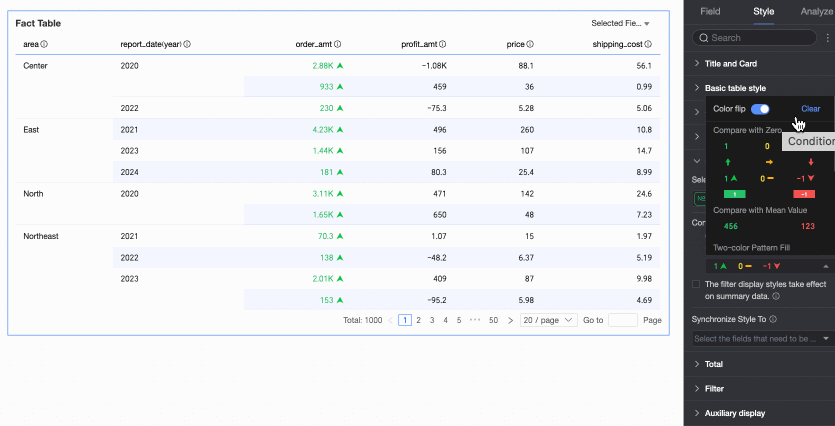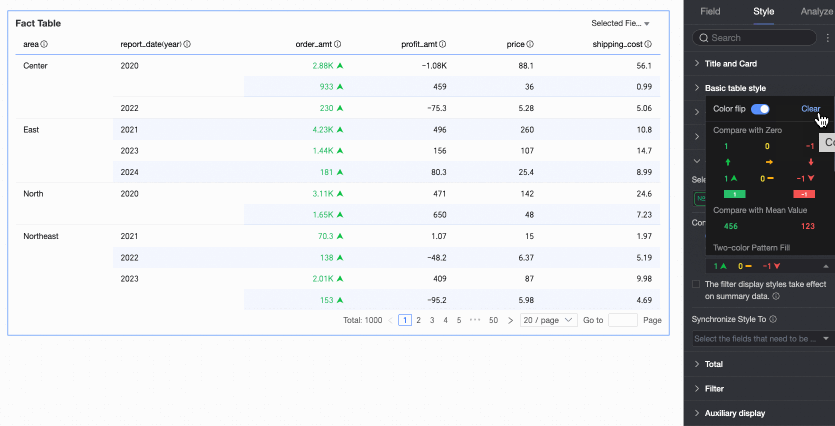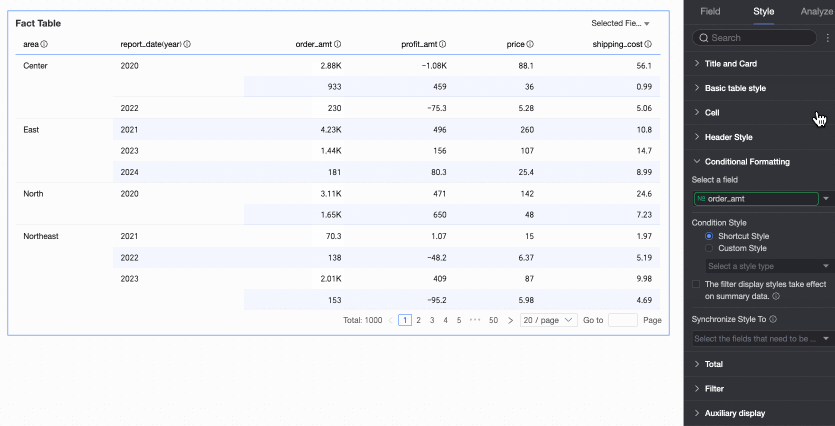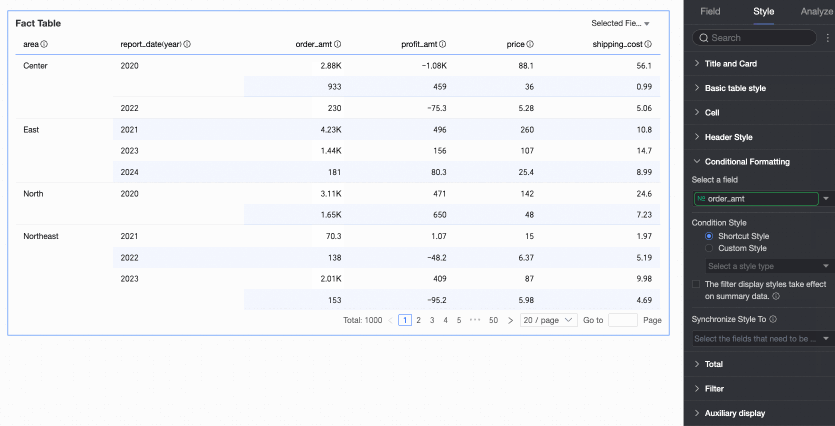
Custom styles
In addition to the quick styles provided by the system, configure custom styles as needed. Both measure fields and dimension fields support custom styles, but the configurable style content differs.
Measure fields: Configure Highlight text/Background, Icons, Color scale, and Data bars.
Highlight text/Background: Configure rules to highlight the text color and background color of field values, effectively emphasizing key data in the table visually.
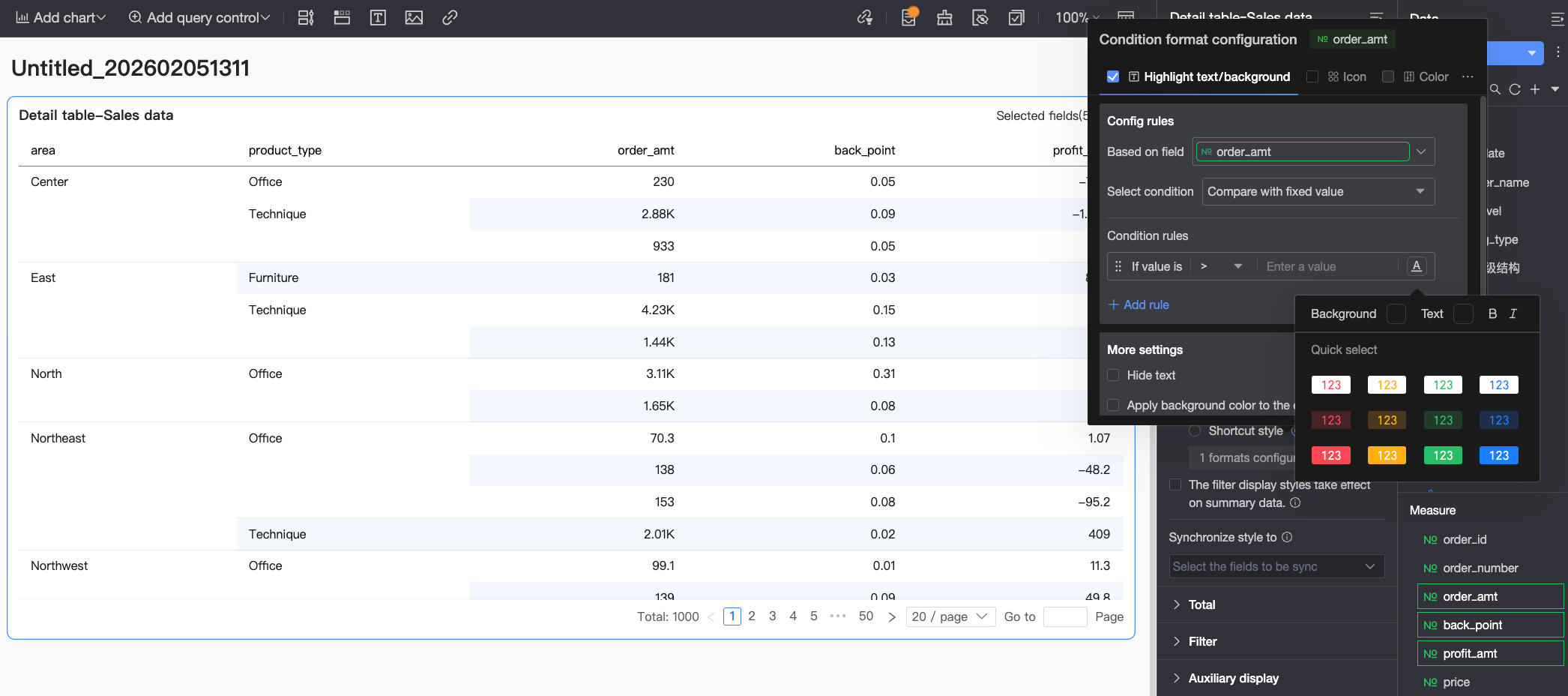 Configure the following information:
Configure the following information:Based on field: Set which data field the conditional rule applies to. This defaults to the field configured in Select fields. You can also select other fields in the chart to configure more complex conditional rules based on their values.
Condition selection: Set the comparison basis for the conditional rule. Options include Compare with static value, Divide by percentage interval, and Compare with dynamic field.
Conditional rule: Set the specific judgment logic for the conditional rule and the display style for the cell text/background when the rule is met. Configure text color, bold, italic, and background fill color.
Add rule: Click to add a new operation rule.
More settings: Set whether to hide the text content of the current field and whether to apply the background color to the entire row.
Icons: Display specific mark icons in corresponding cells based on numerical comparison results, clearly showing the relationship between current data and target data.
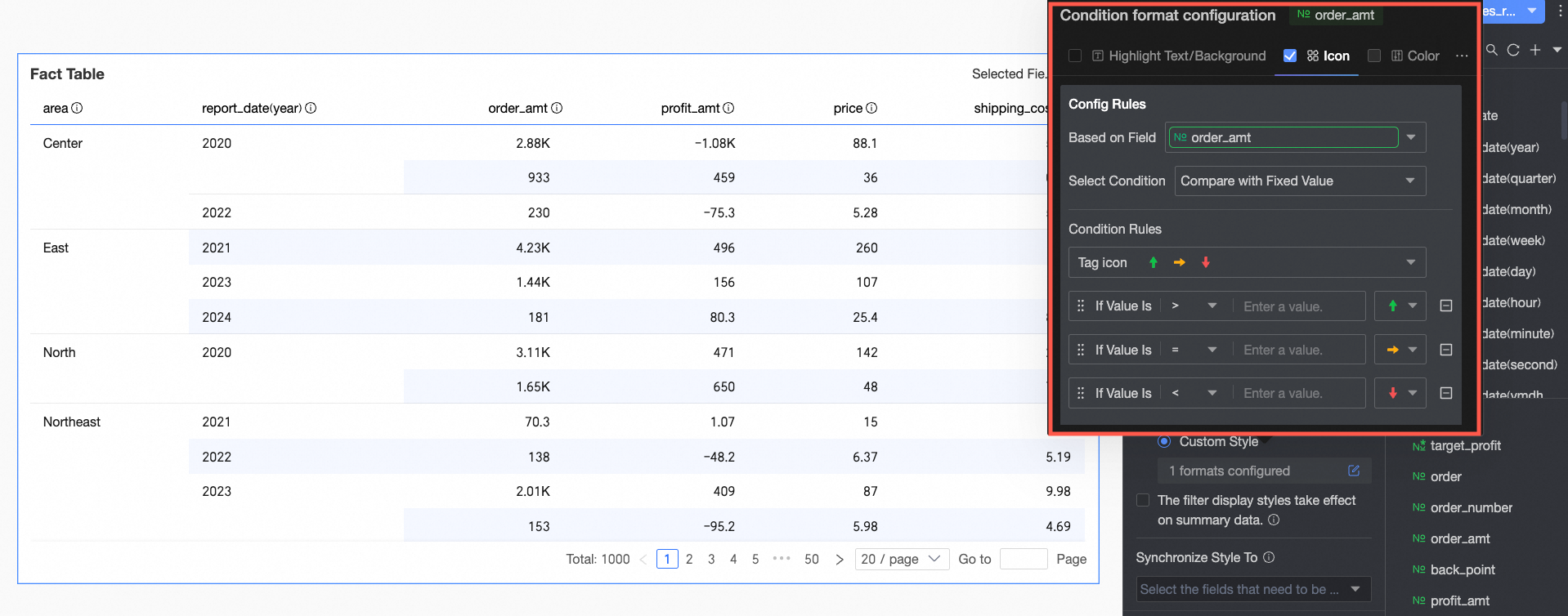 Configure the following information:
Configure the following information:Based on field: Set which data field the conditional rule applies to. This defaults to the field configured in Select fields. You can also select other fields in the chart to configure more complex conditional rules based on their values.
Condition selection: Set the comparison basis for the conditional rule. Options include Compare with static value, Divide by percentage interval, and Compare with dynamic field.
Conditional rule: Click the Mark icon selection box. Select the appropriate icon type from the icon styles provided by the system as needed. Set the specific judgment logic for the data condition corresponding to an icon. You can also select a mark icon individually for each comparison rule.
Add rule: Click to add a new operation rule.
More settings: Set whether to hide the text of the current field.
Color scale: Based on numerical values, display different colors from a specified color scale in the cell background, clearly showing data distribution and change trends.
NoteOnly configure color scales if you do not select highlight text/background, icons, and data bars.
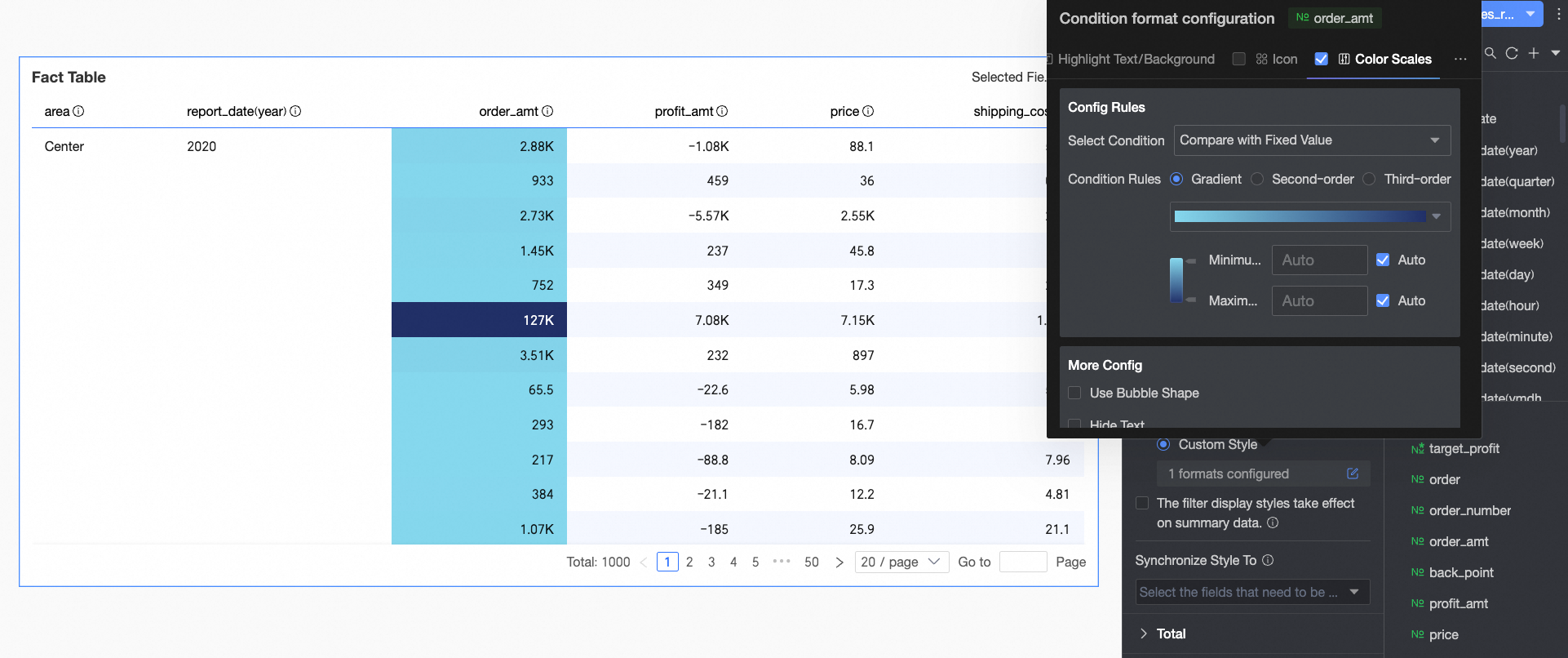 Configure the following information:
Configure the following information:Condition selection: Set the comparison basis for the conditional rule. Options include Compare with static value and Divide by percentage interval.
Conditional rule: Set the color scale style (gradient, one-step, two-step). Specify the maximum, minimum, and boundary values for the current style, and the corresponding colors for each numerical interval.
In More settings: Set the shape of the color scale bar and whether to hide the text of the current field.
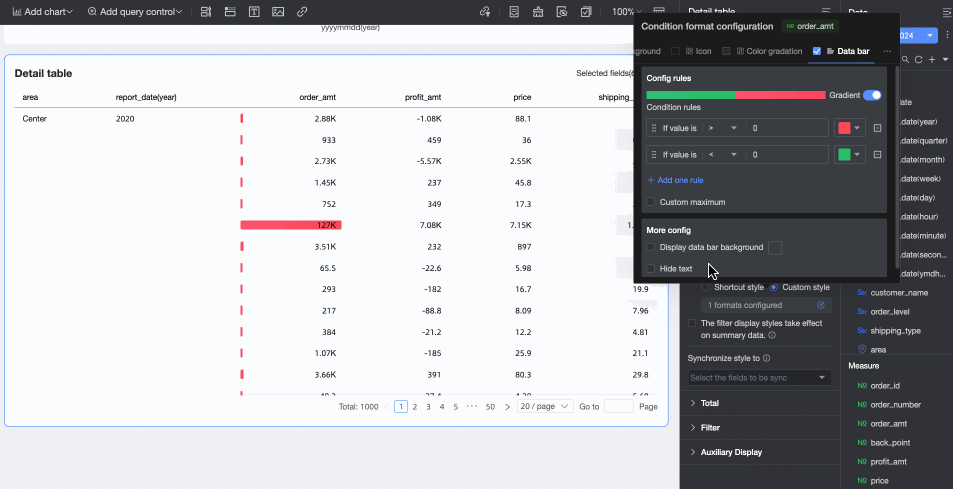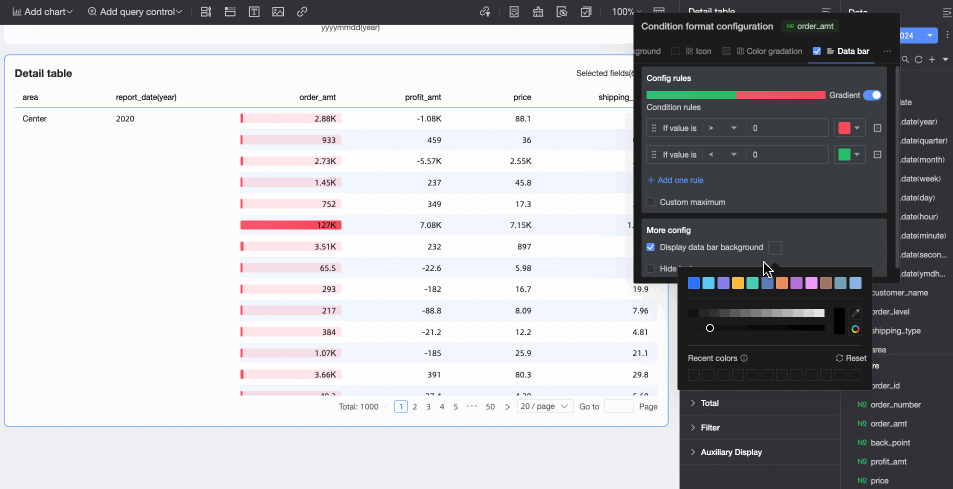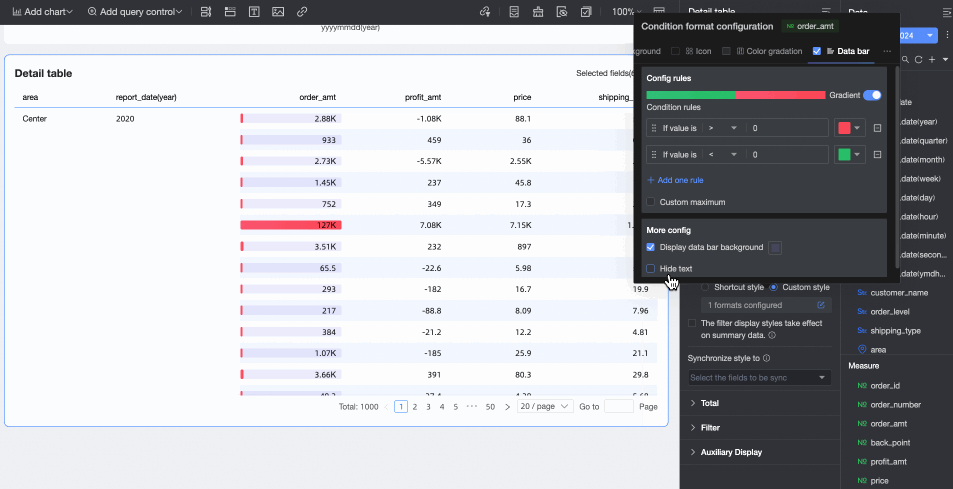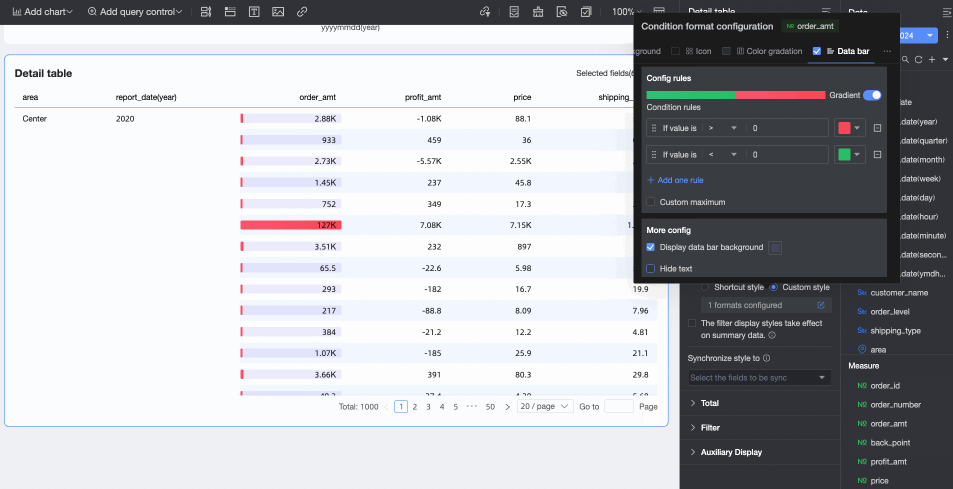
Data bars: Display cell values as visual lengths and colors, more intuitively showing the relative size or comparison of data.
 Configure the following information:
Configure the following information:Conditional rule: Set the display rules for the data bars of the current measure field. Specify the corresponding display color for each rule.
Add rule: Click to add a new operation rule.
Customize max/min values: After selecting, customize the specific maximum and minimum values. In automatic mode, the maximum value defaults to the highest value in the current field, and the minimum value defaults to the lowest value.
More settings: Set whether to display the data bar background and customize its color. Set whether to hide the text of the current field.
Dimension fields: Configure Highlight text/Background and Icons.
Highlight text/Background
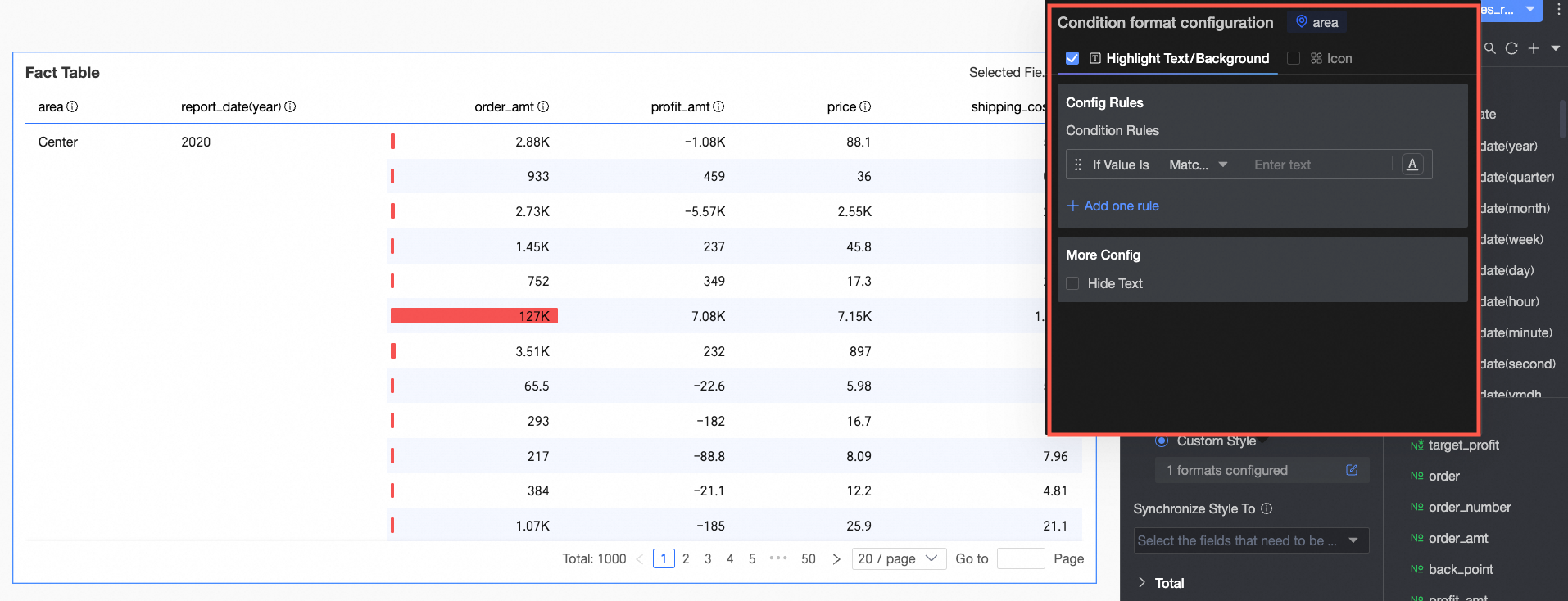
In Rule creation: Set conditional rules to highlight the text of the current dimension field. The condition here judges dimension values, so the condition value input box only accepts text.
In More settings: Set whether to hide the text of the current field.
Icons
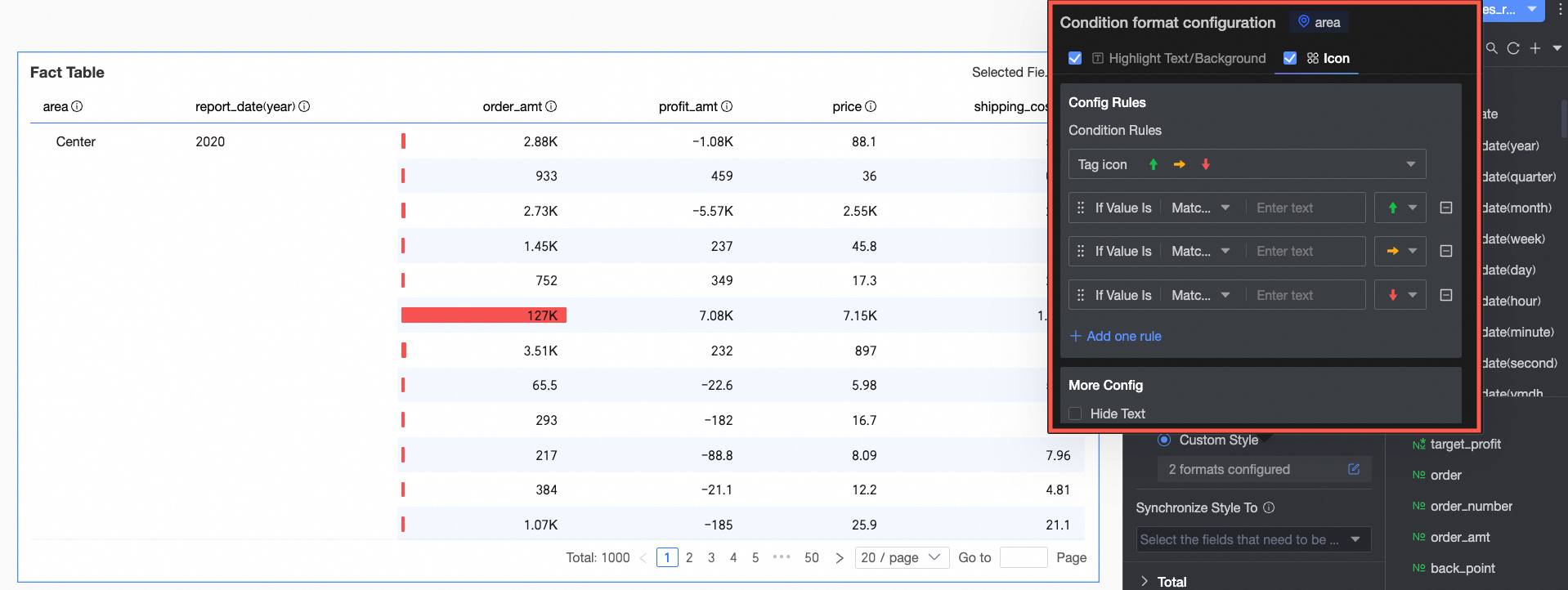
In Rule creation: Set icon mark rules for the current dimension field. The condition here judges dimension values, so the condition value input box only accepts text.
In More settings: Set whether to hide the text of the current field.
Conditional styles apply to aggregated data
After checking, the configured conditional styles also apply to aggregated data.
Sync styles to
Sync the current conditional format to other fields.
In Totals/Subtotals, you can click the toggle icon
 to enable column totals. When enabled, the system sums all values in the column.
to enable column totals. When enabled, the system sums all values in the column.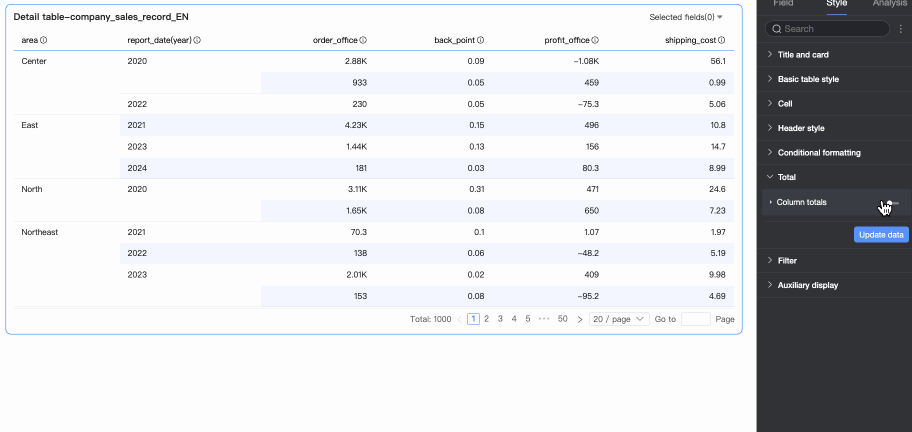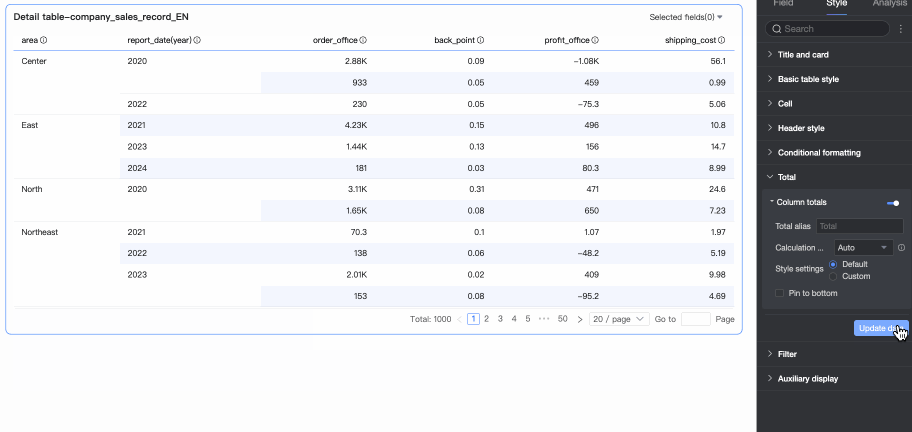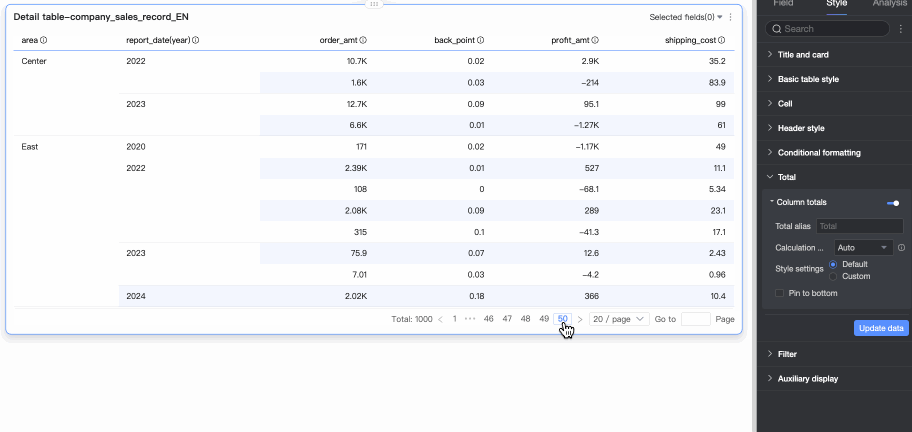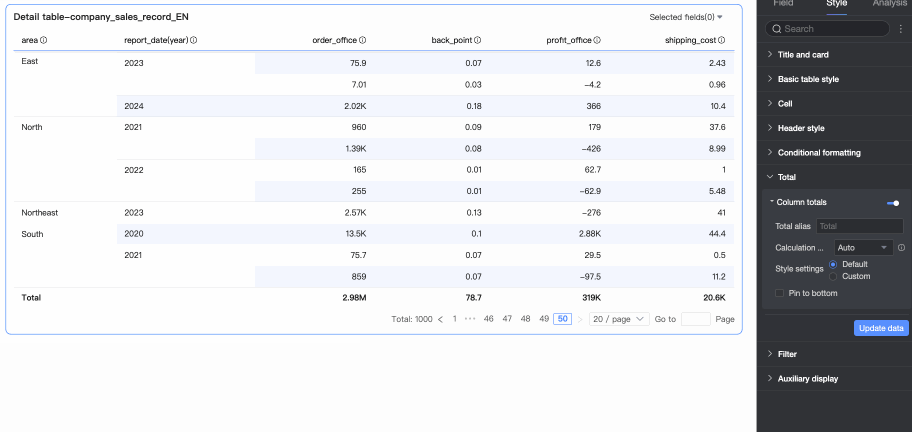
Configuration Item
Description
Overall Totals (Column Totals)
Total Alias
Set the display name for total data based on business meaning. Example: Total Sales by Region.
Calculation
Choose one aggregation method for all fields. If a field is a calculated field, this setting does not apply—the original aggregation method remains.
To assign different aggregation methods per field, select Custom from the dropdown. Then configure each field’s logic in the Custom Calculation section.
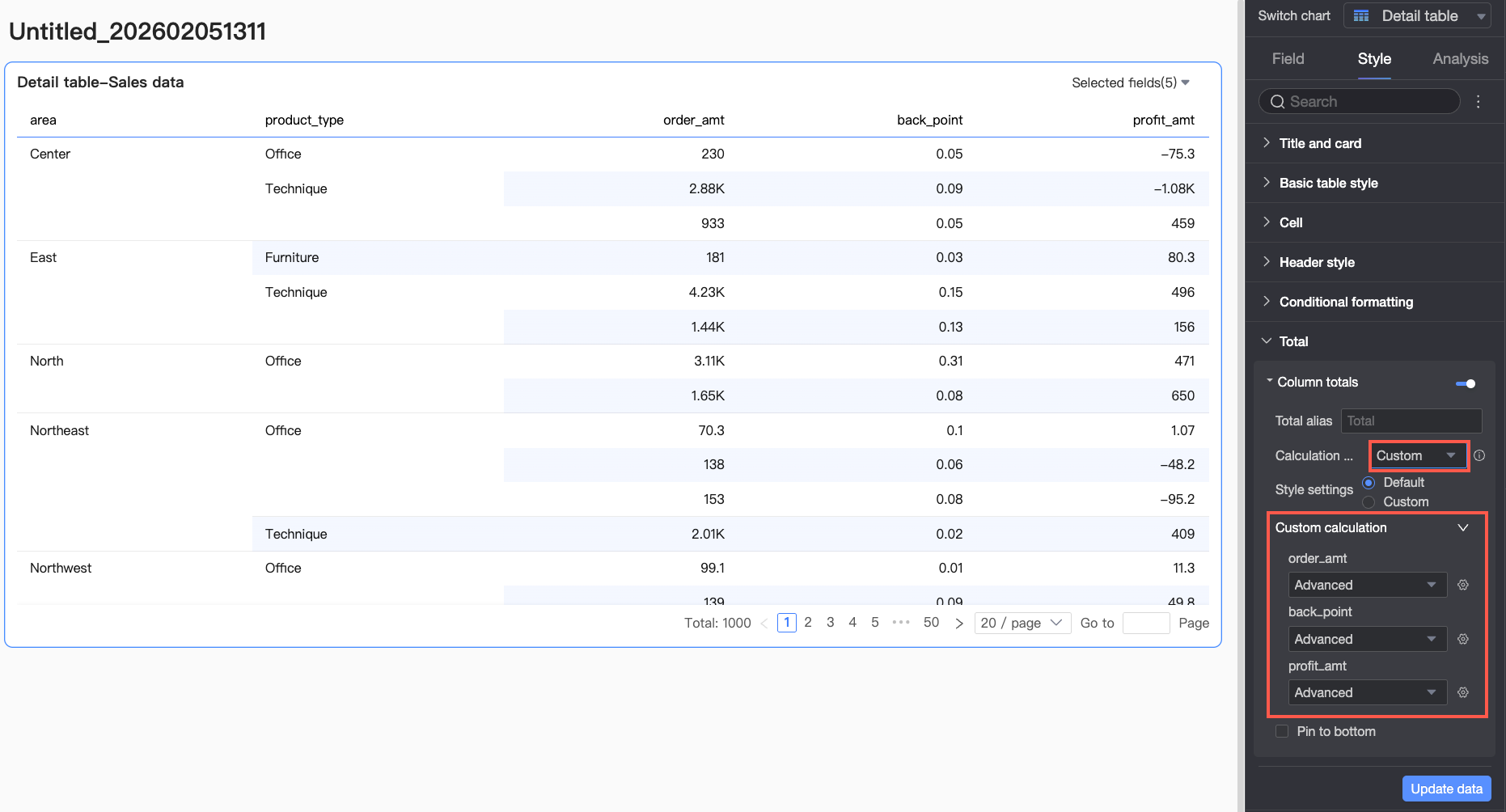
Style Configuration
Set the text style for total data. Choose to follow the system default or customize font color, background color, and weight.
Pin to Bottom
Choose whether to pin column totals to the bottom.
NoteFor common questions about totals, see Totals Configuration FAQ.
In Filter:
You can select Enable Field Content Filtering. In preview mode, click the Selected Fields dropdown to filter or sort fields.
You can select Enable Quick Filter. In preview mode, click the Filter dropdown to filter fields.
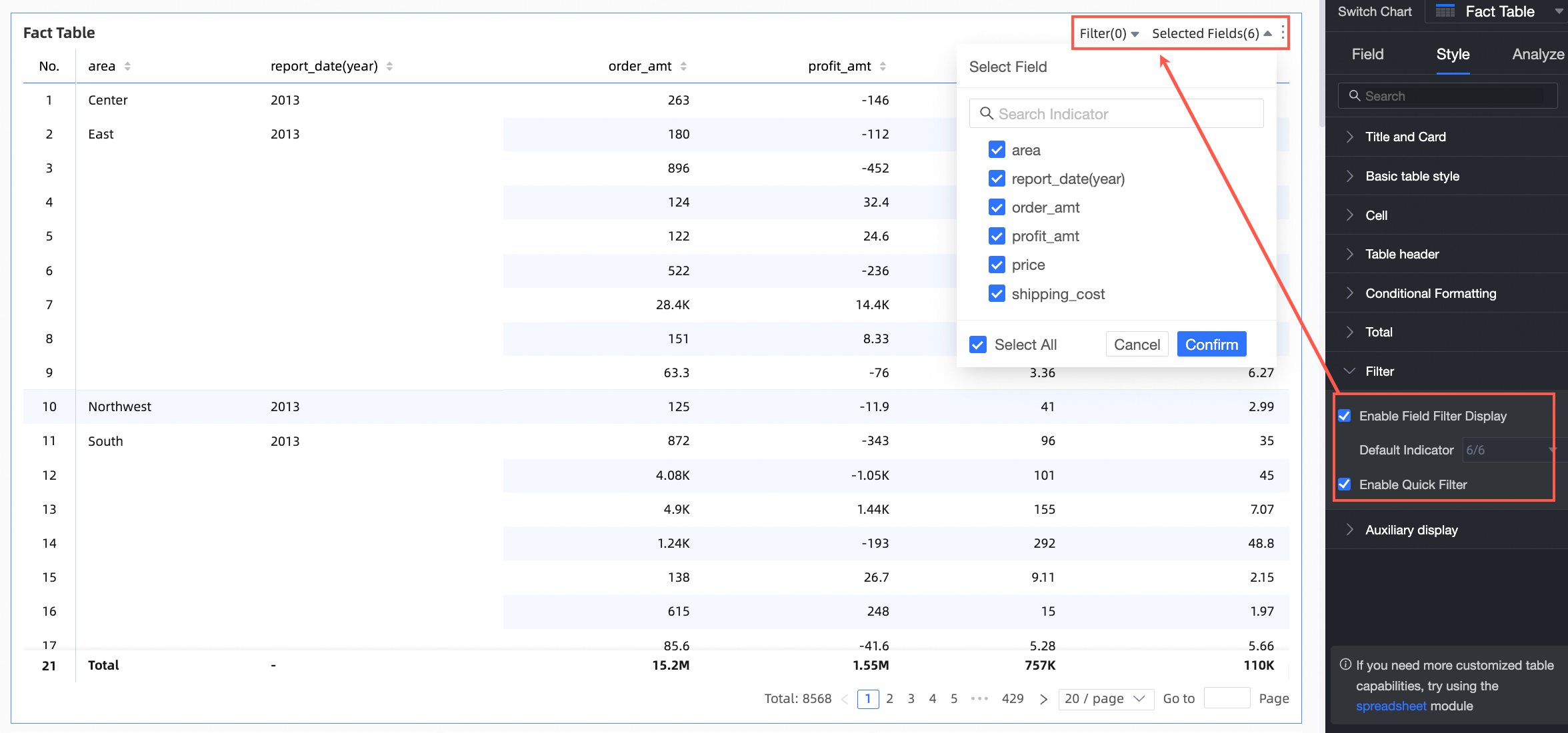
In Assisted Display, you can configure Scrollbar Visibility and Scrollbar Thickness.
You can set visibility to Show on Hover to display scrollbars only when the mouse pointer is over the table.
You can choose Always Show to keep scrollbars visible at all times.
You can adjust Thickness to make scrollbars more prominent.
Chart Analysis Configuration
Configuration Item | Name | Description |
Data Interaction | Drilling | When you configure drilling, set the display style for drill-level rows. For details, see Drilling. |
Filter Interaction | When your analysis spans multiple charts, use filter interaction to link them. This enables coordinated analysis. For setup steps, see Filter Interaction. | |
Jump | When your analysis spans multiple dashboards, use dashboard jump to link them. Jump supports Parameter Jump and External Link. For setup steps, see Jump. | |
Advanced Settings | Event | Select this option to enable data entry in the detail table. When column dimensions exist, only row dimensions can be added to configure events. For setup steps, see Event. |
Enable Secondary Metrics | Select this option to configure secondary metrics. For details, see Enable Secondary Metrics. |
Enable Secondary Metrics
After configuring your main metrics, you can enable and configure secondary metrics.

After selecting Enable Secondary Metrics, the comparison metric dropdown shows all available measures.
Comparison Date Field: You can choose a date field from your dataset.
NoteIf the chart includes a date field, the comparison date must be the finest-grained date field in the chart.
If the chart has no date field, you can choose any date field from the dataset.
Comparison Method: Based on the granularity of the date field, the system shows relevant comparison options. Up to four options appear. For example, if the comparison date is daily, options include Day-over-Day, Week-over-Week, Month-over-Month, and Year-over-Year. If the comparison date is monthly, options include Month-over-Month and Year-over-Year.
Display Content: Difference Percentage is selected by default. You can also select Difference or Original Value.
Difference: The format matches the main metric’s display format.
When Difference is selected, you can also select Calculate Difference in Percentage Points. By default, this option is off. If enabled and the metric displays as a percentage, the system calculates the difference directly. For example, 5.2% − 4.1% = 1.1 pp.
Difference Percentage: This option displays with two decimal places.
Same-Period Comparison (Applies only when filters are bound to daily granularity): If you configure a filter, same-period comparison applies the same filter. For example, if the filter is 2022-01-02, the Year-over-Year calculation for 2021 also uses 2021-01-02. Day-over-Day comparison automatically supports same-period comparison. Dynamic comparisons do not support same-period comparison.
When Previous Period Value Is Negative: You can choose the formula used to calculate difference percentage. This formula applies only to items where the previous period value is negative. Options include the following:
(Current Value / Previous Value − 1) × 100%: Default
1 − (Current Value / Previous Value) × 100%
Show as −
Sync Comparison Metrics: You can sync the current metric’s configuration to N other metrics.
Display Position: The default is Right of Metric. Other supported options include the following: Separate Right and Below Metric.
Right of Metric: This option adds a new column to the right of the current metric. The column header shows the comparison method, such as Year-over-Year, Day-over-Day, Month-over-Month, or Week-over-Week.
When metrics are in columns, secondary metrics appear sequentially to the right.

Separate Right: The last column dimension splits to show Day-over-Day, Week-over-Week, Month-over-Month, and Year-over-Year. Each appears in its own column, placed to the right of the current metric.

Below Metric: This option adds multiple rows below the current metric. Alignment matches the metric: text is left-aligned, and numbers are right-aligned.
Secondary metrics share the same cell row as the current metric. Their headers appear in a new row below the current metric’s header, such as Day-over-Day, Week-over-Week, Month-over-Month, or Year-over-Year.

Display Style: You can choose colors for positive and negative values. Options include the following: follow Global Semantic Color Settings (i.e., Page Settings > Global Styles > Semantic Colors), Positive in Red, Negative in Green, or Positive in Green, Negative in Red.
Totals Configuration FAQ
About Totals Calculations
If your source data is GMV (Sum), totals and subtotals default to Auto. The calculation logic is GMV (Sum). If you switch totals to Custom and select Average, the logic becomes GMV (Average).
If your source data is ID (Distinct Count), totals and subtotals default to Auto. The calculation logic is ID (Distinct Count). If you switch totals to Custom and select Count, the logic becomes ID (Count).
How do you calculate a ratio?
You can define the ratio.
In this example, the ratio is (Metric A / Metric B).
You can create a calculated field in your dataset. Define the expression as rate = sum(A) / sum(B).
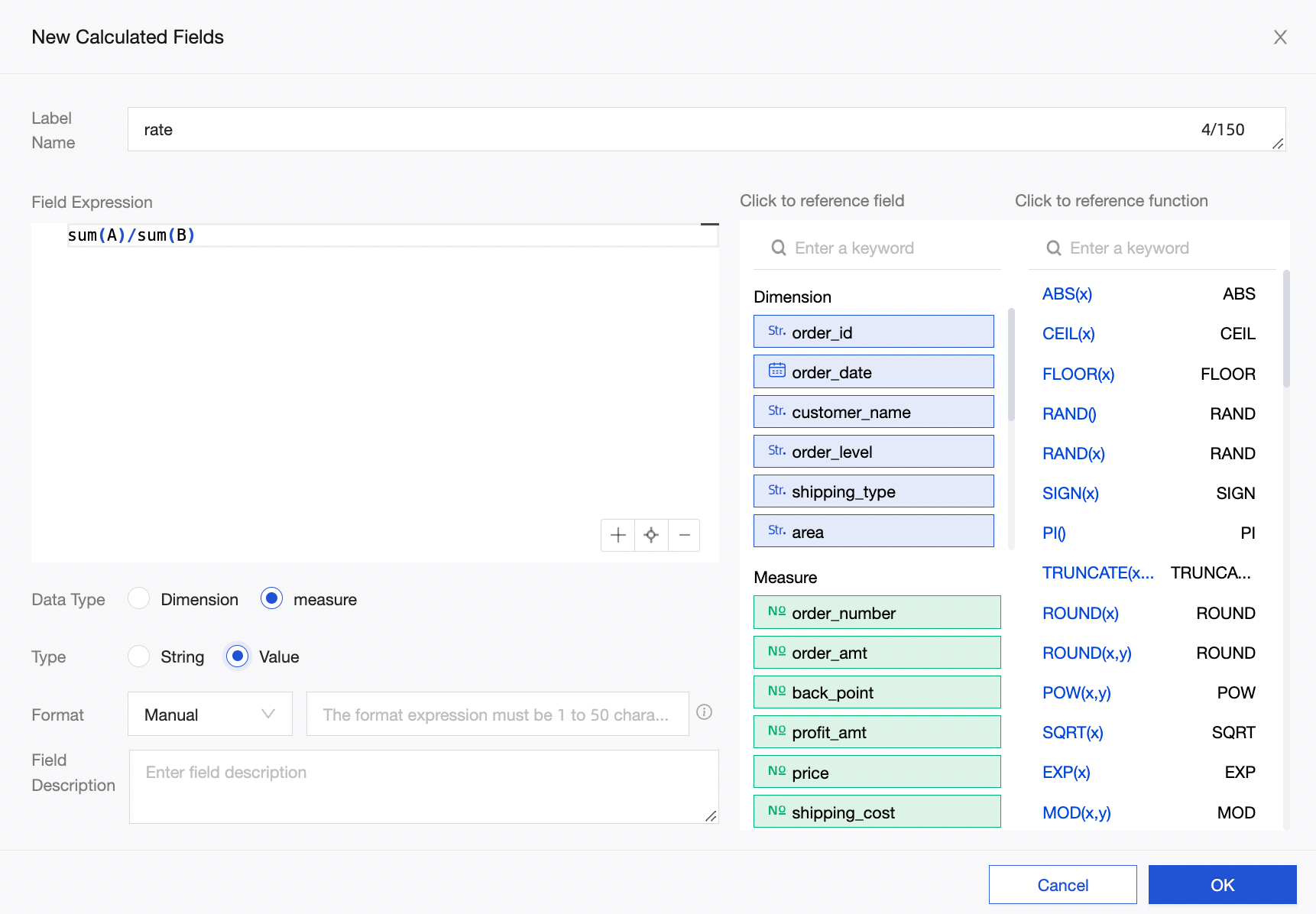
In the dashboard’s data panel, you can select the rate (Sum) metric and enable totals and subtotals. The default logic is rate (Sum), so totals and subtotals compute as sum(A) / sum(B).
NoteIf your dataset expression is rate = A / B, and you enable totals and subtotals, the system computes A / B (Sum). This may produce ratios over 100%, which results in incorrect output.