You can configure and manage the always-confidential database feature for PolarDB-X in Data Security Center (DSC), not in the PolarDB-X console. This approach provides a centralized and consistent data security administration experience. The process involves granting permissions to DSC, connecting to database assets, and defining encryption rules.
Prerequisites
Instance version:
polardb-2.5.0_5.4.20-20250714_xcluster8.4.20-20250703or later.NoteFor information about the instance version naming rules, see Release notes.
For information about how to view the version of an instance, see View and update the version of an instance.
Instance region:
Region Type
Region Name
The Chinese mainland
China (Qingdao), China (Beijing), China (Zhangjiakou), China (Hohhot), China (Hangzhou), China (Shanghai), China (Shenzhen), China (Guangzhou), and China (Chengdu).
Outside the Chinese mainland
China (Hong Kong), Singapore (Singapore), Malaysia (Kuala Lumpur), Indonesia (Jakarta), and Germany (Frankfurt).
Billing overview
The always-confidential database feature is free of charge.
However, this feature relies on Data Security Center (DSC) for encryption configuration and management. You must purchase DSC and ensure that you have a sufficient quota for column encryption authorization. For more information about billing, see Billing overview.
Feature overview
The always-confidential database feature for PolarDB-X is provided by DSC. It corresponds to the Column Encryption feature in DSC. It uses the AES-128-GCM and SM4-128-GCM encryption algorithms and local keys. You can configure encryption for sensitive data columns in your database. This ensures that sensitive data is stored as ciphertext. Authorized users can use an always-confidential client to decrypt the ciphertext and access the plaintext data. You can select and modify the scope of PolarDB-X instances, databases, tables, and columns to be encrypted.
Preparations
Before you can enable column encryption, you must complete the following steps: activate or upgrade DSC, grant DSC permissions to access cloud resources, grant permissions to database assets, connect to the database, and run a sensitive data detection task.
1. Activate or upgrade DSC
2. Grant DSC permissions to access cloud resources
3. Grant permissions to database assets
4. Connect to the database and run a sensitive data detection task
Enable column encryption
Log on to the Data Security Center console. In the navigation pane on the left, choose .
ImportantYou can enable and configure column encryption for a database only if the Encryption Check column shows Passed. If it shows Failed, the database's major or minor engine version may not support column encryption. For more information, see the FAQ section in this topic.
Click Rapid Encryption above the list of database instances to configure column encryption for all unencrypted columns.
Alternatively, click Rapid Encryption in the Actions column of a target database instance to configure column encryption for that instance.
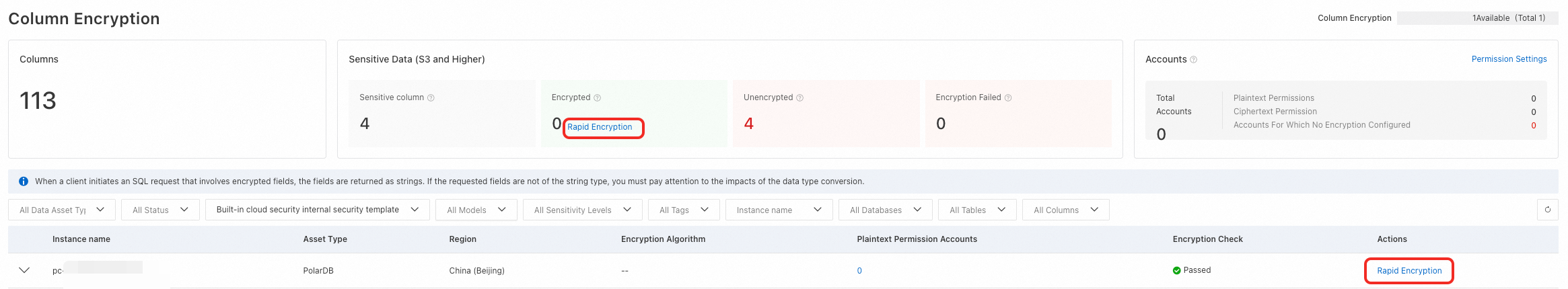
In the Encryption Configuration panel, select the Asset Type, Instance name, and Plaintext Permission Accounts. Then, select the target Databases, Table, and Column for which you want to configure column encryption, and click OK. Note the following:
DSC supports multiple encryption algorithms. However, PolarDB-X currently supports only the
AES-128-GCMandSM4-128-GCMalgorithms with local encryption.After you configure encryption, PolarDB-X database accounts have Ciphertext Permission (JDBC Decryption) by default. These accounts access the ciphertext of encrypted columns by default. You can use client code with a local key to decrypt the data and view the original plaintext.
To access plaintext data directly, add the corresponding database account to the Plaintext Permission Accounts list. This account will have plaintext permission and can directly access the plaintext data of encrypted columns.
ImportantTo classify and categorize the latest data in your database, the database account used as the credential (the account used to connect DSC to the PolarDB-X cluster) must have plaintext permission.
Modify the column encryption configuration
Modify the scope of encrypted columns
After you enable column encryption, you can modify its scope by enabling or disabling the feature for specific columns in a database instance.
Log on to the Data Security Center console. In the navigation pane on the left, choose .
Expand the target instance in the instance list. In the database list, find the target Databases, Table, and Column name. Click Enable Encryption or Disable Encryption to configure encryption for a single column.

Modify database account permissions
Except for accounts that are set to have Plaintext Permissions, all other accounts in the database instance have Ciphertext Permission (JDBC Decryption). You can change an account's permission to Plaintext Permissions or Ciphertext Permission (JDBC Decryption) based on your business scenario.
Log on to the Data Security Center console.
On the page, click Permission Settings in the Accounts area.
Alternatively, click Edit in the Actions column of the instance list. In the Edit panel, click Configure for Account Permissions.
In the Permission Settings panel, search for the target instance and account to view the current permissions.
NoteIf a newly added database account is not in the list, you can perform an Asset synchronization and then check again.
In the Actions column of the target account, click Modify Permissions.
You can also select multiple target accounts that have the same permission and click Batch Modify Permissions below the list.
In the Modify Permission dialog box, select the target permission and click OK.
Verify the column encryption results
You can verify data access for encrypted columns based on the configured column encryption and database account permissions.
The column encryption feature is not fully compatible with third-party clients. For example, viewing encrypted data through Data Management (DMS) may cause exceptions. We recommend that you use the column encryption driver (JDBC) client to access encrypted data.
For example, the birth_date column of the students01 table in a test PolarDB-X cluster is encrypted. One database account in the cluster is granted Plaintext Permissions, while another account retains Ciphertext Permission (JDBC Decryption).

Connect to the database using the account with Ciphertext Permission (JDBC Decryption). Run the
SELECT * FROM students01;statement to view the data table. The query returns ciphertext for the encrypted column.
Connect to the database using the account with Plaintext Permissions. Run the
SELECT * FROM students01;statement to view the data table. The query returns plaintext for the encrypted column.
Client usage instructions
If your database account has Ciphertext Permission (JDBC Decryption), you can use the column encryption driver (JDBC) to connect to the target database. This allows your Java application to access the encrypted data. The JDBC driver automatically decrypts the ciphertext and returns plaintext in a process that is transparent to the application. For more information, see Column encryption driver (JDBC).
FAQ
Related content
For information about the features and principles of database column encryption, see Column encryption overview.
If the sensitive data in a database column changes after authorization, you must rescan it. For more information, see Scan for sensitive data using a detection task.


