Data Security Center (DSC) provides robust data discovery and classification capabilities. By managing Identification Tasks, DSC scans your connected data assets to detect sensitive information. It then classifies and grades this data based on its sensitivity level and type. This visibility allows you to implement precise access controls and improve your overall data security posture. This topic describes how to configure and manage identification tasks to identify sensitive data.
Prerequisites
You must authorize DSC to access the data assets you intend to scan. For more information, see asset authorization.
Identification task overview
An identification task scans data in connected assets using specific identification rules (defined in Identification Templates). It generates scan results and automatically tags identified sensitive data. For details on templates, see View and configure identification templates.
Task types
DSC supports two types of identification tasks: default tasks and custom identification tasks.
Default tasks
Once you authorize an asset, DSC automatically creates a scan task for that asset instance using the main identification templates. These are referred to as default tasks.
The following table describes the logic and behavior of default tasks.
Setting | Description |
Identification template | Default tasks always use the main identification template configured for DSC. This cannot be changed for individual tasks.
|
Scan trigger and cycle (default) |
Note: The minimum interval between two scans is 24 hours. |
Scan scope | For all authorized assets, the scan scope is applied as follows:
Changes to the main identification template do not trigger an immediate scan. The new rules apply only to the next scheduled run. |
Custom identification tasks
Create a custom identification task when you need to scan specific data assets by using one or more enabled identification templates. If a template is currently disabled, you must enable it before it can be selected for a custom task. For more information, see Enable an identification template.

Scan mechanism and limits
Limits
To balance detection coverage with system performance, DSC applies specific sampling rules and limits.
Structured data/Big data (RDS, PolarDB, Tablestore, MaxCompute): By default, the first 200 rows of a table are sampled. You can manually increase this limit to a maximum of 1,000 rows. Within the sampled rows, only the first 10 KB of data per field is scanned.
Unstructured data (OSS or Simple Log Service):
Files larger than 200 MB are skipped. Files 200 MB or smaller are scanned.
Data stored in OSS:
You can manually set the maximum file size for scanning, up to 1,000 MB per file.
For compressed or archived files, only the first 1,000 child files are scanned.
When scanning a single OSS bucket, a maximum of 4 objects are scanned concurrently.
QPS limit: A single scan task is limited to 100 API requests per second against the OSS bucket.
Bandwidth limit: A single scan task is limited to 200 MB/s of internal outbound bandwidth from the OSS bucket.
DSC supports scanning for over 800 OSS file types, including text, office documents, images, design files, code, binaries, archives, applications, audio, video, and chemical structure files. For more information, see OSS file types that can be identified.
For comprehensive details on identification task limits, see Limits.
Scanned objects
Database assets:
<Instance>/<Database>/<Table>. Each table represents a single data object.Big data:
<Instance>/<Table>. Each table represents a single data object.OSS assets:
<Bucket>/<File>. Each file represents a single data object.Simple Log Service assets:
<Project>/<Logstore>/<Time Segment>. Data is processed in 5-minute segments. Each 5-minute segment represents a single data object.
Scan speed
The following estimates are provided for reference only. Actual scan speeds may vary based on system load and data complexity.
Structured data (RDS, PolarDB) and big data (Tablestore, MaxCompute): For large databases containing over 1,000 tables, the scan rate is approximately 1,000 columns per minute (based on a sample size of 200 rows per column).
Unstructured data (OSS, SLS): Scanning 1 TB of data typically takes between 6 to 48 hours, averaging 24 hours. The actual duration depends on the distribution of file types within the dataset.
Scan logic
Task type | First scan | Subsequent scans |
Default task | Performs a full scan of all authorized data in the asset. | Scans new or modified data objects. You can trigger scans manually or configure an automatic scan cycle. |
Custom identification task | Scans data according to the specified identification scope. | Scans only new or modified data objects within the specified scope. |
Data objects that have not changed since the last scan are skipped.
Scan results
Sensitivity levels are determined by the identification rules matched in the task's template. If a data object matches multiple rules, the highest sensitivity level takes precedence. DSC classifies sensitive data on a scale from S1 to S10, where a higher number indicates a higher level of sensitivity. A result of N/A indicates that no sensitive data was detected.
The valid range of sensitivity levels depends on the configuration of the associated identification template. For more information, see Set the sensitivity level for an identification template.
Recommendations
Recommendation | Description |
Confirm scan scope and priority | Prioritize high-risk assets. If you cannot immediately scan all data due to volume, evaluate your assets first. Prioritize scanning data that has a higher risk profile, such as assets that are frequently accessed, modified, or subject to unknown operations. |
Specify scope of the first scan | Perform a targeted pilot scan. Limit your initial scan to a specific database or OSS bucket. This allows you to validate and tune your identification rules before a full-scale rollout. Optimize identification rules. Do not enable all identification features indiscriminately. Generic rules (e.g., Date, Time, URL) can generate excessive false positives in large datasets. Enable only the specific rules relevant to your business context. Ensure sufficient sampling. For structured data, ensure the sample size is large enough to capture representative data; otherwise, sensitive information may be missed. |
Specify a task start time | Align schedules with data updates. Configure tasks to run automatically (daily, weekly, or monthly) based on your data update frequency. Regular scanning ensures timely detection of new sensitive data and helps identify trends or anomalies in your security posture. We recommend scheduling scans during off-peak hours to minimize performance impact. |
Manage default identification tasks
View default tasks
Log on to the Data Security Center console.
In the navigation pane on the left, select .
On the Tasks page, click the Identification Tasks tab, and then click Default Tasks.
On the Discovery Task Monitoring page, view the list of default tasks.
You can perform the following operations on a default identification task:
Rescan: Triggers an immediate scan to update results. Use this if you have updated the main identification template, upgraded the identification model, or if significant data changes occurred.
Pause: Temporarily halts a running default task (e.g., if you detect database performance issues).
Terminate: Stops the execution of the current task and prevents the default task from running in future cycles.
Enable: Re-activate a terminated task.
NoteDefault tasks cannot be deleted.
Configure scan settings
You can customize the schedule for default tasks. We recommend aligning the scan cycle with your data update frequency (minimum: Daily).
On the Discovery Task Monitoring page, select the check box of the task for which you want to configure the scan cycle, and then click Scan Settings above the task list.
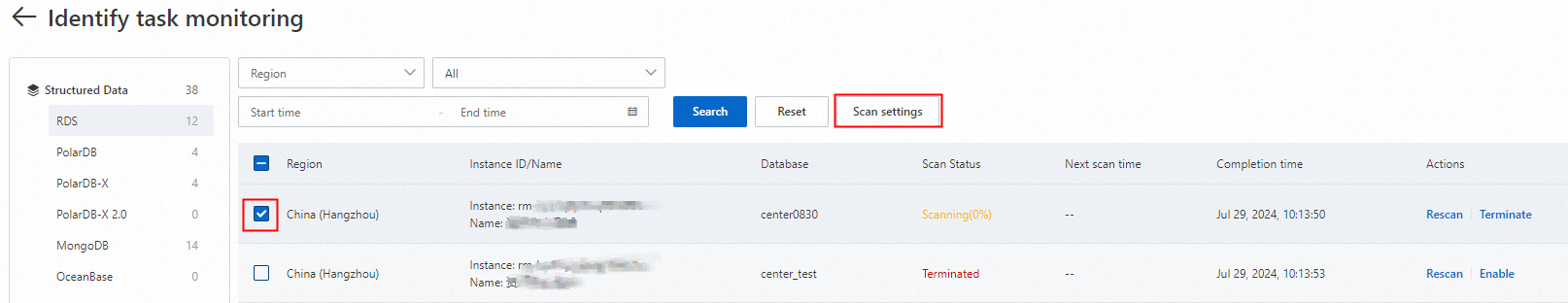
In the Scan Settings dialog box, configure the scan cycle and automatic scan start time, and then click OK.
ImportantSet the start time to off-peak hours to minimize database impact.
Monitor CPU/Memory usage during scans. If abnormalities occur, pause or terminate the task immediately.
Create custom identification tasks
Create a custom task when you need to scan specific assets using a specific (non-main) identification template, or to scan historical SLS data.
The system supports a maximum of 5 active identification tasks (tasks with a periodic schedule). Once you reach this limit, you cannot create additional periodic tasks.
Create a custom identification task
In the navigation pane on the left, select .
On the Identification Tasks tab, select the Asset Type for which you want to create an identification task, and then click Create.

In the Create panel, configure the parameters and click OK.
Category
Parameter
Description
Basic Information
Asset Type
Displays the asset type selected in the previous step. It cannot be modified.
Task Name
Enter a task name.
Task notes
Enter the task notes.
Task and Plan
Select a task start time. Valid values:
Immediate Scan: Runs the task immediately upon creation.
Periodic Scan: Runs the task on a scheduled frequency. You must configure the Scan Frequency and Scan Time (Structured Data Only). To trigger an immediate run alongside the schedule, select Scan Once Now.
NoteThe Scan Time setting applies only to structured data assets. Unstructured data scans run according to system resource availability.
Identification Template
Select up to two enabled identification templates to apply to this scan. For For details on enabling templates, see Use identification templates.
Identification Scope
Identification Scope of Structured Data
Select the scope for structured assets (e.g., RDS, PolarDB):
Global Scan: Scans all authorized structured assets.
Specify Scan Scope: Allows granular selection of specific Instances and Databases.
Instance Name and Database name: To add multiple instances, click Add Identification Scope.
Scan Limit: Defines the number of rows sampled per table. Defaults to the first 200 rows. Maximum value is 1,000 rows.
Unstructured Data OSS Identification Scope
Select Object, Sampling Method, Scan Depth, and Scan Limit for unstructured data (OSS).
Valid values of Object:
Global Scan: Scans all authorized OSS buckets.
Specify Scan Scope: Select specific buckets. You can apply filters (Prefix, Directory, Suffix) to include or exclude specific files.
After you specify the objects to scan, you can configure filters for fine‑grained scanning. You can set Prefix, Directory, and Suffix to include or exclude specific values to filter the scan scope.
Sampling Method: Retrieves data from OSS by using the
ListObjectsAPI and scans data based on the configuration.Global Scan: Scans all data.
Custom Depth: Sampling Rate. Scans data based on the sampling ratio.
NoteFor example, if you set Sampling Rate to 1/10, the system scans the 1st file, skips 9, and scans the 11th.
Valid values of Scan Depth:
Global Scan: Scans the full directory path.
Specify Scan Scope: Limits the directory depth (Levels 1–10). For example, "5" scans only the top 5 directory levels.
Scan Limit: Limits the scanned size per file. Default: 200 MB. Max: 1,000 MB. Excess data beyond the limit is skipped.
Synchronize All Identification Results to SLS: Select this option to send full logs to Simple Log Service.
Unstructured Data SLS Identification Scope
Set Asset Scope and Time Range for SLS.
Valid values of Asset Scope:
Global Scan: Scans all authorized SLS Projects.
Specify Scan Scope: Select specific Projects and Logstores.
Valid values of Time Range:
Last 15 Minutes, Last 1 hour, Yesterday, Last 1 Day, Last 7 Days, or Last 30 Days.
Custom: The unit of the time range is minute, and the step size is 5 minutes.
Other Settings
Tagging Result Overwriting
Determines how to handle conflicts with previously manually corrected data:
Skip Manual Tagging Result: Preserves your manual corrections. The system will not overwrite them.
Overwrite Manual Tagging Result: Replaces manual corrections with the new system scan results.
Modify or delete a custom identification task
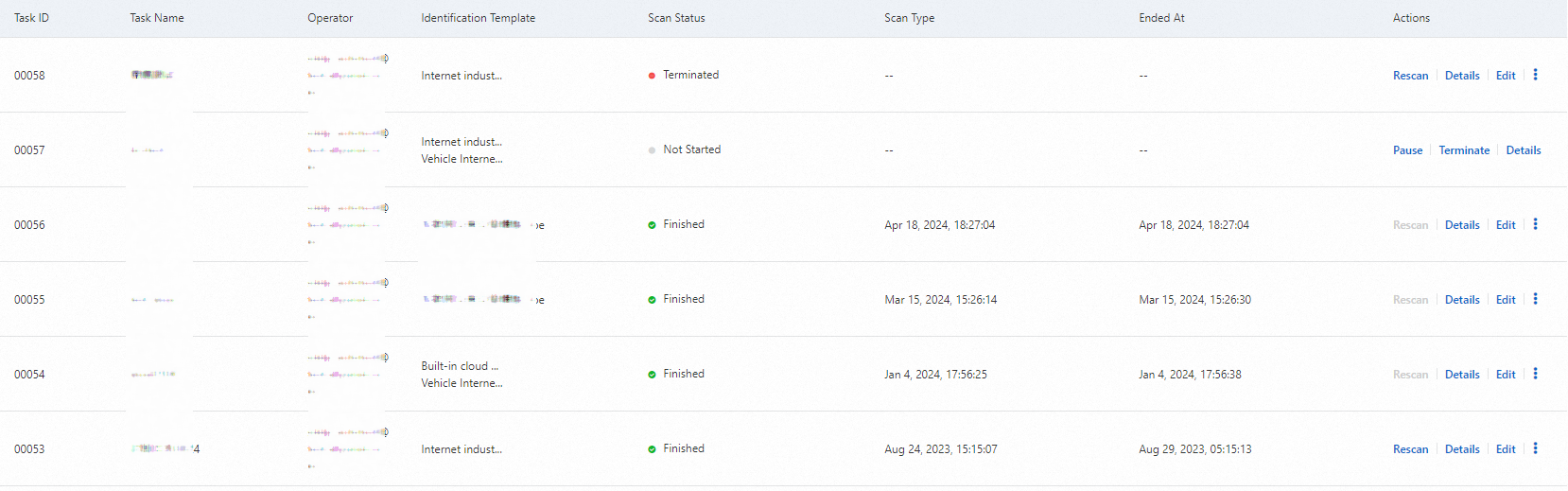
Edit: Reconfigures the custom identification task. You can modify all parameters.
 > Delete: Deletes redundant custom identification tasks.
> Delete: Deletes redundant custom identification tasks.
Manage task operations
Rescan a task
If the identification model is upgraded or your database data has changed, you can perform a rescan to update the results immediately. A Rescan triggers an immediate full scan of the specified asset. Perform this operation during off-peak hours to minimize the impact on system performance.
Before performing a Rescan, ensure that the relevant identification templates are enabled.
The Rescan operation is not supported for custom tasks with the Scan Type set to Immediate Scan.
On the Identification Tasks tab, perform the rescan operation:
Rescan a custom identification task: In the task list, click Rescan in the Actions column of the custom identification task.
Rescan a default task: Click Default Tasks, find the target asset, and then click Rescan in the Actions column.
You can view the scan progress in the Scan Status column of the identification task.
Pause or Terminate a task

Pause: Temporarily halts a running task. Useful during service anomalies. Click Pause in the Actions column of the custom identification task.
Terminate: Stops the execution of the current and subsequent identification tasks (custom identification tasks and default tasks).
Correct identification results
If DSC incorrectly identifies data (false positive) or misses data (false negative), you can manually correct the results. This "manual correction" teaches the system to be more accurate.
On the Tasks page, click the Revision Tasks tab.
In the navigation pane on the left, click the asset type that you want to manage.
Click Revision or Resume in the Actions column of the target sensitive data. Follow the instructions on the page to modify Revised Model, and then click OK.
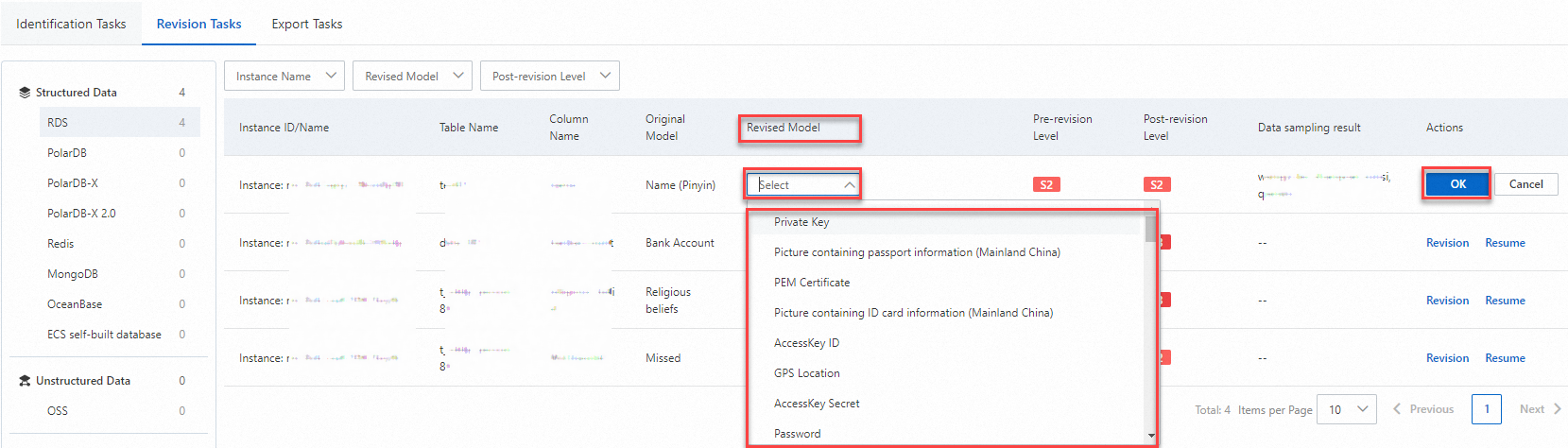
After you perform the restoration operation, the previous identification model is restored.
View and export results
The latest scan results generated by the main identification template are visible on the page. For more information, see View sensitive data identification results.
Create an export task to download sensitive data identification results detected. Specify the target identification template and data assets to generate and download a report.
You can only export results for assets and templates that have completed a successful identification task.
Create an export task
Follow this prodecure to create an export task and download the results:
On the Tasks page, click the Export Tasks tab.
On the Export Tasks tab, click Create.
Configure the export task and click OK.
In the Basic Information section, enter a task name and select an identification template that is used by the identification task.
You can select only an enabled identification template.
In the Export Dimension section, select Asset Type or Asset Instance.
Asset Type: Select the asset types that you want to export.
Asset Instance: Select the asset instances that you want to export.
After you create the export task, its status is displayed in the export task list. A larger amount of data requires a longer export period.
Download exported results
After the Export Status becomes Finished, click Download in the Actions column of the target export task.

After the export is complete, download the exported data within three days. After three days, the task expires and you can no longer download the exported sensitive data.
References
View and configure identification templates - Describes identification templates used in identification tasks and the types of sensitive data that can be identified.
Supported data asset types - Lists the types of data assets from which DSC can identify sensitive data.
Data scanning and identification - Provides common issues and troubleshooting guidance for identification tasks.
FAQ
How does the scan mechanism work for unstructured data (OSS/SLS)?
Does the MongoDB full table scan impact I/O or online services?
Can DSC identify sensitive data in compressed or text files within OSS?
Is exporting sensitive data identification results supported?
Do API queries for sensitive data include metadata (Instance/DB/Table) and risk levels?
Why am I unable to select the common identification template?
Why is my identification task stuck in the Waiting state (Free Edition)?