You can use Data Transmission Service (DTS) to migrate data between PolarDB for PostgreSQL (Compatible with Oracle) clusters.
Overview
PolarDB for PostgreSQL (Compatible with Oracle) is an enterprise-level relational database management system that has a wide range of applications and provides strong community support. Each new release brings many new features and improvements to enhance performance, availability, and security. PolarDB for PostgreSQL (Compatible with Oracle) 2.0 can significantly improve database performance and user experience.
PolarDB for PostgreSQL (Compatible with Oracle) 2.0 introduces new query optimization algorithms and a storage engine to improve the query speed and concurrent processing capabilities. It can process large amounts of data faster and improve the responsiveness and performance of the database. PolarDB for PostgreSQL (Compatible with Oracle) 2.0 also uses many new features and enhancements to provide better user experience and developer tools. For example, enhanced support for JSON data types makes it easier to process and query JSON data. Abundant monitoring and diagnostic tools help you better understand and optimize the performance of your database. Database security and reliability are strengthened. Stricter RAM policies and permission management features protect your data from potential security threats. Backup and recovery improvements provides better data protection and restoration.
After you upgrade to PolarDB for PostgreSQL (Compatible with Oracle) 2.0, you can gain more resources and supports from the PostgreSQL community to help you solve problems and learn about database best practices. We recommend that you upgrade to PolarDB for PostgreSQL (Compatible with Oracle) 2.0 to make full use of its benefits.
Prior evaluation
If you have purchased a PolarDB for PostgreSQL (Compatible with Oracle) 1.0 cluster, you can use the migration evaluation feature to verify the compatibility of the cluster before you migrate the cluster. This way, you can identify and handle precondition that affect the migration progress in advance to reduce processing and resource costs.
Supported regions
The migration evaluation feature is available in the following regions:
China (Hangzhou), China (Shanghai), China (Shenzhen), China (Beijing), China (Zhangjiakou), China (Ulanqab), China (Chengdu), China (Hong Kong), Japan (Tokyo), Singapore, Indonesia (Jakarta), US (Silicon Valley), and US (Virginia).
Impacts
The migration evaluation does not affect your workloads.
Create a migration evaluation task
Log on to the PolarDB console.
In the upper-left corner of the console, select the region in which the cluster that you want to manage is deployed.
Create a migration evaluation task. PolarDB provides the following methods for creating an evaluation task:
From the Clusters page: Click Migration/Upgrade Evaluation in the upper-left corner.

From the Migration/Upgrade page: Click Migration/Upgrade Evaluation in the upper-left corner.

In the Migration /Upgrade Evaluation dialog box, configure the parameters and click Next.
Parameter
Description
Creation Method
Select Upgrade from PolarDB.
Source PolarDB Version
Select Oracle 1.0.
Source PolarDB Cluster
Select the source cluster.
Destination Database Engine
Select Oracle 2.0.
Database Name
Select the source database.
In the Migration/Upgrade Evaluation dialog box, you can check the overview and details about the compatibility of the cluster.
Check the overview.

Check the details.
 Note
NoteYou can focus on the incompatible objects in the compatibility evaluation results.
You can ignore Oracle native objects.
You must adapt the incompatible objects involved in the SQL statements. If you cannot adapt them at the business side, you can contact us. The R&D engineers will help you.
Manage the migration evaluation task
To view the details of the created evaluation task, go to the Migration/Evaluation page.
The evaluation task is retained for seven days and then automatically deleted. If your evaluation task has expired, create a new one.
Prerequisites
The source and destination PolarDB for PostgreSQL (Compatible with Oracle) clusters are created. For more information, see Create a PolarDB for PostgreSQL (Compatible with Oracle) cluster.
The wal_level parameters for the source and destination PolarDB for PostgreSQL (Compatible with Oracle) clusters are set to logical. For more information, see Configure cluster parameters.
The available storage space of the destination database is larger than the total size of the data in the source database.
Limits
During schema synchronization, DTS synchronizes foreign keys from the source database to the destination database.
During full data synchronization and incremental data synchronization, DTS temporarily disables the constraint check and cascade operations on foreign keys at the session level. If cascade updates or deletions are executed on the source database during data synchronization, data inconsistency may occur.
Item | Description |
Limits on the source database (PolarDB for PostgreSQL (Compatible with Oracle) 1.0) |
|
Other limits |
|
Billing rules
Synchronization type | Instance configuration fee |
Schema synchronization and full data synchronization | Free of charge. |
Incremental data synchronization | Charged. For more information, see Billing overview. |
Migration types
Migration type | Notes |
Schema migration 1 | DTS migrates the schemas of the required objects to the destination database. DTS supports schema migration for the following types of objects: table, view, synonym, trigger, stored procedure, stored function, package, and user-defined type. Note In this scenario, DTS does not support schema migration for triggers. We recommend that you delete the triggers of the source database to prevent data inconsistency caused by the triggers. For more information, see Configure a data synchronization or migration task for a source database that contains a trigger. |
Full data migration | DTS migrates the historical data of objects from the source database to the destination database. Note During schema migration and full data migration, do not perform DDL operations on the objects to be migrated. Otherwise, the objects may fail to be migrated. |
Incremental data migration | DTS retrieves WAL log files from the source database. Then, DTS synchronizes incremental data from the source database to the destination PolarDB for PostgreSQL (Compatible with Oracle) cluster. Incremental data migration allows you to ensure service continuity when you migrate data between PolarDB for PostgreSQL (Compatible with Oracle) clusters. |
SQL statements that can be synchronized
Type | SQL statement |
DML | INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE |
DDL | Important
If the database account of the source database is a privileged account, data synchronization tasks support the following DDL operations:
Important
|
Permissions required for database accounts
Database | Required permission |
Source PolarDB for PostgreSQL (Compatible with Oracle) cluster | The permissions of the privileged account. |
Destination PolarDB for PostgreSQL (Compatible with Oracle) cluster | The permissions of the database owner. Important You can specify the database owner when you create a database. For more information about how to create and authorize a database account, see Create a database account. |
Configure a data synchronization task
Use one of the following methods to go to the Data Migration page and select the region in which the data migration instance resides.
DTS console
Log on to the DTS console.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Data Migration.
In the upper-left corner of the page, select the region in which the data migration instance resides.
DMS console
NoteThe actual operation may vary based on the mode and layout of the DMS console. For more information, see Simple mode and Customize the layout and style of the DMS console.
Log on to the DMS console.
In the top navigation bar, move the pointer over .
From the drop-down list to the right of Data Migration Tasks, select the region in which the data synchronization instance resides.
Click Create Task and configure the source and destination databases.
NoteSet Database Type to PolarDB for PostgreSQL (Compatible with Oracle).
Section
Parameter
Description
N/A
Task Name
The name of the task. DTS automatically assigns a name to the task. We recommend that you specify a name that can help you identify the task. You do not need to specify a unique task name.
Source Database (PolarDB for PostgreSQL (Compatible with Oracle) 1.0)
Select Existing Connection
The database instance that you want to use. You can choose whether to select an existing instance based on your business requirements.
If you select an existing instance, DTS automatically populates the parameters for the instance.
If you do not use an existing instance, you must configure parameters for the destination database.
Database Type
Select PolarDB for PostgreSQL (Compatible with Oracle).
Access Method
The access method of the destination database. Select Alibaba Cloud Instance.
Instance Region
The region where the source PolarDB for PostgreSQL (Compatible with Oracle) cluster is deployed.
Replicate Data Across Alibaba Cloud Accounts
Specifies whether to synchronize data across Alibaba Cloud accounts. In this example, No is selected.
Instance ID
The ID of the source PolarDB for PostgreSQL (Compatible with Oracle) cluster.
Database Name
The name of the source PolarDB for PostgreSQL (Compatible with Oracle) cluster.
Database Account
The database account of the source PolarDB for PostgreSQL (Compatible with Oracle) cluster.
Database Password
The password of the database account.
Destination Database (PolarDB for PostgreSQL (Compatible with Oracle) 2.0)
Select Existing Connection
The database instance that you want to use. You can choose whether to select an existing instance based on your business requirements.
If you select an existing instance, DTS automatically populates the parameters for the instance.
If you do not use an existing instance, you must configure parameters for the destination database.
Database Type
Select PolarDB for PostgreSQL (Compatible with Oracle).
Access Method
The access method of the destination database. Select Alibaba Cloud Instance.
Instance Region
The region where the destination PolarDB for PostgreSQL (Compatible with Oracle) cluster is deployed.
Instance ID
The ID of the destination PolarDB for PostgreSQL (Compatible with Oracle) cluster.
Database Name
The name of the destination PolarDB for PostgreSQL (Compatible with Oracle) cluster.
Database Account
The privileged database account of the destination PolarDB for PostgreSQL (Compatible with Oracle) cluster. For more information, see Create a database account.
Database Password
The password of the database account.
In the lower part of the page, click Test Connectivity and Proceed.
DTS adds the CIDR blocks of DTS servers to the whitelist of the destination cluster.
WarningIf the CIDR blocks of DTS servers are automatically or manually added to the IP address whitelist of the database or instance, or to the ECS security group rules, security risks may arise. Therefore, before you use DTS to migrate data, you must understand and acknowledge the potential risks and take preventive measures, including but not limited to the following measures: enhance the security of your username and password, limit the ports that are exposed, authenticate API calls, regularly check the whitelist or ECS security group rules and forbid unauthorized CIDR blocks, or connect the database to DTS by using Express Connect, VPN Gateway, or Smart Access Gateway.
Select the objects to be migrated and configure advanced settings.
NoteAll namespaces in the source database are listed. Select a namespace based on your business requirements.
Parameter
Description
Synchronization Type
The synchronization types. By default, Incremental Data Synchronization is selected. You must also select Schema Synchronization and Full Data Synchronization. After the precheck is complete, DTS synchronizes the historical data of selected objects from the source instance to the destination instance. The historical data is the basis for subsequent incremental synchronization.
NoteYou must select all synchronization types.
Synchronization Topology
One-way synchronization: Only one-way synchronization links are established from the source database to the destination database, including the existing data synchronization link and incremental synchronization link.
Two-way synchronization: Two-way synchronization links are established from the source database to the destination database. Incremental data synchronization is performed from the source database to the destination database, and reverse data transmission is performed from the destination database to the source database.
NoteReverse data transmission supports only data synchronization, but not DDL operations.
Processing Mode in Existed Target Table
Precheck and Report Errors: checks whether the destination database contains tables that have the same names as tables in the source database. If the source and destination databases do not contain identical table names, the precheck is passed. Otherwise, an error is returned during the precheck, and the data synchronization task cannot be started.
NoteIf the source and destination databases contain identical table names and the tables in the destination database cannot be deleted or renamed, you can use the object name mapping feature to rename the tables that are synchronized to the destination database. For more information, see Map object names.
Ignore Errors and Proceed: skips the precheck for identical table names in the source and destination databases.
WarningIf you select Ignore Errors and Proceed, data inconsistency may occur, and your business may be exposed to potential risks.
If the source and destination databases have the same schemas, and a data record has the same primary key value as an existing data record in the destination database:
During full data synchronization, DTS does not synchronize the data record to the destination database. The existing data record in the destination database is retained.
During incremental data synchronization, DTS synchronizes the data record to the destination database. The existing data record in the destination database is overwritten.
If the source and destination databases have different schemas, data may fail to be initialized, only some columns are synchronized, or the data synchronization task fails. Operate with caution.
Capitalization of Object Names in Destination Instance
The capitalization of database names, table names, and column names in the destination instance. By default, DTS default policy is selected. You can select other options to make sure that the capitalization of object names is consistent with that in the source or destination database. For more information, see Specify the capitalization of object names in the destination instance.
Source Objects
Select one or more objects from the Source Objects section and click the
 icon to add the objects to the Selected Objects section. Note
icon to add the objects to the Selected Objects section. NoteYou can select columns, tables, or databases as the objects to be synchronized. If you select tables or columns as the objects to be synchronized, DTS does not synchronize other objects such as views, triggers, or stored procedures to the destination database.
Selected Objects
To rename an object that you want to synchronize to the destination instance, right-click the object in the Selected Objects section. For more information, see Map object names.
To change the names of multiple objects to be synchronized, click Batch Edit in the upper-right corner of the Selected Objects section. For more information, see Database-table column name mapping.
NoteTo synchronize SQL operations that are performed on a specific database or table, right-click the object in the Selected Objects section. In the dialog box that appears, select the SQL operations that you want to synchronize. For more information, see the SQL operations that can be synchronized section of this topic.
To specify WHERE conditions to filter data, right-click the object in the Selected Objects section. In the dialog box that appears, specify the conditions. For more information, see Use SQL conditions to filter data.
Click Next: Advanced Settings to configure advanced settings.
Parameter
Description
Dedicated Cluster for Task Scheduling
A DTS dedicated cluster consists of multiple Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instances of the same specifications in a region. A DTS dedicated cluster is used to manage and configure DTS data migration, data synchronization, and change tracking tasks. Compared with DTS public clusters, DTS dedicated clusters are characterized by exclusive resources, better stability, better performance, and reduced costs. For more information, see What is a DTS dedicated cluster.
Specify the retry time range for failed connections
The retry time range for failed connections. If the source or destination database fails to be connected after the data synchronization task is started, DTS immediately retries a connection within the time range. Valid values: 10 to 1440. Unit: minutes. Default value: 720. We recommend that you set the parameter to a value greater than 30. If DTS reconnects to the source and destination databases within the specified time range, DTS resumes the data synchronization task. Otherwise, the data synchronization task fails.
NoteIf you set different retry time ranges for multiple DTS tasks that have the same source or destination database, the shortest retry time range that is set takes precedence.
When DTS retries a connection, you are charged for the DTS instance. We recommend that you specify the retry time range based on your business requirements, or release the DTS instance at the earliest opportunity after the source and destination instances are released.
Retry Time for Other Issues
The retry time range for other issues. For example, if the DDL or DML operations fail to be performed after the data synchronization task is started, DTS immediately retries the operations within the time range. Valid values: 1 to 1440. Unit: minutes. Default value: 10. We recommend that you set the parameter to a value greater than 10. If the failed operations are successfully performed within the specified time range, DTS resumes the data synchronization task. Otherwise, the data synchronization task fails.
ImportantThe value of the Retry Time for Other Issues parameter must be smaller than the value of the Retry Time for Failed Connections parameter.
Enable Throttling for Full Data Migration
During full data migration, concurrent reads are enabled for the source database and concurrent writes are enabled for the destination database. This behavior may bring pressure on your database. If you do not want to affect the databases, you can limit the migration rate.
Enable Throttling for Incremental Data Migration
During incremental data migration, concurrent reads are enabled for the source database and concurrent writes are enabled for the destination database. If one database has high business pressure, the other database may encounter write pressure. If you do not want to affect the databases, you can limit the migration rate.
Environment Tag
Environment tags help identify the importance of DTS tasks. They do not affect the normal running of tasks.
Configure ETL
Specifies whether to configure the extract, transform, and load (ETL) feature. For more information, see What is ETL. Valid values:
Yes: configures the ETL feature. You can enter data processing statements in the code editor. For more information, see Configure ETL in a data migration or data synchronization task.
No: does not configure the ETL feature.
Monitoring and Alerting
Specifies whether to configure alerting for the data synchronization task. If the task fails or the synchronization latency exceeds the specified threshold, alert contacts will receive notifications.
Select No if you do not want to set alerts.
If you select Yes, you must also specify the alert threshold and alert contacts. For more information, see Configure monitoring and alerting.
Click Next Step: Data Verification. On the Data Verification page, configure the following parameters.
Parameter
Description
Data Verification Mode
Full Data Verification: verifies all data. If you select Full Data Verification, you must configure the verification parameters and the objects. For more information, see Configure the data verification feature for a data synchronization or migration task in DTS.
Incremental Data Verification: verifies data that is incrementally synchronized or migrated. This option is selected by default.
Schema Verification: verifies the schemas of the selected objects.
In the lower part of the page, click Next: Save Task Settings and Precheck.
To view the parameters in the relevant API operations for configuring the DTS task, move the pointer over Next: Save Task Settings and Precheck and click Preview OpenAPI parameters.
If you do not need to view or have viewed the parameters, click Next: Save Task Settings and Precheck in the lower part of the page.
NoteBefore you can start the data synchronization task, DTS performs a precheck. You can start the data synchronization task only after the task passes the precheck.
If the task fails the precheck, click View Details next to each failed item. After you analyze the causes based on the check results, troubleshoot the issues. Then, run a precheck again.
If an alert is generated for an item during the precheck, perform the following operations based on the scenario:
If the alert item cannot be ignored, click View Details next to the failed item and troubleshoot the issues. Then, run a precheck again.
If the alert item can be ignored, click Confirm Alert Details. In the View Details dialog box, click Ignore. In the message that appears, click OK. Then, click Precheck Again to run a precheck again. If you ignore the alert item, data inconsistency may occur and your business may be exposed to potential risks.
Wait until the success rate becomes 100%. Then, click Next: Purchase Instance.
On the Purchase Instance page, configure the Billing Method and Instance Class parameters for the data synchronization instance. The following table describes the parameters.
Section
Parameter
Description
New Instance Class
Billing Method
Subscription: You pay for your subscription when you create an instance. The subscription billing method is more cost-effective than the pay-as-you-go billing method for long-term use.
Pay-as-you-go: A pay-as-you-go instance is charged on an hourly basis. The pay-as-you-go billing method is suitable for short-term use. If you no longer require a pay-as-you-go instance, you can release the instance to reduce costs.
Resource Group
The resource group on which the instance is run. Default value: default resource group. For more information, see What is Resource Management?
Instance Class
DTS provides various synchronization specifications that provide different performance. The synchronization speed varies based on the synchronization specifications that you select. You can select a synchronization specification based on your business scenario. For more information, see Specifications of data synchronization instances.
Duration
If you select the subscription billing method, specify the subscription duration and the number of instances that you want to create. The subscription duration can be one to nine months, one year, two years, three years, or five years.
NoteThis parameter is displayed only if you select the subscription billing method.
Read and select the check box for Data Transmission Service (Pay-as-you-go) Service Terms.
Click Buy and Start to start the data synchronization task. You can view the progress of the task in the task list.
Execute the data synchronization task
Procedure
Precheck: The preparation phase before the data migration or synchronization process starts. It is used to confirm whether all required conditions are met. For example, network connectivity, system permissions, data format and integrity are checked.
Front facing module: In a data processing process, the pre-module usually preprocesses data. In this process, some necessary triggers are created to process subsequent data.
Incremental data collection: Only the data that has been modified or added after the last collection operation is collected. It helps improve efficiency and avoids unchanged data.
Schema migration 1: involves transferring data from one system to another system or converting data from one format or another format while maintaining schema consistency. This is usually a preliminary migration step to create the schema for the new environment. Most migration elements such as schemas, sequences, functions, stored procedures, views, and indexes are created in this step.
Full data migration: Migrate all data from a database or a data warehouse to another system.
Schema migration 2: The second schema adjustment, which is used to fine-tune and optimize the schema, or to solve the issues that occur in the initial migration. Foreign keys are created on some tables in this step.
Incremental write: After the full data migration is completed, the new and modified data needs to be identified and migrated to the destination system. The step implements incremental data writes.
Back facing module: After data migration or synchronization is complete, the post-module performs a series of wrap-up tasks. Clearing data, creating indexes, or performance optimization may be involved.
Full data verification: After data migration, verification is required to ensure data integrity and accuracy. Full data verification checks all the migrated data to confirm whether the data is correctly copied to the new system.
Incremental data verification: is similar to full data verification. Incremental data verification focuses on incremental data. It ensures that any data changes made since the last verification are accurately captured and migrated.
Examples
You can log on to the Data Synchronization page of the new DTS console to view migration details.
Precheck
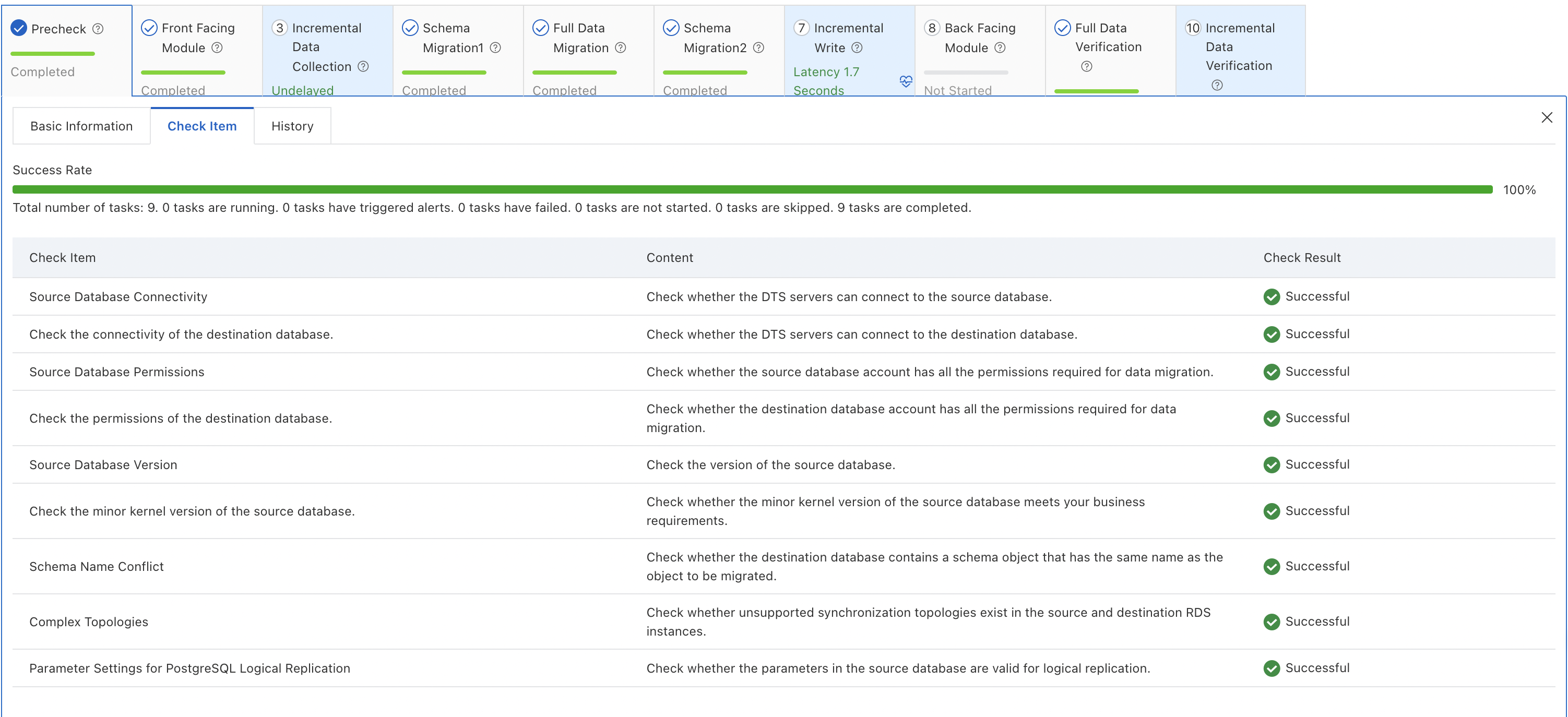 Note
NoteThis step is automatically executed.
Front facing module
 Note
NoteThis step is automatically executed.
Incremental data collection
 Note
NoteThis step is automatically executed.
Schema migration
Most tables, indexes, and sequences are migrated automatically. The a table is migrated.
NoteIf a failed task occurs during the schema migration, you can use the schema revision feature to manually correct the SQL statements used in the migration.

Full data migration
The data of all tables within the specified range is migrated. You can view the data traffic and transmission speed on the Data Synchronization page.

Schema migration 2
This step focuses on migrating the foreign key constraints of tables. Adding foreign keys is important to ensure data consistency across tables after the data is migrated.

Incremental write
One-way data synchronization from the source database is performed. All data of the source database is subscribed and forwarded, and then processed and applied on the destination database.

Back facing module

Full data verification
This step compares data in the source and destination databases. In the example, 835,266 rows in the
t1table of the source database and in thet1table of the destination database are compared. The data is consistent, so the verification is successful.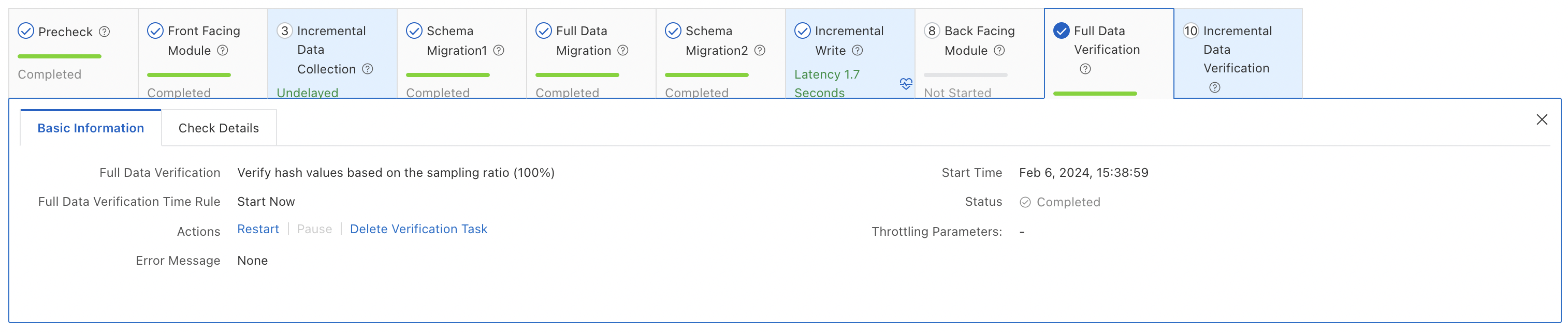
Incremental data verification
Once all the preceding tasks are completed, the system automatically starts the incremental synchronization and incremental data verification steps. In the incremental data verification step, the system compares incremental data differences between the two databases.
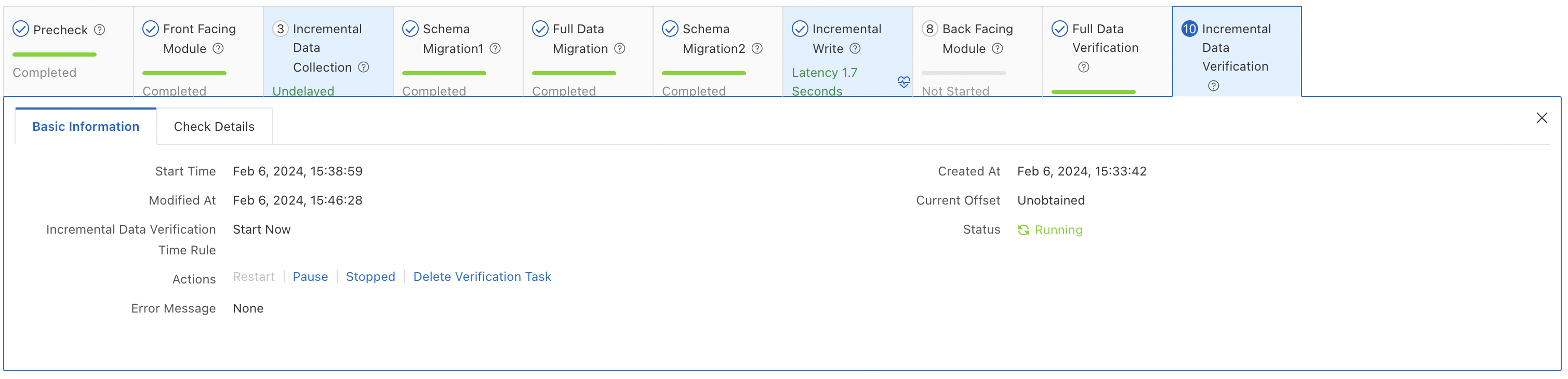
Cutover and release
After the migration is complete, we recommend that you add the destination database to a test environment and test it in a comprehensive manner. The data of the source database must be completely synchronized to the destination database (slight latency is normal during data replay). The test duration may vary depending on your business requirements. We recommend that you perform the test for at least one week to ensure that the destination database is running normally before you start cutover and release.
You must plan a cutover time window, such as 10 hours. During this period, the source database is out of service. After data replay is complete on the destination database, you can update the database connection string in the business and restart the business system. Then, you can start necessary basic business tests. If no issues are found in the tests, the destination database can go into service.
We recommend that you retain the source database for a period of time until you confirm that the destination database is completely stable and then discard the source database.
References
PolarDB for PostgreSQL (Compatible with Oracle) 2.0 available for commercial use
