When analytical or mixed workloads generate slow queries, manually identifying each query and creating indexes is time-consuming. Automatic IMCI-based query acceleration monitors slow queries through SQL Trace and creates in-memory column indexes (IMCIs) on the relevant tables. The system continuously adjusts acceleration policies based on workload patterns, reducing manual tuning.
How it works
After you enable automatic IMCI-based query acceleration, PolarDB records slow queries through SQL Trace and creates IMCIs on the relevant tables. IMCIs are stored on read-only IMCI nodes, which handle accelerated queries separately from the primary row-store nodes.
The feature uses nonblocking DDL to add IMCIs. If the MDL-X lock is not acquired, new transactions can still access the target table, so index creation does not block your workload.
Supported editions and versions
| Edition | Requirements |
|---|---|
| Enterprise Edition | Cluster Edition. MySQL 8.0.1 (revision 8.0.1.1.45.2 or later) or MySQL 8.0.2 (revision 8.0.2.2.27 or later) |
| Standard Edition | X86 CPU architecture. MySQL 8.0.1 (revision 8.0.1.1.45.2 or later) |
The following configurations are not supported:
Multi-master Cluster (Database/Table) Edition clusters
Serverless clusters
To check your cluster's engine version, see Query the engine version.
Enable automatic IMCI-based query acceleration
Prerequisites
Before you begin, make sure that you have:
A PolarDB for MySQL cluster that meets the edition and version requirements listed above
At least one read-only IMCI node in the cluster (you can add one during or after enablement)
Procedure
Log on to the PolarDB console, click Clusters in the navigation pane on the left, select the Region where the cluster is deployed, and then click the cluster ID to open the cluster details page.
On the Basic Information page, click Enable for the Automatic IMCI-based Query Acceleration option.
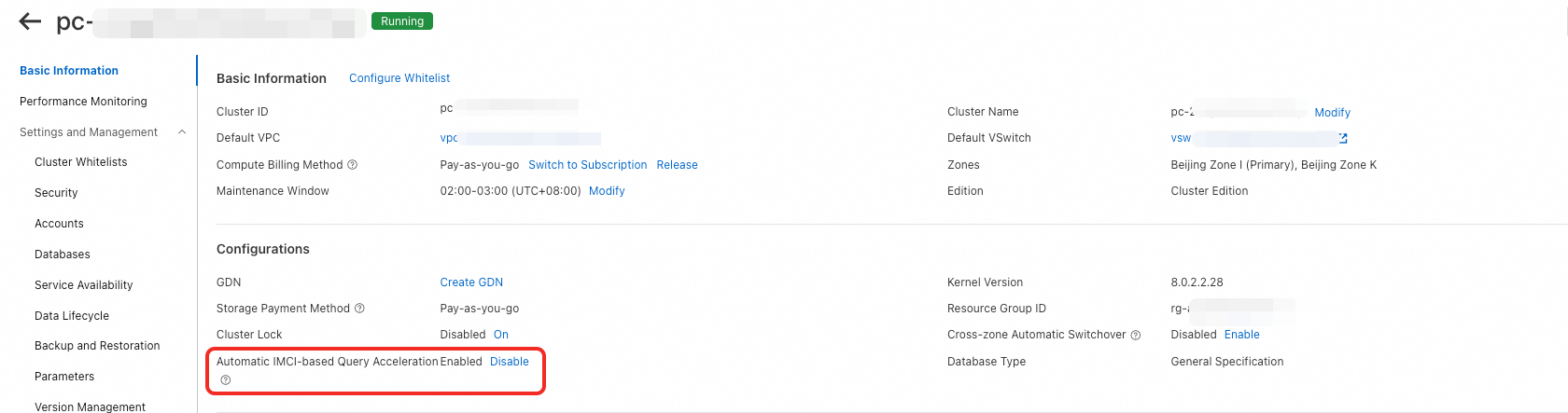
In the Enable Automatic IMCI-based Query Acceleration dialog box, click OK. What happens next depends on your cluster configuration:
Cluster already has read-only IMCI nodes -- The feature is enabled immediately.
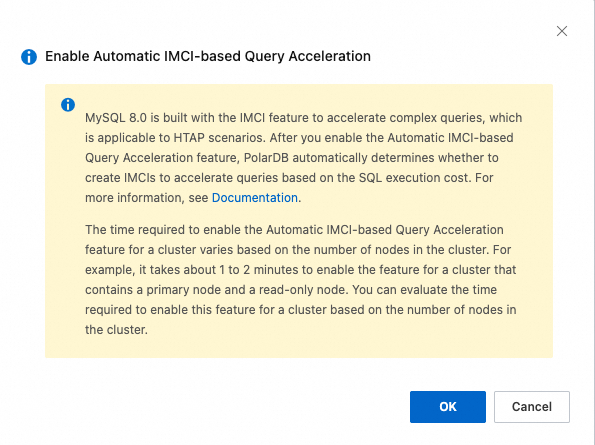
Cluster does not have read-only IMCI nodes -- After you click OK, you are redirected to the page for adding read-only IMCI nodes.
If your cluster does not have a read-only IMCI node, you can add one now or later. For instructions, see Add a read-only IMCI node. The feature takes effect only after at least one read-only IMCI node is available.
Disable automatic IMCI-based query acceleration
Log on to the PolarDB console, click Clusters in the navigation pane on the left, select the Region where the cluster is deployed, and then click the cluster ID to open the cluster details page.
On the Basic Information page, click Disable for the Automatic IMCI-based Query Acceleration option.
In the Disable Automatic IMCI-based Query Acceleration dialog box, click OK.
Disabling the feature stops automatic IMCI creation, but your existing read-only IMCI nodes, IMCIs, and related data are retained. To remove them, delete the read-only IMCI nodes in the console and delete IMCIs with DDL statements.
Billing and resource usage
| Item | Details |
|---|---|
| Read-only IMCI nodes | Billed as standard compute nodes. For details, see Billing rules of compute nodes. |
| IMCI storage | IMCIs created by the system occupy storage space. |
| SQL Trace overhead | SQL Trace, used to record slow query execution history, typically consumes no more than 3% of database node resources. |
| Behavior without IMCI nodes | Without a read-only IMCI node, the system records slow query history through SQL Trace but does not create IMCIs for acceleration. |