After you train a model, you can use PAI-EAS to deploy it as an online service. This makes the model accessible from other applications.
PAI-EAS
Elastic Algorithm Service (EAS) is a PAI platform for online model services. It lets you deploy models as online inference services or AI-powered web applications with a single click. EAS provides features such as elastic scaling, resource group management, versioning, and resource monitoring. These features help you run stable, high-concurrency online model services cost-effectively. For more information, see Overview of EAS model services.
Billing description
The example in this topic uses public resources to create an EAS service. The billing method is pay-as-you-go. When you no longer need the service, promptly stop or delete it to avoid further charges.

Use EAS to deploy a model
For a complete example of how to develop a model in DSW and deploy it with EAS, see Deploy a model as an online service using EAS.
Log on to the PAI console. In the top navigation bar, select the destination region and workspace. In the navigation pane on the left, click Elastic Algorithm Service (EAS) > Deploy Service > Custom Deployment.
Configure the following key parameters. Leave other parameters at their default values. For a complete list of configuration parameters, see Parameters for custom deployment in the console.
Deployment Method: Select Image-based Deployment.
Image Configuration: An image provides the runtime environment for the model. You can use an official image, a custom image, or an image specified by an address.
If you developed your model in DSW, you can select the Image Address and copy the image URL from DSW.

Alternatively, you can use the DSW image creation feature to push the image to Container Registry (ACR) for use by EAS. For more information, see Create a DSW instance image.
Mount storage: Allows you to upload your application code files to OSS and configure the mount address.

This topic uses a simple example for testing. The code file is uploaded to the OSS path shown in the preceding figure.
Command: Enter the command to start the sample code.

Port Number: Enter
9000for the web.py port.Third-party Library Settings: Use this section to add third-party libraries that are not included in the image. For example:
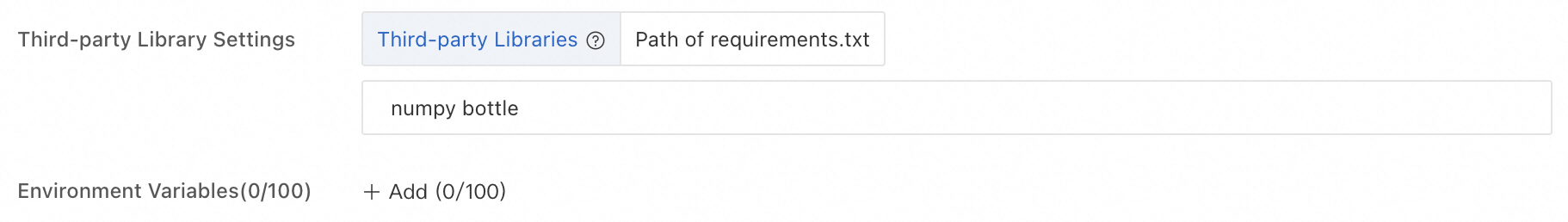
For Resource Type, select Public Resources. For Resource Type, select
ecs.gn7i-c16g1.4xlarge.
Click Deploy. The deployment is successful when the service status is Running.
Test the service invocation
After the model is successfully deployed, you can test the service endpoint using the online debugging feature of EAS.
On the EAS instance list page, click the instance name. On the instance details page, click Online Debugging.
In the web.py application from the preceding example, enter the request URL and click Send Request. A "hello World!" response indicates that the request was successful.
To invoke the service from the Internet or a VPC, see Service invocation methods.

References
For more information about EAS features, see Overview of service deployment.
For a complete list of EAS console configuration parameters, see Parameters for custom deployment in the console.
If you encounter problems when you deploy or invoke a service, see EAS FAQ.