Data Science Workshop (DSW) provides a cloud-based Integrated Development Environment (IDE) for AI development that includes a variety of built-in environments. If you are familiar with Notebooks or VS Code, you can quickly start developing models. This topic demonstrates how to develop a model in DSW using the MNIST handwritten digit recognition task as an example.
The MNIST handwritten digit recognition task is one of the most classic introductory tasks in deep learning. The goal is to build a machine learning model to recognize 10 handwritten digits (0 to 9).

Prerequisites
Activate Platform for AI (PAI) with your Alibaba Cloud account and create a workspace. Log on to the PAI console, select a region in the upper-left corner, and follow the prompts to authorize and activate the service.
Billing information
The example in this topic uses public resources to create a DSW instance and an Elastic Algorithm Service (EAS) model service. These resources are billed on a pay-as-you-go basis. For more information about the billing rules, see DSW billing and EAS billing.
Create a DSW instance
Go to the DSW page.
Log on to the PAI console.
In the upper-left corner of the page, select the destination region.
In the navigation pane on the left, click Workspace, and then click the name of the workspace that you want to manage.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose . Then, click Create Instance.
On the Create Instance page, configure the following key parameters and use the default values for the other parameters.
Resource Type: Select Public Resources. The billing method for this resource type is pay-as-you-go.
Instance Type: Select
ecs.gn7i-c8g1.2xlarge.If the inventory for this instance type is insufficient, you can select another GPU-accelerated instance type.
Image config: Select Alibaba Cloud Image, and then search for and select the following image:
modelscope:1.26.0-pytorch2.6.0-gpu-py311-cu124-ubuntu22.04.To avoid environment issues, select the same image as the one used in this topic.
Storage Path Mounting: To persistently store files from the model development process, this topic uses Object Storage Service (OSS). Click OSS, click the
 icon, select a Bucket, and create a folder, such as
icon, select a Bucket, and create a folder, such as pai_test. The complete parameter configuration is as follows.If you have not activated OSS or do not have an available bucket in the current region, follow these steps to activate OSS and create a bucket:
Uri:
oss://**********oss-cn-hangzhou-internal.aliyuncs.com/pai_test/.Mount Path:
/mnt/data/.
Click OK to create the DSW instance.
If the instance fails to start, see Common Issues with Instance Startup and Release for troubleshooting.
Develop a model in DSW
Open the DSW instance. Click Open to enter the DSW development environment.
The PAI-DSW interface appears as shown in the following figure:
Write the model development code. This topic uses a Notebook development environment as an example. The training code for the MNIST handwritten digit recognition task is provided. Click mnist.ipynb to download the code, then click the
 icon in the upper-left corner of DSW to upload the code file.
icon in the upper-left corner of DSW to upload the code file.
Run the model training code. Open the
mnist.ipynbfile, find the cell containing the training code as shown below, and click the button to run the code. This code automatically downloads the MNIST dataset to the
button to run the code. This code automatically downloads the MNIST dataset to the dataSetdirectory and saves the best checkpoint from the training to theoutputdirectory. The training process takes about 10 minutes.
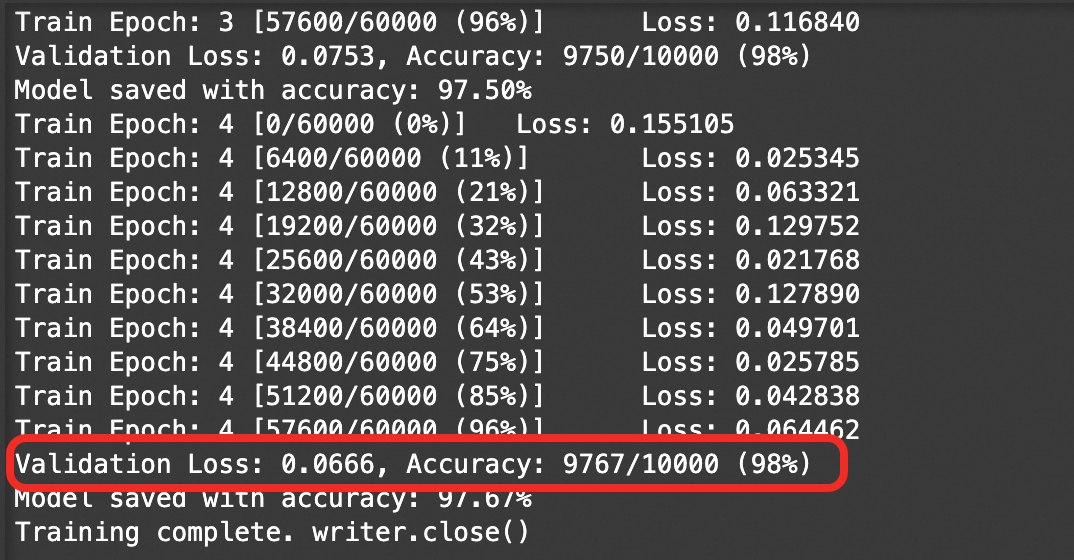
During training, the output prints the model's accuracy on the validation set. This value indicates the model's generalization ability on unseen data. As you can see, the accuracy on the validation set for this training run is 98%, which indicates that the model is performing well. You can proceed to the next steps.
View the loss curve in TensorBoard to understand the training progress. Run the following cell and click the TensorBoard page URL
http://localhost:6006/.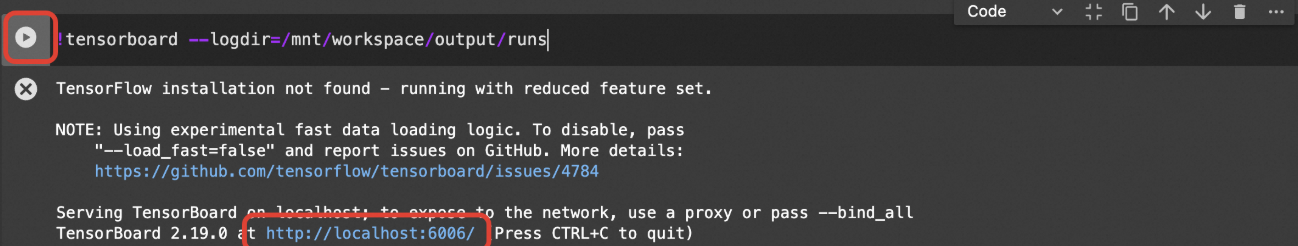
In TensorBoard, you can see the
train_losscurve (the loss on the training set) and thevalidation_losscurve (the loss on the validation set).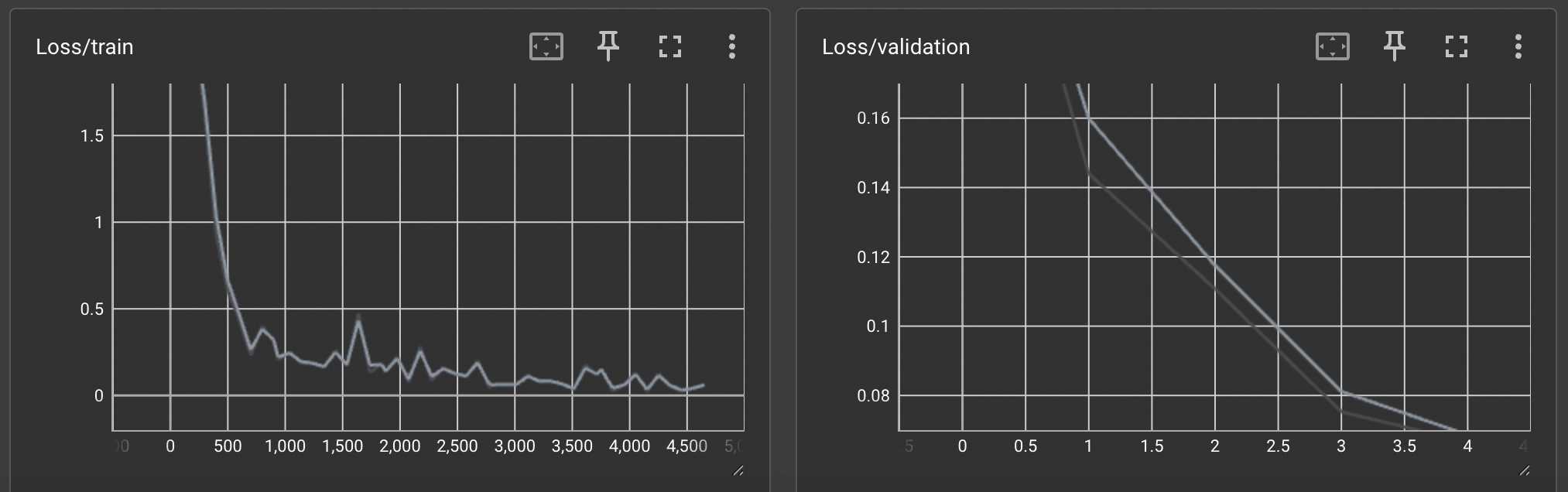
After you view the graph, click the
 icon in the cell to stop TensorBoard.
icon in the cell to stop TensorBoard.Test the trained model's performance. Run the cell shown in the figure. This displays 20 test images and outputs their true label and the model's prediction.
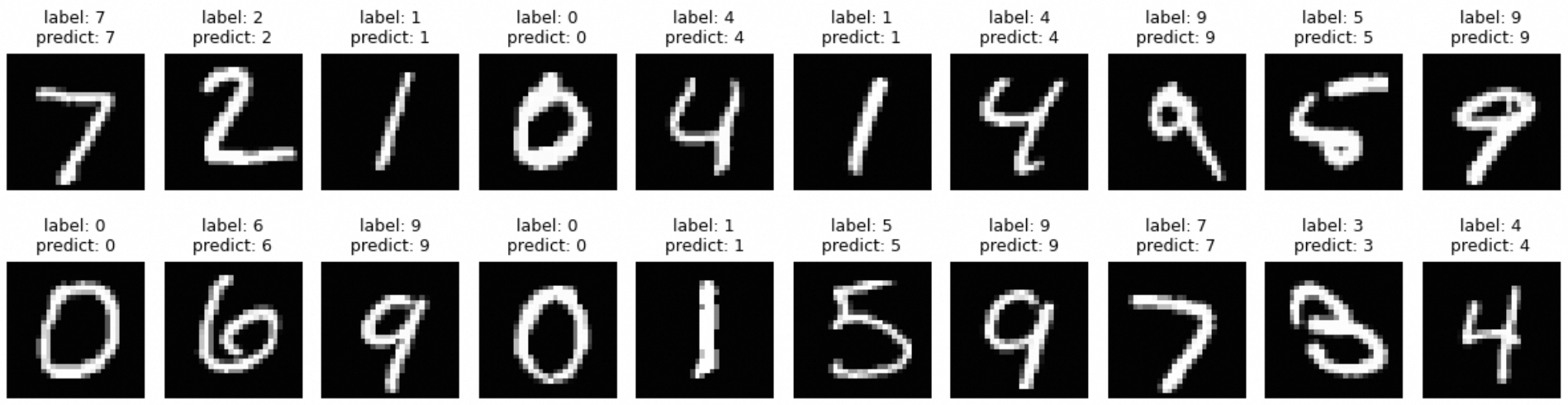
Sample output:
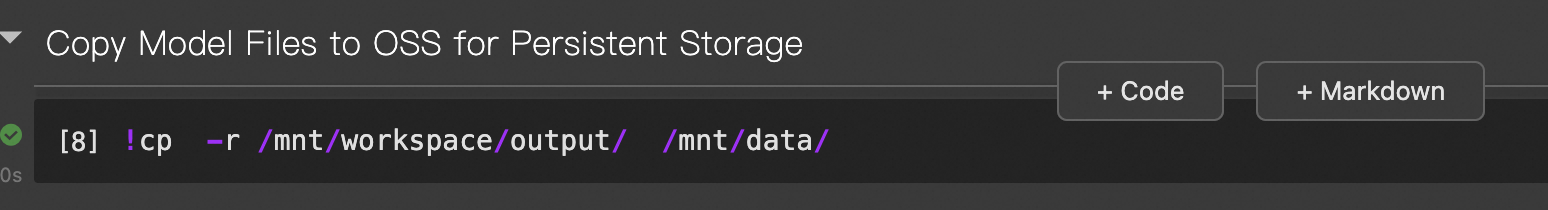
Copy the model files to OSS for persistent storage. Because this DSW instance uses public resources, its files are stored on a temporary Cloud Disk. If the instance remains stopped for more than 15 days, the content of the Cloud Disk will be deleted. Therefore, copy the model files to OSS for persistent storage. This also makes it easier to deploy the model using PAI-EAS later.
Log on to the OSS console to view the file:
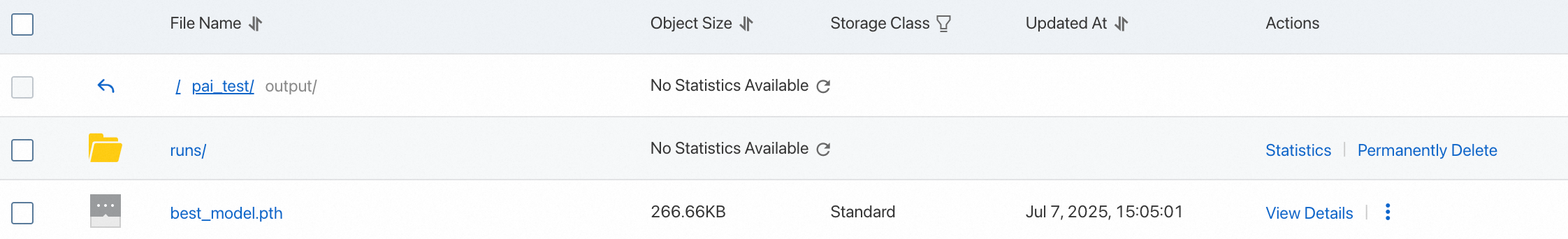
At this point, the model development is complete. To call this model from other applications in a production environment, see Deploy the model as an online service using EAS.
The DSW instance in this quickstart is a pay-as-you-go resource created from public resources. To avoid further charges, stop or delete the instance when you are finished.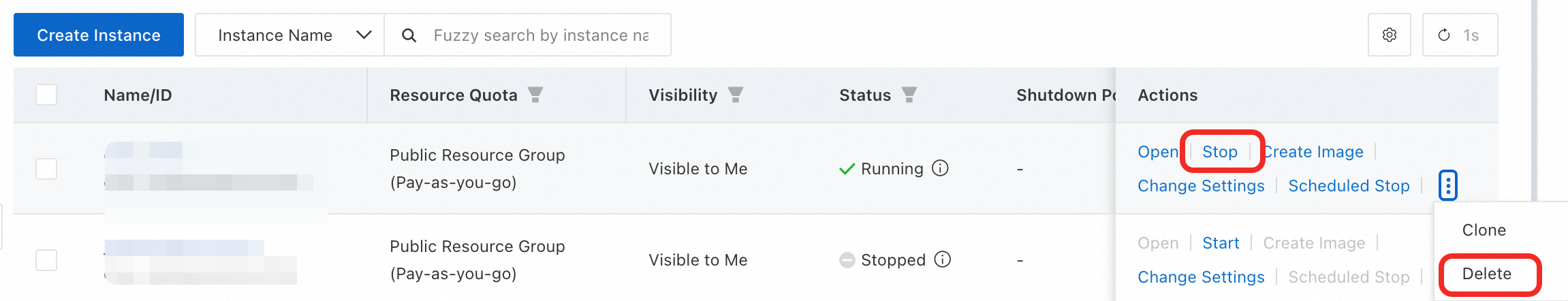
Deploy the model as an online service using EAS
Elastic Algorithm Service (EAS) allows you to quickly deploy trained models as online inference services or AI web applications. EAS supports heterogeneous resources and integrates automatic scaling, one-click stress testing, canary releases, and real-time monitoring to ensure service stability in high-concurrency scenarios at a lower cost.
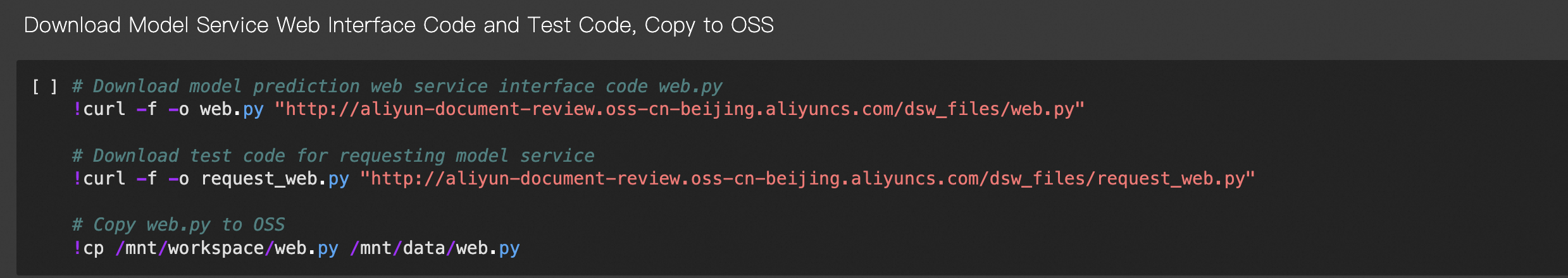
Run the following cell to write the web API code for the model service and copy it to OSS.
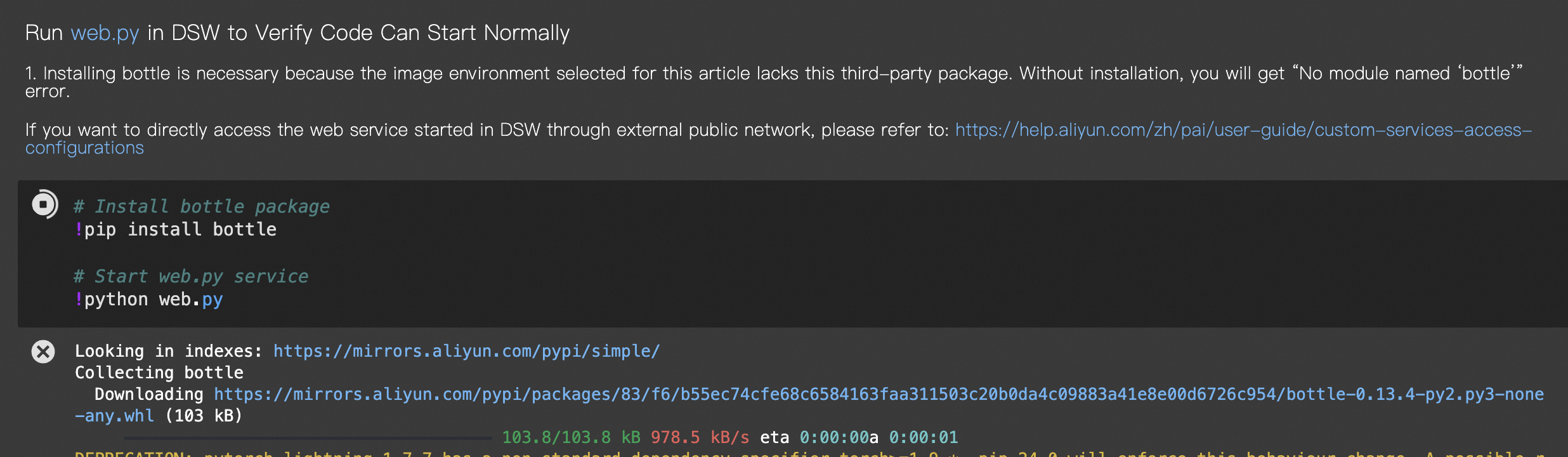
(Optional) Verify the web API in DSW. Run the following cell to install the missing third-party packages and start the service.
Run the test code for the service API. At the top of the page, click WebIDE. In the left pane, click the
request_web.pycode file, and then click the button to run the code and send a request to the service API.
button to run the code and send a request to the service API.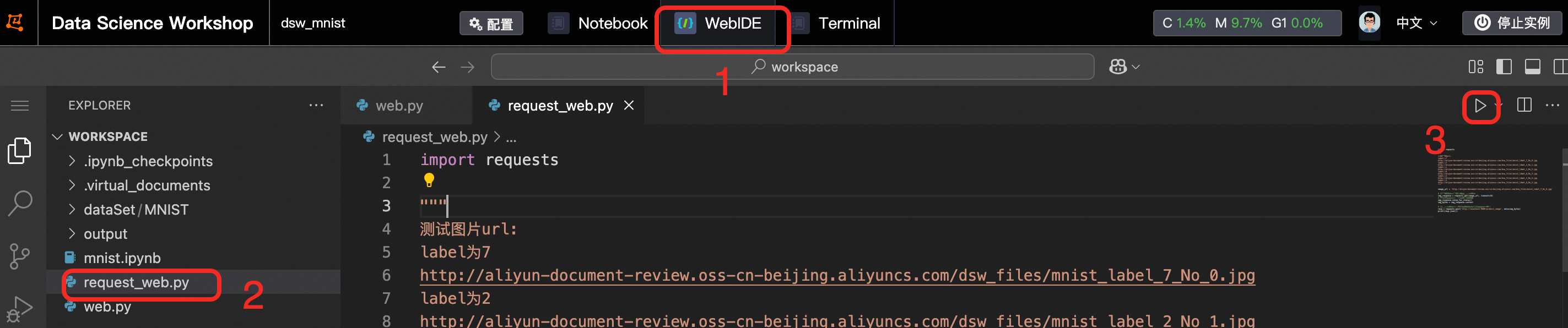
The following result is returned:
{"prediction": 7}NoteTo access the web service running in DSW directly from the public internet, you also need to configure a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC), NAT Gateway, and Elastic IP Address (EIP) for DSW. For more information, see Access a service in an instance over the internet.
Configure EAS. In the PAI console, in the navigation pane on the left, click Elastic Algorithm Service (EAS) > Deploy Service > Custom Deployment.
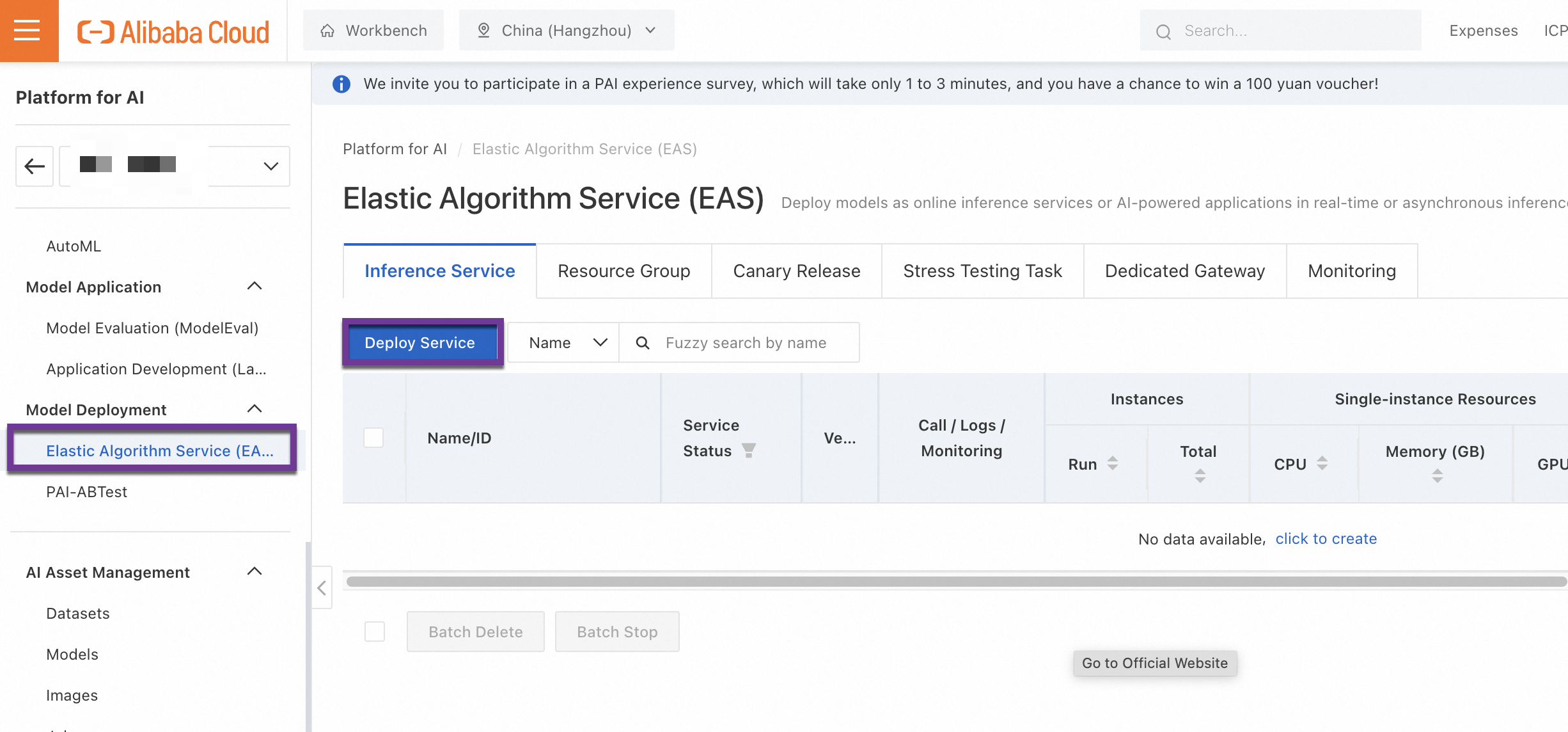
Configure the following key parameters and use the default values for the other parameters:
Deployment Method: Image-based Deployment
Image Configuration: Select Image Address. Copy and paste the URL of the image that is used for the DSW instance.
Use the same Image for deployment. It has been verified in DSW to run the service code and will help prevent environment issues.
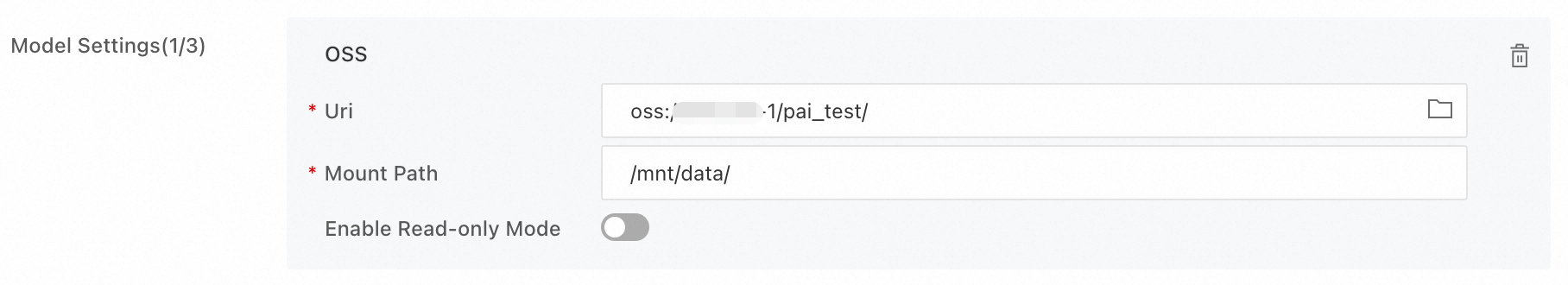
Mount storage: The model files and service API code are in OSS. Therefore, click OSS and select the corresponding OSS path.
Command: The startup command is the same as the one used in DSW. However, since
web.pyis now mounted to/mnt/data/, you need to modify the path toweb.pyaccordingly. The final command is:python /mnt/data/web.pyPort: Enter
9000, the port specified inweb.py.Third-party Library Configuration: The selected Image is missing the
bottlelibrary, so you need to add it in the third-party library configuration.
Resource Type: Select Public Resources. For Resource Specification, select
ecs.gn7i-c8g1.2xlarge.Configure a system disk: Click Show More and set Extra System Disk to 20 GB.
Because the Image is large, you must configure an additional system disk to prevent the service from failing to start due to insufficient space.
Click Deploy to create the service. The creation process takes about 5 minutes. When the status changes to Running, the deployment is successful.
View endpoint information. On the model service details page, click View Invocation Information to obtain the Public Endpoint and Token.
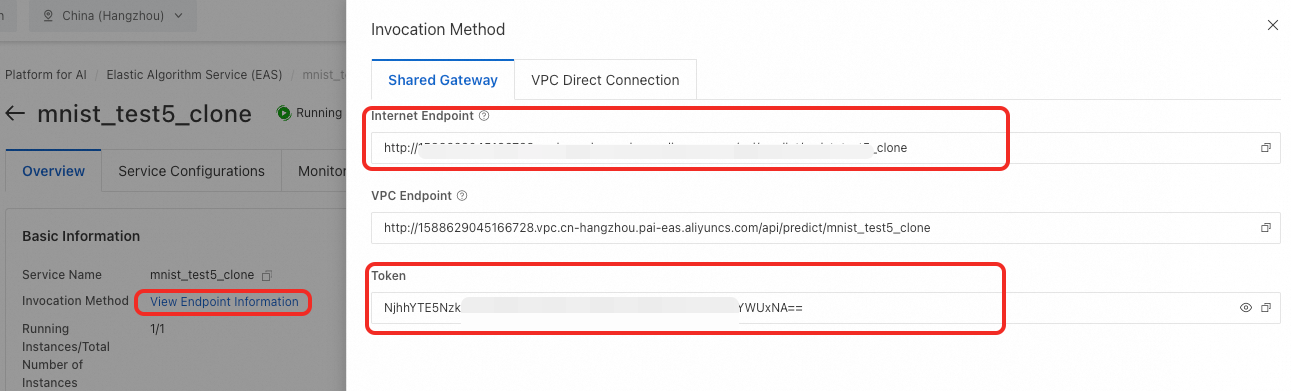
Call the service. Run the following service request code. Remember to replace the Endpoint and Token in the code with your actual endpoint and token.
import requests """ Test image URLs: label is 7 http://aliyun-document-review.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/dsw_files/mnist_label_7_No_0.jpg label is 2 http://aliyun-document-review.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/dsw_files/mnist_label_2_No_1.jpg label is 1 http://aliyun-document-review.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/dsw_files/mnist_label_1_No_2.jpg label is 0 http://aliyun-document-review.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/dsw_files/mnist_label_0_No_3.jpg label is 4 http://aliyun-document-review.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/dsw_files/mnist_label_4_No_4.jpg label is 5 http://aliyun-document-review.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/dsw_files/mnist_label_9_No_5.jpg """ image_url = 'http://aliyun-document-review.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/dsw_files/mnist_label_7_No_0.jpg' # The client downloads the image to get the binary data. img_response = requests.get(image_url, timeout=10) # Automatically check if the request is successful based on the status code. img_response.raise_for_status() img_bytes = img_response.content # Header information. Replace YOUR_TOKEN with the actual token. # In a production environment, we recommend that you set the token as an environment variable to prevent sensitive information leaks. # For more information about how to configure environment variables, see https://www.alibabacloud.com/help/en/sdk/developer-reference/configure-the-alibaba-cloud-accesskey-environment-variable-on-linux-macos-and-windows-systems headers = {"Authorization": "YOUR_TOKEN"} # Send the binary data as the body of a POST request to the model service. resp = requests.post('YOUR_ENDPOINT/predict_image', data=img_bytes, headers=headers) print(resp.json())The following result is returned:
{"prediction": 7}
The EAS service in this quickstart is a pay-as-you-go resource created from public resources. To avoid further charges, stop or delete the service when you are finished.

References
For more information about how to troubleshoot DSW instance startup failures, see Create a DSW instance.
For more information about DSW billable items and billing methods, see DSW billing.
For more information about the core features of DSW, see DSW overview.
For more information about how to access a web service that is running in DSW directly from the internet, see Access a service in an instance over the internet.
For more information about the core features of EAS, see Overview of EAS.