This topic describes how to use the fault tolerance monitoring feature, which is based on AIMaster and provided by DLC.
Background information
Deep learning is widely used. As models and data scale up, distributed training becomes a common practice. When the number of job instances increases, exceptions in the software stack and hardware environment can cause jobs to fail.
To ensure stable operation for large-scale distributed deep learning jobs, DLC provides AIMaster-based fault tolerance monitoring. AIMaster is a job-level component. When you enable this monitoring, an AIMaster instance runs alongside the other instances of your job to provide job monitoring, fault tolerance assessment, and resource control.
Limitations
AIMaster currently supports the following frameworks: PyTorch, MPI, TensorFlow, and ElasticBatch.
Step 1: Configure fault tolerance monitoring parameters
This section describes all parameters for fault tolerance monitoring. You can refer to the common configuration examples to plan your settings. When you enable the feature, you can configure these parameters in the Other Configuration section as needed.
Parameter description
Category | Feature | Parameter | Description | Default value |
General configuration | Job execution type | --job-execution-mode | Sets the job execution type. Valid values:
Fault tolerance behavior for a retriable error differs by job type:
| Sync |
Job restart settings | --enable-job-restart | Specifies whether the job can restart when fault tolerance conditions are met or a runtime exception is detected. Valid values:
| False | |
--max-num-of-job-restart | The maximum number of times a job can restart. If this number is exceeded, AIMaster marks the job as failed. | 3 | ||
Runtime configuration Note This applies to scenarios where no instance fails to run. | Anomaly detection for hung tasks | --enable-job-hang-detection | Specifies whether to enable hang detection for running jobs. This feature only supports Synchronous jobs. Valid values:
| False |
--job-hang-interval | The duration in seconds that a job can pause before AIMaster considers it hung. Must be a positive integer. If the pause exceeds this value, AIMaster flags the job as abnormal and restarts it. | 1800 | ||
--enable-c4d-hang-detection | Specifies whether to enable the Calibrating Collective Communication over Converged ethernet - Diagnosis (C4D) detection to quickly diagnose and locate slow and faulty nodes that cause a job hang. Note This parameter is effective only when --enable-job-hang-detection is also enabled. | False | ||
Hang detection for exiting jobs | --enable-job-exit-hang-detection | Specifies whether to enable hang detection when a job is about to exit. This feature only supports synchronous jobs. Valid values:
| False | |
--job-exit-hang-interval | The duration in seconds that a job can pause during exit. Must be a positive integer. If the pause exceeds this value, the job is marked as abnormal and restarts. | 600 | ||
Fault tolerance configuration Note This applies to scenarios where an instance fails to run. | Fault tolerance policy | --fault-tolerant-policy | The fault tolerance policy. Valid values:
| ExitCodeAndErrorMsg |
Maximum occurrences of the same error | --max-num-of-same-error | The maximum number of times the same error can occur on a single instance. If the error count exceeds this value, AIMaster marks the job as failed. | 10 | |
Maximum fault tolerance rate | --max-tolerated-failure-rate | The maximum tolerated failure rate. If the proportion of failed instances exceeds this value, AIMaster marks the job as failed. The default value of -1 disables this feature. For example, a value of 0.3 means the job is marked as failed if more than 30% of workers encounter an error. | -1 |
Sample configurations
The following examples show common parameter configurations for different training jobs.
Synchronous training job (common for PyTorch)
Restart the job when an instance fails and meets the fault tolerance conditions.
--job-execution-mode=Sync --enable-job-restart=True --max-num-of-job-restart=3 --fault-tolerant-policy=ExitCodeAndErrorMsgAsynchronous training jobs (common for TensorFlow jobs)
For a retriable error, restart only the failed worker instance. By default, the job does not restart if a PS or Chief instance fails. To enable job restart, set --enable-job-restart to True.
--job-execution-mode=Async --fault-tolerant-policy=OnFailureOffline inference jobs (common for ElasticBatch jobs)
Instances are independent, similar to an asynchronous job. When an instance fails, AIMaster restarts only that instance.
--job-execution-mode=Async --fault-tolerant-policy=OnFailure
Step 2: Enable the fault tolerance monitoring
You can enable fault tolerance monitoring in the console or by using an SDK when you submit a DLC job.
Enable fault tolerance monitoring in the console
When you submit a DLC training job in the console, go to the Fault Tolerance and Diagnosis section, turn on Automatic Fault Tolerance, and configure additional parameters. For more information, see Create a training job. DLC then starts an AIMaster role to monitor the job end-to-end and handle errors.
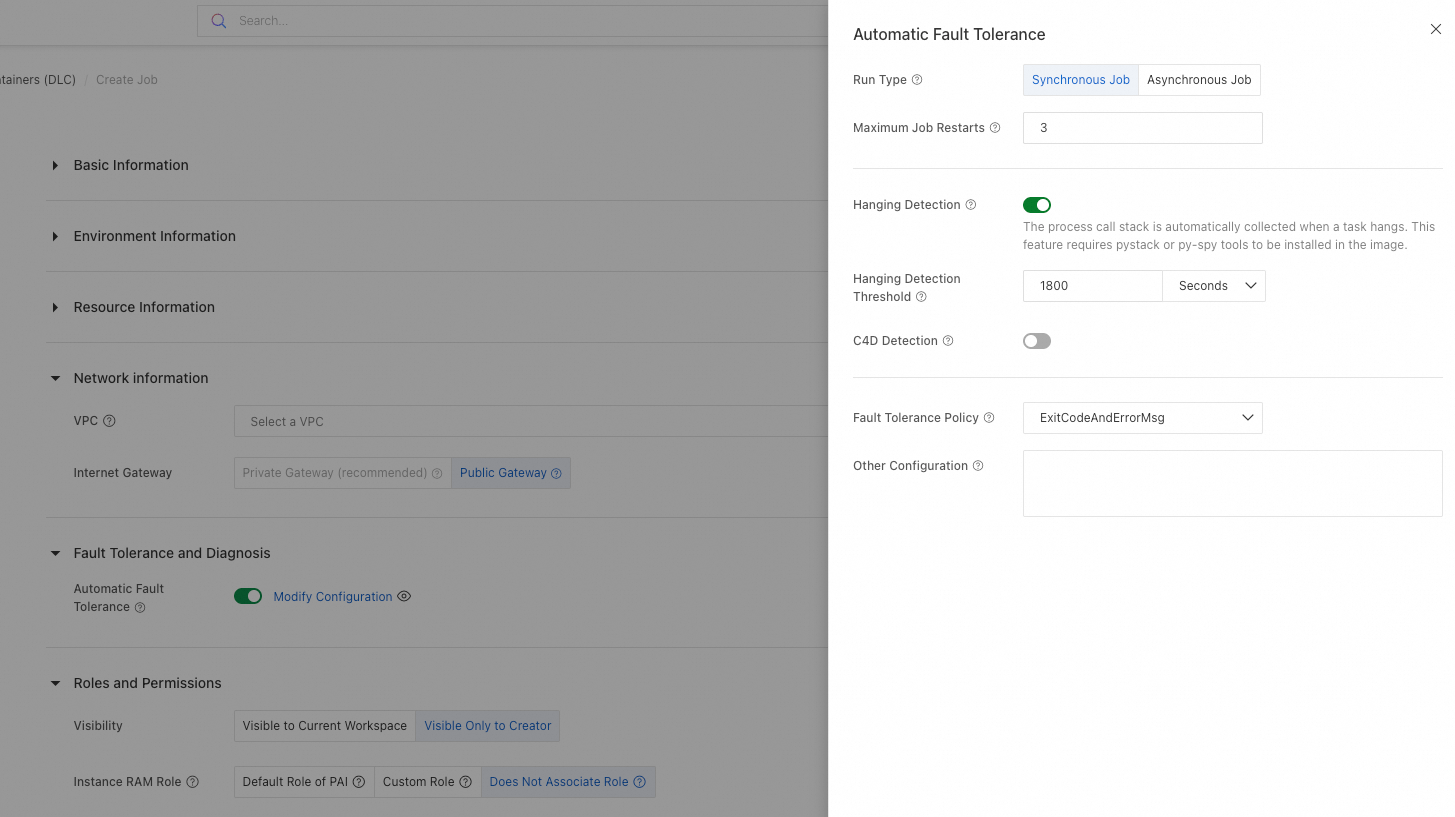
Details are as follows:
You can configure additional parameters in the Other Configuration text box. For parameter details, see Step 1: Configure fault tolerance monitoring parameters.
After you enable Hanging Detection, you can enable the C4D Detection feature. C4D is a diagnostic tool from Alibaba Cloud for identifying slow nodes or hangs in LLM training. For more information, see Use C4D.
NoteC4D depends on ACCL (Alibaba Cloud high-performance collective communication library). Ensure that ACCL is installed. For more information, see ACCL: Alibaba Cloud high-performance collective communication library.
C4D detection is currently available only for DLC jobs that use Lingjun AI Computing Service resources.
Enable fault tolerance monitoring by using the DLC SDK
Use the Go SDK
Enable fault tolerance monitoring when you submit a job by using the Go SDK.
createJobRequest := &client.CreateJobRequest{} settings := &client.JobSettings{ EnableErrorMonitoringInAIMaster: tea.Bool(true), ErrorMonitoringArgs: tea.String("--job-execution-mode=Sync --enable-job-restart=True --enable-job-hang-detection=True --job-hang-interval=3600"), } createJobRequest.SetSettings(settings)Parameters:
EnableErrorMonitoringInAIMaster: Specifies whether to enable the fault tolerance monitoring feature.
ErrorMonitoringArgs: The additional parameters for fault tolerance monitoring.
Use the Python SDK
Enable fault tolerance monitoring when you submit a job by using the Python SDK.
from alibabacloud_pai_dlc20201203.models import CreateJobRequest, JobSettings settings = JobSettings( enable_error_monitoring_in_aimaster = True, error_monitoring_args = "--job-execution-mode=Sync --enable-job-restart=True --enable-job-hang-detection=True --job-hang-interval=30" ) create_job_req = CreateJobRequest( ... settings = settings, )where:
enable_error_monitoring_in_aimaster: Specifies whether to enable the fault tolerance monitoring feature.
error_monitoring_args: The additional parameters for fault tolerance monitoring.
Step 3: Configure advanced fault tolerance monitoring features
Use these advanced features to customize fault tolerance monitoring for your job.
Configure fault tolerance notifications
After you enable fault tolerance monitoring for a job, to receive notifications for fault tolerance events, go to the Workspace Details page. Choose . Then, click Create Event Rule and set the event type to DLC Jobs > Automatic Fault Tolerance. For more information, see Event Center for a workspace.
When a training job encounters an exception, such as a NaN loss, you can use the AIMaster SDK in your code to send a custom notification message:
To use this feature, install the AIMaster wheel package. For more information, see FAQ.
from aimaster import job_monitor as jm
job_monitor_client = jm.Monitor(config=jm.PyTorchConfig())
...
if loss == Nan and rank == 0:
st = job_monitor_client.send_custom_message(content="The training loss of the job is NaN.")
if not st.ok():
print('failed to send message, error %s' % st.to_string())Configure custom fault tolerance keywords
Fault tolerance monitoring has built-in detection for common retriable errors. You can also define custom keywords. If a failed instance's log contains one of these keywords, AIMaster treats the error as retriable. The monitoring module scans the end of the failed instance's logs to find these keywords.
Set the Fault tolerance policy to ExitCodeAndErrorMsg.
Example of configuring custom fault tolerance keywords for a PyTorch job
from aimaster import job_monitor as jm jm_config_params = {} jm_config = jm.PyTorchConfig(**jm_config_params) monitor = jm.Monitor(config=jm_config) monitor.set_retryable_errors(["connect timeout", "error_yyy", "error_zzz"])The parameters configured in monitor.set_retryable_errors are the custom fault tolerance keywords.
Example of configuring custom fault tolerance keywords for a TensorFlow job
from aimaster import job_monitor as jm jm_config_params = {} jm_config = jm.TFConfig(**jm_config_params) monitor = jm.Monitor(config=jm_config) monitor.set_retryable_errors(["connect timeout", "error_yyy", "error_zzz"])
Configure staged job hang detection
By default, hang detection settings apply to the entire job. However, jobs run in stages. For example, during initialization, nodes may take longer to establish communication, while during training, logs update more frequently. To detect hangs faster during the training process, DLC provides staged hang detection, which allows you to configure different detection intervals for different stages.
monitor.reset_config(jm_config_params)
# Example:
# monitor.reset_config(job_hang_interval=10)
# or
# config_params = {"job_hang_interval": 10, }
# monitor.reset_config(**config_params)The following is an example of staged hang detection for a PyTorch job.
import torch
import torch.distributed as dist
from aimaster import job_monitor as jm
jm_config_params = {
"job_hang_interval": 1800 # Global 30-minute detection.
}
jm_config = jm.PyTorchConfig(**jm_config_params)
monitor = jm.Monitor(config=jm_config)
dist.init_process_group('nccl')
...
# impl these two funcs in aimaster sdk
# user just need to add annotations to their func
def reset_hang_detect(hang_seconds):
jm_config_params = {
"job_hang_interval": hang_seconds
}
monitor.reset_config(**jm_config_params)
def hang_detect(interval):
reset_hang_detect(interval)
...
@hang_detect(180) # reset hang detect to 3 min, only for func scope
def train():
...
@hang_detect(-1) # disable hang detect temporarily, only for func scope
def test():
...
for epoch in range(0, 100):
train(epoch)
test(epoch)
self.scheduler.step()
Use C4D
C4D is a proprietary tool from Alibaba Cloud for diagnosing slow nodes or hangs in large model training. C4D depends on ACCL. Ensure that ACCL is installed. For more information, see ACCL: Alibaba Cloud high-performance collective communication library. Currently, you can use the C4D detection feature when you select Lingjun resources for a DLC job.
Feature overview
C4D aggregates status information from all nodes to determine if a node has problems in the communication layer or elsewhere. The following diagram shows the system architecture.

Parameter description
Once you enable the C4D detection feature, you can configure the following parameters in the Other Configuration text box:
Parameter | Description | Example value |
--c4d-log-level | Sets the C4D output log level. Valid values:
The default value is Warning, which outputs logs at the Warning and Error levels. We recommend using the default value for normal operation. To troubleshoot performance issues, you can set it to Info. |
|
--c4d-common-envs | Sets environment variables for C4D execution. Use the format
|
|
For Error-level logs, AIMaster automatically isolates the corresponding node and restarts the job. The handling logic for each log level is as follows:
Error level | Error description | Action |
Error | By default, a communication-layer job hang exceeding three minutes will cause the job to fail. You can modify this default by configuring the C4D_HANG_TIMEOUT and C4D_HANG_TIMES parameters. | AIMaster directly isolates the node reported in the log. |
Warn | By default, a communication-layer job hang exceeding 10 seconds will affect performance but not cause the job to fail. You can modify this default by configuring the C4D_HANG_TIMEOUT parameter. | The node in the log is not automatically isolated and requires manual confirmation. |
A non-communication-layer job hang exceeding 10 seconds might cause the job to fail. | The node in the log is not automatically isolated and requires manual confirmation. | |
Info | Communication-layer slowness and non-communication-layer slowness. | These diagnostic logs are primarily for performance issues and require manual confirmation. |
If you find that a DLC job is running slow or is hung, go to the DLC job list, and click the job name to go to the job details page. In the Instance section at the bottom, view the AIMaster node log to see the C4D diagnostic results. For more information about the diagnosis results, see Diagnostic result examples.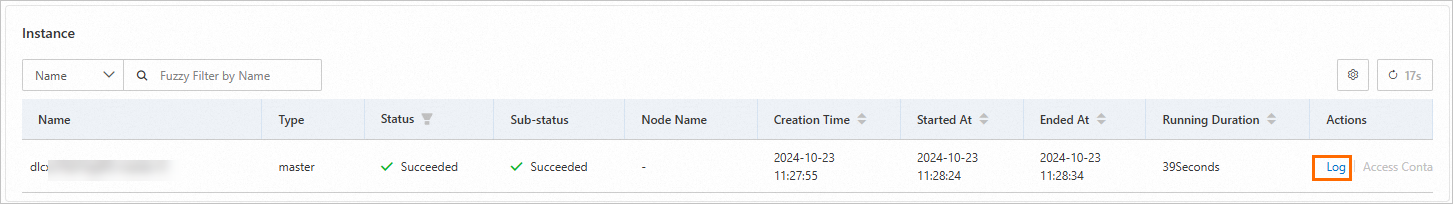
Diagnostic result examples
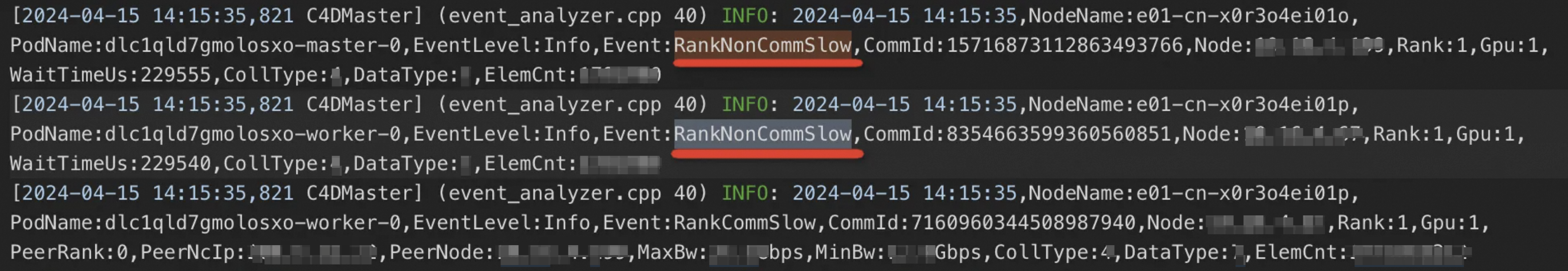
RankCommHang: Indicates a hang in the communication layer of a node.
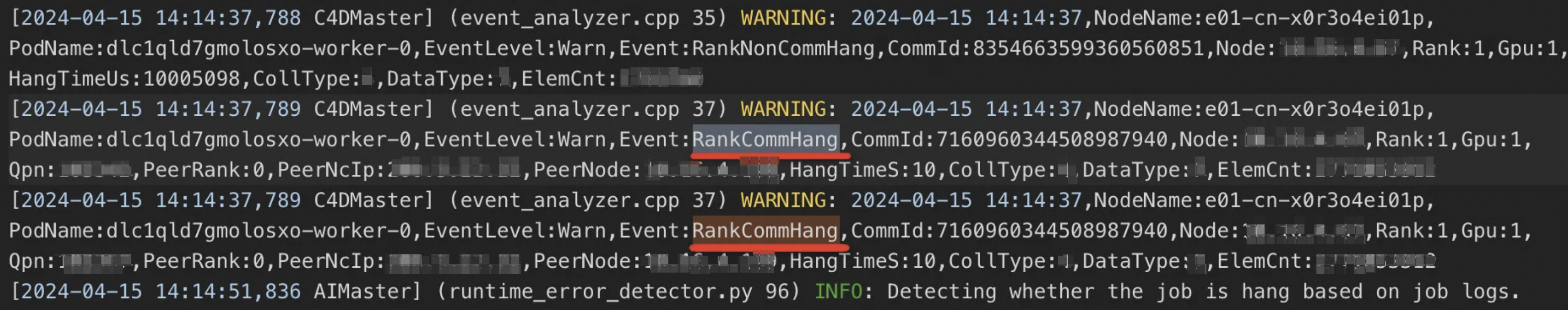
RankNonCommHang: Indicates a hang on a node outside the communication layer (e.g., in the compute process).
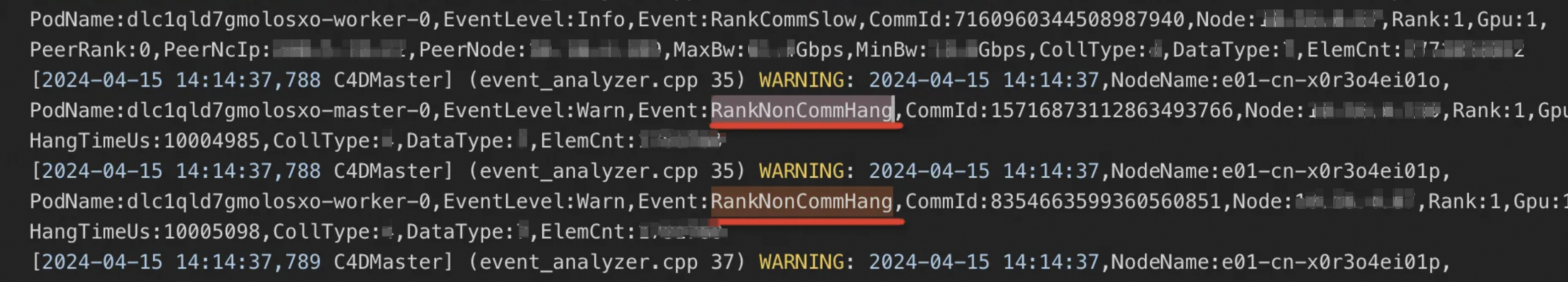
RankCommSlow: Indicates slowness in the communication layer of a node.
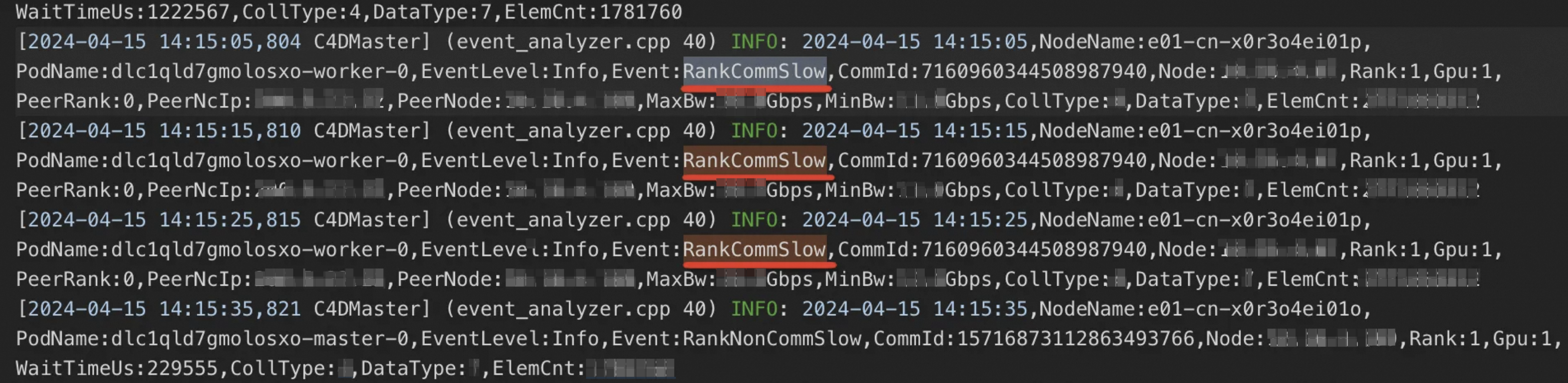
RankNonCommSlow: Indicates slowness on a node outside the communication layer.
FAQ
How do I install the AIMaster SDK for a specific Python version (3.6, 3.8, or 3.10)?
Install the AIMaster SDK using pip with the direct URL for the wheel (.whl) file that matches your Python environment. Choose the command that corresponds to your Python version:
# Python 3.6
pip install -U http://odps-release.cn-hangzhou.oss.aliyun-inc.com/aimaster/pai_aimaster-1.2.1-cp36-cp36m-linux_x86_64.whl
# Python 3.8
pip install -U http://odps-release.cn-hangzhou.oss.aliyun-inc.com/aimaster/pai_aimaster-1.2.1-cp38-cp38-linux_x86_64.whl
# Python 3.10
pip install -U http://odps-release.cn-hangzhou.oss.aliyun-inc.com/aimaster/pai_aimaster-1.2.1-cp310-cp310-linux_x86_64.whl