This topic describes how to enable the tracing feature when you deploy a service.
Background information
As Large Language Model (LLM) technology becomes more widespread, enterprises face many challenges when building LLM-based applications. These challenges include unpredictable outputs, complex call paths, difficulty in identifying performance bottlenecks, and a lack of granular observability. To address these challenges, Elastic Algorithm Service (EAS) offers a tracing feature.
The core goal of tracing is to improve application observability and help you evaluate your LLM applications. When you enable tracing, EAS automatically integrates with Alibaba Cloud's Application Real-Time Monitoring Service (ARMS) to provide the following capabilities:
Trace visualization: Visualize the complete path of a request with clear trace logs.
Performance monitoring: Track key performance indicators, such as response time, token consumption, and error counts, to promptly identify performance bottlenecks.
Issue detection and root cause analysis: Quickly locate issues by using a Trace ID and perform root cause analysis with contextual information.
Evaluation tools: Use evaluation tools based on trace data to verify the accuracy and reliability of LLM application outputs.
Basic concepts
Trace
A trace represents the complete execution path of a transaction or request in a distributed system. It records how the request flows through various services or modules. A trace consists of multiple spans. With a trace, you can visualize the request's journey and quickly locate performance bottlenecks or the source of errors. A Trace ID uniquely identifies a trace. You can use the Trace ID to query the details and logs of a specific call.
Span
A span is a basic unit within a trace. It represents a single, named, and timed operation, recording details such as the operation name, start time, and end time.
Python probe
A Python probe is a tool that automatically collects trace data and performance metrics from Python applications. You enable tracing by installing the Python probe when deploying an EAS service.
Evaluation
This refers to the comprehensive assessment of the answers generated by an LLM application in response to user questions, measured across multiple dimensions. Contact your business manager to confirm the specific evaluation dimensions.
Limitations
The EAS tracing feature only supports Python-based LLM applications developed with LangChain, LlamaIndex, or Dashscope.
Prerequisites
You have activated ARMS. For more information, see Activate ARMS.
You have activated LangStudio. For more information, see Authorize the PAI service account. The
AliyunServiceRoleForPaiLLMTracerole is required.If you are using a RAM user or RAM role, grant the
AliyunPAILLMTraceFullAccesspermission to the user or role before using this feature. For more information, see Grant permissions to a RAM role and Grant permissions to a RAM user.
Step 1: Prepare the application
To provide an end-to-end walkthrough from service deployment and invocation to trace viewing, this topic uses a simple prediction service as an example.
This code is a simple prediction service developed based on the Dashscope API. It uses the Flask framework to build a web service and calls a model for text generation via the Generation.call method of Dashscope. Before using Dashscope for the first time, activate it and obtain an API key. For more information, see Call the Dashscope API for the first time. Then, set DASHSCOPE_API_KEY as an environment variable when deploying the service to access the API service. The following is an example of the app.py code file:
import os
import json
import flask
import dashscope
app = flask.Flask(__name__)
def run_query(query):
"""Run a query."""
response = dashscope.Generation.call(
api_key=os.getenv('DASHSCOPE_API_KEY'),
model="qwen-plus",
messages=[
{'role': 'system', 'content': 'You are a helpful assistant.'},
{'role': 'user', 'content': query}
],
result_format='message'
)
return response
@app.route('/api/trace_demo', methods=['POST'])
def query():
"""
POST data example:
{
"query": "capital of china"
}
"""
data = flask.request.get_data("utf-8")
query = json.loads(data).get('query', '')
response = run_query(query)
return response.output.choices[0].message.content
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=8000)Step 2: Enable tracing
When you deploy an EAS service, you can enable tracing by turning on the Tracing switch in the Service features section. Follow the prompts to determine if the image you are using has the tracing component pre-installed. If not, you must configure commands to install the probe and start the application with the ARMS Python probe. For more configuration details, see Manually install a Python probe.
If you select an image with the tracing component built-in: Turn on the Tracing switch to enable the feature with one click. No additional configuration is required.
If you select an image without the tracing component built-in: Turn on the Tracing switch and configure the third-party libraries and startup command according to the prompts:
Parameter
Description
Startup Command
Add
<br>aliyun-bootstrap -a install && aliyun-instrument python app.py<br>. This command installs the probe and starts the application using the ARMS Python probe.app.pyis the main file in your image that provides the prediction service. The Third-party Library Configuration must includealiyun-bootstrap.Third-party Library Configuration
Add
<br>aliyun-bootstrap<br>to download the probe installer from the PyPI repository.

This topic demonstrates the process using an image without the built-in tracing component and the provided example code. The following table describes the key parameter configurations for deploying a custom EAS service. For detailed instructions, see Deploy a service in the console. After the service is deployed:
View the service deployment status on the Elastic Algorithm Service (EAS) page.
View the registered application on the Application List page in the ARMS console. The application name is the same as the EAS service name.
Parameter | Description | |
Environment Context | Deployment Method | Select Image Deployment. |
Image Configuration | This topic uses the default image: . You can also enter a prepared custom image on the Image URL tab. | |
Direct Mount | Since the example code is not integrated into the image, you must mount it to the service instance. To mount from OSS, click OSS and configure the following parameters:
If you use a custom image and have already configured the main file for the prediction service in the image, you can skip this configuration. | |
Startup Command | This topic sets the command to | |
Environment Variables | Because the sample code calls the Dashscope API, click Add and configure the following environment variable:
| |
Third-party Library Configuration | Set the third-party libraries to | |
Service Registration | Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) | To use the tracing feature, you must configure a virtual private cloud (VPC). Select a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC), VSwitch, and Security Group in the region. By default, EAS services cannot access the Internet. To run the sample code, which needs to call the Dashscope API, you must configure a VPC with Internet access for the EAS service. This ensures that the service can access the Internet. For specific instructions, see Scenario 1: Allow an EAS service to access the Internet. |
VSwitch | ||
Security Group Name | ||
Service Features | Tracing | Turn on the Tracing switch and configure the third-party libraries and startup command in the Environment Context section. |
Step 3: View traces
After calling the service, follow these steps to view the generated traces.
Call the EAS service
This topic uses online debugging as an example. You can also call the EAS service using an API. For more information, see API calls.
On the Elastic Algorithm Service (EAS) page, find the target service and click
 > Online Debug in the Actions column.
> Online Debug in the Actions column.On the Body tab, send a request to the specified address according to your prediction service definition.
This example uses the service interface defined in the
app.pyfile. The following figure shows the sample result: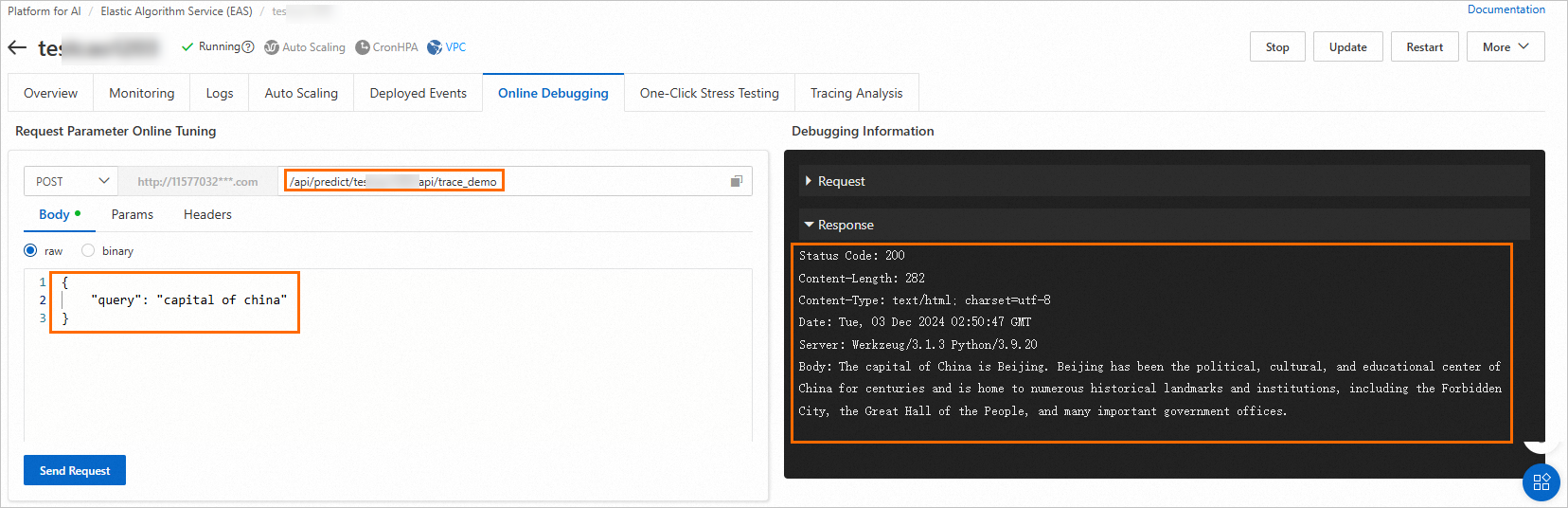
View trace information
Trace data is stored for 30 days by default. If you need to extend this period, contact the ARMS team for custom configuration.
Switch to the Trace Query tab on the Tracing tab to view trace information.

Find the target trace and click View Trace in the Actions column to go to the Trace Details page.
The trace data on this page lets you view the service's input, output, and related log information.
Note: If you use a RAM user or a RAM role, you must grant the
AliyunARMSReadOnlyAccesspermission to use this feature.
To share trace details, click the share icon
 to generate a one-time address.
to generate a one-time address.Note: If you are using a RAM user or RAM role, grant the
cms:CreateTicketpermission to the user or role before using this feature.
Step 4: Evaluate application performance
EAS provides evaluation tools based on trace data to verify the accuracy and reliability of LLM application outputs. Two evaluation methods are available, each suitable for different scenarios:
Method 1: Evaluate a single trace: Manually select and evaluate a specific trace from the EAS service. This is suitable for debugging a specific trace during development or testing to verify its logic and performance.
Method 2: Evaluate traces in batches online: Periodically evaluate a sample of traces generated by the EAS service during runtime. This is suitable for large-scale performance testing or functional verification, helping you understand the overall system status and trace collaboration.
Trace data is stored for 30 days by default. If you need to extend this period, contact the ARMS team for custom configuration.
Method 1: Evaluate a single trace
On the Trace Query tab of the Tracing tab, find the target trace and click Evaluate in the Actions column. Then, in the Evaluate configuration panel, configure the following parameters.

Evaluation Metrics: This is a fixed configuration and cannot be changed. The evaluation is performed based on the following dimensions.
Evaluation Metric
Description
Correctness
Determines whether the answer correctly addresses the question based on the input and reference text.
Faithfulness
Determines whether the answer is generated based on the input and reference text and checks for hallucinations.
Retrieval Relevance
Determines whether the retrieved results are relevant to the input question. It includes the following four metrics:
nDCG: Normalized Discounted Cumulative Gain
Hit Rate
Precision@K
MRR: Mean Reciprocal Rank
Model Configuration: The large language model (LLM) used to evaluate the trace. After the initial setup, this configuration is automatically backfilled for subsequent evaluations.
Parameter
Description
Model Selection
The following two models are supported:
PAI Judge Model
qwen-max (Model Studio model)
NoteTo use a Model Studio model, you need to configure an Internet connection for EAS.
Calls to Model Studio models are billed separately. For more information, see Billing.
Model Token
Enter the token for the selected model:
Judge model: Go to the Judge Model page, activate the PAI judge model, and obtain a token.
qwen-max: To learn how to obtain a token for the Model Studio qwen-max model, see Call the Tongyi Qianwen API for the first time.
Extraction Configuration: In the Query Extraction Configuration, Answer Extraction Configuration, and Context Extraction Configuration sections, configure the parameters in the following table to extract the corresponding content:
Query Extraction Configuration: Extracts the user query content (input).
Answer Extraction Configuration: Extracts the system-generated answer (output).
Context Extraction Configuration: Extracts the text or background information provided to the system (documents).
Parameter
Description
SpanName
Finds a span that matches the SpanName.
JsonPathInSpan
The format is a.b.c. This parameter cannot be empty. It extracts a value from a specified element of the matched span.
JsonPathInSpanValue
The format is a.b.c. This parameter can be empty. After the element corresponding to JsonPathInSpan is found, if the element's content is a JSON string, JsonPathInSpanValue is used to extract the corresponding value.
You can click View Trace in the Actions column to obtain the configuration content from the Trace Details page. The following table shows configuration examples:
Extraction Configuration
How to obtain
Example value
Query Extraction Configuration
This topic provides an example where JsonPathInSpanValue has no value:

For an example where JsonPathInSpanValue has a value, see the following figure.

JsonPathInSpanValue has no value
SpanName: LLM
JsonPathInSpan: attributes.input.value
JsonPathInSpanValue: Because the content of the JsonPathInSpan element is not a JSON string, this parameter is empty.
JsonPathInSpanValue has a value
SpanName: LLM
JsonPathInSpan:
attributes.input.valueJsonPathInSpanValue: Because the content of the JsonPathInSpan element is a JSON string, enter
text[0]here.
Answer Extraction Configuration

SpanName: LLM
JsonPathInSpan:
attributes.output.valueJsonPathInSpanValue: This parameter is empty.
Context Extraction Configuration
The sample service in this topic does not include a context extraction configuration. For an example of a context extraction configuration, see the following figure:

SpanName: retrieve
JsonPathInSpan:
attributes.retrieval.documents[*].document.contentImportantOnly the context configuration supports using an asterisk (*).
JsonPathInSpanValue: Because the content of the JsonPathInSpan element is not a JSON string, this parameter is empty.
After you configure the parameters, click OK.
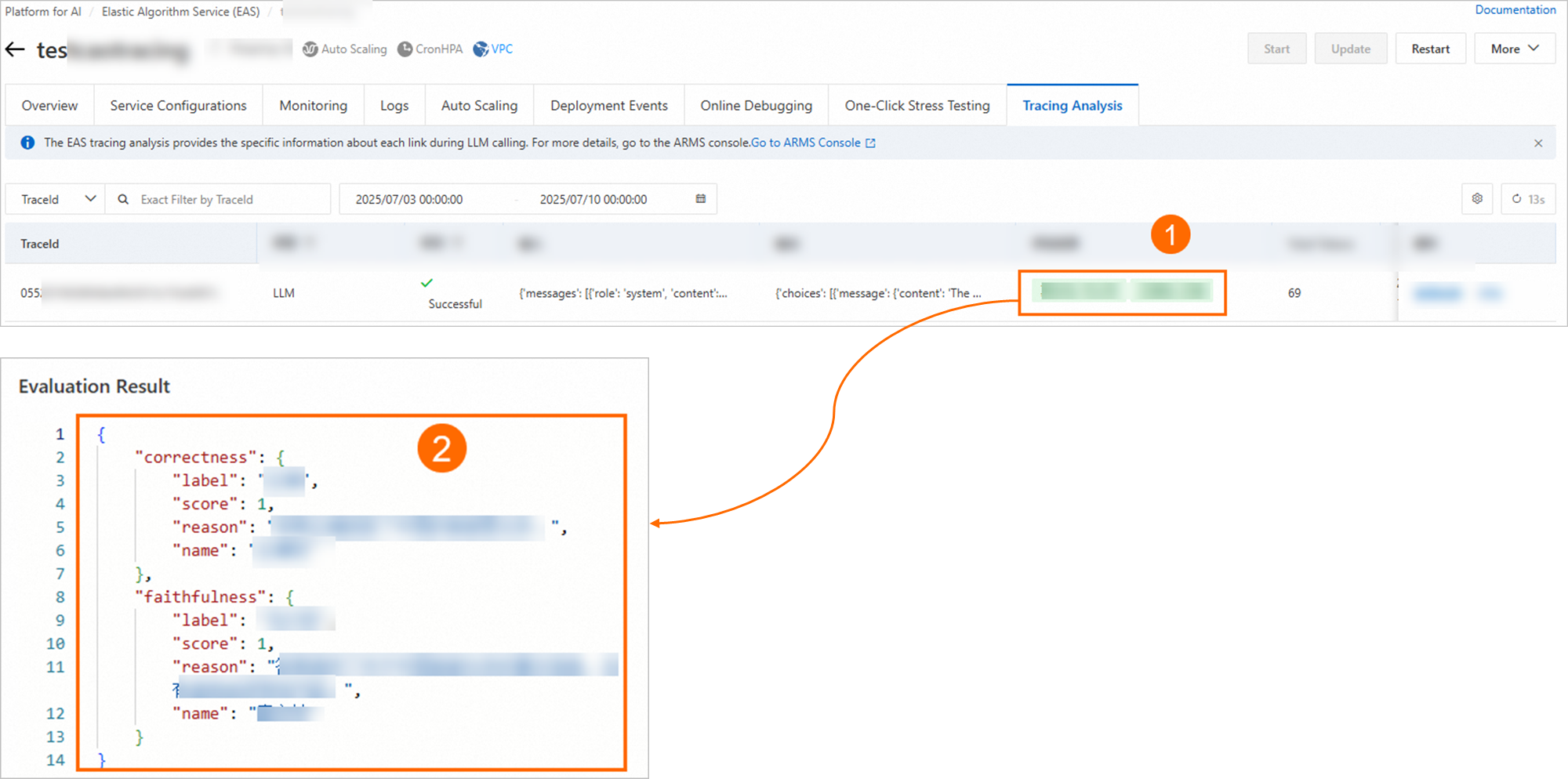
When a result appears in the Evaluation Result column as shown in the following figure, the evaluation is successful. You can click the evaluation result to view its details.
Method 2: Evaluate traces in batches online
On the Online Evaluation tab of the Tracing tab, click Create Evaluation.
On the Create Evaluation Task page, configure the following parameters and then click OK.
Parameter
Description
Basic Configuration
Task Name
Enter a custom task name based on the prompts on the interface.
Evaluation Configuration
Evaluation Metrics
This is a fixed configuration and cannot be changed. The evaluation is performed based on the following dimensions:
Correctness: Determines whether the answer correctly addresses the question based on the input and reference text.
Faithfulness: Determines whether the answer is generated based on the input and reference text and whether it contains hallucinations.
Retrieval Relevance: Determines whether the retrieved content is relevant to the input question. It includes the following four metrics:
nDCG: Normalized Discounted Cumulative Gain
Hit Rate
Precision@K
MRR: Mean Reciprocal Rank
Model Selection
Two models are supported:
PAI Judge Model
qwen-max (Model Studio model)
NoteTo use a Model Studio model, you need to configure an Internet connection for EAS.
Calls to Model Studio models are billed separately. For more information, see Billing.
Model Token
Enter the token for the selected model:
Judge model: Go to the Judge Model page to activate the service and obtain a token.
qwen-max: To obtain a token for the Model Studio qwen-max model, see Call the Tongyi Qianwen API for the first time.
Sampling Start and End Time
Select the start and end dates for sampling.
Sampling Policy
Two sampling policies are supported:
Sample by time window: Samples one trace every x minutes.
Sample by probability: Randomly samples a specified percentage of traces.
QCA Extraction Configuration: Trace data is a JSON-formatted string. QCA extraction configuration specifies the path of the Q, C, and A (Question, Context, Answer) within the JSON string. The value at that path constitutes the QCA content.
Query Extraction Configuration
Query extraction configuration: Extracts the user's query (input).
Answer extraction configuration: Extracts the answer generated by the system (output).
Context extraction configuration: Extracts the text or background information provided to the system (documents).
Configure the SpanName, JsonPathInSpan, and JsonPathInSpanValue parameters to extract the corresponding content. For more information about how to configure these parameters, see Extraction Configuration.
Answer Extraction Configuration
Context Extraction Configuration
When the evaluation task Status is Completed, all sampling evaluation operations have finished, and the task will not generate any new evaluation results.
After the evaluation is complete, you can view the results in the Evaluation Result column of the task list. You can also click the task name to view its details.
View evaluation results: The system dynamically calculates and displays the average score from successful traces. A value closer to 1 indicates stronger relevance.

View evaluation details:

You can perform management operations on the evaluation task, such as Update, Stop, Delete, and Clone. The Clone action copies the task configuration to create a new evaluation task.