When you no longer need a bucket, delete it to stop billing. Object Storage Service (OSS) charges are primarily for resources within a bucket. Before you can delete a bucket, you must clear all of its resources. Deleting the bucket is the most reliable way to ensure that you do not miss any billable resources and incur unexpected fees. Note that data cannot be recovered after it is deleted. The bucket name also becomes available for other users to register. To stop using the OSS service completely, you must delete all buckets under your account.

Risk assessment before deletion
Risk of data being unrecoverable
Deleting a bucket permanently removes all files, including previous versions and parts. This operation is irreversible. Make sure to back up your data in advance.
Risk of business interruption
Deleting the bucket causes immediate interruptions for websites, apps, or CDN services that depend on it. Make sure that no services are accessing the bucket.
Risk of bucket name squatting
After a bucket is deleted, its name enters a cool-down period of 4 to 8 hours before it is released. To reserve the name, empty the files instead of deleting the bucket.
Risk of synchronous deletion
If cross-region or same-region replication is enabled, the delete operation may also clear data from the destination bucket. Check your configuration.
Cost and time estimation
Cleaning up many files may incur API request fees and take several hours or longer, depending on the number of files.
Check resources that must be deleted
If you attempt to delete a bucket that contains resources such as Files, Parts, Access Points, Accelerators, or RTMP Ingest URLs, an error message indicates that the bucket is not empty. Use the deletion wizard in the OSS console. The wizard automatically scans for and lists all items that must be deleted.
Log on to the OSS console.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Buckets. On the Buckets page, find and click the desired bucket.
In the left navigation pane, scroll to the bottom and click Delete Bucket.
On the Delete Bucket page, click the Delete Bucket button. You can then view the items that must be cleared.

Clean up resources that must be deleted
Before you can delete a bucket, you must clear all resources within it. Clean up the remaining resources that are detected by the system. If you have many files, we recommend that you use lifecycle rules to process them automatically.
Clean up files
If the status column for the Files resource shows that the HDFS feature is enabled, you must delete the HDFS files first. If versioning is enabled, the OSS file list displays both current and previous versions. Therefore, when you select and delete all files, all their versions are also deleted.
OSS objects
Use the OSS console
On the Delete Bucket page, click Delete Bucket. Then, find the Objects resource and click Delete.
Select all the objects and click Permanently Delete at the bottom.
In the dialog box that appears, click OK.
Use ossutil
Delete all files in the bucket, including current and previous versions.
ossutil rm oss://examplebucket/ -rFor more information, see rm (delete).
HDFS files
Use the OSS console
For the Objects resource, click Pause Now in the status column to pause the HDFS background task.
Click Delete to navigate to the HDFS tab.
Click Permanently Delete for each HDFS file.
Use HDFS Shell commands
hdfs dfs -rm -r -skipTrash oss://examplebucket.cn-hangzhou.oss-dls.aliyuncs.com/*For more information, see Perform common operations for the OSS-HDFS service using HDFS shell commands.
Clean up parts
Parts are unmerged file fragments that are generated by the multipart upload feature.
Use the OSS console
On the Delete Bucket page, click Delete Bucket and then click Delete for the Parts resource.
On the Object page, click the Parts tab.
In the Parts panel, click Delete All.
In the dialog box, click OK.
Use ossutil
Delete all parts from incomplete or canceled multipart uploads.
ossutil rm oss://examplebucket -m -r -fFor more information, see rm (delete).
Delete access points
In the left navigation pane, click Access Point.
For each access point, click Delete Access Point.
Follow the instructions to delete the corresponding access policy.
After you delete the access policy, return to the access point list. Enter the access point name as prompted and click OK to complete the deletion.
Delete accelerators
Note that deleting an accelerator only clears the data cached in the accelerator. The data in the OSS bucket is not affected.
In the left navigation pane, click Bucket Settings > Accelerator.
In the OSS accelerator list, click Delete in the Actions column.
Enter the accelerator name and click OK to confirm the deletion.

Clean up RTMP ingest URLs
You cannot view or delete LiveChannels for a bucket using tools or the console. You can perform these operations by calling an API or an SDK. For more information, see the DeleteLiveChannel API documentation. The following Java code provides an example of how to delete a specified LiveChannel.
import com.aliyun.oss.ClientBuilderConfiguration;
import com.aliyun.oss.OSS;
import com.aliyun.oss.OSSClientBuilder;
import com.aliyun.oss.OSSException;
import com.aliyun.oss.common.auth.CredentialsProviderFactory;
import com.aliyun.oss.common.auth.EnvironmentVariableCredentialsProvider;
import com.aliyun.oss.common.comm.SignVersion;
import com.aliyun.oss.model.LiveChannelGenericRequest;
/**
* This sample code shows how to delete a specified LiveChannel.
* This program demonstrates how to delete a LiveChannel in Alibaba Cloud OSS.
*/
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// The OSS endpoint. Select an endpoint based on the region. This example uses the endpoint of the China (Hangzhou) region.
String endpoint = "https://oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com";
// Obtain access credentials from environment variables. Before you run this code, make sure that the OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID and OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET environment variables are set.
EnvironmentVariableCredentialsProvider credentialsProvider = CredentialsProviderFactory.newEnvironmentVariableCredentialsProvider();
// Specify the bucket name, for example, examplebucket.
String bucketName = "examplebucket";
// Specify the LiveChannel name.
String liveChannelName = "yourLiveChannelName";
// Specify the region where the bucket is located. For example, if the bucket is in the China (Hangzhou) region, set Region to cn-hangzhou.
String region = "cn-hangzhou";
// Create an OSSClient instance.
// When the OSSClient instance is no longer needed, call the shutdown method to release its resources.
ClientBuilderConfiguration clientBuilderConfiguration = new ClientBuilderConfiguration();
clientBuilderConfiguration.setSignatureVersion(SignVersion.V4);
OSS ossClient = OSSClientBuilder.create()
.endpoint(endpoint)
.credentialsProvider(credentialsProvider)
.clientConfiguration(clientBuilderConfiguration)
.region(region)
.build();
try {
// Create a request to delete the LiveChannel.
LiveChannelGenericRequest request = new LiveChannelGenericRequest(bucketName, liveChannelName);
// Execute the delete operation.
ossClient.deleteLiveChannel(request);
} catch (OSSException oe) {
// Handle exceptions returned by the OSS service.
oe.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("Caught an OSSException, which means your request made it to OSS, "
+ "but was rejected with an error response for some reason.");
System.out.println("Error Message:" + oe.getErrorMessage());
System.out.println("Error Code:" + oe.getErrorCode());
System.out.println("Request ID:" + oe.getRequestId());
System.out.println("Host ID:" + oe.getHostId());
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Caught an unexpected exception:");
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (ossClient != null) {
// Release the OSSClient resources.
ossClient.shutdown();
}
}
}
}Delete the bucket
After you confirm that all resources in the bucket are deleted, you can delete the bucket.
Use the OSS console
Navigate to the Delete Bucket page for the target bucket.
Click Delete Bucket. In the dialog box that appears, click Delete, then OK.
ossutil
The following command deletes the examplebucket bucket.
ossutil api delete-bucket --bucket examplebucketFor more information, see delete-bucket.
OSS SDK
The following sections provide code examples for deleting a bucket using common SDKs. For code examples that use other SDKs, see SDK overview.
Java
import com.aliyun.oss.*;
import com.aliyun.oss.common.auth.*;
import com.aliyun.oss.common.comm.SignVersion;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// In this example, the endpoint of the China (Hangzhou) region is used. Specify your actual endpoint.
String endpoint = "https://oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com";
// Obtain access credentials from environment variables. Before you run the sample code, make sure that the OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID and OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET environment variables are configured.
EnvironmentVariableCredentialsProvider credentialsProvider = CredentialsProviderFactory.newEnvironmentVariableCredentialsProvider();
// Specify the name of the bucket. Example: examplebucket.
String bucketName = "examplebucket";
// Specify the region in which the bucket is located. For example, if the bucket is located in the China (Hangzhou) region, set the region to cn-hangzhou.
String region = "cn-hangzhou";
// Create an OSS Client instance.
// Call the shutdown method to release associated resources when the OSS Client is no longer in use.
ClientBuilderConfiguration clientBuilderConfiguration = new ClientBuilderConfiguration();
clientBuilderConfiguration.setSignatureVersion(SignVersion.V4);
OSS ossClient = OSSClientBuilder.create()
.endpoint(endpoint)
.credentialsProvider(credentialsProvider)
.clientConfiguration(clientBuilderConfiguration)
.region(region)
.build();
try {
// Delete the bucket.
ossClient.deleteBucket(bucketName);
} catch (OSSException oe) {
System.out.println("Caught an OSSException, which means your request made it to OSS, "
+ "but was rejected with an error response for some reason.");
System.out.println("Error Message:" + oe.getErrorMessage());
System.out.println("Error Code:" + oe.getErrorCode());
System.out.println("Request ID:" + oe.getRequestId());
System.out.println("Host ID:" + oe.getHostId());
} catch (ClientException ce) {
System.out.println("Caught an ClientException, which means the client encountered "
+ "a serious internal problem while trying to communicate with OSS, "
+ "such as not being able to access the network.");
System.out.println("Error Message:" + ce.getMessage());
} finally {
if (ossClient != null) {
ossClient.shutdown();
}
}
}
} Python
import argparse
import alibabacloud_oss_v2 as oss
# Create a command-line argument parser and describe that this script is used to delete a specified OSS bucket.
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Delete a specified OSS bucket.")
# Add the --region command-line argument, which specifies the region where the bucket is located. This argument is required.
parser.add_argument('--region', help='The region in which the bucket is located.', required=True)
# Add the --bucket command-line argument, which specifies the name of the bucket. This argument is required.
parser.add_argument('--bucket', help='The name of the bucket to delete.', required=True)
# Add the --endpoint command-line argument, which specifies the domain name that other services can use to access OSS. This argument is not required.
parser.add_argument('--endpoint', help='The domain names that other services can use to access OSS.')
def main():
"""
The main function, which is used to parse command-line arguments and delete the specified bucket.
"""
args = parser.parse_args() # Parse command-line arguments.
# Load credentials from environment variables for identity verification.
credentials_provider = oss.credentials.EnvironmentVariableCredentialsProvider()
# Use the default configurations of the SDK and set the credential provider and region.
cfg = oss.config.load_default()
cfg.credentials_provider = credentials_provider
cfg.region = args.region
# If the endpoint parameter is provided, set the endpoint in the configuration.
if args.endpoint is not None:
cfg.endpoint = args.endpoint
# Create an OSS client based on the configurations.
client = oss.Client(cfg)
# Construct a request to delete the specified bucket.
request = oss.DeleteBucketRequest(bucket=args.bucket)
try:
# Send the request and obtain the response.
result = client.delete_bucket(request)
# Print the status code and request ID of the response.
print(f'status code: {result.status_code},'
f' request id: {result.request_id}')
except oss.exceptions.OssError as e:
# Catch and print possible exceptions.
print(f"Failed to delete bucket: {e}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main() # The script entry point. The main function is called when the file is run.
Go
package main
import (
"context"
"flag"
"log"
"github.com/aliyun/alibabacloud-oss-go-sdk-v2/oss"
"github.com/aliyun/alibabacloud-oss-go-sdk-v2/oss/credentials"
)
var (
region string
bucketName string
)
func init() {
// Define command line parameters to specify the region and name of the bucket.
flag.StringVar(®ion, "region", "", "The region in which the bucket is located.")
flag.StringVar(&bucketName, "bucket", "", "The name of the bucket.")
}
func main() {
// Parse command line parameters.
flag.Parse()
// Check whether the name of the bucket is specified.
if len(bucketName) == 0 {
flag.PrintDefaults()
log.Fatalf("invalid parameters, bucket name required")
}
// Check whether the region is specified.
if len(region) == 0 {
flag.PrintDefaults()
log.Fatalf("invalid parameters, region required")
}
// Load the default configurations and specify the credential provider and region.
cfg := oss.LoadDefaultConfig().
WithCredentialsProvider(credentials.NewEnvironmentVariableCredentialsProvider()).
WithRegion(region)
// Create an OSS client.
client := oss.NewClient(cfg)
// Create a request object for deletion.
request := &oss.DeleteBucketRequest{
Bucket: oss.Ptr(bucketName),
}
// Call the DeleteBucket method.
result, err := client.DeleteBucket(context.TODO(), request)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("failed to delete bucket %v", err)
}
// Display the result.
log.Printf("delete bucket result:%#v\n", result)
}
PHP
<?php
require_once __DIR__ . '/../vendor/autoload.php'; // Automatically load objects and dependency libraries.
use AlibabaCloud\Oss\V2 as Oss;
// Specify command line parameters.
$optsdesc = [
"region" => ['help' => The region in which the bucket is located.', 'required' => True], // (Required) Specify the region in which the bucket is located. Example: oss-cn-hangzhou.
"endpoint" => ['help' => The domain names that other services can use to access OSS.', 'required' => False], // (Optional) Specify the endpoint that can be used by other services to access OSS.
"bucket" => ['help' => The name of the bucket, 'required' => True], // (Required) Specify the name of the bucket.
];
$longopts = \array_map(function ($key) {
return "$key:"; // Add a colon (:) to the end of each parameter to indicate that a value is required.
}, array_keys($optsdesc));
// Parse the command line parameters.
$options = getopt("", $longopts);
// Check whether the required parameters are configured.
foreach ($optsdesc as $key => $value) {
if ($value['required'] === True && empty($options[$key])) {
$help = $value['help'];
echo "Error: the following arguments are required: --$key, $help"; // Specifies that the required parameters are not configured.
exit(1);
}
}
// Obtain the values of the command line parameters.
$region = $options["region"]; // The region in which the bucket is located.
$bucket = $options["bucket"]; // The name of the bucket.
// Use environment variables to load the credential information (AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret).
$credentialsProvider = new Oss\Credentials\EnvironmentVariableCredentialsProvider();
// Use the default configurations of the SDK.
$cfg=Oss\Config::loadDefault(); // Load the default configurations of the SDK.
$cfg->setCredentialsProvider($credentialsProvider); // Specify the credential provider.
$cfg->setRegion($region); // Specify the region.
if (isset($options["endpoint"])) {
$cfg->setEndpoint($options["endpoint"]); // Specify the endpoint if an endpoint is provided.
}
// Create an OSSClient instance.
$client = new Oss\Client($cfg);
// Create a request to delete the bucket.
$request = new Oss\Models\DeleteBucketRequest($bucket);
// Use the deleteBucket method to delete the bucket.
$result = $client->deleteBucket($request);
// Display the returned result.
printf(
'status code:' . $result-> statusCode. PHP_EOL . // The HTTP response status code.
'request id:' . $result->requestId // The unique identifier of the request.
);
Node.js
const OSS = require('ali-oss');
const client = new OSS({
// Specify the region in which the bucket is located. For example, if the bucket is located in the China (Hangzhou) region, set the region to oss-cn-hangzhou.
region: 'yourregion',
// Obtain access credentials from environment variables. Before you run the sample code, make sure that you have configured environment variables OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID and OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET.
accessKeyId: process.env.OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID,
accessKeySecret: process.env.OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET,
authorizationV4: true,
// Specify the name of your bucket.
bucket: 'yourBucketName',
});
async function deleteBucket() {
try {
// Specify the name of the bucket.
const result = await client.deleteBucket('yourbucketname');
console.log(result);
} catch (err) {
console.log(err);
}
}
deleteBucket();.NET
using System;
using Aliyun.OSS;
using Aliyun.OSS.Common;
namespace Samples
{
public class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Specify the endpoint of the region in which the bucket is located. For example, if the bucket is located in the China (Hangzhou) region, set the endpoint to https://oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com.
var endpoint = "https://oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com";
// Obtain access credentials from environment variables. Before you run the sample code, make sure that the OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID and OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET environment variables are configured.
var accessKeyId = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID");
var accessKeySecret = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET");
// Specify the name of the bucket. Example: examplebucket.
var bucketName = "examplebucket314";
// Specify the region in which the bucket is located. For example, if the bucket is located in the China (Hangzhou) region, set the region to cn-hangzhou.
const string region = "cn-hangzhou";
// Create a ClientConfiguration instance and modify parameters as required.
var conf = new ClientConfiguration();
// Use the signature algorithm V4.
conf.SignatureVersion = SignatureVersion.V4;
// Create an OSSClient instance.
var client = new OssClient(endpoint, accessKeyId, accessKeySecret, conf);
client.SetRegion(region);
try
{
client.DeleteBucket(bucketName);
Console.WriteLine("Delete bucket succeeded");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine("Delete bucket failed. {0}", ex.Message);
}
}
}
}Android
DeleteBucketRequest deleteBucketRequest = new DeleteBucketRequest("bucketName");
// Asynchronously delete the bucket.
OSSAsyncTask deleteBucketTask = oss.asyncDeleteBucket(deleteBucketRequest, new OSSCompletedCallback<DeleteBucketRequest, DeleteBucketResult>() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(DeleteBucketRequest request, DeleteBucketResult result) {
Log.d("asyncDeleteBucket", "Success!");
}
@Override
public void onFailure(DeleteBucketRequest request, ClientException clientException, ServiceException serviceException) {
// Handle request exceptions.
if (clientException != null) {
// Handle client exceptions, such as network exceptions.
clientException.printStackTrace();
}
if (serviceException != null) {
// Handle service exceptions.
Log.e("ErrorCode", serviceException.getErrorCode());
Log.e("RequestId", serviceException.getRequestId());
Log.e("HostId", serviceException.getHostId());
Log.e("RawMessage", serviceException.getRawMessage());
}
}
});iOS
OSSDeleteBucketRequest * delete = [OSSDeleteBucketRequest new];
// Specify the name of the bucket. Example: examplebucket.
delete.bucketName = @"examplebucket";
OSSTask * deleteTask = [client deleteBucket:delete];
[deleteTask continueWithBlock:^id(OSSTask *task) {
if (!task.error) {
NSLog(@"delete bucket success!");
} else {
NSLog(@"delete bucket failed, error: %@", task.error);
}
return nil;
}];
// Implement synchronous blocking to wait for the task to complete.
// [getdeleteTask waitUntilFinished];C++
#include <alibabacloud/oss/OssClient.h>
using namespace AlibabaCloud::OSS;
int main(void)
{
/* Initialize information about the account that is used to access OSS. */
/* Specify the endpoint of the region in which the bucket is located. For example, if the bucket is located in the China (Hangzhou) region, set the endpoint to https://oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com. */
std::string Endpoint = "yourEndpoint";
/* Specify the region in which the bucket is located. For example, if the bucket is located in the China (Hangzhou) region, set the region to cn-hangzhou. */
std::string Region = "yourRegion";
/* Specify the name of the bucket. Example: examplebucket. */
std::string BucketName = "examplebucket";
/* Initialize resources, such as network resources. */
InitializeSdk();
ClientConfiguration conf;
conf.signatureVersion = SignatureVersionType::V4;
/* Obtain access credentials from environment variables. Before you run the sample code, make sure that the OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID and OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET environment variables are configured. */
auto credentialsProvider = std::make_shared<EnvironmentVariableCredentialsProvider>();
OssClient client(Endpoint, credentialsProvider, conf);
client.SetRegion(Region);
/* Delete the bucket. */
DeleteBucketRequest request(BucketName);
auto outcome = client.DeleteBucket(request);
if (outcome.isSuccess()) {
std::cout << "Delete bucket successfully." << std::endl;
} else {
std::cout << "Failed to delete bucket. Error code: " << outcome.error().Code()
<< ", Message: " << outcome.error().Message()
<< ", RequestId: " << outcome.error().RequestId() << std::endl;
}
/* Release resources, such as network resources. */
ShutdownSdk();
return 0;
}C
#include "oss_api.h"
#include "aos_http_io.h"
/* Specify the endpoint of the region in which the bucket is located. For example, if the bucket is located in the China (Hangzhou) region, set the endpoint to https://oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com. */
const char *endpoint = "yourEndpoint";
/* Specify the name of the bucket. Example: examplebucket. */
const char *bucket_name = "examplebucket";
/* Specify the region in which the bucket is located. For example, if the bucket is located in the China (Hangzhou) region, set the region to cn-hangzhou. */
const char *region = "yourRegion";
void init_options(oss_request_options_t *options)
{
options->config = oss_config_create(options->pool);
/* Use a char* string to initialize data of the aos_string_t type. */
aos_str_set(&options->config->endpoint, endpoint);
/* Obtain access credentials from environment variables. Before you run the sample code, make sure that the OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID and OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET environment variables are configured. */
aos_str_set(&options->config->access_key_id, getenv("OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID"));
aos_str_set(&options->config->access_key_secret, getenv("OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET"));
// Specify two additional parameters.
aos_str_set(&options->config->region, region);
options->config->signature_version = 4;
/* Specify whether to use CNAME to access OSS. A value of 0 indicates that CNAME is not used. */
options->config->is_cname = 0;
/* Configure network parameters, such as the timeout period. */
options->ctl = aos_http_controller_create(options->pool, 0);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
/* Call the aos_http_io_initialize method in main() to initialize global resources, such as network resources and memory resources. */
if (aos_http_io_initialize(NULL, 0) != AOSE_OK) {
exit(1);
}
/* Create a memory pool to manage memory. aos_pool_t is equivalent to apr_pool_t. The code used to create a memory pool is included in the APR library. */
aos_pool_t *pool;
/* Create a memory pool. The value of the second parameter is NULL. This value indicates that the pool does not inherit other memory pools. */
aos_pool_create(&pool, NULL);
/* Create and initialize options. This parameter includes global configuration information, such as endpoint, access_key_id, access_key_secret, is_cname, and curl. */
oss_request_options_t *oss_client_options;
/* Allocate the memory resources in the memory pool to the options. */
oss_client_options = oss_request_options_create(pool);
/* Initialize oss_client_options. */
init_options(oss_client_options);
/* Initialize the parameters. */
aos_string_t bucket;
aos_table_t *resp_headers = NULL;
aos_status_t *resp_status = NULL;
/* Assign char* data to a bucket of the aos_string_t type. */
aos_str_set(&bucket, bucket_name);
/* Delete the bucket. */
resp_status = oss_delete_bucket (oss_client_options, &bucket, &resp_headers);
if (aos_status_is_ok(resp_status)) {
printf("delete bucket succeeded\n");
} else {
printf("delete bucket failed\n");
}
/* Release the memory pool. This operation releases the memory resources allocated for the request. */
aos_pool_destroy(pool);
/* Release the allocated global resources. */
aos_http_io_deinitialize();
return 0;
}Ruby
require 'aliyun/oss'
client = Aliyun::OSS::Client.new(
# In this example, the endpoint of the China (Hangzhou) region is used. Specify your actual endpoint.
endpoint: 'https://oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com',
# Obtain access credentials from environment variables. Before you run the sample code, make sure that the OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID and OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET environment variables are configured.
access_key_id: ENV['OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID'],
access_key_secret: ENV['OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET']
)
# Specify the name of the bucket. Example: examplebucket.
client.delete_bucket('examplebucket')Automatically clean up large numbers of files and parts
When a bucket contains many files, such as millions or more, configuring a lifecycle rule is the most efficient and cost-effective way to clean them up. This method involves setting a rule to delete expired objects. The system then automatically deletes all data in the bucket after a specified time. If you are not familiar with lifecycle rules, test them in a test bucket first.
Note that file deletion is irreversible. Proceed with caution.
For buckets with versioning disabled
For buckets with versioning disabled, you can configure a single lifecycle rule to automatically and quickly delete all files and parts (unmerged parts from multipart uploads).
Log on to the OSS console. Go to the Buckets page and find the target bucket.
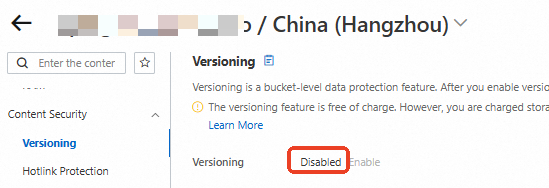
In the navigation pane on the left, choose . Verify that versioning is disabled for the bucket.
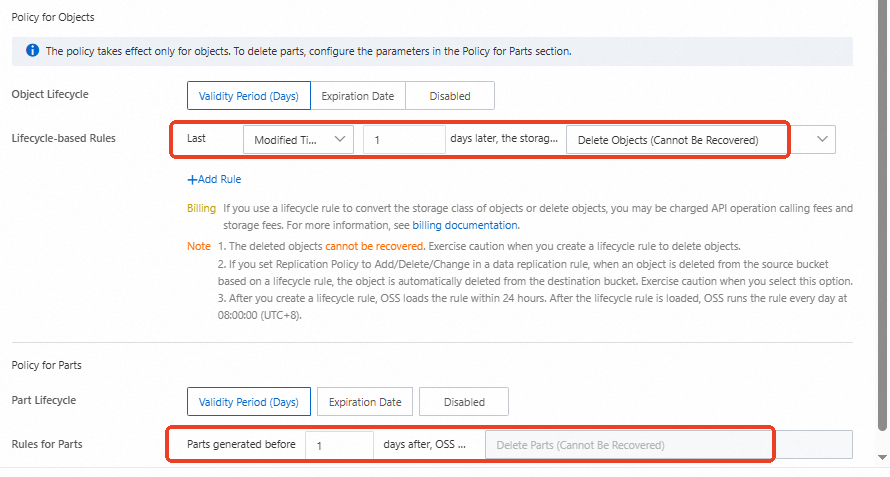
In the navigation pane on the left, choose . Set a lifecycle rule that automatically deletes files 1 day after their last modification and deletes parts that are more than 1 day old.
For buckets with versioning enabled
When versioning is enabled, a bucket can contain current file versions, previous file versions, parts, and delete markers. You can configure a single lifecycle rule to automatically and quickly clean up these items.
Log on to the OSS console. Go to the Buckets page and find the target bucket.
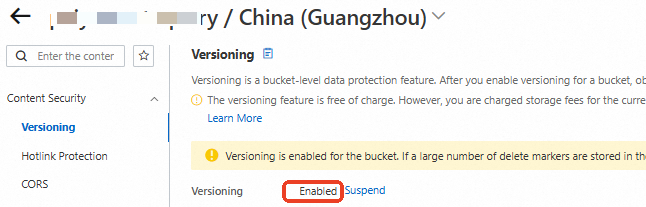
In the navigation pane on the left, choose . Verify that versioning is enabled for the bucket.
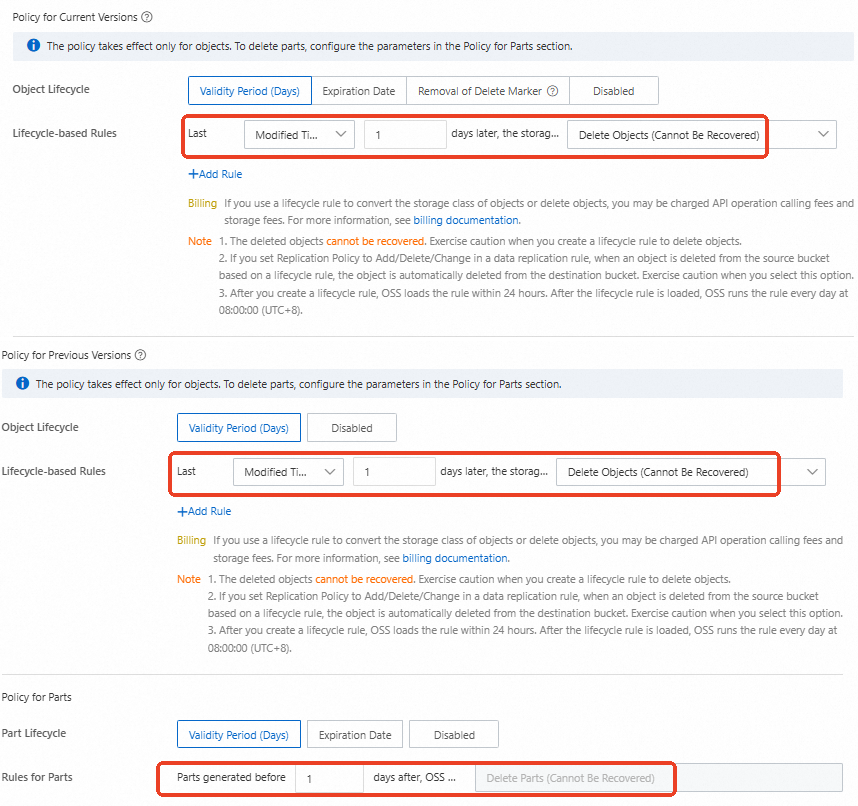
In the navigation pane on the left, choose . Set a lifecycle rule to automatically delete all current and previous file versions 1 day after they are last modified, delete parts that are more than 1 day old, and remove delete markers.
FAQ
What do I do if I get a "Bucket is not empty" error?
This error indicates that the bucket still contains resources. Use the OSS console to check for remaining resources. Then, clean up the resources and try to delete the bucket again. For more information, see Clean up resources that must be deleted.
Why can't I immediately create a bucket with the same name after I delete it?
After you delete a bucket, its name enters a cool-down period of 4 to 8 hours. During this period, no user can create a new bucket with the same name. To create a bucket immediately, you must use a different name.
After the cool-down period ends, the name becomes available to all users. If you do not recreate the bucket promptly, another user may register the name before you can.
How do I delete multiple buckets in a batch operation?
Batch deletion is a high-risk operation that can cause permanent data loss. Before you proceed, double-check the list of buckets that you want to delete and make sure that you have backed up all necessary data.
The OSS console does not support batch deletion. However, you can write a script that uses ossutil to perform this operation.
The core logic is as follows:
Prepare a list: Create an accurate text file or list that contains the names of all the buckets that you want to delete.
Execute in a loop: Your script must traverse the list and perform the following two key steps for each bucket name.
Empty the resources: Call the ossutil command to empty the bucket.
Delete the empty bucket: After you confirm that the previous step is successful, call the ossutil command to delete the bucket.
What do I do if I get an "Insufficient permissions" error during deletion?
To delete a bucket, you must first clear all of its resources. This process requires multiple permissions, such as list and delete permissions. We recommend that you contact an administrator to grant the AliyunOSSFullAccess permission to your RAM identity. This prevents deletion failures that are caused by missing permissions.
How do I completely stop billing for OSS?
To stop all charges for Object Storage Service (OSS) completely, you must delete all buckets under your account. As long as a bucket exists in your account, even if it is empty, or if you have outstanding bills, you may still incur OSS-related charges.
Can I recover a bucket after I accidentally delete it?
No, you cannot. A delete operation is irreversible. Always back up your data before you delete a bucket.