Network Attached Storage (NAS) volumes are ideal for scenarios such as big data analytics, data sharing, web applications, and log persistence. Instead of manually creating and configuring static storage resources, you can use a persistent volume claim (PVC) and a StorageClass to dynamically provision them. Doing so allows the system to automatically create a persistent volume (PV) for you. You can mount a dynamically provisioned NAS volume using three methods: subpath, sharepath, and filesystem.
Prerequisites
The CSI plug-in is installed in the cluster. If an upgrade is required, refer to Upgrade csi-plugin and csi-provisioner.
NoteIf your cluster uses FlexVolume, upgrade to CSI, because FlexVolume is deprecated. For details, see Upgrade from FlexVolume to CSI. To verify your storage component type, go to the Add-ons page, and click the Storage tab.
The File Storage NAS service is activated.
If you are using it for the first time, follow the on-screen instructions on the File Storage NAS product page to activate the service.
Limitations
Mounting NAS file systems that use the SMB protocol is not supported.
NAS file systems can only be mounted to pods within the same virtual private cloud (VPC). Cross-VPC mounting is not supported.
NoteWithin the same VPC, NAS volumes can be mounted across different availability zones (AZs).
General-purpose and Extreme NAS file systems have different constraints regarding connectivity, the number of file systems, and protocol types. For details, see Limits.
Usage notes
NAS is a shared storage service. A single NAS volume can be mounted to multiple pods. If multiple pods write data simultaneously, applications must independently ensure data consistency.
For more information about the limits on concurrent writes to NAS, see How do I prevent exceptions that may occur when multiple processes or clients concurrently write data to a log file? and How do I resolve the latency in writing data to an NFS file system?
If your application template includes the
securityContext.fsgroupparameter, kubelet performschmodorchownoperations after mounting, which can increase mount time.Avoid this setting to reduce latency. For more details, see Extended mount times for NAS volumes.
Do not delete the NAS mount target after mounting. Doing so may cause the system to become unresponsive.
Mounting methods
The volumeAs parameter in a StorageClass defines the relationship between a PV and a NAS file system or its subdirectory. Select a mounting method as needed.
Mounting method | Description | Use cases |
Creates a subdirectory-type PV, where each PV corresponds to a unique subdirectory within the same NAS file system. |
| |
Creates PVs that all point to the same shared directory specified in the StorageClass. No new subdirectories are created per PV. | Multiple pods across different namespaces need to mount the same NAS subdirectory. | |
Using filesystem (Not recommended) | Automatically creates a NAS file system for each PV. One PV corresponds to an entire NAS file system. | An application requires a dedicated NAS file system that needs to be dynamically created and deleted with the workload. |
Mount using the subpath method
The subpath method requires Container Storage Interface (CSI) component version 1.31.4 or later. To upgrade, see Upgrade csi-plugin and csi-provisioner.
Step 1: Get NAS file system and mount target information
Log on to the NAS console. In the left navigation pane, choose .
Create a NAS file system and a mount target.
Ensure the file system uses the Network File System (NFS) protocol and the mount target is in the same VPC as your cluster nodes.
If you have an existing NAS file system, make sure that it meets these requirements.
If you don't have an existing NAS file system, create one. For instructions, see Create a file system and Manage mount targets.
Get the mount target address.
Click the file system ID. In the left navigation pane, click Mount Targets.
In the Mount Target section, confirm the status is Available and copy the mount target address.
Step 2: Create a StorageClass
kubectl
Modify the following YAML manifest and save it as
alicloud-nas-subpath.yaml.apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1 kind: StorageClass metadata: name: alicloud-nas-subpath mountOptions: - nolock,tcp,noresvport - vers=3 parameters: volumeAs: subpath server: "0cd8b4a576-g****.cn-hangzhou.nas.aliyuncs.com:/k8s" archiveOnDelete: "true" provisioner: nasplugin.csi.alibabacloud.com reclaimPolicy: Retain allowVolumeExpansion: trueParameter
Description
mountOptionsThe Mount options for the NAS volume, including the NFS protocol version. We recommend using NFSv3. Extreme NAS only supports NFSv3.
parametersvolumeAsThe mount method. In this example, the value is set to
subpathto create a subdirectory-type PV. One PV corresponds to one subdirectory in a NAS file system.serverThe address of the mount target and the subdirectory of the NAS file system to mount. The format is
<NAS mount target address>:<mount directory>. If you do not specify a subdirectory, the root directory/is mounted by default.archiveOnDeleteSpecifies whether to delete the backend storage data when
reclaimPolicyis set toDelete. This parameter is added for confirmation because NAS is a shared storage service.true(default): The directory or file is retained and is renamed toarchived-{pvName}.{timestamp}.false: The backend storage resource is permanently deleted.
NoteFor high-traffic workloads, setting this parameter to
falseis not recommended. For more information, see NAS volume FAQ.To completely delete the backend storage data, you must set
parameters.archiveOnDeletetofalseusing kubectl.
provisionerThe driver type. The value must be set to
nasplugin.csi.alibabacloud.com, indicating that the Alibaba Cloud NAS CSI plugin is used.reclaimPolicyThe PV reclaim policy. The default value is
Delete.Retainis also supported.Delete: This value must be used witharchiveOnDelete.When
archiveOnDeleteistrue, the files in the NAS file system are renamed but not deleted when the PVC is deleted.When
archiveOnDeleteisfalse, the files in the NAS file system are deleted when the PVC is deleted.ImportantThe subpath directory and its files in the NAS file system will be deleted. The NAS file system itself is retained. To delete the NAS file system, see Delete a file system.
Retain: When the PVC is deleted, the PV and the files in the NAS file system are retained. You must manually delete them.
If data security is a high priority, we recommend setting this parameter to
Retainto prevent accidental data loss.allowVolumeExpansionSupported for General-purpose NAS file systems only. If set to
true, a directory quota is configured for the PV that is dynamically created by the StorageClass to limit the available capacity. You can also update the PVC to expand the volume capacity. For more information, see Expand a dynamically provisioned NAS volume.NoteThe NAS quota takes effect asynchronously. After a PV is dynamically created, the directory quota may not take effect immediately. If you write a large amount of data in a short period, the storage usage may exceed the capacity limit. See Directory quotas.
Create the StorageClass.
kubectl create -f alicloud-nas-subpath.yaml
Console
Log on to the ACK console. In the left navigation pane, click Clusters.
On the Clusters page, find the cluster you want and click its name. In the left-side pane, choose .
On the StorageClasses page, click Create.
In the dialog box that appears, configure the parameters and click OK.
The following table describes the configurations:
Configuration
Description
Example
Name
The StorageClass name. See the UI for formatting requirements.
alicloud-nas-subpath
PV Type
Select NAS.
NAS
Select Mount Target
The address of the NAS file system's mount target.
0cd8b4a576-g****.cn-hangzhou.nas.aliyuncs.com
Volume Mode
The access mode of the volume. In this example, select Subdirectory to use the subpath method. A unique subdirectory is automatically created under the mount path for each PV. Data is stored at
<NAS mount target>:<mount path>/<pv-name>/.NoteThis mode requires CSI component version 1.31.4 or later. Otherwise, the system defaults to Shared Directory mode.
Subdirectory
Mount Path
The subdirectory on the NAS file system to mount.
If not set, the root directory is mounted by default.
If the specified directory does not exist, it will be automatically created and then mounted.
NoteThe root directory is
/for General-purpose NAS file system and/sharefor Extreme NAS file system. When mounting a subdirectory on an Extreme NAS file system, thepathmust start with/share, such as/share/data./k8s
Reclaim Policy
The reclaim policy for the PV. Retain is recommended to prevent accidental data loss.
Delete: This parameter must be configure with
archiveOnDelete. In the console, selecting Delete will not actually delete the data on the NAS volume when you delete the PVC. This is because the underlyingarchiveOnDeleteparameter cannot be configured through the UI. To configurearchiveOnDelete, create the PV using a YAML manifest. For a YAML template, see the kubectl tab.Retain: When the PVC is deleted, the PV and the data on the NAS volume are not deleted. You must manually delete them.
Retain
Mount Options
The Mount options for the NAS volume, including the NFS protocol version. We recommend using NFSv3. Extreme NAS only supports NFSv3.
Keep the default value
After the StorageClass is created, you can view it in the StorageClasses list.
Step 3: Create a PVC
kubectl
Modify the YAML manifest and save it as
nas-pvc.yaml.kind: PersistentVolumeClaim apiVersion: v1 metadata: name: nas-csi-pvc spec: accessModes: - ReadWriteMany storageClassName: alicloud-nas-subpath resources: requests: storage: 20GiParameter
Description
accessModesThe access mode for the volume. The default value is
ReadWriteMany.ReadWriteOnceandReadOnlyManyare also supported.storageClassNameThe name of the StorageClass to bind.
storageThe capacity of the volume that you want to request.
ImportantBy default, the actual available capacity of a NAS volume is not limited by this configuration. It is determined by the specifications of the NAS file system. For more information, see General-purpose NAS and Extreme NAS.
If you use a General-purpose NAS file system and set
allowVolumeExpansionof the StorageClass totrue, the CSI component sets a directory quota based on this configuration to limit the available capacity of the NAS volume.
Create the PVC.
kubectl create -f nas-pvc.yamlVerify that the PV was created and bound to the PVC.
kubectl get pvcThe output should show the
STATUSasBound, indicating that the CSI component automatically created a PV based on the StorageClass and bound the PV to the PVC.NAME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES RECLAIM POLICY STATUS CLAIM STORAGECLASS VOLUMEATTRIBUTESCLASS REASON AGE nas-a7540d97-0f53-4e05-b7d9-557309****** 20Gi RWX Retain Bound default/nas-csi-pvc alicloud-nas-subpath <unset> 5m
Console
In the left-side navigation pane of the details page, choose .
On the Persistent Volume Claims page, click Create.
On the Create PVC dialog box, configure the parameters and click OK.
Configuration
Description
Example
PVC Type
Select NAS.
NAS
Name
The PVC name. It must be unique within the namespace.
pvc-nasAllocation Mode
In this example, select Use StorageClass.
Use StorageClass
Existing StorageClass
Click Select StorageClass and select the one you created in the previous step.
alicloud-nas-subpathCapacity
The capacity of the volume. This setting does not limit the maximum capacity the application can use.
ImportantBy default, the actual available capacity of a NAS volume is not limited by this configuration. It is determined by the specifications of the NAS file system. For more information, see General-purpose NAS and Extreme NAS.
If you use a General-purpose NAS file system and set
allowVolumeExpansionof the StorageClass totrue, the CSI component sets a directory quota based on this configuration to limit the available capacity of the NAS volume.
20Gi
Access Mode
The default value is ReadWriteMany. You can also select ReadWriteOnce or ReadOnlyMany.
ReadWriteMany
Step 4: Create an application and mount the NAS volume
kubectl
Create two Deployments and mount the same PVC to them. This allows them to share the same subdirectory in the same NAS file system.
To assign different pods to unique subdirectories on the same NAS file system, create a distinct StorageClass and PVC for each target directory.
Modify the following YAML manifest and save the files as
nginx-1.yamlandnginx-2.yamlrespectively.The following configurations in
nginx-1.yamlandnginx-2.yamlare the same, except for themetadata.namevalue. The two applications are bound to the same PVC.nginx-1.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: nas-test-1 labels: app: nginx spec: selector: matchLabels: app: nginx template: metadata: labels: app: nginx spec: containers: - name: nginx image: anolis-registry.cn-zhangjiakou.cr.aliyuncs.com/openanolis/nginx:1.14.1-8.6 ports: - containerPort: 80 volumeMounts: - name: nas-pvc mountPath: "/data" # The path where the NAS volume is mounted in the container volumes: - name: nas-pvc persistentVolumeClaim: claimName: nas-csi-pvc # Used to bind the PVCnginx-2.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: nas-test-2 labels: app: nginx spec: selector: matchLabels: app: nginx template: metadata: labels: app: nginx spec: containers: - name: nginx image: anolis-registry.cn-zhangjiakou.cr.aliyuncs.com/openanolis/nginx:1.14.1-8.6 ports: - containerPort: 80 volumeMounts: - name: nas-pvc mountPath: "/data" # The path where the NAS volume is mounted in the container volumes: - name: nas-pvc persistentVolumeClaim: claimName: nas-csi-pvc # Used to bind the PVCCreate the two Deployments.
kubectl create -f nginx-1.yaml -f nginx-2.yamlVerify the pods are running.
kubectl get pod -l app=nginxThe output indicates that the same subdirectory of the same NAS file system is mounted to different applications.
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE nas-test-1-b75d5b6bc-vqwq9 1/1 Running 0 51s nas-test-2-b75d5b6bc-8k9vx 1/1 Running 0 44s
Console
Repeat the following steps to create two Deployments that mount the same PVC, enabling them to share a single subdirectory within the NAS file system.
In the navigation pane on the left of the cluster details page, go to .
On the Deployments page, click Create From Image.
Configure the parameters to create the application.
The following table describes the key parameters. You can keep the default settings for other parameters. For more information, see Create a stateless workload (Deployment).
Configuration step
Parameter
Description
Example
Basic Information
Name
Enter a custom name for the Deployment. The name must meet the format requirements displayed in the console.
deployment-nas-1Replicas
Number of pod replicas.
1
Container
Image Name
The address of the image used to deploy the application.
anolis-registry.cn-zhangjiakou.cr.aliyuncs.com/openanolis/nginx:1.14.1-8.6Required Resources
The required vCPU and memory resources.
0.25 vCPU, 512 MiB
Volume
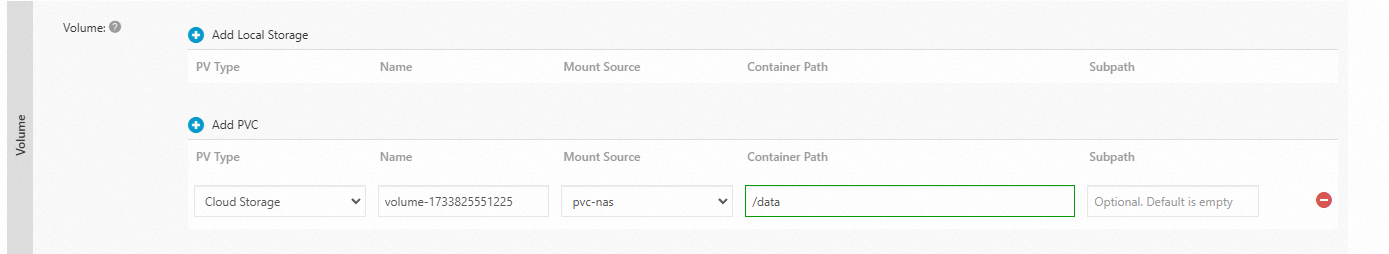
Click Add PVC and configure the parameters.
Mount Source: Select the PVC that you created.
Container Path: Specify the container path to which you want to mount the NAS file system.
Mount Source:
pvc-nasContainer Path:
/data
View the application deployment status.
On the Deployments page, click the name of the application.
On the Pods tab, confirm pods are in the Running state.
Mount using the sharepath method
Step 1: Get NAS file system and mount target information
Log on to the NAS console. In the left navigation pane, choose .
Create a NAS file system and a mount target.
Ensure the file system uses the Network File System (NFS) protocol and the mount target is in the same VPC as your cluster nodes.
If you have an existing NAS file system, make sure that it meets these requirements.
If you don't have an existing NAS file system, create one. For instructions, see Create a file system and Manage mount targets.
Get the mount target address.
Click the file system ID. In the left navigation pane, click Mount Targets.
In the Mount Target section, confirm the status is Available and copy the mount target address.
Step 2: Create a StorageClass
kubectl
Create a file named
alicloud-nas-sharepath.yamlwith the following YAML manifest and modify the parameters as needed.apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1 kind: StorageClass metadata: name: alicloud-nas-sharepath mountOptions: - nolock,tcp,noresvport - vers=3 parameters: volumeAs: sharepath server: "0cd8b4a576-g****.cn-hangzhou.nas.aliyuncs.com:/sharepath" provisioner: nasplugin.csi.alibabacloud.com reclaimPolicy: RetainParameter
Description
mountOptionsThe Mount options for the NAS volume, including the NFS protocol version. We recommend using NFSv3. Extreme NAS only supports NFSv3.
parametersvolumeAsThe mount method. In this example, the value is set to
sharepath, which indicates that when a PV is created, no actual directory will be created. Instead, the path specified in the StorageClass will be used. This means that each PV will map to the same NAS directory.serverThe mount target address and the subdirectory of the NAS file system to be mounted. The format is
<NAS mount target address>:<mount directory>.If you do not specify a subdirectory, the root directory
/is mounted by default.If the directory does not exist in the NAS file system, it will be automatically created and then mounted.
The root directory of a General-purpose NAS file system is
/, while for Extreme NAS file system is/share. When mounting a subdirectory of an Extreme NAS file system, thepathmust start with/share, such as/share/data.provisionerThe driver type. The value must be set to
nasplugin.csi.alibabacloud.com, indicating that the Alibaba Cloud NAS CSI plugin is used.reclaimPolicyThe PV reclaim policy. When you use the sharepath method, you must set this parameter to
Retain.Create the StorageClass.
kubectl create -f alicloud-nas-sharepath.yaml
Console
Log on to the ACK console. In the left navigation pane, click Clusters.
On the Clusters page, find the cluster you want and click its name. In the left-side pane, choose .
On the StorageClasses page, click Create.
In the dialog box that appears, configure the parameters and click OK.
The following table describes the key configurations:
Configuration
Description
Example
Name
The StorageClass name. See the UI for formatting requirements.
alicloud-nas-sharepathPV Type
Select NAS.
NAS
Select Mount Target
The address of the NAS file system's mount target.
0cd8b4a576-g****.cn-hangzhou.nas.aliyuncs.comVolume Mode
The access mode of the volume. In this example, select Shared Directory to use the sharepath method. When a PV is created, no actual directory is created. Instead, the path specified in the StorageClass is used. This means that each PV will map to the same NAS directory. This method is ideal for scenarios where you need to share a directory across namespaces.
Shared Directory
Mount Path
The subdirectory on the NAS file system to mount.
If not set, the root directory is mounted by default.
If the specified directory does not exist, it will be automatically created and then mounted.
NoteThe root directory is
/for General-purpose NAS file system and/sharefor Extreme NAS file system. When mounting a subdirectory on an Extreme NAS file system, thepathmust start with/share, such as/share/data./sharepathReclaim Policy
When you use the sharepath method, you must set this parameter to
Retain.Retain
Mount Options
The Mount options for the NAS volume, including the NFS protocol version. We recommend using NFSv3. Extreme NAS only supports NFSv3.
Keep the default value
After the StorageClass is created, you can view it in the Storage Classes list.
Step 3: Create a PVC
The following example shows how to create PVCs in two different namespaces.
kubectl
To mount a NAS volume to pods in different namespaces, first create two namespaces.
Create the
ns1andns2namespaces.kubectl create ns ns1 kubectl create ns ns2Modify the following YAML manifest and save it as
pvc.yaml.kind: PersistentVolumeClaim apiVersion: v1 metadata: name: nas-csi-pvc namespace: ns1 spec: accessModes: - ReadWriteMany storageClassName: alicloud-nas-sharepath resources: requests: storage: 20Gi --- kind: PersistentVolumeClaim apiVersion: v1 metadata: name: nas-csi-pvc namespace: ns2 spec: accessModes: - ReadWriteMany storageClassName: alicloud-nas-sharepath resources: requests: storage: 20GiParameter
Description
accessModesThe access mode for the volume. The default value is
ReadWriteMany.ReadWriteOnceandReadOnlyManyare also supported.storageClassNameThe name of the StorageClass to bind.
storageThe capacity of the volume that you want to request.
ImportantBy default, the actual available capacity of a NAS volume is not limited by this configuration. It is determined by the specifications of the NAS file system. For more information, see General-purpose NAS and Extreme NAS.
If you use a General-purpose NAS file system and set
allowVolumeExpansionof the StorageClass totrue, the CSI component sets a directory quota based on this configuration to limit the available capacity of the NAS volume.
Create the PVCs.
kubectl create -f pvc.yamlVerify that the PV was created and bound to the PVC.
kubectl get pvThe output should show that the CSI component automatically created two PVs based on the StorageClass and bound them to the two PVCs in different namespaces.
NAME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES RECLAIM POLICY STATUS CLAIM STORAGECLASS VOLUMEATTRIBUTESCLASS REASON AGE nas-0b448885-6226-4d22-8a5b-d0768c****** 20Gi RWX Retain Bound ns1/nas-csi-pvc alicloud-nas-sharepath <unset> 74s nas-bcd21c93-8219-4a11-986b-fd934a****** 20Gi RWX Retain Bound ns2/nas-csi-pvc alicloud-nas-sharepath <unset> 74s
Console
Create the
ns1andns2namespaces. For details, see Create a namespace.In the left-side navigation pane of the details page, choose .
Create a PVC in the
ns1namespace.On the Persistent Volume Claims page, set Namespace to ns1 and click Create.
On the Create PVC dialog box, configure the parameters and click OK.
Configuration
Description
Example
PVC Type
Select NAS.
NAS
Name
The PVC name. It must be unique within the namespace.
pvc-nasAllocation Mode
In this example, select Use StorageClass.
Use StorageClass
Existing StorageClass
Click Select StorageClass and select the one you created.
alicloud-nas-sharepathCapacity
The capacity of the volume.
20Gi
Access Mode
The default value is ReadWriteMany. You can also select ReadWriteOnce or ReadOnlyMany.
ReadWriteMany
Repeat the preceding steps to create another PVC in the
ns2namespace.Return to the Persistent Volume Claims page. In the
ns1andns2namespaces, make sure that the two PVCs are bound to the automatically created PVs.
Step 4: Create an application and mount the NAS volume
Create applications in two different namespaces and mount the PVCs in the corresponding namespaces. The applications will share the NAS directory defined in the StorageClass.
kubectl
Save the following YAML content as
nginx-ns1.yamlandnginx-ns2.yamlrespectively, and modify them as needed.The following configurations in
nginx-ns1.yamlandnginx-ns2.yamlare the same, except for themetadata.namespacevalue. The two applications are bound to the PVC in their respective namespaces.nginx-ns1.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: nas-test namespace: ns1 spec: selector: matchLabels: app: nginx template: metadata: labels: app: nginx spec: containers: - name: nginx image: anolis-registry.cn-zhangjiakou.cr.aliyuncs.com/openanolis/nginx:1.14.1-8.6 ports: - containerPort: 80 volumeMounts: - name: nas-pvc mountPath: "/data" volumes: - name: nas-pvc persistentVolumeClaim: claimName: nas-csi-pvcnginx-ns2.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: nas-test namespace: ns2 spec: selector: matchLabels: app: nginx template: metadata: labels: app: nginx spec: containers: - name: nginx image: anolis-registry.cn-zhangjiakou.cr.aliyuncs.com/openanolis/nginx:1.14.1-8.6 ports: - containerPort: 80 volumeMounts: - name: nas-pvc mountPath: "/data" volumes: - name: nas-pvc persistentVolumeClaim: claimName: nas-csi-pvcCreate the two Deployments.
kubectl create -f nginx-ns1.yaml -f nginx-ns2.yamlVerify that the pods are running.
kubectl get pod -A -l app=nginxThe output indicates that the same subdirectory of the same NAS file system is mounted to pods in different namespaces.
NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE ns1 nas-test-b75d5b6bc-ljvfd 1/1 Running 0 2m19s ns2 nas-test-b75d5b6bc-666hn 1/1 Running 0 2m11s
Console
In the navigation pane on the left of the cluster details page, go to .
Create a Deployment in the
ns1namespace and mount the corresponding PVC.Set Namespace to ns1 and click Create From Image.
Configure the parameters to create the application.
The following table describes the key parameters. You can keep the default settings for other parameters. For more information, see Create a stateless workload (Deployment).
Configuration step
Parameter
Description
Example
Basic Information
Name
Enter a custom name for the Deployment. The name must meet the format requirements displayed in the console.
nginxReplicas
Number of pod replicas.
2
Container
Image Name
The address of the image used to deploy the application.
anolis-registry.cn-zhangjiakou.cr.aliyuncs.com/openanolis/nginx:1.14.1-8.6Required Resources
The required vCPU and memory resources.
0.25 vCPU, 512 MiB
Volume
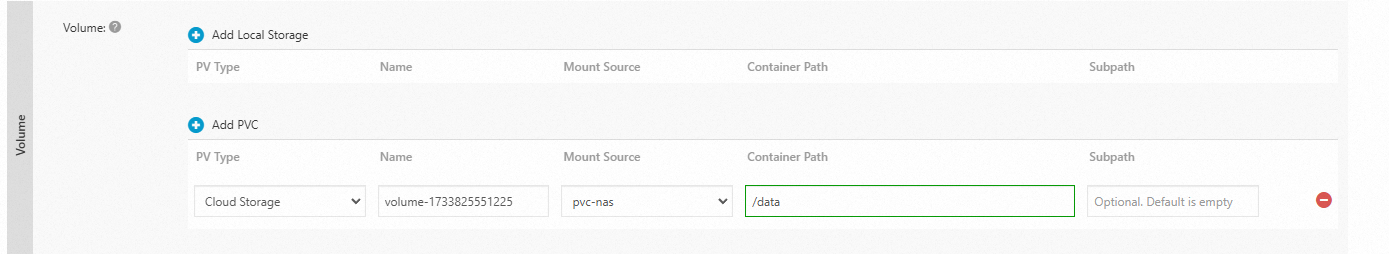
Click Add PVC and configure the parameters.
Mount Source: Select the PVC that you created.
Container Path: Specify the container path to which you want to mount the NAS file system.
Mount Source:
pvc-nasContainer Path:
/data
Repeat the preceding steps to create another Deployment in the
ns2namespace and mount the corresponding PVC.Return to the Deployments page. In the
ns1andns2namespaces, view the two Deployment statuses. Confirm the pods are running and the corresponding PVCs are mounted.
Mount using the filesystem method
If your application needs to dynamically create and delete NAS file systems and mount targets, use the filesystem method to mount a NAS volume. A pod that uses a filesystem-type NAS volume can create only one file system and one mount target.
By default, when a filesystem-type dynamically provisioned NAS volume is deleted, the file system and mount target are retained. To release the NAS file system and mount target at the same time as the PV resource is released, you must set reclaimPolicy to Delete and deleteVolume to true in the StorageClass.
Step 1: Grant RAM permissions (Required for ACK dedicated clusters only)
Step 2: Create a StorageClass
Step 3: Create a PVC
Step 4: Create an application and mount the NAS volume
Verify the shared and persistent storage of NAS
The pods created in the preceding example all mount the same NAS file system. You can use the following steps to verify its behavior:
To verify shared storage, create a file from one pod and confirm that it is visible from a second pod.
To verify persistence, restart the Deployment and check that the file still exists after the new pods are running.
View the pod information.
kubectl get pod | grep nas-testSample result:
nas-test-*****a 1/1 Running 0 40s nas-test-*****b 1/1 Running 0 40sVerify shared storage.
Create a file in a pod.
In this example, the
nas-test-*****apod is used:kubectl exec nas-test-*****a -- touch /data/test.txtView the file from the other pod.
In this example, the
nas-test-*****bpod is used:kubectl exec nas-test-*****b -- ls /dataExpected output shows that the newly created file
test.txtis shared:test.txt
Verify persistent storage.
Recreate the Deployment.
kubectl rollout restart deploy nas-testWait until the pods are recreated.
kubectl get pod | grep nas-testSample result:
nas-test-*****c 1/1 Running 0 67s nas-test-*****d 1/1 Running 0 49sLog on to a recreated pod and check whether the file still exists in the file system.
In this example, the
nas-test-*****cpod is used:kubectl exec nas-test-*****c -- ls /dataThe following output shows that the file still exists in the NAS file system and can be accessed from the mount directory in the recreated pod.
test.txt
FAQs
If you encounter issues when mounting or using NAS volumes, refer to:
References
You can use Container Network File System (CNFS) to manage NAS file systems independently and to enhance their performance and Quality of Service (QoS) control.
General-purpose NAS file systems mounted using the
subpathmethod support the directory quota feature. Set capacity limits for subdirectory PVs to improve resource utilization. For instructions, see Expand a dynamically provisioned NAS volume.