This topic describes how to use Data Transmission Service (DTS) to migrate an Elastic Compute Service (ECS)-hosted self-managed MongoDB database that uses the sharded cluster architecture to an ApsaraDB for MongoDB instance. DTS can be used to migrate historical and incremental data without business interruptions.
This topic describes how to perform data migration in the DTS console of the previous version. For more information about how to migrate data in the DTS console of the new version, see Migrate data from a self-managed MongoDB database that uses the sharded cluster architecture to an ApsaraDB for MongoDB sharded cluster instance.
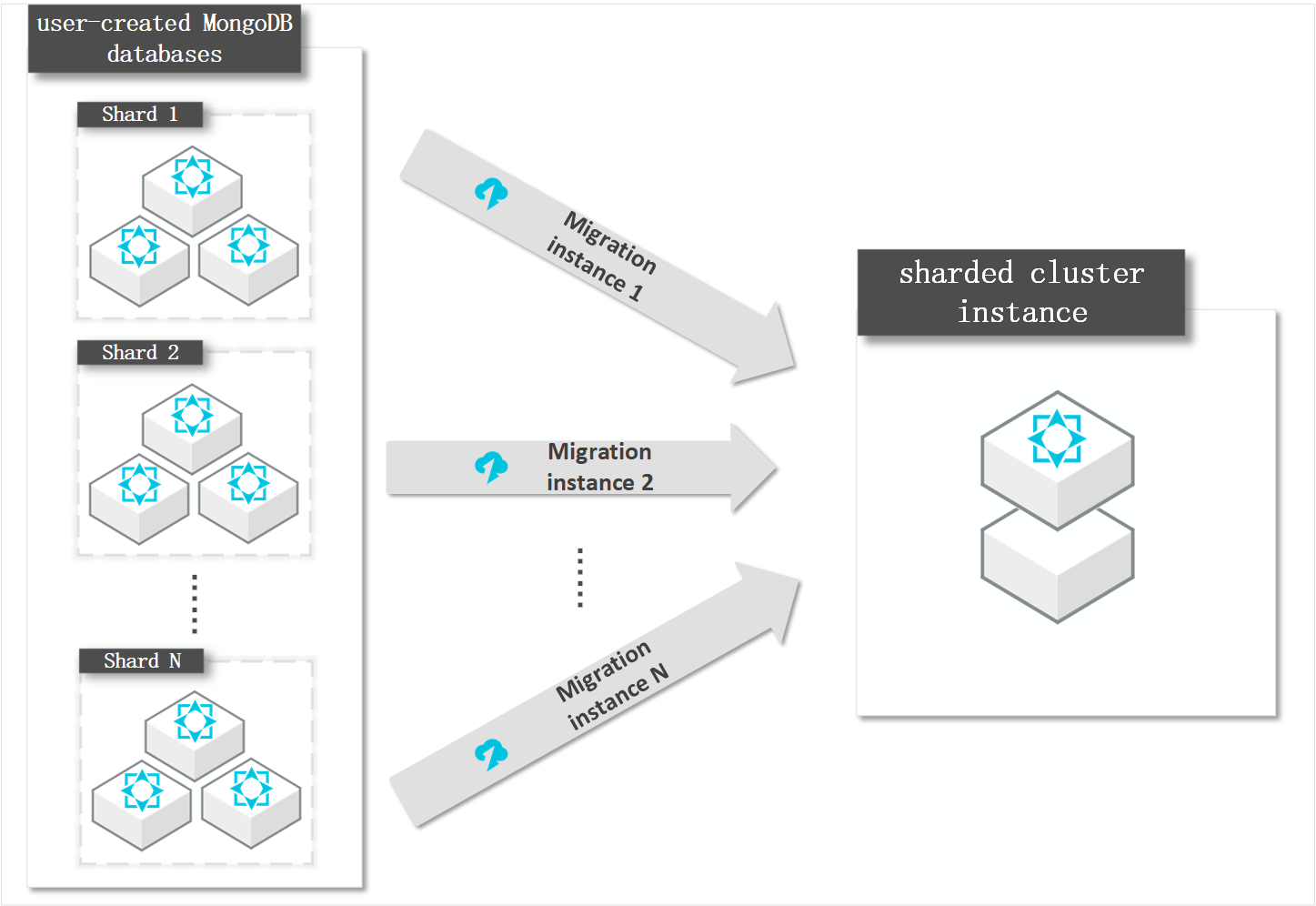
How it works
DTS migrates a self-managed MongoDB database by migrating each shard in the database. You must create a data migration task for each shard.
The distribution of migrated data in the destination ApsaraDB for MongoDB instance is based on the shard key that you specify. For more information, see Configure sharding to maximize the performance of shards.
Prerequisites
The self-managed MongoDB database runs MongoDB 3.0 or later.
Each shard in the destination sharded cluster instance has sufficient storage space.
NoteFor example, a self-managed MongoDB database has three shards, and one of these shards occupies the most storage space, which is 500 GB. In this case, the storage space of each shard in the ApsaraDB for MongoDB instance must be greater than 500 GB.
Usage notes
DTS uses the resources of the source and destination databases during full data migration. This may increase the loads on the database servers. If you migrate a large volume of data or if the server specifications do not meet your requirements, database services may become unavailable. Before you migrate data, evaluate the impact of data migration on the performance of the source and destination databases. We recommend that you migrate data during off-peak hours.
If the source and destination MongoDB databases run different MongoDB versions or use different storage engines, make sure that the MongoDB versions or storage engines are compatible. For more information, see MongoDB versions and storage engines.
The data is concurrently written to the destination database. Therefore, the storage space occupied in the destination database is 5% to 10% larger than the size of the data in the source database.
Make sure that the destination ApsaraDB for MongoDB instance does not have the same primary key as that in the source database. The default primary key is _id. Otherwise, data may be lost. If the destination instance has the same primary key as that in the source database, delete the same document that corresponds to the _id primary key in the destination instance as that in the source database without affecting your business.
The admin or local database is not used as the source or destination database.
The number of mongos nodes in the source MongoDB database that uses the sharded cluster architecture cannot exceed 10.
Billing
Migration type | Task configuration fee | Internet traffic fee |
Full data migration | Free of charge. | Charged only when data is migrated from Alibaba Cloud over the Internet. For more information, see Data Transmission Service Pricing. |
Incremental data migration | Charged. For more information, see . Data Transmission Service Pricing. |
Migration types
Full data migration: All existing data in the source MongoDB database is migrated to the destination MongoDB database.
NoteDTS can migrate the following types of objects: database, collection, and index.
Incremental data migration: After full data migration is complete, DTS migrates the incremental data of the source MongoDB database to the destination MongoDB database.
NoteDTS can migrate the create and delete operations that are performed on databases, collections, and indexes.
Synchronizes added, deleted, and updated documents.
Permissions required for database accounts
Data Source Migration | Full data migration | Incremental data migration |
Self-managed MongoDB database hosted on ECS | Read permissions on the source database | Read permissions on the source database, the admin database, and the local database |
Destination ApsaraDB for MongoDB instance | Read and write permissions on the destination database | Read and write permissions on the destination database |
For more information about how to create a database account and grant permissions to the database account, see the following topics:
ApsaraDB for MongoDB instances: Manage user permissions on MongoDB databases
Self-managed MongoDB databases: db.createUser()
Preparations
Disable the balancer for the source database and delete orphaned documents. For more information, see Migrate a self-managed MongoDB database that uses the sharded cluster architecture to ApsaraDB for MongoDB using DTS.
Procedure
- Log on to the DTS console.
In the navigation pane on the left, click Data Migration.
At the top of the Data Migration Tasks page, select the region where the ApsaraDB for MongoDB instance resides.
In the upper-right corner of the page, click Create Task.
Configure Source and Destination Databases.
Section
Parameter
Description
Task Name
-
DTS automatically generates a task name. You do not need to use an unique task name.
We recommend that you specify a name that can help you identify the task.
Source Database
Instance Type
The type of the source database. Select Self-managed Database on ECS.
Instance Region
The region where the ECS instance is deployed.
The ID of the ECS instance.
The ID of the ECS instance. DTS migrates each shard of the source database in turn. In this example, enter the ID of the ECS instance on which the first shard is deployed.
For the second migration task, enter the ID of the ECS instance on which the second shard is deployed. You must repeat this procedure until all shards are migrated.
Database Type
The type of the destination database. Select MongoDB.
Port Number
The service port of the shard. In this example, enter the service port of the first shard.
For the second migration task, enter the service port of the second shard. You must repeat this procedure until all shards are migrated.
Database Name
The name of the database used for authentication.
Database Account
The account used to connect to the self-managed MongoDB database. For information about the permissions required for the account, see Permissions required for database accounts.
Database Password
The password of the database account used to connect to the self-managed MongoDB database.
Destination Database
Instance Type
The type of the destination database. Select MongoDB Instance.
Instance Region
The region where the destination ApsaraDB for MongoDB instance resides.
MongoDB Instance ID
The ID of the destination ApsaraDB for MongoDB instance.
Database Name
The name of the database used for authentication.
Database Account
The account used to connect to the destination database. For information about the permissions required for the account, see Permissions required for database accounts.
Database Password
The password of the database account used to connect to the destination database.
NoteAfter you specify the information of the destination database, you can click Test Connectivity and Proceed to check whether the information is valid. If the information is valid, the Passed message appears. If the information is invalid, the Failed message appears. In this case, you must click Check next to the Failed message to modify the information.
In the lower-right corner of the page, click Set Whitelist and Next.
NoteYou do not need to modify the security settings for Alibaba Cloud database instances (such as ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instances and ApsaraDB for MongoDB instances) and ECS-hosted self-managed databases. DTS automatically adds the CIDR blocks of DTS servers to the IP whitelists of Alibaba Cloud database instances or the security rules of ECS instances. For more information, see Add the CIDR blocks of DTS servers to the security settings of on-premises databases.
If the data source or destination is a self-managed database and the public CIDR blocks of DTS servers are added to the IP whitelist of the self-managed database to allow access from DTS servers, security risks may occur. We recommend that you strengthen authentication with accounts and passwords, restrict allowed ports, or connect to the database over Express Connect, VPN Gateway, or Smart Access Gateway.
After data migration is complete, we recommend that you remove the CIDR blocks of DTS servers from the whitelists.
Select the migration types and the objects that you want to migrate.
Parameter
Description
Migration Type
To perform only full data migration, select only Full Data Migration.
NoteTo ensure data consistency, do not write new data to the self-managed MongoDB database during full data migration.
To ensure service continuity during data migration, select both Full Data Migration and Incremental Data Migration.
Source Objects
Select one or more objects from the Source Objects section and click the
 icon to add the objects to the Selected Objects list. Note
icon to add the objects to the Selected Objects list. NoteDTS cannot migrate data from the admin or local database.
The config database is an internal database. We recommend that you do not migrate data from the config database.
A migration object can be a database, collection, or function.
By default, after an object is migrated to the destination database, the name of the object remains unchanged. You can change the names of the objects in the destination database using the object name mapping feature provided by DTS. For more information, see Object name mapping.
In the lower-right corner of the page, click Next: Save Task Settings and Precheck.
NoteBefore you can start the data migration task, DTS performs a precheck. You can start the data migration task only after the task passes the precheck.
If the task fails to pass the precheck, click View Details next to each failed item. After you analyze the causes based on the check results, troubleshoot the issues. Then, run a precheck again.
If an alert is triggered for an item during the precheck:
If an alert item cannot be ignored, click View Details next to the failed item and troubleshoot the issues. Then, run a precheck again.
If the alert item can be ignored, click Confirm Alert Details. In the View Details dialog box, click Ignore. In the message that appears, click OK. Then, click Precheck Again to run a precheck again. If you ignore the alert item, data inconsistency may occur, and your business may be exposed to potential risks.
Click Next: Purchase Instance.
In the Purchase dialog box, specify the Instance Class parameter and select the check box to agree to Data Transmission Service (Pay-As-You-Go) Service Terms.
Click Buy and Start to start the data migration task.
Repeat step 4 to step 11 to create migration tasks for the remaining shards.
Stop the data migration tasks.
Full data migration
We recommend that you do not manually stop a task during full data migration. Otherwise, the data migrated to the destination database will be incomplete. You can wait until the full data migration task automatically stops.
Incremental data migration
An incremental data migration task does not automatically stop. You must manually stop the task.
NoteWe recommend that you select an appropriate time to manually stop a data migration task. For example, you can stop the task during off-peak hours or before you switch your workloads to the ApsaraDB for MongoDB instance.
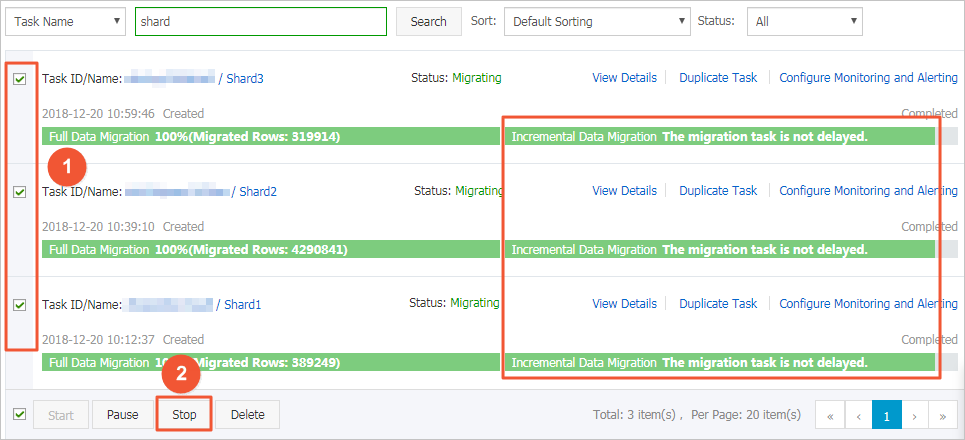
Wait until Incremental Data Migration and The migration task is not delayed are displayed in the progress bar of the data migration task. Then, stop writing data to the source database for a few minutes. The latency of incremental data migration may be displayed in the progress bar.
After the status of incremental data migration changes to The migration task is not delayed again, manually stop the migration tasks for all shards.
Switch your workloads to the destination ApsaraDB for MongoDB instance.