The log management feature of Simple Message Queue (formerly MNS) pushes message request logs to Simple Log Service (SLS). You can then use the query and analysis features of SLS to troubleshoot issues.
Scenarios
Have you encountered the following issues when you send and receive messages?
A message is sent to a queue, but the consumer cannot receive it. Where did the message go?
Who consumed the message? How many times was it consumed?
The consumer is unavailable. When can a failed message be consumed again?
A message is published to a topic, but the endpoint does not receive it. Why is there a delay?
You can solve these issues using the log management feature of Simple Message Queue (formerly MNS). The methods are as follows:
Push logs to SLS and view the complete message trace in the console.
Use the query tool on the official website. Specify the required parameters to view the message processing logs.
Billing
Simple Message Queue (formerly MNS) does not charge extra fees for the log management feature.
Simple Message Queue (formerly MNS) pushes logs to SLS. SLS charges you based on factors such as storage space, traffic, and the number of requests. For more information, see Billing overview.
Queue log format
Queue message operation logs are generated from operations on queue messages, such as sending, consuming, and deleting messages. Each operation log contains multiple fields. Each field has a specific meaning. The fields included in a log vary depending on the operation. The following sections describe the meaning of each field and list the fields that are included for different operations.
Log field descriptions
Each operation log contains multiple fields. The following table describes these fields.
Field
Description
Time
The time when the operation occurred.
MessageId
The ID of the message that is processed in the operation.
QueueName
The name of the queue for which the operation is performed.
AccountId
The ID of the account that owns the queue.
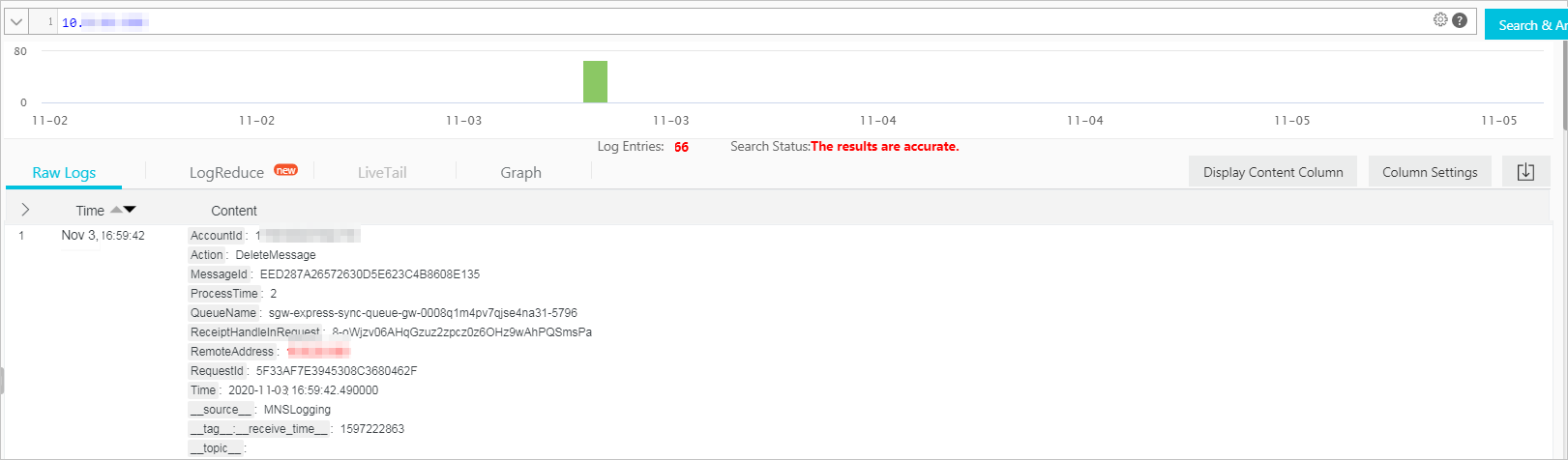
RemoteAddress
The IP address of the client that initiated the operation.
NextVisibleTime
The next time the message becomes visible after the operation is complete.
ReceiptHandleInRequest
The ReceiptHandle parameter that the client passes in for the operation.
ReceiptHandleInResponse
The ReceiptHandle that is returned to the client after the operation is complete.
ProcessTime
The time it takes to process the operation.
RequestId
The ID of the task.
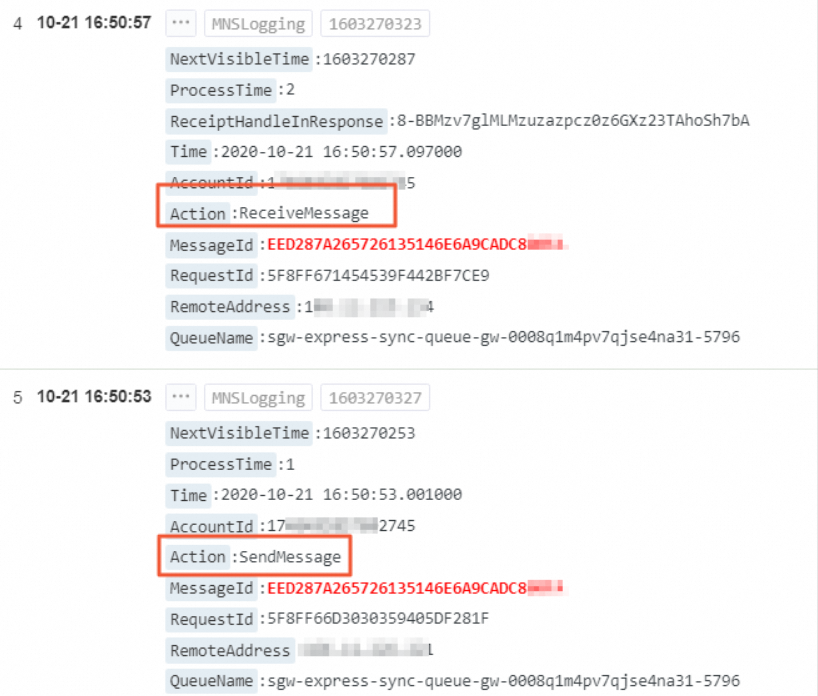
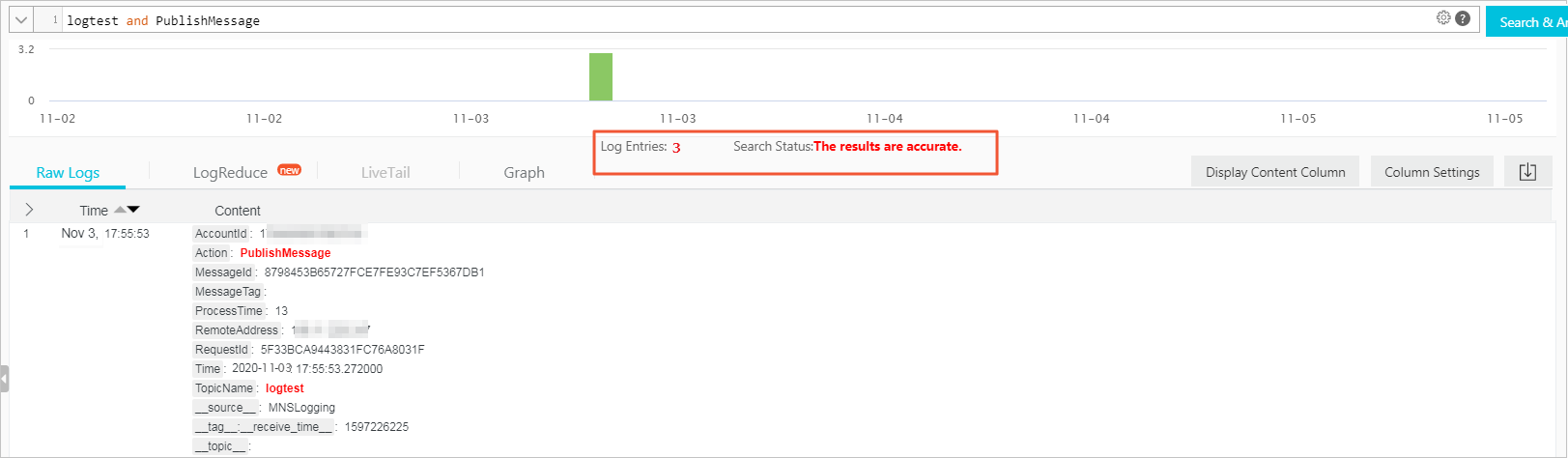
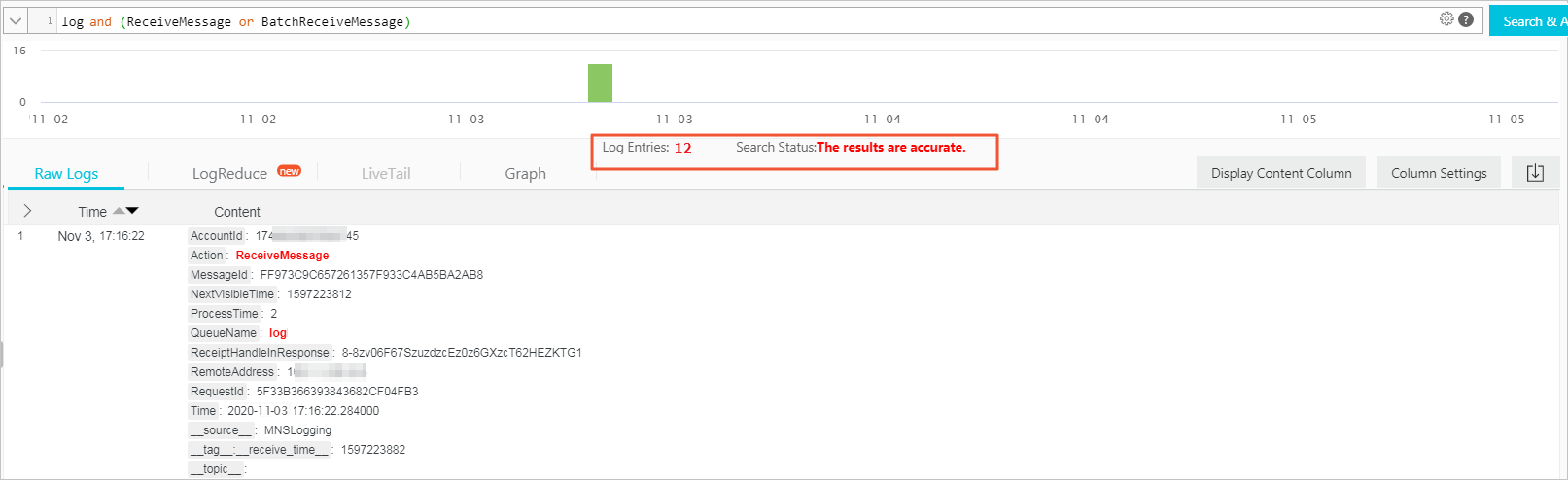
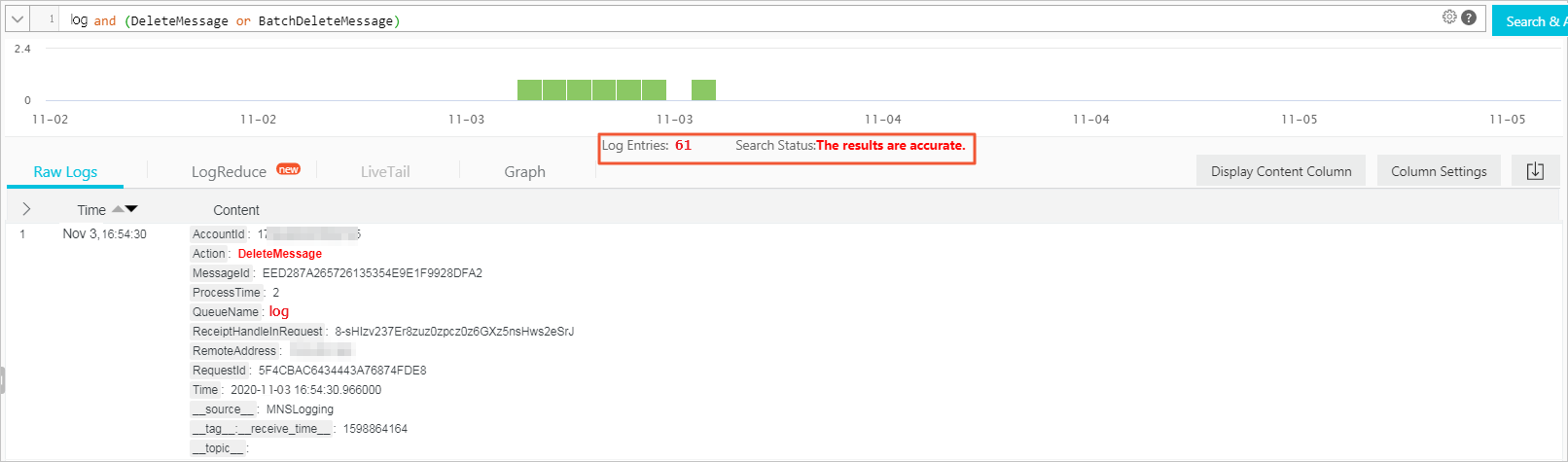
Action
The action, such as delete or send.
Fields for each operation
The fields included in a log vary depending on the operation. The following table lists the fields for each operation.
Operation
Time
QueueName
AccountId
MessageId
RemoteAddress
NextVisibleTime
ReceiptHandleInResponse
ReceiptHandleInRequest
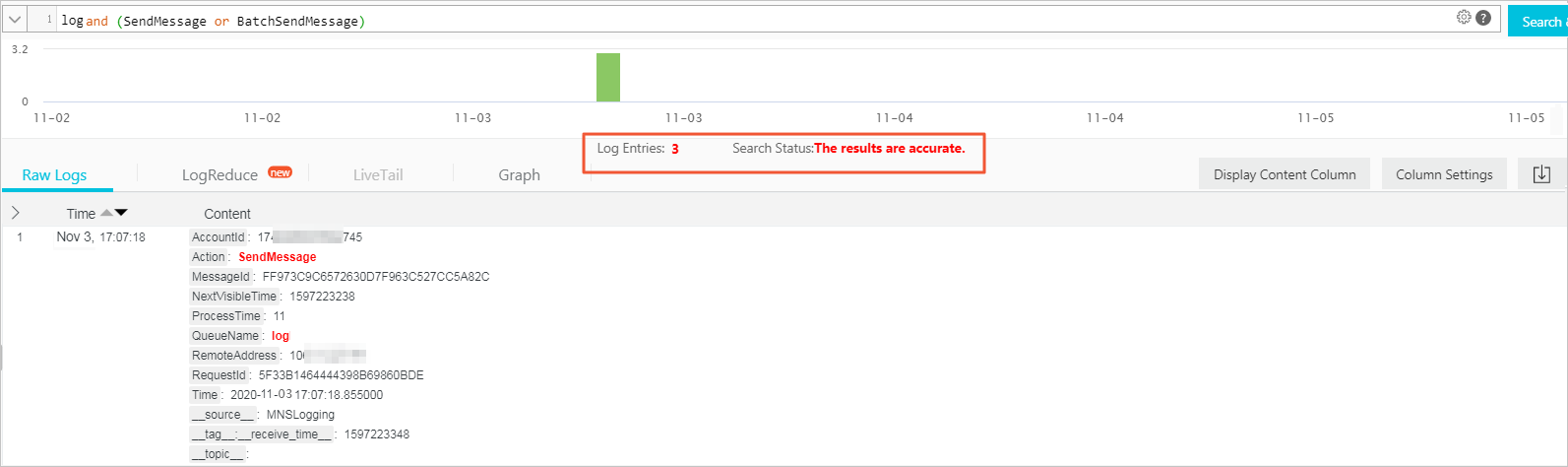
SendMessage/BatchSendMessage
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes.
Yes.
No
None
PeekMessage/BatchPeekMessage
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes.
No
No
No
ReceiveMessage/BatchReceiveMessage
Yes.
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
ChangeMessageVisibility
Yes.
Yes
Yes.
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes.
DeleteMessage/BatchDeleteMessage
Yes
Yes.
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
Yes
Topic log format
Topic message operation logs are generated from operations on topic messages. These operations are primarily of two types: publishing messages and pushing messages. The following sections describe the meaning of each field in a topic message operation log and list the fields that are included for different operations.
Log field descriptions
Each operation log contains multiple fields. The following table describes these fields.
Field
Description
Time
The time when the operation occurred.
MessageId
The ID of the message that is processed in the operation.
TopicName
The name of the topic for which the operation is performed.
SubscriptionName
The name of the subscription for which the operation is performed.
AccountId
The ID of the account that owns the topic.
RemoteAddress
The IP address of the client that initiated the operation.
NotifyStatus
The HTTP status code or error information that is returned by the user when Simple Message Queue (formerly MNS) pushes a message.
ProcessTime
The time it takes to process the operation.
MessageTag
The message tag.
RequestId
The ID of the task.
Action
The action, such as delete or send.
Fields for each operation
The fields included in a log vary depending on the operation. The following table lists the fields for each operation.
Operation
Time
MessageId
TopicName
SubscriptionName
AccountId
RemoteAddress
NotifyStatus
Subscription Name
PublishMessage
Yes.
Yes
Yes
No
Yes
Yes
None
No
Notify
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
Yes.
Yes
NotifyStatus
NotifyStatus is a field specific to message push logs. This field helps you troubleshoot failures that occur when Simple Message Queue (formerly MNS) pushes messages to an endpoint. You can resolve issues based on the suggestions that are provided in the following table for different NotifyStatus values.
Error code
Description
Suggested solution
2xx
The message is pushed successfully.
None.
Other HTTP status codes
The endpoint returns a non-2xx status code when the message is pushed.
Check the processing logic at the endpoint.
InvalidHost
The endpoint specified in the subscription is invalid.
Confirm that the endpoint in the subscription is valid. You can use curl or telnet to check.
ConnectTimeout
The connection to the endpoint specified in the subscription timed out.
Confirm that the endpoint in the subscription is accessible. You can use curl or telnet to check.
ConnectFailure
Failed to connect to the endpoint specified in the subscription.
Confirm that the endpoint in the subscription is accessible. You can use curl or telnet to check.
UnknownError
An unknown error occurred.
Contact Simple Message Queue (formerly MNS) technical support.
Log management operations
Before you use the log feature, complete the following prerequisites:
Create a queue and a topic in Simple Message Queue (formerly MNS). For more information, see Queue operations and Topic operations.
Create a project and a Logstore in Simple Log Service. For more information, see Manage a project and Create a Logstore.
Your MNS operation logs can only be pushed to an SLS project in the same region.
Grant the AliyunMNSLoggingRole role to MNS to export logs.
Click Cloud Resource Access Authorization and follow the on-screen instructions to grant the permissions.
WarningDo not revoke the authorization or delete the RAM role. Otherwise, Simple Message Queue (formerly MNS) logs cannot be pushed to Simple Log Service.
 > Edit
> Edit