The Delta Lake and Apache Hudi storage mechanisms are commonly used in data lake solutions. These storage mechanisms provide stream processing and batch processing capabilities for data lakes. MaxCompute allows you to build a data lakehouse solution that supports the Delta Lake or Apache Hudi storage mechanism. This solution is developed based on open source Hadoop clusters. You can use MaxCompute to query real-time data and gain instant insight into the changes of business data.
Background information
MaxCompute allows you to build a data lakehouse solution that supports the Delta Lake and Apache Hudi storage mechanism based on open source Hadoop clusters and Alibaba Cloud E-MapReduce (EMR). The following figure shows the architecture of such a data lakehouse solution.
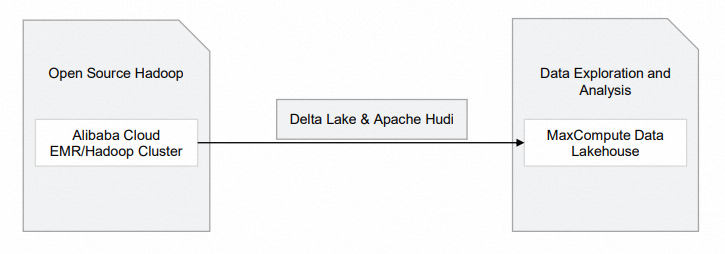
Module | Alibaba Cloud service | Description |
Open source Hadoop |
| Raw data is stored in Hadoop clusters. |
Build a data lakehouse solution that supports the Delta Lake or Apache Hudi storage mechanism based on Hadoop clusters
Prerequisites
A MaxCompute project is created. This project is not an external project. For more information about how to create a MaxCompute project, see Create a MaxCompute project.
Limits
When you build a data lakehouse solution that supports the Delta Lake or Apache Hudi storage mechanism based on Hadoop clusters, take note of the following limits:
The data lakehouse solution is supported only in the following regions: China (Hangzhou), China (Shanghai), China (Beijing), China (Shenzhen), China (Hong Kong), Singapore, and Germany (Frankfurt).
Procedure
In this topic, a data lakehouse solution is built based on an EMR Hadoop cluster. Perform the following steps:
Step 1: Create an EMR cluster.
You do not need to create a cluster if a Hadoop cluster that is built in a data center or built on virtual machines in the cloud exists.
Create a database in the cluster and prepare data.
Step 3: Analyze data in the Hadoop cluster in real time based on MaxCompute.
Create an external project on the Lake and Warehouse Integration (Data Lakehouse) page in the DataWorks console to analyze data of the Hadoop cluster.
Step 1: Create an EMR cluster
Create a Hadoop cluster in the EMR console.
For more information about how to create an EMR Hadoop cluster, see the "Step 1: Create a cluster" section in Quick start for EMR. The following table describes the parameters that you must take note of when you create a Hadoop cluster. For more information about other parameters, see the parameter descriptions in EMR documentation.
Step
Parameter
Example
Description
Software Configuration
Business Scenario
Custom Cluster
Select a business scenario based on your business requirements.
Product Version
EMR-3.43.0
Select an EMR V3.X version that is built on top of Hadoop 2.X or Hive 2.X.
Optional Services (Select One At Least)
Hadoop-Common, HDFS, Hive, YARN, Spark3, Deltalake, Hudi, and ZooKeeper
If you select the Hadoop, HDFS, Hive, Spark, Delta Lake, and Hudi components, their related service processes are automatically enabled.
Metadata
Built-in MySQL
Select Built-in MySQL or Self-managed RDS.
Self-managed RDS: Metadata is stored in a self-managed ApsaraDB RDS database.
If you select Self-managed RDS, you must configure the parameters that are related to database connections. For more information, see Configure a self-managed ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL database.
Built-in MySQL: Metadata is stored in an on-premises MySQL database of the cluster.
NoteSelect this option only in test scenarios. In production scenarios, we recommend that you select Self-managed RDS.
After the cluster is created, click Nodes in the Actions column of the cluster.
On the Nodes tab, click the ID of the destination node in the emr-master node group to go to the Elastic Compute Service (ECS) console.
Select a tool to connect to the ECS instance. For more information, see Connection methods.
NoteIn this example, Workbench is used to connect to the instance. The logon password is the password that you configure when you create the cluster.
Step 2: Prepare data
After you log on to the cluster, you can use Spark SQL to create Delta Lake tables or Hudi tables.
EMR Hudi 0.8.0 allows you to use Spark SQL to perform read and write operations on Hudi tables. For more information, see Integrate Hudi with Spark SQL. In this example, a Hudi table is created. Run the following command on the terminal to start Spark SQL:
spark-sql \ --conf 'spark.serializer=org.apache.spark.serializer.KryoSerializer' \ --conf 'spark.sql.extensions=org.apache.spark.sql.hudi.HoodieSparkSessionExtension'After you start Spark SQL, execute the following statements to create a table and insert data into the table:
NoteIf no database is created, data is automatically stored in the default database.
-- Create a table. CREATE TABLE h0 ( id BIGINT, name STRING, price DOUBLE, ts LONG ) USING hudi tblproperties ( primaryKey="id", preCombineField="ts" ); -- Insert data into the table. INSERT INTO h0 VALUES (1, 'a1', 10, 1000); -- Query data from the table. SELECT id, name, price, ts FROM h0;
Step 3: Analyze data in the Hadoop cluster in real time based on MaxCompute
Create an external project for the Hadoop cluster based on the created MaxCompute project and table data in the Hadoop cluster, and map the external project to the MaxCompute project. This way, you can use the mapped MaxCompute project to analyze the data of the external project. Only the owner of the MaxCompute project or users who are assigned the Admin or Super_Administrator role can create an external project.
You can assign the tenant-level Super_Administrator role to a user on the Users tab in the MaxCompute console. Only the Alibaba Cloud account or a RAM user that is assigned the tenant-level Super_Administrator role can assign roles to users. For more information, see Assign a role to a user.
Create an external project in the DataWorks console.
Log on to the DataWorks console and select a region.
In the left-side navigation pane of the DataWorks console, choose Others > Lake and Warehouse Integration (Data Lakehouse).
On the Lake and Warehouse Integration (Data Lakehouse) page, click Start.
On the Create Data Lakehouse page, configure the parameters. The following tables describe the parameters.
Table 1. Parameters in the Create Data Lakehouse step
Parameter
Description
External Project Name
The name of the external project. Example: test_extproject_ddd.
MaxCompute Project
The name of the MaxCompute project. Example: test_lakehouse.
Table 2. Parameters in the Create Data Lake Connection step
Parameter
Description
Heterogeneous Data Platform Type
Select Alibaba Cloud E-MapReduce/Hadoop Cluster.
Network Connection
Select an existing network connection. For more information, see Create an external data lake connection.
External Data Source
Select an existing external data source. For more information, see Create an external data lake connection.
Table 4. Create Data Mapping
Parameter
Description
External Data Source Object
By default, this parameter is set to the value of External Data Source.
Destination Database
The database in the Hadoop cluster.
Click Complete Creation and Preview, and click Preview. If the information about the database tables in the Hadoop cluster can be previewed, the operation is successful.
NoteThe external project is created in the DataWorks console. For more information about how to use SQL statements to manage external projects, see Use SQL statements to manage an external project.
In the left-side navigation pane of the DataWorks console, choose Others > Lake and Warehouse Integration (Data Lakehouse).
In the DataWorks console, create an ODPS SQL node on the Ad Hoc Query page to view tables in the external project. Sample statement:
SHOW TABLES IN test_extproject_ddd; -- The following result is returned: ALIYUN$***@test.aliyunid.com:h0NoteFor more information about how to perform ad hoc queries in DataWorks, see Use an ad hoc query node to execute SQL statements (Optional).
On the Ad Hoc Query page in the DataWorks console, query the table data of the external project. Sample statement:
SELECT * FROM test_extproject_ddd.h0;The following figure shows the returned result.

Log on to the Hadoop cluster by using Workbench, and go to the Spark SQL terminal. In the command execution section, enter an SQL statement to update data in the h0 table. Sample statement:
INSERT INTO h0 VALUES (2, 'a2', 11, 1000);On the Ad Hoc Query page in the DataWorks console, view the data update result. Sample statement:
SELECT * FROM test_extproject_ddd.h0 WHERE id ='2';The following figure shows the returned result.

References
For more information about how to build a data lakehouse that supports the Delta Lake or Apache Hudi storage mechanism based on DLF, ApsaraDB RDS or Realtime Compute for Apache Flink, and OSS, see Delta Lake or Apache Hudi storage mechanism based on DLF, ApsaraDB RDS or Realtime Compute for Apache Flink, and OSS.