This topic describes the system architecture, key features, and common use cases of the MaxCompute Query Acceleration (MCQA) feature.
MaxCompute is scheduled to launch MaxQA (MaxCompute Query Accelerator 2.0) on the Alibaba Cloud China website (www.aliyun.com) and the Alibaba Cloud International website (www.alibabacloud.com) on Monday, November 24, 2025 (UTC+8) and Thursday, November 27, 2025 (UTC+8), respectively. After the launch, the MCQA feature described in this document will no longer be available to new customers.
Introduction
The MaxCompute Query Acceleration (MCQA) feature provides the following capabilities:
Accelerates and optimizes queries on small and medium-sized datasets. This feature reduces query times from minutes to seconds and is fully compatible with existing MaxCompute query features.
Supports mainstream business intelligence (BI) tools for ad hoc queries and BI analysis.
Uses independent resource pools that do not occupy offline computing resources. This feature automatically identifies query jobs to reduce queuing pressure and improve user experience.
Writes the results of MCQA jobs to a temporary cache. When you run the same query job again, MaxCompute returns the cached results to accelerate execution.
Query flow
The following figure shows the query processing architecture of MaxCompute. After a query is received, the smart routing feature routes it to a specific rules tree for processing by Query Acceleration (MCQA), standard SQL execution, or multi-engine computing.

In the preceding architecture, MCQA writes the results of query jobs to a temporary cache. When you run the same query job again, MaxCompute returns the cached results to accelerate execution. For more information about the caching mechanism, see Caching mechanism.
Use cases
Use case | Description | Characteristics |
Ad hoc query | You can use MCQA to optimize query performance on small to medium-sized datasets of up to several hundred gigabytes. This lets you perform low-latency queries directly on MaxCompute tables to quickly complete data development and data analytics. |
|
Business intelligence (BI) | When you build an enterprise data warehouse using MaxCompute, extract, transform, and load (ETL) processes transform data into business-oriented aggregate data. MCQA provides low latency, elastic concurrency, and data caching. Combined with optimizations such as MaxCompute table partitions and bucketing, it can meet the needs of report generation, statistical analysis, and fixed report analysis with high concurrency and fast response at a low cost. |
|
Detailed query analysis of massive data | MCQA can automatically identify the features of a query job. It can respond quickly to small-scale jobs and automatically match resource requirements for large-scale jobs. This meets the needs of analysts who work with query jobs of varying scales and complexities. |
|
Limitations
Version requirements:
MaxCompute client (odpscmd) version 0.40.8 or later is required.
ODPS-JDBC version 3.3.0 or later is required.
ODPS-SDK version 0.40.8-public or later is required.
Only data query statements that start with SELECT are supported. If you submit a statement that is not supported by MCQA, the MaxCompute client, Java Database Connectivity (JDBC), and software development kit (SDK) can be configured to fall back to the standard offline execution mode. Other tools do not support this fallback. After a query job falls back to a standard SQL job, it is billed based on the standard SQL job billing method.
Row limit: By default, you can query a maximum of 1,000,000 rows of data. You can add the LIMIT keyword to your SQL statement to exceed this limit.
Feature limits:
Limitation
Description
Feature
Supports MaxCompute Standard Edition and pay-as-you-go services.
Supports the subscription billing method.
Does not support the Developer Edition of MaxCompute. You must upgrade to the Standard Edition.
Query
A one-time execution job supports a maximum of 2,000 concurrent workers.
MCQA jobs submitted through the client time out after 30 seconds by default. MCQA jobs submitted through DataWorks ad hoc queries time out after 20 seconds by default. After a timeout, the MCQA job falls back to a standard query job by default.
Only data from tables in the ALIORC storage format can be cached in memory for acceleration.
Query concurrency
Subscription mode.
Free Edition (without an MCQA interactive resource group).
Each project is limited to 5 concurrent jobs and a maximum of 500 jobs per day. If the limit is exceeded, jobs automatically fall back to standard jobs by default. If fallback is disabled, the system reports the following error:
ODPS-1800001: Session exception - Failed to submit sub-query in session because:Prepaid project run outoffree query quota.MCQA interactive resource group.
The maximum number of concurrent MCQA jobs for each project is 120. If this limit is exceeded, submitted jobs fall back to standard job mode.
When you configure a quota group of the interactive resource type, the minimum and maximum reserved CUs for MCQA jobs must be the same. Otherwise, the configuration does not take effect.
The interactive resource type must meet the following requirements. Otherwise, jobs cannot be submitted.
Reserved CUs [minCU]must be equal toReserved CUs [maxCU].The number of reserved CUs must be greater than or equal to
50.
After you configure an interactive resource quota group, only jobs that can be identified for acceleration can be submitted to the interactive resource quota group for all projects. The free trial for the query acceleration feature is no longer available.
A quota group of the interactive resource type cannot be used as the default quota for a project. When you use the query acceleration feature, the interactive quota group takes effect for all projects without being attached to a project.
Pay-as-you-go mode.
The maximum number of concurrent MCQA jobs for a single MaxCompute project is 120. If this limit is exceeded, jobs fall back to standard job mode.
Caching mechanism
For each MCQA query job, MaxCompute creates a temporary dataset to cache the query results. The cache size of the temporary dataset is limited to 10 GB.
The owner of the temporary dataset is the user who runs the query job that generates the cached results.
The temporary dataset is not visible to users, and its content cannot be viewed.
MaxCompute automatically grants the user who runs the query job access permissions to the temporary dataset.
To retrieve data from cached query results, the query job and its context configuration must be identical to the original query job. When you run a duplicate query job, MaxCompute reuses the cached results.
Billing for cached results
Cached query results do not incur storage or computing fees. This can effectively reduce resource usage costs.
Deletion of cached results
MaxCompute deletes cached results in the following situations:
MaxCompute deletes cached results in advance when the resource usage of a MaxCompute project is high.
If a table or view referenced by the cached results is changed, the cached results immediately become invalid. MaxCompute deletes the invalid cached results. If you run the same query job again, the cached data is not retrieved.
The cached results have expired.
Cache verification
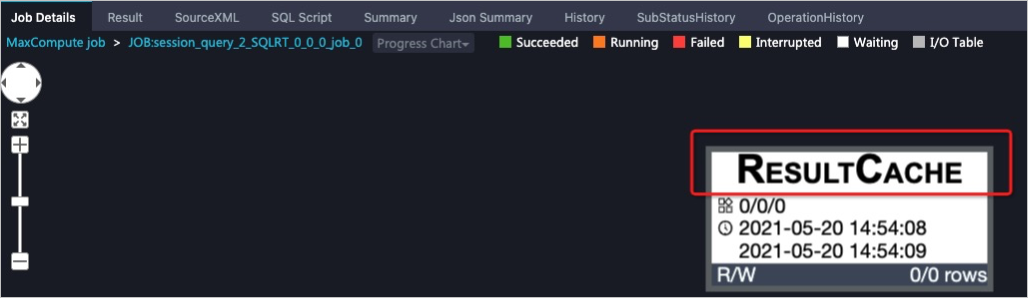
You can use Logview 2.0 to view the Logview information for a query job. As shown in the following figure, on the Job Details tab, you can see that the query job results have been written to the cache:
Enable MCQA for subscription instances
Procedure
Follow these steps to use the query acceleration feature to accelerate projects in a subscription MaxCompute instance.
The subscription MCQA quota determines the scan concurrency during a query, which in turn affects the amount of data scanned in the target table. The approximate ratio is that 1 CU can scan 0.6 GB of data. For example, if you purchase an MCQA quota of 50 CUs, you can scan about 30 GB of data at the same time. Currently, MCQA supports scanning a maximum of 300 GB.
Log on to the MaxCompute console and select a region in the top-left corner.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose .
On the Quotas page, find the target quota and click Quota Configuration in the Actions column.
Configure basic quota settings.
On the Quota Configuration page, select the Basic Configurations tab and click Edit Basic Configurations.
Click Add Level-2 Quota or configure basic parameters for an existing level-2 quota.
Enter a custom Quota Name and set Type to Interactive. For more information about the parameters, see Configure a quota.
Configure quota scaling.
On the Quota Configuration page, select the Scaling Configuration tab.
On the Scaling Configuration tab, click Add Configuration Plan or find an existing configuration plan and click Edit in the Actions column to update the plan.
In the Add Configuration Plan or Edit Configuration Plan dialog box, configure Reserved CUs [minCU,maxCU] for the MCQA resource group.
The minimum number of CUs (minCU) must be equal to the maximum number of CUs (maxCU).
The minimum number of CUs must be greater than or equal to
50. If you do not need interactive resources, set this parameter to0.Elastic reserved CUs are not supported for interactive quotas.
Click OK to save the quota configuration.
On the Scaling Configuration tab, find the target configuration plan and click Apply Immediately in the Actions column to immediately apply the plan. You can also use an existing plan when you configure Scheduled Scaling Management.
Configure a time-based plan.
You can configure a time-based plan to enable different quota plans at different times of the day. This implements time-based logic for quota configuration.
Scheduling policy
Interactive quota groups cannot be explicitly specified. They are automatically scheduled by the service based on rules. The specific scheduling policy depends on the number of interactive quota groups under the tenant:
If there is only one interactive quota group, all query acceleration jobs under the tenant are scheduled to this quota group.
If the tenant has multiple interactive quota groups, the automatic routing rule selects one based on user configuration. For more information, see Quota rules.
Fallback policy
If a query acceleration job falls back to a standard query job due to usage limits, the quota dedicated to running MCQA jobs in a subscription instance falls back to the quota resource attached to the current project.
You can use the SDK (version 0.40.7 or later) to specify the execution quota resource for a fallback job.
SQLExecutorBuilder builder = SQLExecutorBuilder.builder(); builder.quotaName("<OfflineQuotaName>");You can use the JDBC connection string parameter
fallbackQuota=XXXto specify the execution quota resource for a fallback job. You cannot specify an interactive quota group as the execution quota for a fallback job. Otherwise, an error is reported.
Connection methods for MCQA
MCQA supports the following connection methods:
Method 1: Enable MCQA using the MaxCompute client
Download the latest version of the MaxCompute client (odpscmd).
Install and configure the client. For more information, see Install and configure the MaxCompute client.
Modify the odps_config.ini file in the conf directory of the client installation path. Add the following commands to the configuration file:
enable_interactive_mode=true -- Enables MCQA interactive_auto_rerun=true -- Specifies that if an MCQA job fails, it automatically falls back to a standard job.Run the MaxCompute client in the bin directory of the client installation path. For Linux, run ./bin/odpscmd. For Windows, run ./bin/odpscmd.bat. The following information indicates that the operation was successful:
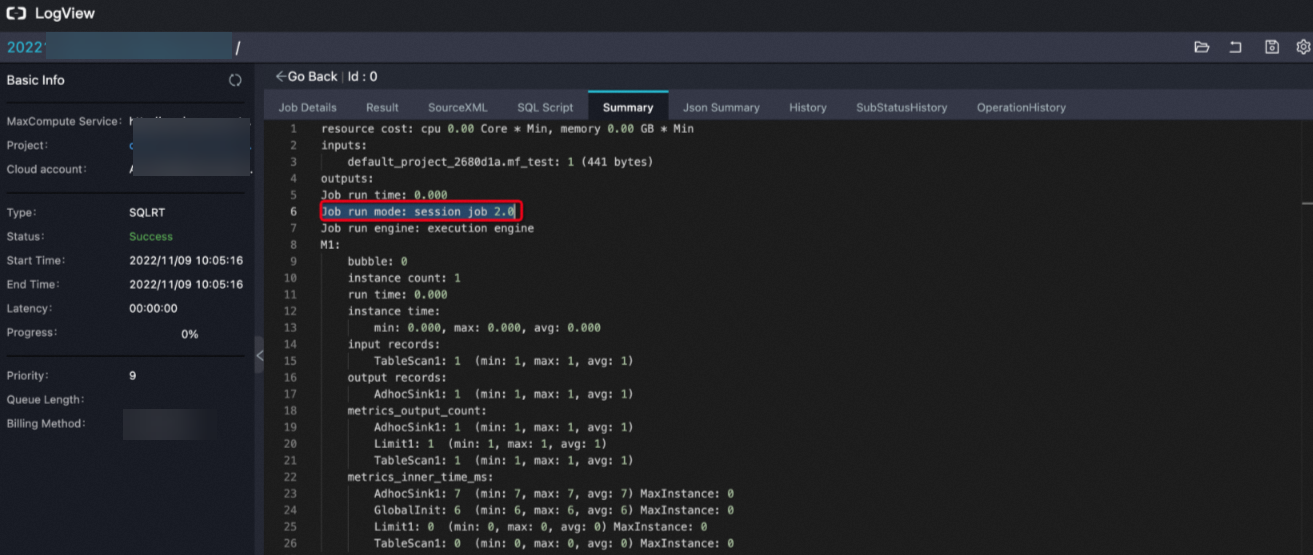
After you run a query job, if the Logview in the client interface contains the following information, MCQA is enabled:
Method 2: Enable MCQA using the ad hoc query or data development feature in DataWorks
The ad hoc query and manually triggered workflow modules in DataWorks have MCQA enabled by default. You do not need to enable it manually.
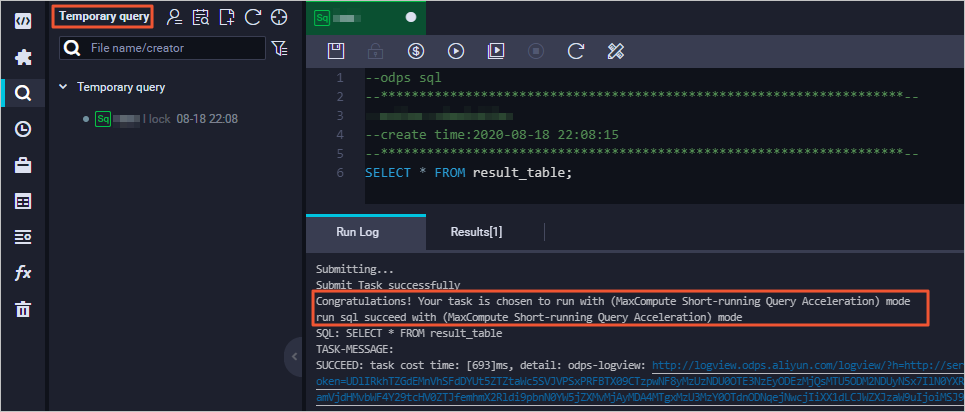
Run a query job in the Ad-hoc Query module. If the returned result contains the following information, MCQA is enabled:
Run a query job in the manually triggered workflow module. If the returned result contains the following information, MCQA is enabled:
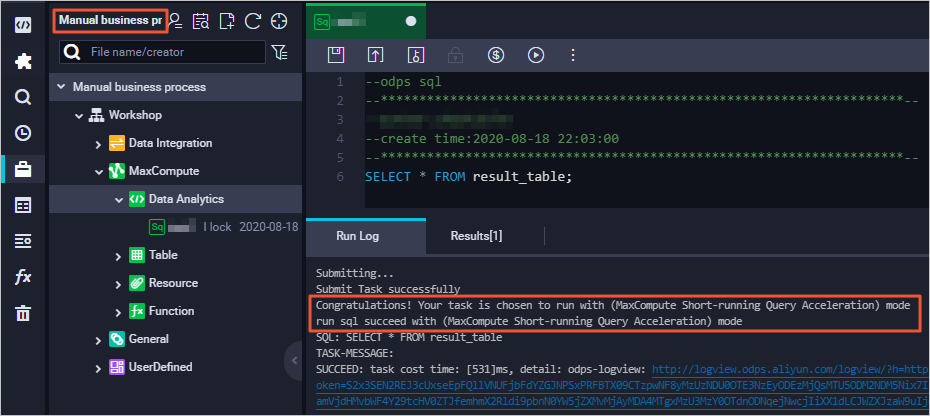
Method 3: Enable MCQA using JDBC
When you use JDBC to connect to MaxCompute, you can perform the following operations to enable MCQA. For more information about how to use JDBC to connect to MaxCompute, see Use JDBC.
Download the JDBC_JAR that supports MCQA or the compilable source code.
Configure the Pom dependency using Maven.
<dependency> <groupId>com.aliyun.odps</groupId> <artifactId>odps-jdbc</artifactId> <version>3.3.0</version> <classifier>jar-with-dependencies</classifier> </dependency>Create a Java program based on the source code and adapt it to your actual information. For more information, see MaxCompute JDBC. The following code provides an example.
// An Alibaba Cloud account AccessKey has full permissions on all APIs and poses a high security risk. We recommend that you create and use a RAM user to make API calls or perform O&M. To create a RAM user, log on to the RAM console. // This example shows how to store the AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret in environment variables. You can also store them in a configuration file as needed. // We strongly recommend that you do not hard-code the AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret in your code. This can lead to security risks. private static String accessId = System.getenv("ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID"); private static String accessKey = System.getenv("ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET"); // your_project_name is the name of the project for which you want to enable MCQA. String conn = "jdbc:odps:http://service.<regionid>.maxcompute.aliyun.com/api?project=<YOUR_PROJECT_NAME>"&accessId&accessKey&charset=UTF-8&interactiveMode=true&alwaysFallback=false&autoSelectLimit=1000000000"; Statement stmt = conn.createStatement(); Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(conn, accessId, accessKey); Statement stmt = conn.createStatement(); String tableName = "testOdpsDriverTable"; stmt.execute("DROP TABLE IF EXISTS " + tableName); stmt.execute("CREATE TABLE " + tableName + " (key int, value string)");You can configure the following parameters in the connection string to refine the processing logic.
Parameter
Description
enableOdpsLogger
Used for log printing. If SLF4J is not configured, we recommend that you set this parameter to True.
fallbackForUnknownError
The default value is False. If you set it to True, the system falls back to offline mode when an unknown error occurs.
fallbackForResourceNotEnough
The default value is False. If you set it to True, the system falls back to offline mode when there are insufficient resources.
fallbackForUpgrading
The default value is False. If you set it to True, the system falls back to offline mode during an upgrade.
fallbackForRunningTimeout
The default value is False. If you set it to True, the system falls back to offline mode when a timeout occurs.
fallbackForUnsupportedFeature
The default value is False. If you set it to True, the system falls back to offline mode when an unsupported MCQA scenario is encountered.
alwaysFallback
The default value is False. If you set it to True, the system falls back to offline mode in all the preceding scenarios. This is supported only in JDBC 3.2.3 and later versions.
Usage examples
Example 1: Use MCQA on Tableau
Add the
interactiveMode=trueproperty to the server to enable MCQA. We recommend that you also add theenableOdpsLogger=trueproperty for log printing. For more information about the configuration, see Configure JDBC to use Tableau.The following code provides a complete server configuration example.
http://service.cn-beijing.maxcompute.aliyun.com/api? project=****_beijing&interactiveMode=true&enableOdpsLogger=true&autoSelectLimit=1000000000"If you perform Tableau operations on only some tables in the project, you can add the
table_list=table_name1, table_name2property to the server parameters to select the required tables. Separate table names with a comma (,). If there are too many tables, Tableau may open slowly. We strongly recommend that you use this method to load only the required tables. The following code provides an example. For tables with many partitions, we do not recommend setting all partition data as the data source. You can filter the required partitions or use custom SQL to retrieve the required data.http://service.cn-beijing.maxcompute.aliyun.com/api?project=****_beijing &interactiveMode=true&alwaysFallback=true&enableOdpsLogger=true&autoSelectLimit=1000000000" &table_list=orders,customersExample 2: Use MCQA with SQL Workbench/J
After you configure the JDBC driver, you can modify the JDBC URL in the Profile configuration interface to enable SQL Workbench/J to use MCQA. For more information about profile configuration, see Configure JDBC to use SQL Workbench/J.
The URL must be in the following format:
jdbc:odps:<MaxCompute_endpoint>? project=<MaxCompute_project_name>&accessId=<AccessKey ID>&accessKey=<AccessKey Secret> &charset=UTF-8&interactiveMode=true&autoSelectLimit=1000000000"The following table describes the parameters.
Parameter
Description
MaxCompute_endpoint
The endpoint of the region where the MaxCompute service is located. For more information, see Endpoints.
MaxCompute_project_name
The name of the MaxCompute project.
AccessKey ID
The AccessKey ID that has access permissions to the specified project.
You can go to the AccessKey Management page to get an AccessKey ID.
AccessKey Secret
The AccessKey secret corresponding to the AccessKey ID.
You can go to the AccessKey Management page to get an AccessKey secret.
charset=UTF-8
The character set encoding format.
interactiveMode
The switch for the MCQA feature.
trueenables MCQA.autoSelectLimit
This parameter must be configured when the data volume exceeds the 1,000,000-row limit.
Method 4: Enable MCQA using the Java SDK
For more information about the Java SDK, see Java SDK overview. You must configure the Pom dependency in Maven. The following code provides an example configuration.
<dependency>
<groupId>com.aliyun.odps</groupId>
<artifactId>odps-sdk-core</artifactId>
<version>3.3.0</version>
</dependency>The following is an example command to create a Java program.
import com.aliyun.odps.Odps;
import com.aliyun.odps.OdpsException;
import com.aliyun.odps.OdpsType;
import com.aliyun.odps.account.Account;
import com.aliyun.odps.account.AliyunAccount;
import com.aliyun.odps.data.Record;
import com.aliyun.odps.data.ResultSet;
import com.aliyun.odps.sqa.*;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.*;
public class SQLExecutorExample {
public static void SimpleExample() {
// Set the account and project information.
// An Alibaba Cloud account AccessKey has full permissions on all APIs and poses a high security risk. We recommend that you create and use a RAM user to make API calls or perform O&M. To create a RAM user, log on to the RAM console.
// This example shows how to store the AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret in environment variables. You can also store them in a configuration file as needed.
// We strongly recommend that you do not hard-code the AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret in your code. This can lead to security risks.
Account account = new AliyunAccount(System.getenv("ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID"), System.getenv("ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET"));
Odps odps = new Odps(account);
odps.setDefaultProject("<YOUR_PROJECT_NAME>");
odps.setEndpoint("http://service.<regionid>.maxcompute.aliyun.com/api");
// Prepare to build the SQLExecutor.
SQLExecutorBuilder builder = SQLExecutorBuilder.builder();
SQLExecutor sqlExecutor = null;
try {
// run in offline mode or run in interactive mode
if (false) {
// Create an executor that runs offline SQL statements by default.
sqlExecutor = builder.odps(odps).executeMode(ExecuteMode.OFFLINE).build();
} else {
// Create an executor that runs accelerated SQL queries by default and automatically falls back to offline query mode if the acceleration fails.
sqlExecutor = builder.odps(odps).executeMode(ExecuteMode.INTERACTIVE).fallbackPolicy(FallbackPolicy.alwaysFallbackPolicy()).build();
}
// You can pass special settings for the query if needed.
Map<String, String> queryHint = new HashMap<>();
queryHint.put("odps.sql.mapper.split.size", "128");
// Submit a query job. Hints are supported.
sqlExecutor.run("select count(1) from test_table;", queryHint);
// The following code provides some common methods for obtaining information.
// UUID
System.out.println("ExecutorId:" + sqlExecutor.getId());
// The Logview of the current query job.
System.out.println("Logview:" + sqlExecutor.getLogView());
// The Instance object of the current query job. In interactive mode, multiple query jobs may share the same instance.
System.out.println("InstanceId:" + sqlExecutor.getInstance().getId());
// The stage progress of the current query job (progress bar in the console).
System.out.println("QueryStageProgress:" + sqlExecutor.getProgress());
// The execution status change log of the current query job, such as fallback information.
System.out.println("QueryExecutionLog:" + sqlExecutor.getExecutionLog());
// Two methods are provided to obtain results.
if(false) {
// Directly obtain all query results. This is a synchronous method and may occupy the current thread until the query succeeds or fails.
// This method reads all result data into the memory at once. We do not recommend using this method for large datasets due to potential memory issues.
List<Record> records = sqlExecutor.getResult();
printRecords(records);
} else {
// Obtain an iterator (ResultSet) for the query results. This is a synchronous method and may occupy the current thread until the query succeeds or fails.
// We recommend using this method to retrieve large datasets because it reads query results in batches.
ResultSet resultSet = sqlExecutor.getResultSet();
while (resultSet.hasNext()) {
printRecord(resultSet.next());
}
}
// run another query
sqlExecutor.run("select * from test_table;", new HashMap<>());
if(false) {
// Directly obtain all query results. This is a synchronous method and may occupy the current thread until the query succeeds or fails.
// This method reads all result data into the memory at once. We do not recommend using this method for large datasets due to potential memory issues.
List<Record> records = sqlExecutor.getResult();
printRecords(records);
} else {
// Obtain an iterator (ResultSet) for the query results. This is a synchronous method and may occupy the current thread until the query succeeds or fails.
// We recommend using this method to retrieve large datasets because it reads query results in batches.
ResultSet resultSet = sqlExecutor.getResultSet();
while (resultSet.hasNext()) {
printRecord(resultSet.next());
}
}
} catch (OdpsException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (sqlExecutor != null) {
// Close the executor to release resources.
sqlExecutor.close();
}
}
}
// SQLExecutor can be reused by pool mode
public static void ExampleWithPool() {
// Set the account and project information.
// An Alibaba Cloud account AccessKey has full permissions on all APIs and poses a high security risk. We recommend that you create and use a RAM user to make API calls or perform O&M. To create a RAM user, log on to the RAM console.
// This example shows how to store the AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret in environment variables. You can also store them in a configuration file as needed.
// We strongly recommend that you do not hard-code the AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret in your code. This can lead to security risks.
Account account = new AliyunAccount(System.getenv("ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID"), System.getenv("ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET"));
Odps odps = new Odps(account);
odps.setDefaultProject("your_project_name");
odps.setEndpoint("http://service.<regionid>.maxcompute.aliyun.com/api");
// Execute a query using a connection pool.
SQLExecutorPool sqlExecutorPool = null;
SQLExecutor sqlExecutor = null;
try {
// Prepare the connection pool, set the pool size and default execution mode.
SQLExecutorPoolBuilder builder = SQLExecutorPoolBuilder.builder();
builder.odps(odps)
.initPoolSize(1) // init pool executor number
.maxPoolSize(5) // max executors in pool
.executeMode(ExecuteMode.INTERACTIVE); // run in interactive mode
sqlExecutorPool = builder.build();
// Get an executor from the connection pool. If the pool is empty, a new executor is created within the max limit.
sqlExecutor = sqlExecutorPool.getExecutor();
// The usage of the executor is the same as in the previous example.
sqlExecutor.run("select count(1) from test_table;", new HashMap<>());
System.out.println("InstanceId:" + sqlExecutor.getId());
System.out.println("Logview:" + sqlExecutor.getLogView());
List<Record> records = sqlExecutor.getResult();
printRecords(records);
} catch (OdpsException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
sqlExecutor.close();
}
sqlExecutorPool.close();
}
private static void printRecord(Record record) {
for (int k = 0; k < record.getColumnCount(); k++) {
if (k != 0) {
System.out.print("\t");
}
if (record.getColumns()[k].getType().equals(OdpsType.STRING)) {
System.out.print(record.getString(k));
} else if (record.getColumns()[k].getType().equals(OdpsType.BIGINT)) {
System.out.print(record.getBigint(k));
} else {
System.out.print(record.get(k));
}
}
}
private static void printRecords(List<Record> records) {
for (Record record : records) {
printRecord(record);
System.out.println();
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
SimpleExample();
ExampleWithPool();
}
}Method 5: Use PyODPS with SQLAlchemy or other SQLAlchemy-compatible third-party tools to accelerate queries
PyODPS integrates with SQLAlchemy, allowing you to use SQLAlchemy to query MaxCompute data. You need to specify the following parameters in the connection string to accelerate queries:
interactive_mode=true: Required. This is the master switch for the query acceleration feature.reuse_odps=true: Optional. Enables forced connection reuse. For some third-party tools, such as Apache Superset, enabling this option can improve performance.
You can configure the fallback_policy=<policy1>,<policy2>,... parameter in the connection string to refine the processing logic. Similar to the JDBC configuration, this controls the fallback behavior when acceleration fails.
generic: The default value is False. If you set it to True, the system falls back to offline mode when an unknown error occurs.noresource: The default value is False. If you set it to True, the system falls back to offline mode when there are insufficient resources.upgrading: The default value is False. If you set it to True, the system falls back to offline mode during an upgrade.timeout: The default value is False. If you set it to True, the system falls back to offline mode when a timeout occurs.unsupported: The default value is False. If you set it to True, the system falls back to offline mode when an unsupported MCQA scenario is encountered.default: Equivalent to specifying unsupported, upgrading, noresource, and timeout at the same time. Iffallback_policyis not specified in the connection string, this is the default value.all: The default value is False. If you set it to True, the system falls back to offline mode in all the preceding scenarios.
Usage example
The following connection string enables query acceleration, enables forced connection reuse, and falls back to offline mode when the query acceleration feature is not yet supported, during an upgrade, or when resources are insufficient.
odps://<access_id>:<ACCESS_KEY>@<project>/?endpoint=<endpoint>&interactive_mode=true&reuse_odps=true&fallback_policy=unsupported,upgrading,noresourceFAQ
Question 1: When I use JDBC to connect to MaxCompute and run an SQL task on subscription resources, the error "ODPS-1800001" is reported. The detailed error message is as follows:
sError:com.aliyun.odps.OdpsException: ODPS-1800001: Session exception - Failed to submit sub-query in session because:Prepaid project run out of free query quota.Possible cause:
The query acceleration feature is currently in public preview. If you purchased a subscription package, you can experience the query acceleration feature for free during the public preview period without performing any extra operations. During the free trial, a single MaxCompute project supports a maximum of 5 concurrent jobs and a cumulative total of 500 accelerated jobs per day. If the number of jobs exceeds 500, the preceding error occurs.
Solution:
When you configure JDBC to enable MCQA, set the alwaysFallback parameter to true. After this parameter is set, you can use MCQA for query acceleration as long as the number of jobs does not exceed 500. Jobs that exceed this limit will fall back to offline mode. For more information about the configuration and parameters, see Connection methods for MCQA.
Question 2: Why does it take longer to send a request and retrieve a result using PyODPS than using DataWorks?
Possible causes:
The
wait_for_xxxmethod was used, which increased the execution time.The polling interval is long.
Solution:
If the request itself runs quickly, do not use the
wait_for_xxxmethod. After you send the request, directly use Tunnel to download the results.Reduce the polling interval:
instance.wait_for_success(interval=0.1). The following code provides an example command.from odps import ODPS, errors max_retry_times = 3 def run_sql(odps, stmt): retry = 0 while retry < max_retry_times: try: inst = odps.run_sql_interactive(stmt) print(inst.get_logview_address()) inst.wait_for_success(interval=0.1) records = [] for each_record in inst.open_reader(tunnel=True): records.append(each_record) return records except errors.ODPSError as e: retry = retry + 1 print("Error: " + str(e) + " retry: " + str(retry) + "/" + str(max_retry_times)) if retry >= max_retry_times: raise e odps = ODPS(...) run_sql(odps, 'SELECT 1')
Question 3: How do I use Logview to troubleshoot Java SDK errors?
Solution: The MaxCompute Java SDK provides a Logview interface. You can use the following command to call the Logview interface to retrieve logs.
String logview = sqlExecutor.getLogView();Question 4: How do I retrieve the MaxCompute Logview URL when using JDBC?
Solution: The MaxCompute JDBC Driver is an encapsulation of the MaxCompute Java SDK. Therefore, when you use the MaxCompute JDBC Driver to execute SQL, a Logview URL is generated, just as it is with the MaxCompute client, MaxCompute Studio, and DataWorks. You can use Logview to view task execution status, track task progress, and retrieve task execution results. The Logview URL can be printed to the terminal screen by configuring the log output (properties.log4j) to use standard output by default.