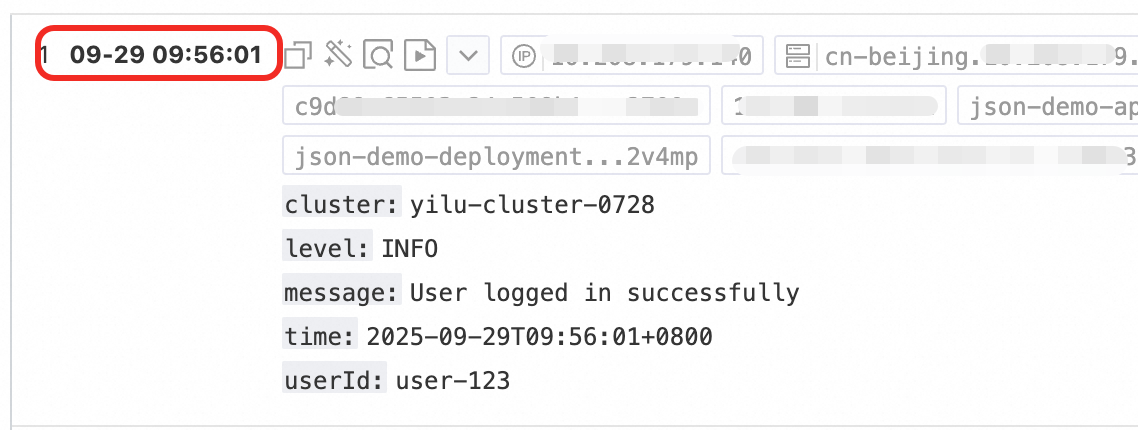
Managing scattered container logs in Kubernetes can be difficult, resulting in inefficient troubleshooting and high maintenance costs. To fix this, deploy LoongCollector in DaemonSet mode and set up a collection configuration in the Simple Log Service (SLS) console. This approach allows for unified log collection and structured processing, enhancing log retrieval, problem diagnosis, and observability analysis.
Applicability
Runtime environment:
Container Service for Kubernetes (ACK) (Managed and Dedicated editions) and self-managed Kubernetes clusters are supported.
Kubernetes 1.10.0 or later that supports
Mount propagation: HostToContainer.Container runtime: Docker and Containerd only
Docker:
Requires access permissions to docker.sock.
Standard output collection supports only the JSON log driver.
Only the overlay and overlay2 storage drivers are supported. For other storage driver types, you must manually mount the log directory.
Containerd: Requires access permissions to containerd.sock.
Resource requirements: LoongCollector (Logtail) runs with high priority as `system-cluster-critical`. Do not deploy it if cluster resources are insufficient. Otherwise, existing pods on the node might be evicted.
CPU: Reserve at least 0.1 core.
Memory: Reserve at least 150 MB for the collection component and at least 100 MB for the controller component.
Actual usage depends on the collection rate, the number of monitored directories and files, and the level of send congestion. Ensure that the actual usage is below 80% of the specified limit.
Permission requirements: The Alibaba Cloud account or RAM user used for deployment must have the
AliyunLogFullAccesspermission.To create custom policies, see the AliyunCSManagedLogRolePolicy system policy. Copy the permissions from the policy and grant them to the target RAM user or role for fine-grained permission configuration.
Collection configuration workflow
Install LoongCollector: Deploy LoongCollector in DaemonSet mode. This ensures that a collection container runs on each node in the cluster to collect logs from all containers on that node.
For information about the Sidecar pattern, see Collect text logs from Kubernetes pods (Sidecar pattern).
Create a Logstore: A logstore is used to store collected logs.
Create and configure log collection rules
Global and input configuration: Define the name of the collection configuration and specify the source and scope of log collection.
Log processing and structuring: Configure processing rules based on the log format.
Multiline logs: This is suitable for single logs that span multiple lines, such as Java exception stacks or Python tracebacks. You can use a first-line regular expression to identify the start of each log entry.
Structured parsing: Configure parsing plugins, such as regular expression, delimiter, or NGINX mode, to extract raw strings into structured key-value pairs for easier querying and analysis.
Log filtering: Configure collection blacklists and content filtering rules to screen for valid log content. This helps reduce redundant data transmission and storage.
Log categorization: Flexibly distinguish logs from different services, containers, or path sources by configuring log topics and tags.
Query and analysis configuration: Full-text indexing is enabled by default to support keyword searches. You can also enable field indexes for precise queries and analysis of structured fields to improve search efficiency.
Verification and troubleshooting: After the configuration is complete, verify that logs are collected successfully. If you encounter issues such as data collection failure, heartbeat failure, or parsing errors, see Troubleshooting FAQ.
Step 1: Install LoongCollector
LoongCollector is the next-generation log collection agent from SLS and is an upgraded version of Logtail. LoongCollector and Logtail cannot coexist. To install Logtail, see Install, run, upgrade, and uninstall Logtail.
This topic describes only the basic installation flow for LoongCollector. For more information about the parameters, see Installation and configuration. If you have already installed LoongCollector or Logtail, skip this step and proceed to Step 2: Create a logstore.
If the host time changes while LoongCollector (Logtail) is running, it might cause duplicate log collection or data loss.
ACK cluster
Install LoongCollector from the Container Service for Kubernetes console. By default, logs are sent to an SLS project under the current Alibaba Cloud account.
Log on to the ACK console. In the navigation pane on the left, choose Clusters.
Click the name of the target cluster.
In the left navigation pane, click Add-ons.
Go to the Logs and Monitoring tab, find loongcollector, and click Install.
NoteWhen you create a cluster, log service is enabled by default on the Advanced Settings section. You can choose to create a project or use the existing project.
After the installation is complete, SLS automatically creates the following resources under the current account. Log on to the Simple Log Service console to view them.
Resource type
Resource name
Function
Project
k8s-log-${cluster_id}A resource management unit that isolates logs of different services.
To create a Project for more flexible log resource management, see Create a Project.
Machine group
k8s-group-${cluster_id}A collection of log collection nodes.
Logstore
config-operation-logImportantDo not delete this logstore.
Stores logs of the loongcollector-operator component. Its billing method is the same as that of a regular logstore. For more information, see Billable items for the pay-by-ingested-data mode. We recommend that you do not create collection configurations in this logstore.
Self-managed cluster
Connect to the Kubernetes cluster and run the command for your cluster's region:
China regions
wget https://aliyun-observability-release-cn-shanghai.oss-cn-shanghai.aliyuncs.com/loongcollector/k8s-custom-pkg/3.0.12/loongcollector-custom-k8s-package.tgz; tar xvf loongcollector-custom-k8s-package.tgz; chmod 744 ./loongcollector-custom-k8s-package/k8s-custom-install.shRegions outside China
wget https://aliyun-observability-release-ap-southeast-1.oss-ap-southeast-1.aliyuncs.com/loongcollector/k8s-custom-pkg/3.0.12/loongcollector-custom-k8s-package.tgz; tar xvf loongcollector-custom-k8s-package.tgz; chmod 744 ./loongcollector-custom-k8s-package/k8s-custom-install.shGo to the
loongcollector-custom-k8s-packagedirectory and modify the./loongcollector/values.yamlconfiguration file.# ===================== Required Information ===================== # The name of the project where logs from this cluster will be collected, for example, k8s-log-custom-sd89ehdq projectName: "" # The region of the project, for example, Shanghai: cn-shanghai region: "" # The UID of the Alibaba Cloud account that owns the project. Enclose it in quotation marks, for example, "123456789" aliUid: "" # The network to use. Optional parameters: Internet, Intranet. The default is Internet. net: Internet # The AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret of the Alibaba Cloud account or RAM user. The account must have the AliyunLogFullAccess system policy permission. accessKeyID: "" accessKeySecret: "" # A custom cluster ID. The name can contain only uppercase letters, lowercase letters, digits, and hyphens (-). clusterID: ""In the
loongcollector-custom-k8s-packagedirectory, run the following command to install LoongCollector and its dependent components:bash k8s-custom-install.sh installAfter the installation is complete, check the running status of the components.
If a pod fails to start, check whether the `values.yaml` configuration is correct and whether the relevant images were pulled successfully.
# Check the pod status kubectl get po -n kube-system | grep loongcollector-dsSLS also automatically creates the following resources. Log on to the Simple Log Service console to view them.
Resource type
Resource name
Function
Project
The value of
projectNamedefined in the values.yaml fileA resource management unit that isolates logs of different services.
To create a Project for more flexible log resource management, see Create a Project.
Machine group
k8s-group-${cluster_id}A collection of log collection nodes.
Logstore
config-operation-logImportantDo not delete this logstore.
Stores logs of the loongcollector-operator component. Its billing method is the same as that of a regular logstore. For more information, see Pay-by-data-written billable items. We recommend that you do not create collection configurations in this logstore.
Step 2: Create a logstore
A logstore is the storage unit in SLS that is used to store collected logs.
Log on to the Simple Log Service console and click the name of the target project.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose
 , click +, and create a logstore:
, click +, and create a logstore:Logstore Name: Enter a name that is unique within the project. This name cannot be modified after creation.
Logstore Type: Select Standard or Query based on the feature comparison.
Billing Mode:
Pay-by-feature: You are billed independently for each resource, such as storage, indexes, and read/write operations. This mode is suitable for small-scale use cases or use cases where feature usage is uncertain.
Pay-by-ingested-Data: You are billed only for the volume of raw data that you write. This mode provides 30 days of free storage and free features, such as data transformation and delivery. It is suitable for business use cases where the storage period is close to 30 days or the data processing pipeline is complex.
Data Retention Period: Specifies the number of days to retain logs. The value can be from 1 to 3,650. A value of 3,650 indicates permanent retention. The default value is 30 days.
Keep the default values for the other settings and click OK. For more information, see Manage a logstore.
Step 3: Create and configure log collection rules
Define which logs LoongCollector collects, how it parses log structures, and how it filters content. Then, apply the configuration to a machine group.
On the
 Logstores page, click
Logstores page, click  to the left of the target logstore name to expand it.
to the left of the target logstore name to expand it.Click the
 icon next to Data Collection. In the Quick Data Import dialog box that appears, select a template based on the log source and click Integrate Now:
icon next to Data Collection. In the Quick Data Import dialog box that appears, select a template based on the log source and click Integrate Now:For container standard output, select K8S - Stdout and Stderr - New Version.
Templates for collecting container standard output are available in new and old versions. We recommend that you use the new version. For more information about the differences between the new and old versions, see Appendix: Comparison of New and Old Container Standard Output Versions.
For cluster text logs, select Kubernetes - File.
Configure the machine group and click Next.
Scenario: Select Kubernetes Clusters.
Deployment Method: Select ACK Daemonset or Self-managed Cluster in Daemonset Mode.
From the source machine group list, add the system-created machine group
k8s-group-${cluster_id}to the applied machine groups list.
On the Logtail Configuration page, specify the following parameters and click Next.
1. Global and input configurations
Before you begin, make sure that you have selected a data import template and applied it to a machine group. In this step, you define the name of the collection configuration, the log source, and the collection scope.
Collect container standard output
Global Configurations
Configuration Name: The name of the collection configuration. The name must be unique within the project and cannot be modified after it is created. The name must meet the following requirements:
It can contain only lowercase letters, digits, hyphens (-), and underscores (_).
It must start and end with a lowercase letter or a digit.
Input Configurations
Turn on the Stdout and Stderr or Standard Error switch (both are enabled by default).
ImportantDo not enable both standard output and standard error at the same time. This might cause confusion in the collected logs.
Collect cluster text logs
Global Configurations:
Configuration Name: The name of the collection configuration. The name must be unique within the project and cannot be modified after it is created. The name must meet the following requirements:
It can contain only lowercase letters, digits, hyphens (-), and underscores (_).
It must start and end with a lowercase letter or a digit.
Input Configurations:
File Path Type:
Path in Container: Collects log files from within the container.
Host Path: Collects local service logs on the host.
File Path: The absolute path of the log file to be collected.
Linux: The path must start with a forward slash (/). For example,
/data/mylogs/**/*.logindicates all files with the .log extension in the/data/mylogsdirectory and its subdirectories.Windows: The path must start with a drive letter, for example,
C:\Program Files\Intel\**\*.Log.
Maximum Directory Monitoring Depth: The maximum directory depth that the wildcard character
**can match in the File Path. The default value is 0, which indicates the current directory only. The value can range from 0 to 1,000.If you set the depth to 0, you must configure the path to the directory where the files are located.
2. Log processing and structuring
Configure log processing rules to convert raw, unstructured logs into structured, searchable data. This improves the efficiency of log querying and analysis. Before you configure the rules, add a log sample:
On the Logtail Configuration page, in the Processor Configurations section, click Add Sample Log and enter the log content that you want to collect. The system identifies the log format based on the sample and helps you generate regular expressions and parsing rules. This simplifies the configuration.
Use case 1: Multiline log processing (such as Java stack traces)
Logs, such as Java exception stacks and JSON objects, often span multiple lines. In the default collection mode, they are split into multiple incomplete records, which causes a loss of context. To resolve this issue, enable multiline collection mode and configure a first-line regular expression to merge the consecutive lines of a log into a single, complete log entry.
Example:
Raw log without any processing | In default collection mode, each line is a separate log, and the stack information is broken up, losing context | Enable multiline mode and use a first-line regular expression to identify the complete log, preserving the full semantic structure. |
|
|
|
Procedure: In the Processor Configurations section of the Logtail Configuration page, enable Multi-line Mode:
Type: Select Custom or Multi-line JSON.
Custom: Because the format of raw logs is not fixed, you must configure the Regex to Match First Line to identify the first line of each log entry.
Regex to Match First Line: Automatically generate or manually enter a regular expression. The regular expression must match an entire line of data. For example, the regular expression that matches the data in the preceding example is
\[\d+-\d+-\w+:\d+:\d+,\d+]\s\[\w+]\s.*.Automatic generation: Click Generate. Then, in the Log Sample text box, select the log content that you want to extract and click Automatically Generate.
Manual input: Click Manually Enter Regular Expression. After you enter the expression, click Validate.
Multi-line JSON: Select this option if all raw logs are in standard JSON format. SLS automatically handles line breaks within a single JSON log.
Processing Method If Splitting Fails:
Discard: If a segment of text fails to match the start-of-line rule, it is discarded.
Retain Single Line: Unmatched text is chunked and retained based on the original single-line pattern.
Use case 2: Structured logs
When raw logs are unstructured or semi-structured text, such as NGINX access logs or application output logs, direct querying and analysis are often inefficient. SLS provides a variety of data parsing plugins that can automatically convert raw logs of different formats into structured data. This provides a solid data foundation for subsequent analysis, monitoring, and alerting.
Example:
Raw log without any processing | Log after structured parsing |
| |
Procedure: In the Processor Configurations section of the Logtail Configuration page:
Add a parsing plugin: Click Add Processor to configure regular expression parsing, separator parsing, JSON parsing, and other plugins that match your log format. For example, to collect NGINX logs, select .
NGINX Log Configuration: Completely copy the
log_formatdefinition from the NGINX server configuration file (nginx.conf) and paste it into this text box.Example:
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ''$request_time $request_length ''$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ''"$http_user_agent"';ImportantThe format definition must be exactly the same as the format that generates the logs on the server. Otherwise, log parsing fails.
Common configuration parameters: The following parameters appear in multiple data parsing plugins. Their functions and usage are consistent.
Original Field: Specify the name of the source field to be parsed. The default value is
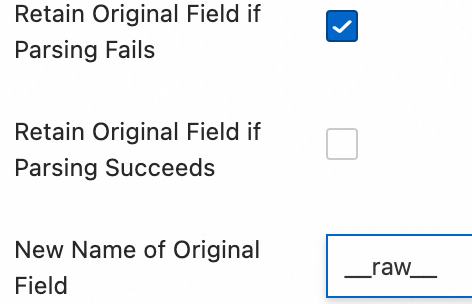
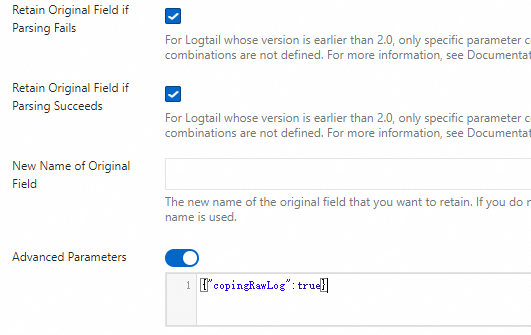
content, which represents the entire collected log content.Retain Original Field if Parsing Fails: We recommend that you select this option. If a log cannot be successfully parsed by the plugin due to a format mismatch, this option ensures that the original log content is not lost and is fully retained in the specified original field.
Retain Original Field if Parsing Succeeds: If you select this option, the original log content is retained even if the log is parsed successfully.
3. Log filtering
During log collection, collecting a large volume of low-value or irrelevant logs, such as DEBUG- or INFO-level logs, can waste storage resources, increase costs, affect query efficiency, and pose data breach risks. To address these issues, use fine-grained filtering policies for efficient and secure log collection.
Reduce costs through content filtering
Filter fields based on log content, such as collecting only logs with a level of WARNING or ERROR.
Example:
Raw log without any processing | Collect only |
| |
Procedure: In the Processor Configurations section of the Logtail Configuration page:
Click Add Processor and choose :
Field Name: The log field to filter.
Field Value: The regular expression used for filtering. Only full-text matching is supported. Partial keyword matching is not supported.
Control collection scope through blacklists
Use the blacklist mechanism to exclude specified directories or files. This prevents irrelevant or sensitive logs from being uploaded.
Procedure: In the Input Configurations section of the Logtail Configuration page, enable Collection Blacklist and click Add.
Full matching and wildcard matching for directories and filenames are supported. The only supported wildcard characters are the asterisk (*) and the question mark (?).
File Path Blacklist: The file paths to ignore. Examples:
/home/admin/private*.log: During collection, all files in the/home/admin/directory that start with `private` and end with `.log` are ignored./home/admin/private*/*_inner.log: During collection, files that end with `_inner.log` in directories that start with `private` under the/home/admin/directory are ignored.
File Blacklist: The names of files to ignore during data collection. Example:
app_inner.log: During collection, all files namedapp_inner.logare ignored.
Directory Blacklist: The directory path cannot end with a forward slash (/). Examples:
/home/admin/dir1/: The directory blacklist will not take effect./home/admin/dir*: All files in the subdirectories of/home/admin/that start with `dir` are ignored./home/admin/*/dir: During collection, all files in subdirectories named `dir` at the second level under the/home/admin/directory are ignored. For example, files in the/home/admin/a/dirdirectory are ignored, but files in the/home/admin/a/b/dirdirectory are collected.
Container filtering
Set collection conditions based on container metadata, such as environment variables, pod labels, namespaces, and container names, to precisely control which containers' logs are collected.
Procedure: In the Processor Configurations section of the Logtail Configuration page, enable Container Filtering and click Add.
Multiple conditions are combined using a logical AND. All regular expression matching is based on the Go language's RE2 engine. This engine has more limitations than other engines, such as PCRE. Therefore, you must write regular expressions that comply with the guidelines in Appendix: Regular Expression Limits (Container Filtering).
Environment Variable Blacklist/Whitelist: Specify the environment variable conditions for the containers from which you want to collect logs.
K8s Pod Label Blacklist/Whitelist: Specify the label conditions for the pod where the containers from which you want to collect logs are located.
K8s Pod Name Regex Match: Specify the containers from which you want to collect logs by pod name.
K8s Namespace Regex Match: Specify the containers from which you want to collect logs by namespace name.
K8s Container Name Regex Match: Specify the containers from which you want to collect logs by container name.
Container Label Blacklist/Whitelist: Collect logs from containers whose labels meet the specified conditions. This is used in Docker use cases and is not recommended for Kubernetes use cases.
4. Log categorization
In use cases where multiple applications or instances share the same log format, it is difficult to distinguish the log source. This leads to a lack of context during querying and inefficient analysis. To resolve this issue, configure log topics and tags for automatic context association and logical categorization.
Configure log topics
If the logs of multiple applications or instances have the same format but different paths, such as /apps/app-A/run.log and /apps/app-B/run.log, it is difficult to distinguish the source of the collected logs. In this case, you can generate topics based on machine groups, custom names, or file path extraction to flexibly distinguish logs from different services or path sources.
Procedure: Choose . Select a topic generation method. The following three types are supported:
Machine Group Topic: If a collection configuration is applied to multiple machine groups, LoongCollector automatically uses the machine group name of the server as the value of the
__topic__field for upload. This is suitable for use cases where logs are divided by host cluster.Custom: The format is
customized://<custom_topic_name>, for example,customized://app-login. This applies to static topic use cases with fixed business identities.File Path Extraction: Extract key information from the full path of the log file to dynamically mark the log source. This is suitable for situations where multiple users or applications share the same log filename but have different paths.
If multiple users or services write logs to different top-level directories but with the same subdirectory paths and filenames, the source cannot be distinguished by filename alone. For example:
/data/logs ├── userA │ └── serviceA │ └── service.log ├── userB │ └── serviceA │ └── service.log └── userC └── serviceA └── service.logConfigure File Path Extraction and use a regular expression to extract key information from the full path. The matched result is then used as the log topic for upload to the logstore.
Extraction rules: Based on regular expression capturing groups
When you configure a regular expression, the system automatically determines the output field format based on the number and naming of capturing groups. The rules are as follows:
In the regular expression for the file path, you must escape the forward slash (/).
Capturing group type
Use cases
Generated field
Regex example
Example matched path
Generated field
Single capturing group (only one
(.*?))Only one dimension is needed to distinguish the source, such as username or environment
Generates the
__topic__field\/logs\/(.*?)\/app\.log/logs/userA/app.log__topic__: userAMultiple capturing groups - unnamed (multiple
(.*?))Multiple dimensions are needed but without semantic labels
Generates the tag field
__tag__:__topic_{i}__, where{i}is the sequence number of the capturing group\/logs\/(.*?)\/(.*?)\/app\.log/logs/userA/svcA/app.log__tag__:__topic_1__userA.__tag__:__topic_2__svcAMultiple capturing groups - named (using
(?P<name>.*?))Multiple dimensions are needed, and clear field meanings are desired for easy querying and analysis
Generates the tag field
__tag__:{name}\/logs\/(?P<user>.*?)\/(?P<service>.*?)\/app\.log/logs/userA/svcA/app.log__tag__:user: userA;__tag__:service:svcA
Log tagging
Enable the log tag enrichment feature to extract key information from container environment variables or Kubernetes pod labels and attach the information as tags for fine-grained log grouping.
Procedure: In the Input Configurations section of the Logtail Configuration page, enable Log Tag Enrichment and click Add.
Environment Variables: Configure an environment variable name and the tag name in which to store the value of the variable.
Environment Variable Name: Specify the name of the environment variable to be extracted.
Tag Name: The name of the environment variable tag.
Pod Labels: Configure the pod label name and the tag name. The value of the pod label is stored as the tag value.
Pod Label Name: The name of the Kubernetes pod label to be extracted.
Tag Name: The name of the tag.
Step 4: Query and analysis configuration
After you configure log processing and plugins, click Next to go to the Query and Analysis Configurations page:
By default, the system enables the full-text index, which lets you search for keywords in the raw content of logs.
To perform a term query by field, click Automatic Index Generation after the Preview Data is loaded. SLS generates a field index based on the first entry in the preview data.
After the configuration is complete, click Next to complete the setup of the collection process.
Step 5: Validation and troubleshooting
After you create a collection configuration and apply it to a machine group, the system automatically deploys the configuration and starts to collect incremental logs.
View reported logs
Confirm that the log file has new content: LoongCollector collects only incremental logs. Run the
tail -f /path/to/your/log/filecommand and trigger a service operation to ensure that new logs are being written.Query logs: Go to the query and analysis page of the target logstore and click Search & Analyze. The default time range is the last 15 minutes. Check whether new logs are flowing in. Each collected container text log contains the following default field information:
Field
Description
__tag__:__hostname__
The name of the container's host.
__tag__:__path__
The path of the log file within the container.
__tag__:_container_ip_
The IP address of the container.
__tag__:_image_name_
The name of the image used by the container.
__tag__:_pod_name_
The name of the pod.
__tag__:_namespace_
The namespace to which the pod belongs.
__tag__:_pod_uid_
The unique identifier (UID) of the pod.
Common troubleshooting issues
Machine group heartbeat status is FAIL
Check the user identifier: If your server type is not ECS, or if the ECS instance and the project belong to different Alibaba Cloud accounts, check whether the correct user identifier exists in the specified directory as shown in the following table.
Linux: Run the
cd /etc/ilogtail/users/ && touch <uid>command to create the user identifier file.Windows: Go to the
C:\LogtailData\users\directory and create an empty file named<uid>.
If a file named with the Alibaba Cloud account ID of the current project exists in the specified path, the user identifier is configured correctly.
Check the machine group identifier: If you are using a machine group with a custom ID, check whether a
user_defined_idfile exists in the specified directory. If the file exists, check whether the content of the file matches the custom ID that is configured for the machine group.Linux:
# Configure the custom user ID. If the directory does not exist, create it manually. echo "user-defined-1" > /etc/ilogtail/user_defined_idWindows: In the
C:\LogtailDatadirectory, create a file nameduser_defined_idand write the custom user ID into the file. If the directory does not exist, you must create it manually.
If both the user identity and the machine group identity are configured correctly, see LoongCollector (Logtail) Machine Group Troubleshooting Guide for more information about troubleshooting.
Log collection errors or format errors
Troubleshooting: This issue indicates that the network connection and basic configuration are normal. The issue is typically caused by a mismatch between the log content and the parsing rules. You must view the specific error message to locate the cause of the issue:
On the Logtail Configuration page, click the name of the LoongCollector (Logtail) configuration that has a collection error. On the Log Collection Error tab, click Select Time Range to set the query time range.
In the section, view the alarm metric of the error log and find the corresponding solution in Common Data Collection Errors.
What to do next
Data visualization: Use visualization dashboards to monitor key metric trends.
Automatic alerting for data anomalies: Set alert policies to detect system anomalies in real time.
Troubleshooting: No data collected from container logs
Check for new logs: After you configure LoongCollector (Logtail) for collection, if there are no new logs in the target log file, LoongCollector (Logtail) does not collect data from that file.
FAQ
How do I send ACK cluster logs to a project in another Alibaba Cloud account?
Manually install the SLS LoongCollector (Logtail) component in the ACK cluster and configure it with the Alibaba Cloud account ID or access credential (AccessKey) of the target account. This lets you send container logs to an SLS project that belongs to another Alibaba Cloud account.
Use case: You want to collect log data from an ACK cluster and send it to an SLS project that belongs to a different Alibaba Cloud account for reasons such as organizational structure, permission isolation, or unified monitoring. Manually install LoongCollector (Logtail) for cross-account configuration.
Procedure: The following procedure describes how to manually install LoongCollector. For information about how to install Logtail, see Install and configure Logtail.
Connect to the Kubernetes cluster and run the command for your cluster's region:
China regions
wget https://aliyun-observability-release-cn-shanghai.oss-cn-shanghai.aliyuncs.com/loongcollector/k8s-custom-pkg/3.0.12/loongcollector-custom-k8s-package.tgz; tar xvf loongcollector-custom-k8s-package.tgz; chmod 744 ./loongcollector-custom-k8s-package/k8s-custom-install.shRegions outside China
wget https://aliyun-observability-release-ap-southeast-1.oss-ap-southeast-1.aliyuncs.com/loongcollector/k8s-custom-pkg/3.0.12/loongcollector-custom-k8s-package.tgz; tar xvf loongcollector-custom-k8s-package.tgz; chmod 744 ./loongcollector-custom-k8s-package/k8s-custom-install.shGo to the
loongcollector-custom-k8s-packagedirectory and modify the./loongcollector/values.yamlconfiguration file.# ===================== Required Information ===================== # The name of the project where logs from this cluster will be collected, for example, k8s-log-custom-sd89ehdq projectName: "" # The region of the project, for example, Shanghai: cn-shanghai region: "" # The UID of the Alibaba Cloud account that owns the project. Enclose it in quotation marks, for example, "123456789" aliUid: "" # The network to use. Optional parameters: Internet, Intranet. The default is Internet. net: Internet # The AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret of the Alibaba Cloud account or RAM user. The account must have the AliyunLogFullAccess system policy permission. accessKeyID: "" accessKeySecret: "" # A custom cluster ID. The name can contain only uppercase letters, lowercase letters, digits, and hyphens (-). clusterID: ""In the
loongcollector-custom-k8s-packagedirectory, run the following command to install LoongCollector and its dependent components:bash k8s-custom-install.sh installAfter the installation is complete, check the running status of the components.
If a pod fails to start, check whether the `values.yaml` configuration is correct and whether the relevant images were pulled successfully.
# Check the pod status kubectl get po -n kube-system | grep loongcollector-dsSLS also automatically creates the following resources. Log on to the Simple Log Service console to view them.
Resource type
Resource name
Function
Project
The value of
projectNamedefined in the values.yaml fileA resource management unit that isolates logs of different services.
To create a Project for more flexible log resource management, see Create a Project.
Machine group
k8s-group-${cluster_id}A collection of log collection nodes.
Logstore
config-operation-logImportantDo not delete this logstore.
Stores logs of the loongcollector-operator component. Its billing method is the same as that of a regular logstore. For more information, see Pay-by-data-written billable items. We recommend that you do not create collection configurations in this logstore.
How can I collect logs from the same file or container standard output using multiple collection configurations?
By default, to prevent data duplication, SLS allows each log source to be collected by only one collection configuration:
A text log file can match only one Logtail collection configuration.
A container's standard output (stdout):
If you use the new version of the standard output template, the standard output can be collected by only one standard output collection configuration by default.
If you use the old version of the standard output template, no extra configuration is required. It supports multiple collections by default.
Log on to the Simple Log Service console and go to the target project.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose
 Logstores and find the target logstore.
Logstores and find the target logstore.Click the
 icon before its name to expand the logstore.
icon before its name to expand the logstore.Click Logtail Configuration. In the configuration list, find the target Logtail configuration and click Manage Logtail Configuration in the Actions column.
On the Logtail configuration page, click Edit and scroll down to the Input Configurations section:
To collect text file logs: Enable Allow File To Be Collected For Multiple Times.
To collect container standard output: Enable Allow Collection By Different Logtail Configurations.
Why do I get a dependency error when uninstalling the loongcollector(logtail-ds) component in ACK?
Problem: When you try to delete the loongcollector (logtail-ds) log collection component in Container Service for Kubernetes (ACK), the system reports an error: `The dependencies of this component are not met`.
Dependencies of addons are not met: terway-eniip depends on logtail-ds(>0.0) whose version is v3.x.x.x-aliyun or will be v3.x.x.x-aliyun.
Cause: The terway-eniip network plugin has the log collection feature enabled, which depends on the loongcollector (logtail-ds) component. Therefore, ACK does not allow you to directly uninstall loongcollector (logtail-ds) before you remove this dependency.
Solution: Follow these steps to remove the dependency and then uninstall the component:
Log on to the ACK console.
In the cluster list, click the name of the target cluster.
In the navigation pane on the left, click Add-ons.
In the component list, search for and find the
terway-eniipcomponent. Click .In the dialog box that appears, click OK.
After the configuration takes effect, try to uninstall the loongcollector (logtail-ds) component again.
Why is the last log entry reported after a long delay? Why is it sometimes truncated?
Cause: Logs are usually truncated if a log file is missing a line feed at the end, or if a multiline log, such as an exception stack, has not been fully written. Because the collector cannot determine whether the log has ended, the last part of the content might be split prematurely or reported with a delay. The handling mechanism differs based on the version of LoongCollector (Logtail):
Versions earlier than 1.8:
If the last line of a log does not have a line feed (carriage return), or if a multiline log paragraph is not finished, the collector waits for the next write to trigger an output. This can cause the last log entry to be held for a long time without being sent until a new log is written.Version 1.8 and later:
A timeout refresh mechanism was introduced to prevent logs from getting stuck. When an incomplete log line is detected, the system starts a timer. After the timeout period ends, the current content is automatically submitted, which ensures that the log is eventually collected.Default timeout: 60 seconds. This ensures integrity in most use cases.
Adjust this value as needed, but do not set it to 0. This might cause logs to be truncated or partially lost.
Solution:
Extend the waiting time to ensure that the complete log is written before it is collected:
Log on to the Simple Log Service console and go to the target project.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose
 Logstores and find the target logstore.
Logstores and find the target logstore.Click the
 icon before its name to expand the logstore.
icon before its name to expand the logstore.Click Logtail Configuration. In the configuration list, find the target Logtail configuration and click Manage Logtail Configuration in the Actions column.
On the Logtail configuration page, click Edit:
Choose . Add the following JSON configuration to customize the timeout period.
{ "FlushTimeoutSecs": 1 }Default value: Determined by the startup parameter
default_reader_flush_timeout, which is usually a few seconds.Unit: Seconds.
Recommended value: ≥1 second. Do not set it to 0. This might cause logs to be truncated or partially lost.
After configuration, click Save.
Why does LoongCollector (Logtail) switch from an internal network domain to the public network during operation? Can it switch back automatically?
If LoongCollector (Logtail) detects an anomaly in internal network domain communication, such as a network failure or connection timeout, the system automatically switches to the public domain name for data transmission. This ensures the continuity and reliability of log collection and prevents log accumulation or loss.
LoongCollector: Automatically switches back to the internal network after the network is restored.
Logtail: Does not automatically switch back. You must manually restart it to resume internal network communication.
Appendix: Detailed explanation of native plugins
In the Processor Configurations section of the Logtail Configuration page, add processors to structure raw logs. To add a processing plugin to an existing collection configuration, follow these steps:
In the navigation pane on the left, choose
 Logstores and find the target logstore.
Logstores and find the target logstore.Click the
 icon before its name to expand the logstore.
icon before its name to expand the logstore.Click Logtail Configuration. In the configuration list, find the target Logtail configuration and click Manage Logtail Configuration in the Actions column.
On the Logtail configuration page, click Edit.
This section introduces only commonly used processing plugins that cover common log processing use cases. For more features, see Extended processors.
Rules for combining plugins (for LoongCollector / Logtail 2.0 and later):
Native and extended processors can be used independently or combined as needed.
Prioritize native processor because they offer better performance and higher stability.
When native features cannot meet your business needs, add extended processors after the configured native ones for supplementary processing.
Order constraint:
All plugins are executed sequentially in the order they are configured, which forms a processing chain. Note: All native processors must precede any extended processors. After you add an extended processor, you cannot add more native processors.
Regular expression parsing
Use regular expressions to extract log fields and parse the log into key-value pairs. Each field can be independently queried and analyzed.
Example:
Raw log without any processing | Using the regex parsing plugin |
| |
Procedure: In the Processor Configurations section of the Logtail Configuration page, click Add Processor and choose :
Regular Expression: Matches logs and supports automatic generation or manual input:
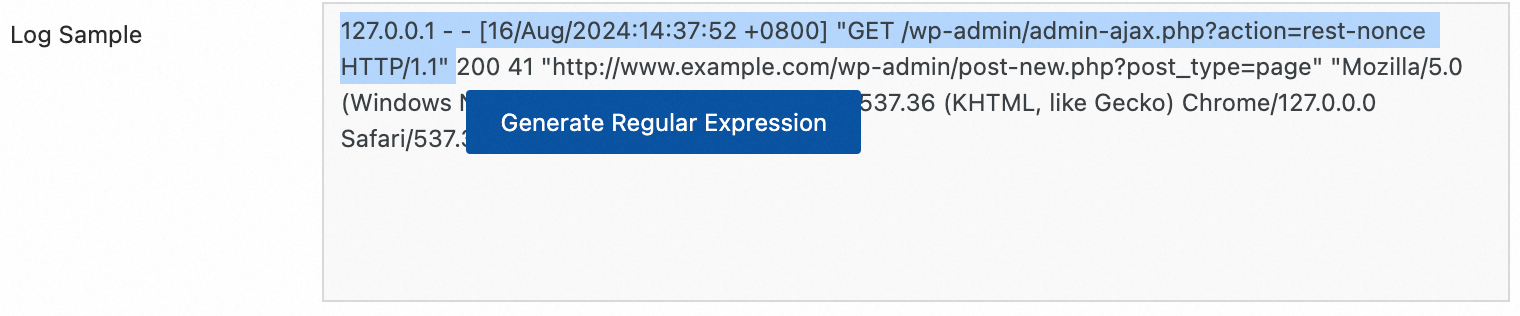
Automatic generation:
Click Generate.
In the Log Sample text box, select the log content that you want to extract.
Click Generate Regular Expression.
Manual input: Click Manually Enter Regular Expression based on the log format.
After configuration, click Validate to test whether the regular expression can correctly parse the log content.
Extracted Field: For the fetched log content (Value), set the corresponding field name (Key).
For more information about the other parameters, see the descriptions of common configuration parameters in Use case 2: Structured logs.
Delimiter-based parsing
Use a delimiter to structure the log content and parse it into multiple key-value pairs. Both single-character and multi-character delimiters are supported.
Example:
Raw log without any processing | Split fields by the specified character |
| |
Procedure: In the Processor Configurations section of the Logtail Configuration page, click Add Processor and choose :
Delimiter: Specifies the character used to split the log content.
For example, for CSV files, select Custom and enter a comma (,).
Quote: If a field value contains a separator, you must specify a quote to enclose that field to prevent incorrect splitting.
Extracted Field: Set a field name (Key) for each column in the order that the columns are separated. The following rules apply:
Field names can contain only letters, digits, and underscores (_).
Field names must start with a letter or an underscore (_).
The maximum length is 128 bytes.
For more information about the other parameters, see the description of common configuration parameters in Use case 2: Structured logs.
Standard JSON parsing
Structure an object-type JSON log and parse it into key-value pairs.
Example:
Raw log without any processing | Standard JSON key-value pairs are automatically extracted |
| |
Procedure: In the Processor Configurations section of the Logtail Configuration page, click Add Processor and choose :
Original Field: The default value is content. This field is used to store the raw log content for parsing.
For more information about the other parameters, see the description of common configuration parameters in Use case 2: Structured logs.
Nested JSON parsing
Parse a nested JSON log into key-value pairs by specifying the expansion depth.
Example:
Raw log without any processing | Expansion depth: 0, with the expansion depth used as a prefix | Expansion depth: 1, with the expansion depth used as a prefix |
| | |
Procedure: In the Processor Configurations section of the Logtail Configuration page, click Add Processor and choose :
Original Field: The name of the source field to expand, such as
content.JSON Expansion Depth: The number of levels to expand in a JSON object. A value of 0 means full expansion (default), 1 means the current level, and so on.
Character to Concatenate Expanded Keys: The delimiter used to join field names during JSON expansion. The default is an underscore _.
Name Prefix of Expanded Keys: Specifies the prefix for field names after JSON expansion.
Expand Array: Expands an array into indexed key-value pairs.
Example:
{"k":["a","b"]}is expanded to{"k[0]":"a","k[1]":"b"}.To rename the expanded fields (for example, changing `prefix_s_key_k1` to `new_field_name`), you can later add a Rename Field plugin to complete the mapping.
For more information about the other parameters, see the description of common configuration parameters in Use case 2: Structured logs.
JSON array parsing
Use the json_extract function to fetch a JSON object from a JSON array.
Example:
Raw log without any processing | Extracted JSON array structure |
| |
Configuration steps: In the Processor Configurations section of the Logtail Configuration page, switch the Processing Method to SPL, configure the SPL Statement, and use the json_extract function to extract JSON objects from a JSON array.
Example: Extract elements from the JSON array in the log field content and store the results in new fields json1 and json2.
* | extend json1 = json_extract(content, '$[0]'), json2 = json_extract(content, '$[1]')Apache log parsing
Structure the log content into multiple key-value pairs based on the definition in the Apache log configuration file.
Example:
Raw log without any processing | Apache Common Log Format |
| |
Procedure: In the Processor Configurations section of the Logtail Configuration page, , click Add Processor and choose :
Log Format: combined
APACHE LogFormat Configuration: The system automatically fills the configuration based on the Log Format.
ImportantMake sure to verify the auto-filled content to ensure it is exactly the same as the LogFormat defined in the Apache configuration file on the server, which is usually located at `/etc/apache2/apache2.conf`.
For more information about the other parameters, see the description of common configuration parameters in Use case 2: Structured logs.
Data masking
Mask sensitive data in logs.
Example:
Raw log without any processing | Masking result |
| |
Procedure: In the Processor Configurations section of the Logtail Configuration page, click Add Processor and choose :
Original Field: The field used to store log content before parsing.
Data Masking Method:
const: Replaces the sensitive content with a specified string.
md5: Replaces the sensitive content with its corresponding MD5 hash.
Replacement String: If you set Data Masking Method to const, you must enter a string to replace the sensitive content.
Content Expression that Precedes Replaced Content: Used to find sensitive content, configured using RE2 syntax.
Content Expression to Match Replaced Content: An expression for sensitive content, configured using RE2 syntax.
Time parsing
Parse the time field in the log and set the parsing result as the log's __time__ field.
Example:
Raw log without any processing | Time parsing |
|
|
Procedure: In the Processor Configurations section of the Logtail Configuration page, click Add Processor and choose :
Original Field: The field that stores the original log content before parsing.
Time Format: Set the time format based on the time content in the log.
Time Zone: Select the time zone of the time field in the log. The default is the machine time zone, which is the time zone of the environment where the Logtail process is running.
Appendix: Regular expression limits (container filtering)
The regular expressions for container filtering are based on the Go RE2 engine. The RE2 engine has several syntax limitations compared to other engines, such as Perl Compatible Regular Expressions (PCRE). Note the following when you write regular expressions:
1. Named group syntax differences
Go uses the (?P<name>...) syntax to define named groups and does not support the (?<name>...) syntax from PCRE.
Correct:
(?P<year>\d{4})Incorrect:
(?<year>\d{4})
2. Unsupported regular expression features
The following common but complex regular expression features are not supported by RE2. Avoid using them:
Assertions:
(?=...),(?!...),(?<=...), or(?<!...)Conditional expressions:
(?(condition)true|false)Recursive matching:
(?R)or(?0)Subprogram references:
(?&name)or(?P>name)Atomic groups:
(?>...)
3. Recommendations
Use a tool such as Regex101 to debug regular expressions. To validate compatibility, select the Golang (RE2) mode. The plugin cannot parse or match expressions that contain unsupported syntax.
Appendix: Comparison of new and old versions of container standard output
To improve log storage efficiency and collection consistency, the log metadata format for container standard output has been upgraded. The new format consolidates metadata into the __tag__ field, which achieves storage optimization and format standardization.
Core advantages of the new standard output version
Significant performance improvement
Refactored in C++, performance is improved by 180% to 300% compared with the old Go implementation.
Supports native plugins for data processing and multi-threading parallel processing, which fully utilizes system resources.
Supports flexible combination of native and Go plugins to meet complex scenario requirements.
Greater reliability
Supports a standard output log rotation queue. The log collection mechanism is unified with the file collection mechanism, which provides high reliability in scenarios with rapid standard output log rotation.
Lower resource consumption
CPU usage is reduced by 20% to 25%.
Memory usage is reduced by 20% to 25%.
Enhanced O&M consistency
Unified parameter configuration: The configuration parameters of the new standard output collection plugin are consistent with the file collection plugin.
Unified metadata management: The naming of container metadata fields and the storage location of tag logs are unified with the file collection scenario. The consumer side needs to maintain only one set of processing logic.
Comparison of new and old version features
Feature dimension
Old version features
New version features
Storage method
Metadata is directly embedded in the log content as a normal field.
Metadata is centrally stored in the
__tag__tag.Storage efficiency
Each log carries the full metadata repeatedly, which consumes more storage space.
Multiple logs in the same context can reuse metadata, which saves storage costs.
Format consistency
Inconsistent with the container file collection format.
Field naming and storage structure are fully aligned with container file collection, which provides a unified experience.
Query access method
Can be queried directly by field name, such as
_container_name_.Requires accessing the corresponding key-value through
__tag__, such as__tag__: _container_name_.Container metadata field mapping table
Old version field name
New version field name
_container_ip_
__tag__:_container_ip_
_container_name_
__tag__:_container_name_
_image_name_
__tag__:_image_name_
_namespace_
__tag__:_namespace_
_pod_name_
__tag__:_pod_name_
_pod_uid_
__tag__:_pod_uid_
In the new version, all metadata fields are stored in the tag area of the log in the format
__tag__:<key>, rather than being embedded in the log content.Impact of new version changes on users
Consumer-side adaptation: Because the storage location has changed from "content" to "tag", the user's log consumption logic needs to be adjusted accordingly. For example, you must access fields through __tag__ during queries.
SQL compatibility: Query SQL has been automatically adapted for compatibility, so users do not need to modify their query statements to process both new and old version logs simultaneously.