Live stream encapsulation converts your live streams into different container formats for playback over various streaming protocols with low latency.
Supported container formats
ApsaraVideo Live supports Real-Time Messaging Protocol (RTMP), HTTP-FLV, and HTTP Live Streaming (HLS). To reduce latency and improve compatibility, live stream encapsulation converts streams into different container formats in the cloud before delivery.
The following table describes the supported container formats:
Container format | Supported streaming protocol | Supported codec |
TS | Low-Latency HLS (LL-HLS) | Audio: AAC, OPUS, AC3, EAC3, MP3 Video: H.264, H.265 |
CMAF | LL-HLS, HLS, DASH | Audio: AAC Video: H.264, H.265 |
How it works
Live stream encapsulation splits streams into segments in TS or CMAF format. The system then distributes the segments via HLS, LL-HLS, or DASH protocols. For each stream, the system generates a manifest file that records segment URLs in sequence. When a client requests the live stream, the server returns the latest manifest.
You can combine this feature with live stream transcoding and time shifting to improve the streaming experience.
Advantages
Implement low-latency live streaming
Compared to standard HLS, LL-HLS divides streams into smaller partial segments (200 ms to 1 second). This approach blocks playlist reloads and reduces end-to-end latency to 3 to 5 seconds.
Enhance compatibility with multiple devices
By default, ApsaraVideo Live distributes live streams over HLS using the TS container format. This format is incompatible with some devices and browsers. Use encapsulation to package content into CMAF format, which supports a wider range of devices, platforms, and codecs (including H.265).
Limitations
GOP size
The GOP size of the ingested stream must remain consistent. If you encapsulate a transcoded stream, ensure its GOP size is also stable.
Each segment duration must be a multiple of the GOP size.
LL-HLS protocol
Stuttering may increase under poor network conditions. We recommend using encapsulation with multi-bitrate transcoding, which automatically adjusts the bitrate.
Set the GOP size to 1 or 2 seconds to prevent stuttering or playback failure.
A main streaming domain can support up to 100,000 viewers. To increase this quota, submit a ticket.
Configuration propagation
When you add an encapsulation configuration for the first time, the system updates content delivery settings. These changes take 3 to 5 minutes to take effect.
Create an encapsulation configuration
Create an encapsulation configuration in the console or by calling an API operation.
For an ongoing stream, the configuration takes effect only after you re-ingest the stream.
Console
Log on to the ApsaraVideo Live console.
In the left navigation pane, choose Feature Management > Encapsulation.
Select a streaming domain, and then click Add.
In the Encapsulation Settings dialog box, configure the following parameters:
Parameter
Description
AppName
Enter an asterisk (
*) to apply to all applications. To target a specific application, enter theAppNamefrom the ingest URL.StreamName
Enter an asterisk (
*) to apply to all streams. To target a specific stream, enter the stream name.Protocol
Select the container format and playback protocol: Valid values:
HLS - CMAF
LL-HLS - CMAF
LL-HLS - TS
DASH - CMAF
HLS & DASH - CMAF
Segment Quantity
Specify the number of segments per manifest file. Valid values: 3 to 5.
Segment Length (s)
For HLS or DASH: Enter an integer from 1 to 10. Set this to a multiple of your GOP size (Recommended GOP: 5s).
For LL-HLS: Enter 1 or 2. Set it to a multiple of your GOP size (Recommended GOP: 1s).
Part Length (ms)
(LL-HLS only) Specify the duration of partial segments. Valid values: 200 to 1,000. We recommend a value slightly larger than one-third of the segment length.
Transcoded Stream
Specify whether to encapsulate transcoded streams. Valid values:
Source Stream Only
Transcoded Stream Included
NoteIf your streaming domain uses a live center outside the Chinese mainland (Singapore, Germany, Japan, or Indonesia), playback delay may increase. Test your configuration before production use.
Click OK.
API
Call the AddLivePackageConfig API to add an encapsulation configuration.
Replace the placeholders, including <Your RegionId>, <Your DomainName>, <Your AppName>, and <Your StreamName>.
For valid protocol values, see AddLivePackageConfig.
Sample code
// This file is auto-generated, don't edit it. Thanks.
package demo;
import com.aliyun.auth.credentials.Credential;
import com.aliyun.auth.credentials.provider.StaticCredentialProvider;
import com.aliyun.core.http.HttpClient;
import com.aliyun.core.http.HttpMethod;
import com.aliyun.core.http.ProxyOptions;
import com.aliyun.httpcomponent.httpclient.ApacheAsyncHttpClientBuilder;
import com.aliyun.sdk.service.live20161101.models.*;
import com.aliyun.sdk.service.live20161101.*;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
import darabonba.core.RequestConfiguration;
import darabonba.core.client.ClientOverrideConfiguration;
import darabonba.core.utils.CommonUtil;
import darabonba.core.TeaPair;
//import javax.net.ssl.KeyManager;
//import javax.net.ssl.X509TrustManager;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.time.Duration;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.io.*;
public class AddLivePackageConfig {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// HttpClient Configuration
/*HttpClient httpClient = new ApacheAsyncHttpClientBuilder()
.connectionTimeout(Duration.ofSeconds(10)) // Set the connection timeout time, the default is 10 seconds
.responseTimeout(Duration.ofSeconds(10)) // Set the response timeout time, the default is 20 seconds
.maxConnections(128) // Set the connection pool size
.maxIdleTimeOut(Duration.ofSeconds(50)) // Set the connection pool timeout, the default is 30 seconds
// Configure the proxy
.proxy(new ProxyOptions(ProxyOptions.Type.HTTP, new InetSocketAddress("<YOUR-PROXY-HOSTNAME>", 9001))
.setCredentials("<YOUR-PROXY-USERNAME>", "<YOUR-PROXY-PASSWORD>"))
// If it is an https connection, you need to configure the certificate, or ignore the certificate(.ignoreSSL(true))
.x509TrustManagers(new X509TrustManager[]{})
.keyManagers(new KeyManager[]{})
.ignoreSSL(false)
.build();*/
// Configure Credentials authentication information, including ak, secret, token
StaticCredentialProvider provider = StaticCredentialProvider.create(Credential.builder()
// Please ensure that the environment variables ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID and ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET are set.
.accessKeyId(System.getenv("ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID"))
.accessKeySecret(System.getenv("ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET"))
//.securityToken(System.getenv("ALIBABA_CLOUD_SECURITY_TOKEN")) // use STS token
.build());
// Configure the Client
AsyncClient client = AsyncClient.builder()
.region("<Your RegionId>") // Region ID
//.httpClient(httpClient) // Use the configured HttpClient, otherwise use the default HttpClient (Apache HttpClient)
.credentialsProvider(provider)
//.serviceConfiguration(Configuration.create()) // Service-level configuration
// Client-level configuration rewrite, can set Endpoint, Http request parameters, etc.
.overrideConfiguration(
ClientOverrideConfiguration.create()
// For endpoints, refer to https://api.alibabacloud.com/product/live
.setEndpointOverride("live.aliyuncs.com")
//.setConnectTimeout(Duration.ofSeconds(30))
)
.build();
// Parameter settings for API request
AddLivePackageConfigRequest addLivePackageConfigRequest = AddLivePackageConfigRequest.builder()
.regionId("<Your RegionId>")
.domainName("<Your DomainName>")
.appName("<Your AppName>")
.streamName("<Your StreamName>")
.setProtocol("<Protocol>");
// Request-level configuration rewrite, can set Http request parameters, etc.
// .requestConfiguration(RequestConfiguration.create().setHttpHeaders(new HttpHeaders()))
.build();
// Asynchronously get the return value of the API request
CompletableFuture<AddLivePackageConfigResponse> response = client.addLivePackageConfig(addLivePackageConfigRequest);
// Synchronously get the return value of the API request
AddLivePackageConfigResponse resp = response.get();
System.out.println(new Gson().toJson(resp));
// Asynchronous processing of return values
/*response.thenAccept(resp -> {
System.out.println(new Gson().toJson(resp));
}).exceptionally(throwable -> { // Handling exceptions
System.out.println(throwable.getMessage());
return null;
});*/
// Finally, close the client
client.close();
}
}For SDK setup instructions, see Use the Java SDK.
After configuration, the original quality streaming URL remains accessible.
Ingest and play an encapsulated stream
Ingest a stream
For smooth playback, keep the GOP size of your ingested stream consistent.
Use Open Broadcaster Software (OBS) with these recommended settings:

Play an encapsulated stream
Obtain the streaming URL. The format varies by protocol:
Protocol
URL format
HLS
http://<DomainName>/<AppName>/<StreamName>.m3u8?aliyunols=on&auth_key=<AuthKey>DASH
http://<DomainName>/<AppName>/<StreamName>.mpd?aliyunols=on&auth_key=<AuthKey>LL-HLS
http://<DomainName>/<AppName>/<StreamName>-llhls.m3u8?aliyunols=on&auth_key=<AuthKey>ImportantThe
aliyunols=onparameter is required for encapsulated stream URLs.You can use the URL generator to generate streaming URLs. The URL format depends on your configuration:
Container format
Protocol
Generated URL types
TS
LL-HLS
LL-HLS and HLS
CMAF
LL-HLS
LL-HLS and HLS
CMAF
HLS
HLS
CMAF
DASH
DASH
CMAF
HLS & DASH
HLS and DASH
Play the stream with a compatible player. We recommend ApsaraVideo Player.
To use the ApsaraVideo Player web demo:
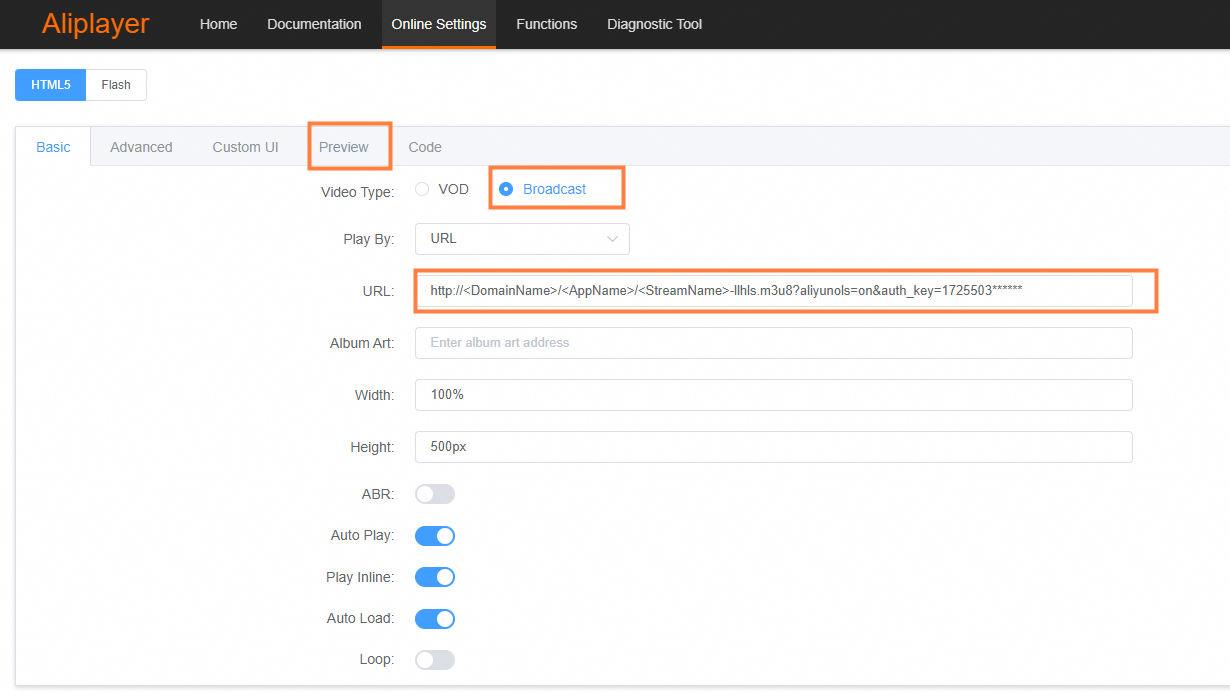
a. Set Video Type to Broadcast.
b. Enter the streaming URL.
c. Click the Preview tab to preview the video.
ImportantTo use the ApsaraVideo Player web version, you must configure HTTPS certificates and set the
Access-Control-Allow-Originheader for cross-domain access. For details, see HTTPS settings and Configure HTTP Headers.
Advanced usage
Encapsulate transcoded streams
You can combine encapsulation with transcoding to package transcoded streams.
Procedure
Configure transcoding for your source stream. For more information, see Live stream transcoding.
When creating an encapsulation configuration, set Transcoded Stream to Transcoded Stream Included in the console or set
IgnoreTranscodetofalsevia the AddLivePackageConfig API:// Include transcoded streams in encapsulation process (default: true = exclude) addLivePackageConfigRequest.setIgnoreTranscode(false);Generate the streaming URL for the encapsulated transcoded stream:
Default or custom transcoding template: Append
_<template-id>toStreamName. Example:http://<DomainName>/<AppName>/<StreamName>_<template-id>-llhls.m3u8?aliyunols=on&auth_key=<AuthKey>Multi-bitrate transcoding template: Append
_<template-group-id>toStreamName.
NoteCombine encapsulation with multi-bitrate transcoding to enable adaptive playback, which allows players to automatically switch to a lower bitrate during poor network conditions.
The behavior of the output URLs differs based on the type of transcoding template used:
For multi-bitrate transcoding:
The encapsulation configuration overrides the output format of the transcoded streams. For example, if you specify an encapsulation format of
DASH - CMAF, the system will only generate DASH - CMAF URLs for the multi-bitrate streams; it will not generate HLS URLs.For default or custom transcoding:
The original transcoded stream URLs are not affected. Instead, the system generates additional encapsulated URLs for those transcoded streams.
Play the stream with a compatible player.
Time shifting for encapsulated streams
You can use time shifting with encapsulated streams. For more information, see time shifting.
When time shifting is enabled, the format of the time-shifted segments inherits the segment length and format specified in your encapsulation configuration.
HLS or LL-HLS (CMAF): The time-shifted segments are in CMAF format.
LL-HLS (TS): The time-shifted segments are in TS format.