Use Real-Time Streaming (RTS) to reduce live streaming latency to under 400 ms and provide viewers with a smooth, real-time experience.
Overview
RTS uses Alibaba Cloud's Global Realtime Transport Network (GRTN) and the WebRTC protocol to achieve an end-to-end latency of 200–400 ms. This solution is also forward-compatible with standard live streaming.

Achieve 200–400 ms end-to-end latency with RTS:
A streamer uses the Push SDK to ingest the live stream over the WebRTC protocol to the nearest point of presence (POP).
GRTN transmits the live stream in real time across its 3,200+ global POPs using smart routing and QoS technologies.
Viewers pull the stream from the nearest POP over the WebRTC protocol for playback on their devices, achieving an end-to-end latency of 200–400 ms.
(Optional) Enable internal relay to support media processing, RTS, and standard live streaming:
After you enable stream relay, ApsaraVideo Live automatically transmuxes the ingested stream to generate an RTMP stream.
You can configure media services such as transcoding, recording, and snapshot capture for this stream.
Viewers can still achieve low-latency playback, with an end-to-end latency of 400–800 ms, by pulling the stream over WebRTC.
To use standard live streaming, pull and play the stream over RTMP, FLV, or HLS.
Implementation
Before you begin
Configured ingest and streaming domains. For more information, see Get started with ApsaraVideo Live.
Configure HTTPS certificates for ingest and streaming domains
Because this topic uses a browser-based demo, you must configure HTTPS certificates for your ingest and streaming domains. This is a security requirement for WebRTC in browsers. For instructions, see Configure HTTPS secure acceleration.
If you use a native SDK for stream ingest and playback, you do not need to configure HTTPS certificates.
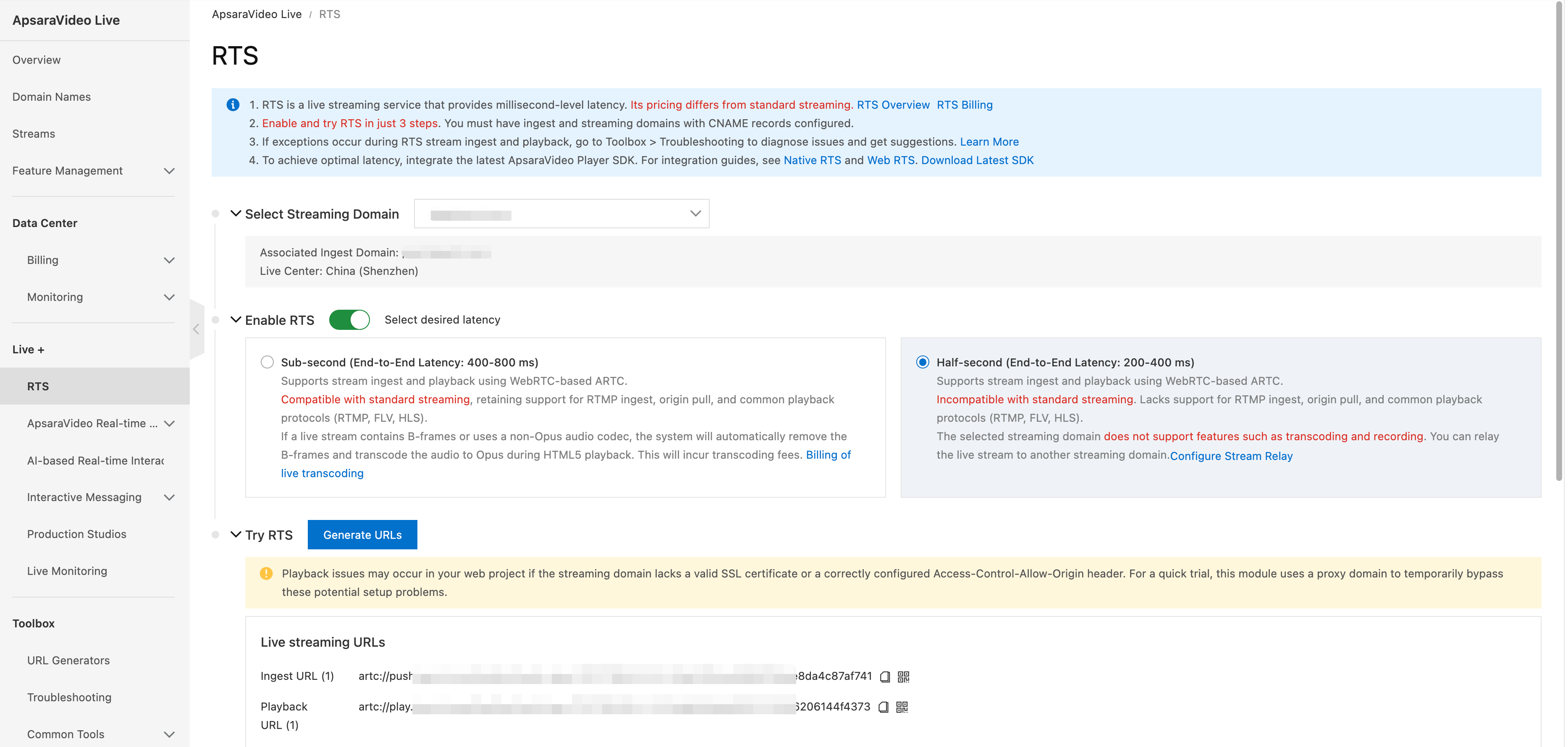
Enable RTS
Log on to the ApsaraVideo Live console.
In the left navigation pane, choose Live + > RTS.
Select a streaming domain.
Turn on the switch and select Half-second (End-to-End Latency: 200-400 ms).

Generate ingest and streaming URLs
Method 1: Generate URLs in the console
After enabling RTS, click Generate URLs. Enter an AppName and StreamName to generate ARTC-based ingest and streaming URLs.
Method 2: Manually assemble URLs
When you manually construct ingest and streaming URLs, check whether the live stream is transcoded and whether URL signing is enabled. You also need the ingest domain, streaming domain, AppName, StreamName, transcoding template ID (if applicable), and access token (if applicable). The following table describes the URL construction rules.
URL type | Format | Construction rule |
Ingest URL | RTMP, RTS, and SRT protocols are supported. We recommend using an RTMP URL for stream ingest. For example: RTMP: Note RTS also supports stream pulling over the ARTC protocol. | Ingest domain + AppName + StreamName + Access token |
Streaming URL | RTMP, FLV, M3U8, and ARTC protocols are supported. We recommend using an ARTC URL for playback. For example: ARTC: | Streaming domain + AppName + StreamName + Access token |
Transcoded stream URL | RTMP, FLV, M3U8, and ARTC protocols are supported. We recommend using an ARTC URL for playback. For example: ARTC: | Streaming domain + AppName + StreamName_Transcoding template ID + Access token |
For associated ingest and streaming domains, you can start stream ingest and playback if the AppName and StreamName are the same for both.
A transcoded stream URL requires a transcoding template. You can view the transcoding template ID in the console. For more information, see Live stream transcoding.
The access token (auth_key) is an encrypted string that is generated by a signing algorithm. This requires the URL signing feature to be enabled. You can use the MD5 algorithm to calculate the access token. For more information, see Construct a signed URL.
Replace {transcoding_template_ID} and {access_token} with the actual data. Do not include the curly braces {}.
Ingest the RTS stream
You can integrate one of the following Push SDKs:
Platform | Reference |
iOS | Note The Push SDK for iOS supports WebRTC-based stream ingest by default. |
Android | Note The Push SDK for Android supports WebRTC-based stream ingest by default. |
Use OBS for stream ingest based on the WHIP protocol |
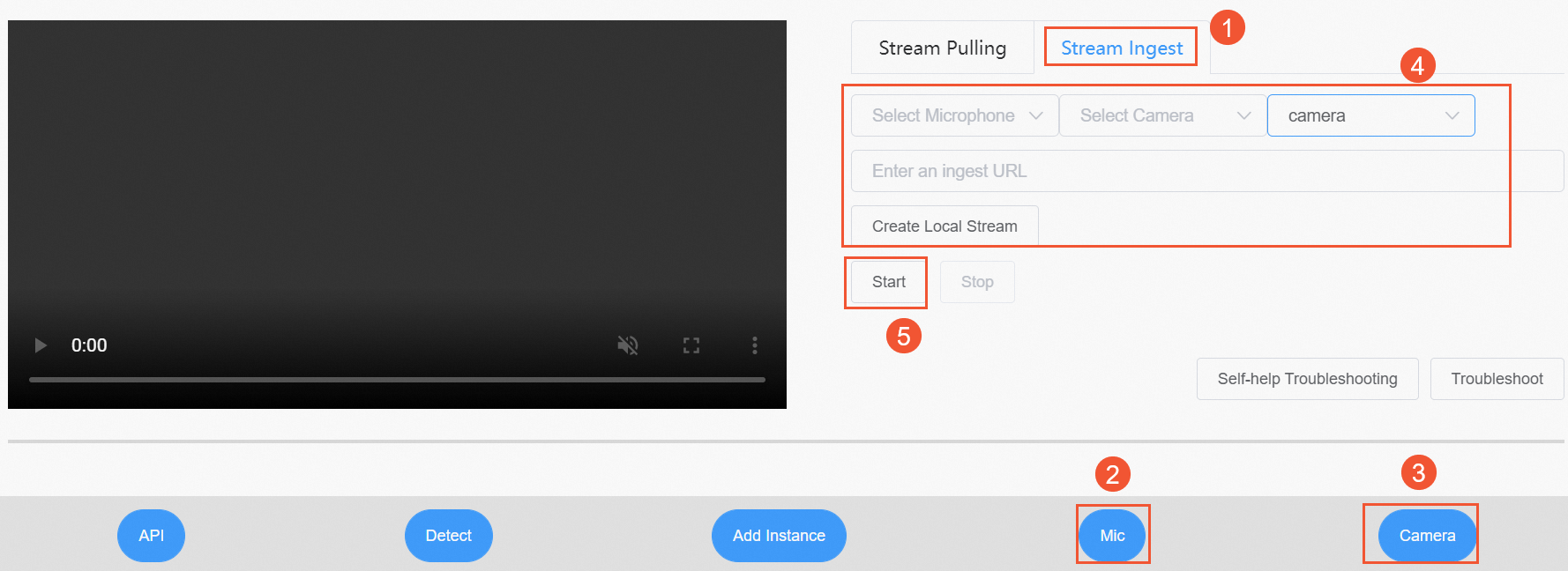
The following example uses the RTS web demo:
Go to the RTS web demo.
In the demo, select the Stream Ingest mode.
From the none drop-down list, select camera or screen.
If you select camera, click the Get devices button to grant the required browser permissions. Then, select your specific microphone and camera from their respective drop-down lists.
Enter the RTS ingest URL that you generated in the Generate ingest and streaming URLs step and click Create Local Stream.
Click Start to begin ingesting the stream.
Play the RTS stream
You can integrate one of the following ApsaraVideo Player SDKs:
Platform | Reference |
Web | |
iOS | |
Flutter | |
Windows | Note To obtain the SDK for Windows, contact the sales team. |
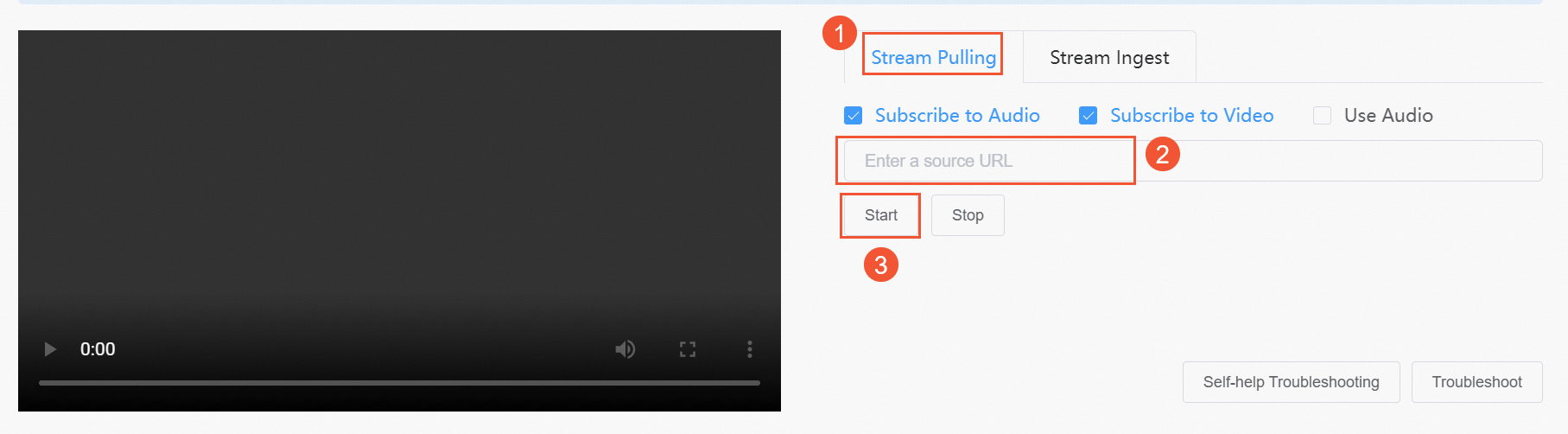
This topic uses the RTS web demo as an example:
Go to the RTS web demo.
In the demo, select the Stream Pulling mode.
Enter the RTS streaming URL that you generated in the Generate ingest and streaming URLs step.
Click Start.
(Optional) Configure stream relay
On the RTS settings page, select Half-second (End-to-End Latency: 200-400 ms).
Click Configure Stream Relay. Enable the feature and select the destination domain to receive the relayed RTMP stream.
For example, the destination ingest domain is push.example.com, and its associated streaming domain is pull.example.com.
You cannot enable the RTS half-second latency mode on the destination ingest domain or its associated streaming domain.
No fees are charged for internal stream relay.

(Optional) Configure media processing for relayed stream
After configuring stream relay, you can configure media processing templates based on the streaming domain (pull.example.com) associated with the destination ingest domain.
In the left navigation pane, choose Feature Management and select the feature you want to configure.

(Optional) Play the relayed stream as a standard live stream
After stream is relayed, you can use the streaming domain (pull.example.com) associated with the destination ingest domain to play the original stream or the transcoded stream using standard live streaming (RTMP/FLV/HLS). For more information, see Play a live stream.