Lingma provides AI Chat capabilities in three modes: Ask, Edit, and Agent. These capabilities help developers solve coding problems, fix errors, debug, and troubleshoot runtime errors. Lingma also offers multi-file edits, autonomous decision-making, codebase awareness, and tool use to complete end-to-end coding tasks.
To get the latest capabilities, update Lingma to version 2.5.0 or later in VS Code and JetBrains IDEs.
Lingma's AI Chat has the following core features:
Multiple chat modes: A conversation flow simultaneously supports Ask, Edit, and Agent modes. Developers can switch between these modes to maximize work efficiency.
Automatic codebase awareness: Automatically detects project frameworks, technology stacks, required code files, and error messages from task descriptions. This eliminates the need to add context manually, making task descriptions easier.
Tool use: Autonomously uses more than ten built-in tools, such as file read/write, code queries, and error troubleshooting. It also supports MCP tool configuration and integrates with the ModelStudio MCP Square, allowing developers to configure freely.
Command execution: Autonomously decides which commands to execute. Then it generates these commands and runs them in the terminal, greatly improving efficiency.
Project-level changes: Autonomously breaks down tasks and modifies code files in the project based on task description. It also iterates on your project and makes step-by-step changes through multi-turn chats or reverting snapshots.
Memory awareness: Features LLM-based autonomous memory. Lingma learns from each chat and builds up memories about you, your project, and your issues, learning more about you with continued use over time.
Start a new chat
Open the AI Chat panel
To start a chat after installing Lingma, click the Lingma icon in the side navigation bar or use the keyboard shortcuts to open the AI Chat panel. Log on, and you can start chatting.
Action | macOS | Windows |
Open/Close AI chat panel |
|
|
For more details, see Install Lingma.
Choose a mode
Lingma offers three chat modes for you to switch between in one chat flow without the need to create a new chat. Support for different development environments is as follows:
For Visual Studio Code: All three modes are supported. But for VS Code plug-in, only the Ask mode is available.
For Lingma IDE and JetBrains IDE plug-in: Only the Ask mode and the Agent mode are supported. The Edit mode is unavailable.
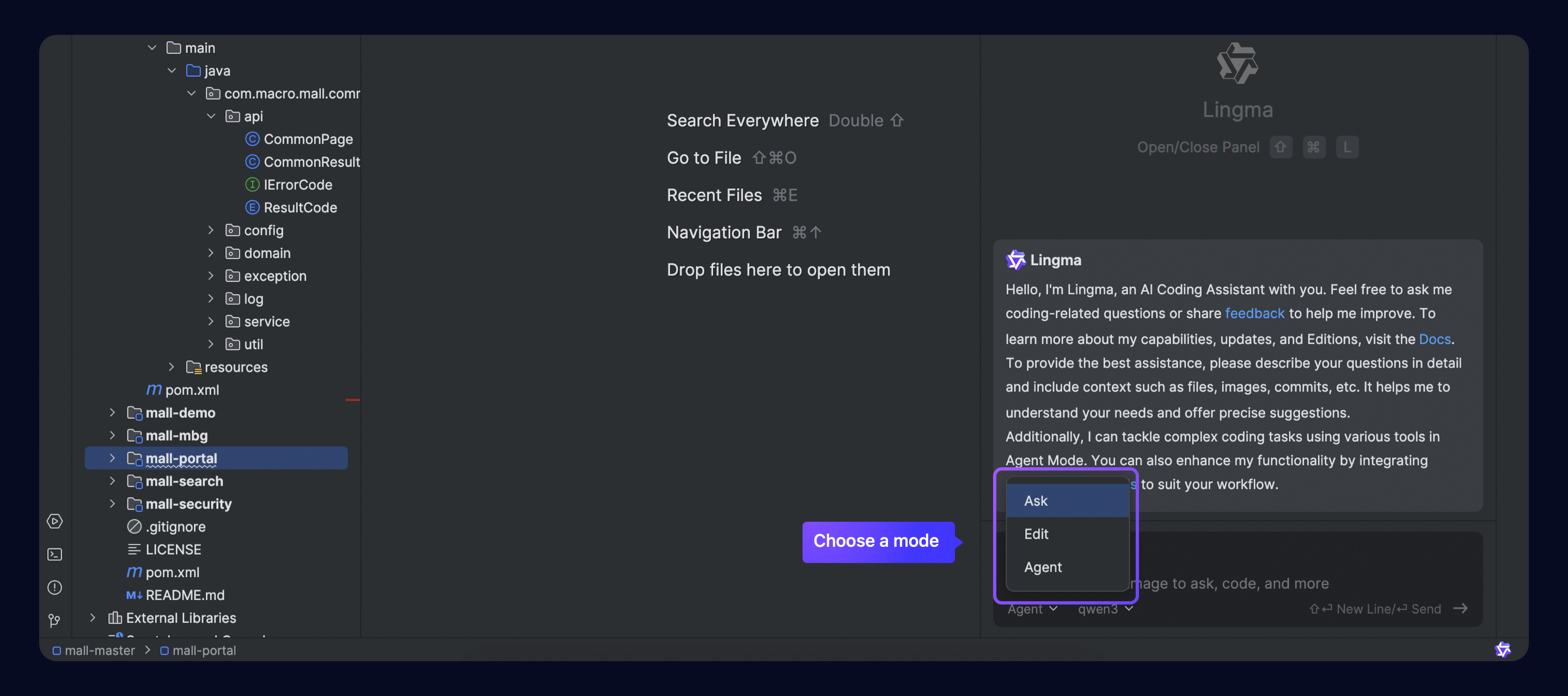
Select a mode that works for you:
A simple Q&A mode that answers coding questions without changing project files directly. It gives solutions and suggestions based on context. | |
A code modification mode that focuses on making exact changes across multiple files. It combines requirement descriptions with the project's current setup to help make code changes efficient and controlled. | |
Agent | An autonomous coding task execution mode that works on coding tasks by itself. It can make its own decisions, understand the codebase, and use tools. It can also get project files, edit files, use the terminal, and other tools to finish coding tasks from start to finish. It supports MCP tool configuration to better align with the developer's workflow. |
Input requirements
When describing your requirements in the chat box, keep the following suggestions in mind:
Structure your request: Clearly state what you need and outline the goals and steps for your coding task.
Provide context: Include files, images, code base, code changes, and other context to help Lingma better understand the background and formulate exact solutions.
Specify expectations: Let Lingma know what language, conventions, format, and change targets you want to use, along with any other specific requirements. For example, "Add English comments for each method."
Interact more and work together step by step: Give feedback on code suggestions or answers to help Lingma improve. For more complex coding tasks, split the work into smaller steps so you and Lingma can work step by step to finish the task.
Code modification and review
Multi-file edits
In Edit or Agent mode, multiple code files in a project may be modified simultaneously. Each modification undergoes the following processes:
Generating: Code suggestions are generated based on task breakdowns.
Applying: Suggestions are integrated with the original files to create new change files.
Applied: Code change files are completed and ready for review.
You can track these statuses in the chat box or workspace.
Use the comparison (Diff) view to see the generation process between the original and modified files.
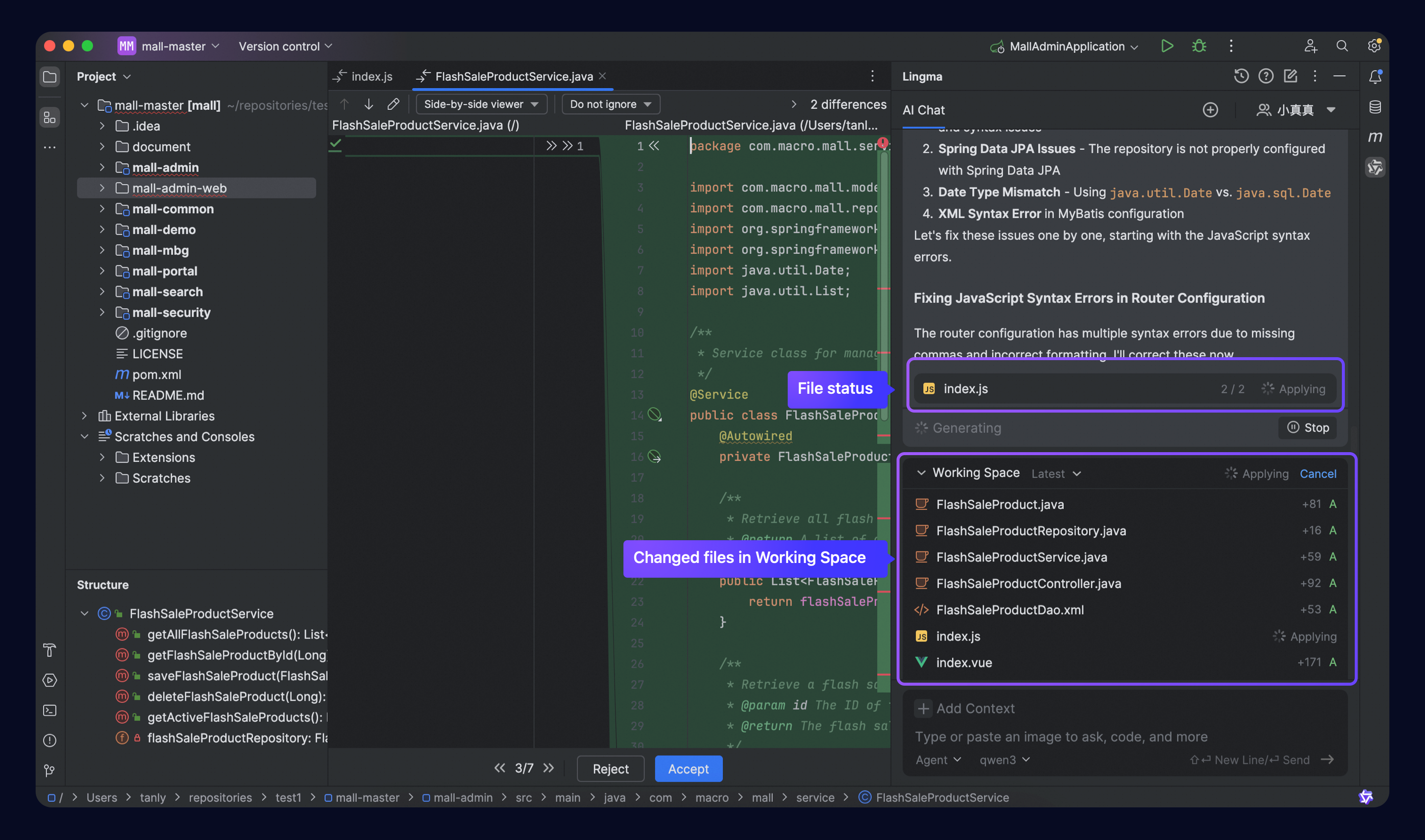
Review, accept, or reject modifications
To review changes:
Click the view changes button in the workspace or on individual files to compare modifications.
Use the arrow keys to navigate between change points and choose to accept or reject changes:
Use the up or down arrow to navigate and view the changes in the current file.
Click Reject or Accept on each change.
Click the forward or backward arrow in the file-level operation area to switch between changed files.
Click Reject or Accept in the file-level operation area.
Partially modify change files.
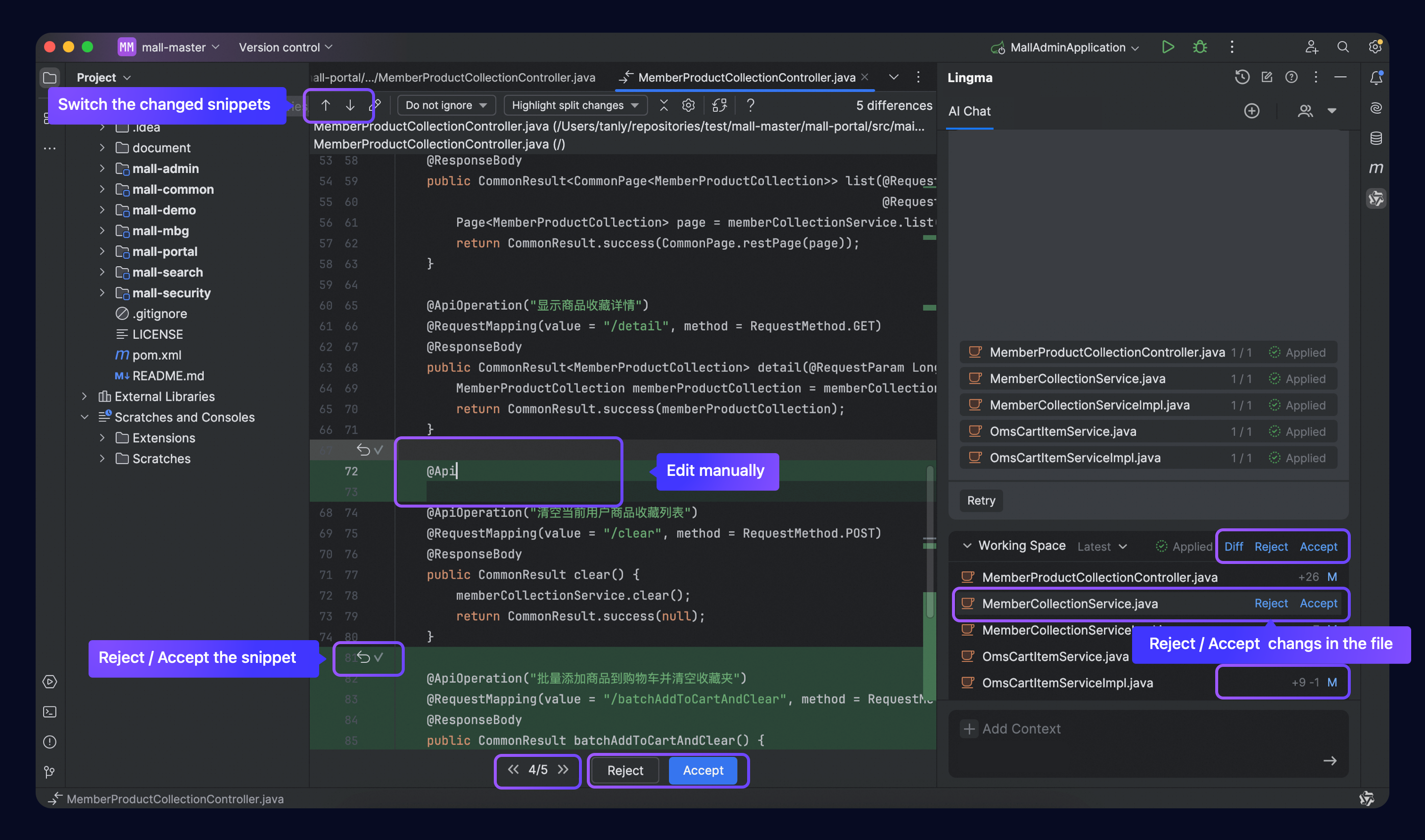
When reviewing changes:
Changes are combined into the most recent code snapshot, and are accepted or rejected collectively.
Changes are merged into the original file after changes to a code snippet or a file are accepted.
After all changes have been rejected or accepted, the current snapshot will change to one of the following statuses:
Accepted: All changes are confirmed. If a file has code changes accepted, that file is considered accepted. If all files are accepted, the current snapshot is in accepted status.
Partially accepted: Some changes are accepted, and others are rejected. If a file has code changes accepted, that file is considered accepted. If some files are accepted, the current snapshot is in partially accepted status.
Rejected: No changes from a file are accepted. If a file has no code changes accepted, that file is considered rejected. If all files are rejected, the current snapshot is in rejected status.
Multi-turn iterations and snapshots
Refine requirements in multiple turns
In Edit or Agent mode, if you need to make more requests after getting code changes in a chat turn, just keep asking questions. Lingma will combine the code changes from the previous turns, look at the new requirements, and create new change files as needed.
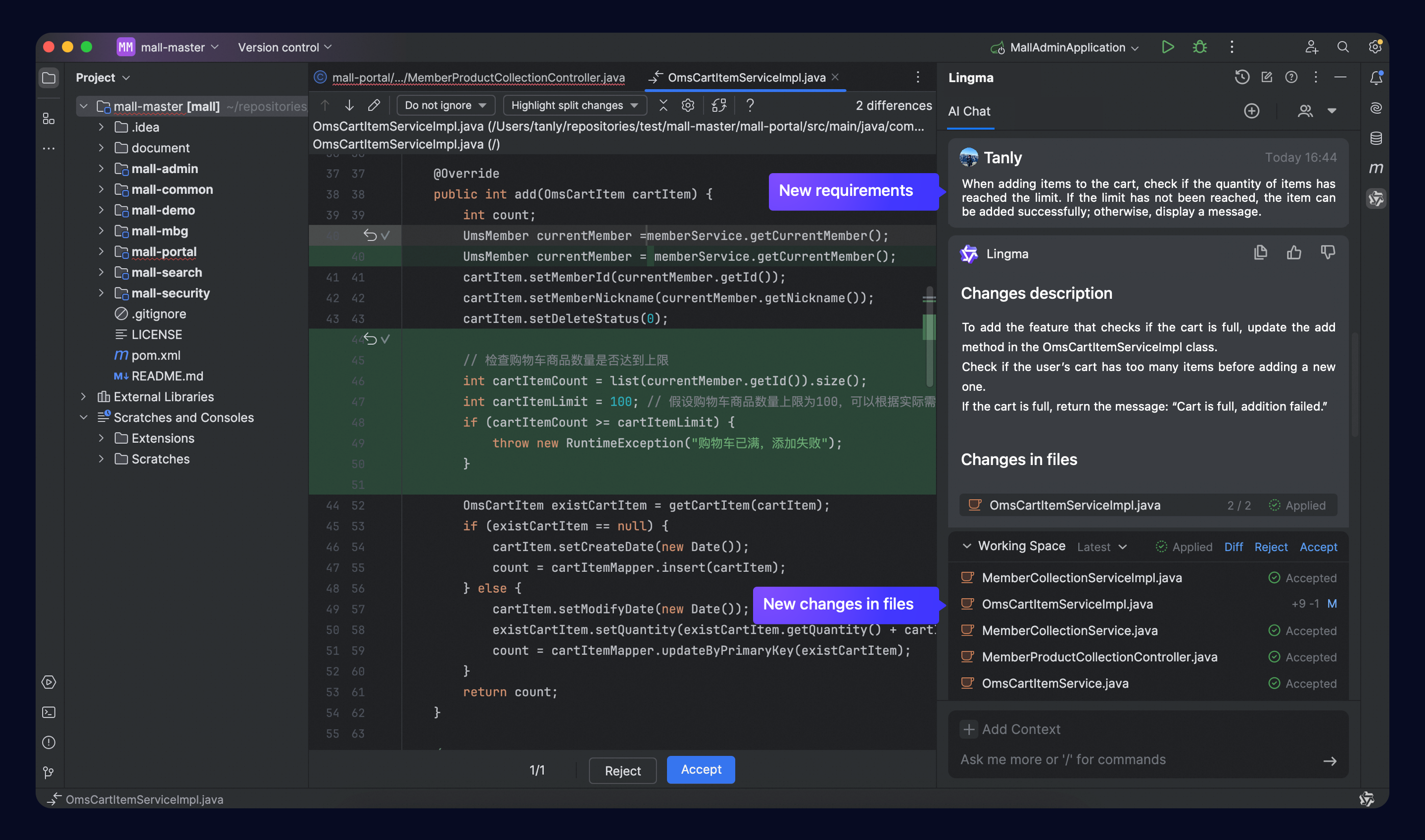
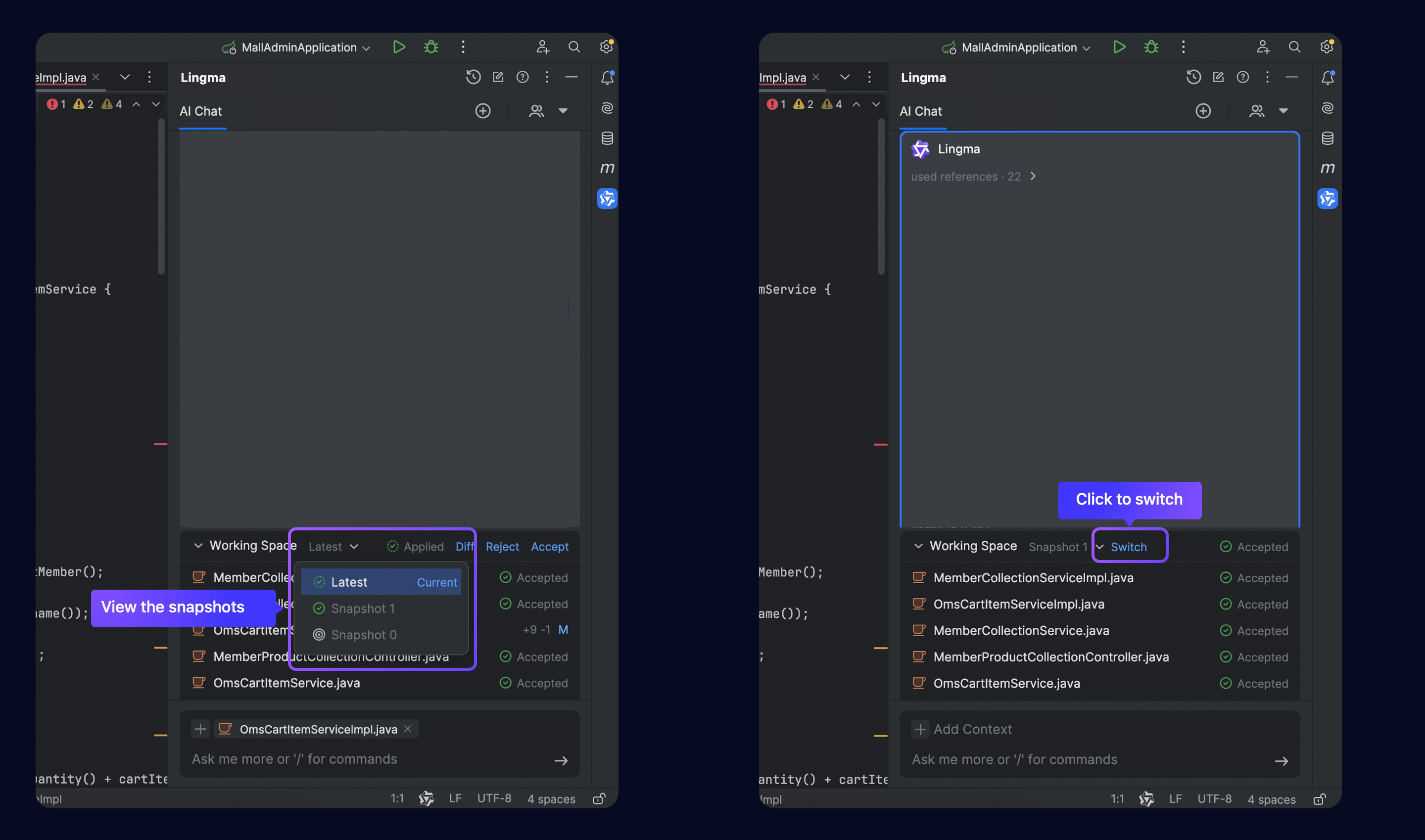
View snapshots and revert changes
Currently viewing and reverting changes are available for Visual Studio Code only. In Lingma IDE or JetBrains IDE, click ![]() icon for reversion.
icon for reversion.
To view or revert changes from previous turns in Visual Studio Code, click the drop-down arrow to view all the snapshots generated in the current session. Select a snapshot to review the related changes or perform switch operations.
Automatically find the response card that generated the snapshot's modified files in a chat flow.
Automatically update the file list to show the modified files associated with the selected snapshot. Click a file to see more details about the code changes.
Click Switch to revert the current code changes to that of the selected snapshot.
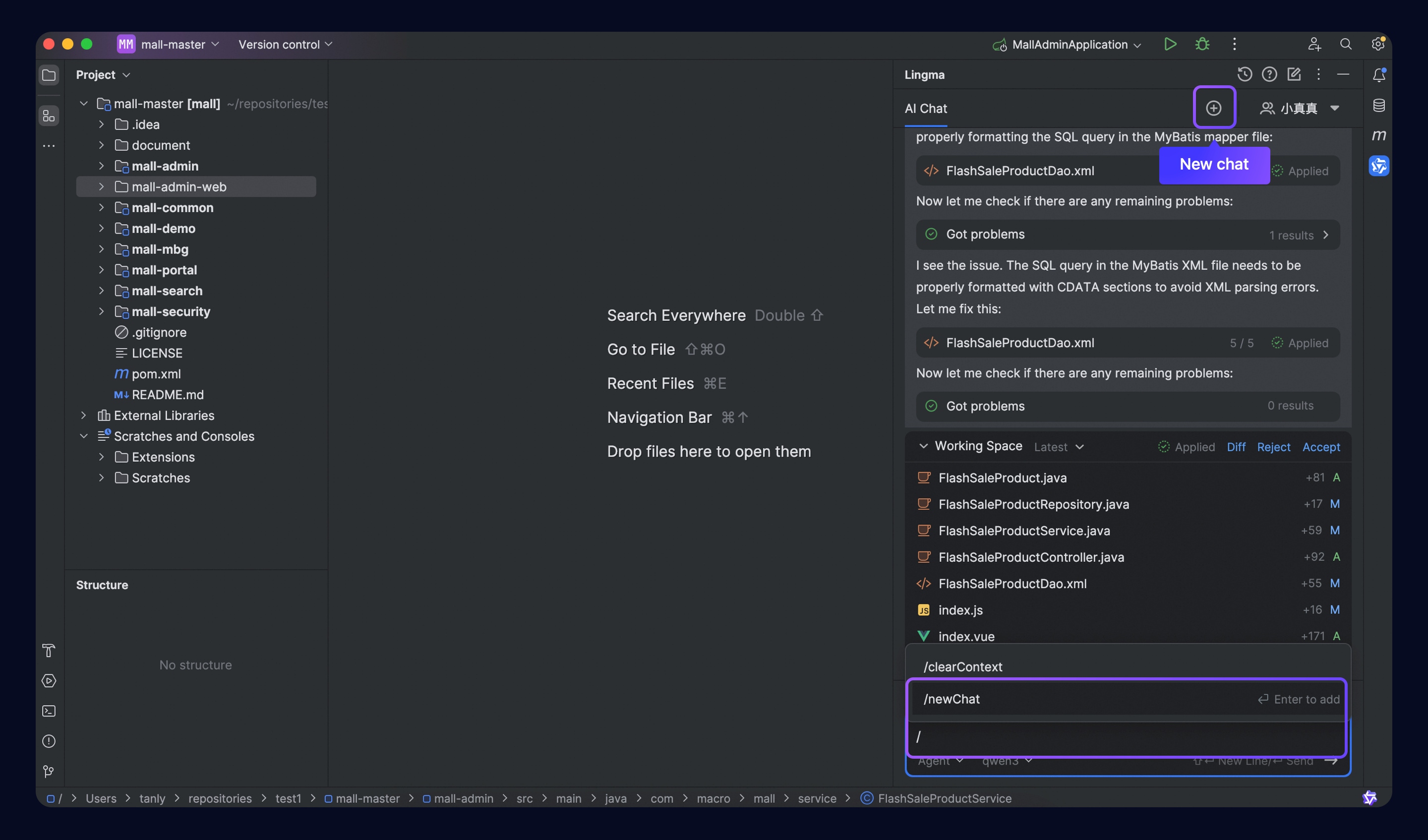
Start a new chat
To start a new chat, use either of the following methods:
Method 1: Click the
 button in the upper-right corner of the AI Chat panel to reset the chat.
button in the upper-right corner of the AI Chat panel to reset the chat.Method 2: Type
/and then select/newChatin the chat box.
View chat history
Click the ![]() icon in the upper-right corner of the AI Chat panel. This will show you all the interactions in the current project.
icon in the upper-right corner of the AI Chat panel. This will show you all the interactions in the current project.
Context
Lingma supports rich context inputs, such as code files, directories, images, gitCommit, and knowledge base. You can freely combine these context inputs with prompts to describe your requirements. Currently knowlege base is not available for context in Lingma IDE.
For more information, see Context.
Memory
Lingma provides long-term memory capabilities. It learns about you, your projects, and the problems you face during chats. It keeps this information organized and up to date. Memory helps Lingma better interact with and learn about you over time.
For more information, see Memory.
Tools
Lingma offers a variety of tools for programming, such as file searching, file reading, directory reading, symbol search in the project, file editing, error checking, and running commands in the terminal. These tools work on their own, without the developer's approval or help.
For more information, see Tools.
MCP
Lingma's Agent mode integrates with MCP services. Developers can configure their MCP services for the agent. This expands the capabilities of the AI coding assistant and fits better with how the developer works.
The agent also connects to a marketplace for third-party MCP services. This allows developers to install the required MCP services with one click.
For more information, see MCP.