Video translation leverages AI and machine learning algorithms to accurately convert video content into one or more languages. It supports subtitle, speech, and lip-sync translation, ensuring a natural, cohesive visual and auditory experience. By breaking down language barriers, video translation makes your content accessible to global audiences.
This service is available in the following regions:
Subtitle translation: China (Shanghai), China (Beijing), China (Shenzhen), China (Hangzhou), Singapore, US (Silicon Valley)
Speech translation: China (Shanghai), China (Beijing), China (Shenzhen), China (Hangzhou), Singapore, US (Silicon Valley)
Lip-sync translation: China (Shanghai), Singapore
Advantages
Support for multiple languages and dialects
Provide translation services in more than 40 national languages and over 10 Chinese dialects.
A translation task supports generating outputs in over 40 languages at a time.
Compatible with multiple video formats
Supported formats include MP4, WebM, MOV, and M3U8.
Rich custom options
Supported audio formats include MP3 and WAV.
Allow you to make personalized configurations to meet specific requirements.
Features
IMS supports subtitle, speech, and lip-sync translation. The machine translation results can be modified.
Feature | Description | Highlights |
Subtitle translation |
| Efficient, accurate text translation, ideal for scenarios that require quick multi-language support. |
Speech translation | On the basis of subtitle translation, It involves the following steps:
| Speech translation helps preserve the speakers' identities and emotions while conveying the translated text content. |
Lip-sync translation | Built upon subtitle and speech translation, it adjusts the lip movements of speakers to match the translated audio. | Lip-sync translation ensures that the visual presentation aligns with the spoken content, ideal for generating highly realistic interaction or promotional content. |
Post-editing |
| This features enables you to adjust translation output to meet personalized needs and achieve optimal results. |
Billing
For billing information, see Video translation billing.
Use video translation
IMS provides three methods to create and manage video translation tasks:
IMS console: Suitable for users who prefer intuitive operations through a graphical interface.
Online editing (Web): Provides users familiar with video editing with a more refined workspace to enable flexible control over translation outputs. Users can directly add materials to their editing project, use video translation to translate content, and do post-editing.
OpenAPI: Provides developers and technical personnel with APIs to use video translation, allowing for integration into third-party systems to automate the processing of large volumes of video translation tasks.
The supported methods vary by translation type:
Subtitle translation: IMS console, online editing (Web SDK), OpenAPI
Speech translation: IMS console, online editing (Web SDK), OpenAPI
Lip-sync translation: IMS console, OpenAPI
Create a translation task
Method 1: Creating in the console
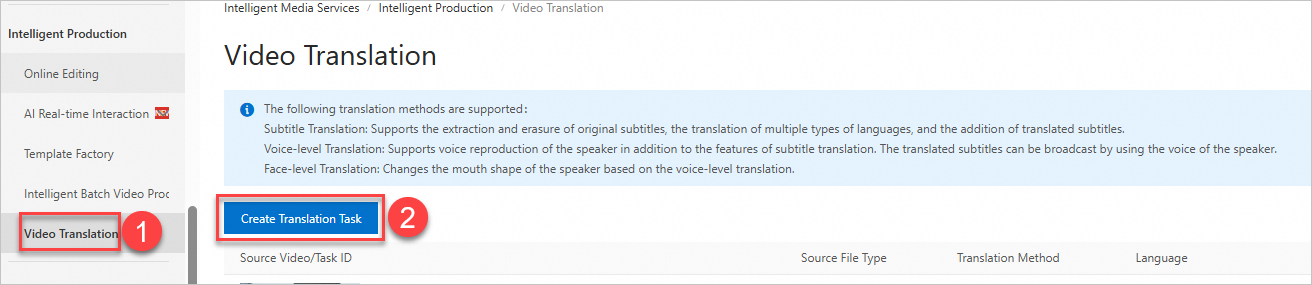
Go to the Video Translation page in the IMS console.
In the upper-left corner, select a region as needed.
Click Create Translation Task.
Configure parameters:
Translation Method: Select Subtitle Translation, Speech Translation, or Lip-sync Translation.
Select Source File: Upload the video file to be translated. MP4, WebM, and MOV formats are supported.
Subtitle Source: Specify whether to erase the original subtitles and the subtitle source. The following methods are supported:
OCR: When you don't have a ready-made caption file but the video includes built-in subtitles, you can extract subtitles using OCR technology. To improve efficiency and accuracy, set the OCR Range.
ASR: If your video doesn't have subtitles, use ASR technology to convert speech into text.
OCR/ASR: Prioritize OCR to extract subtitles. When it fails, the system uses ASR.
Specified SRT File: If you have a ready-made caption file, load it into the video editing software to play synchronously with the video.
All: Subtitles are recognized by ASR and refined through OCR, such as correcting typos.
Target Language: Select one or more target languages. The system generates corresponding output videos.
Storage Directory and File Name: Specify the storage location and name for the output file.
Click Submit Translation Task to create a task.
View the task status, configurations, and translation results in the task list. When the status changes to Processed, click View Details to view its basic information, advanced settings, and outputs.

Method 2: Creating using online editing
Preparations
If you are not familiar with Online Editing, learn its basic operations.
Procedure
Go to the Online Editing in the IMS console.
In the upper-left corner, select a region as needed.
Click Create Editing Project to create a project. Then, click Edit in the Actions column to enter Online Editing.

On the Materials tab, click Import and select the materials you want to translate in the right-side pane. After they are added to Materials, click the plus sign
 of the file or drag it to the editing area below.
of the file or drag it to the editing area below.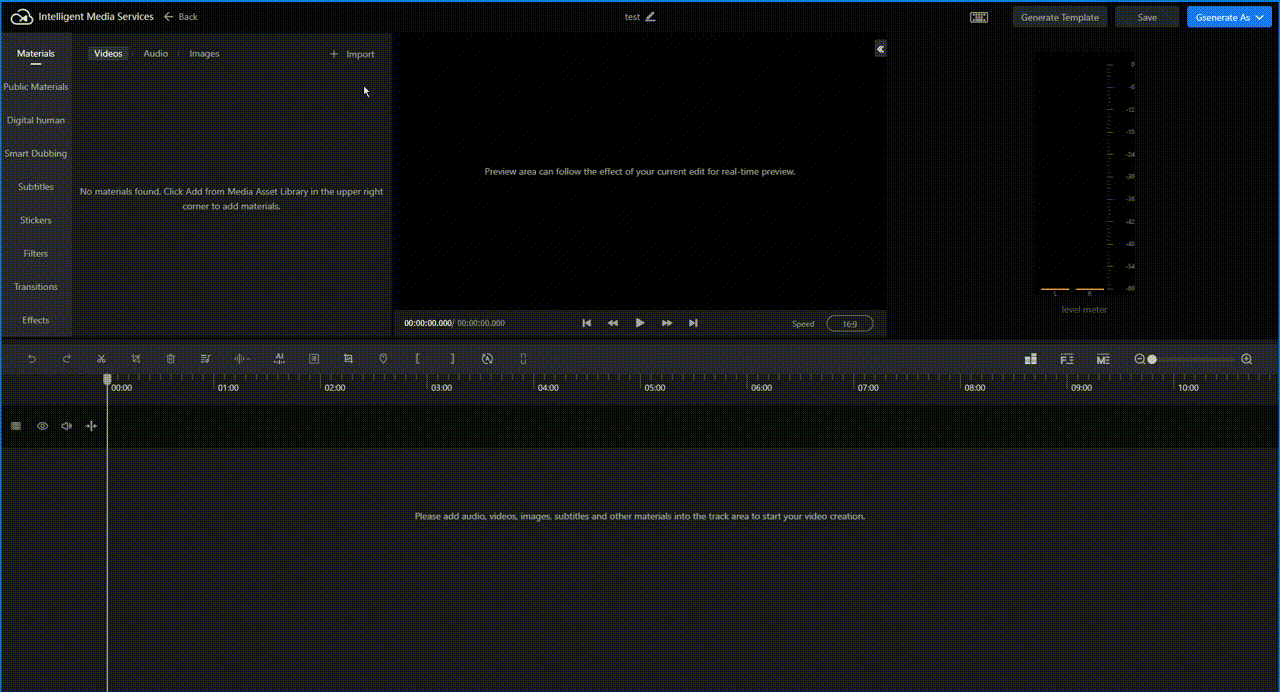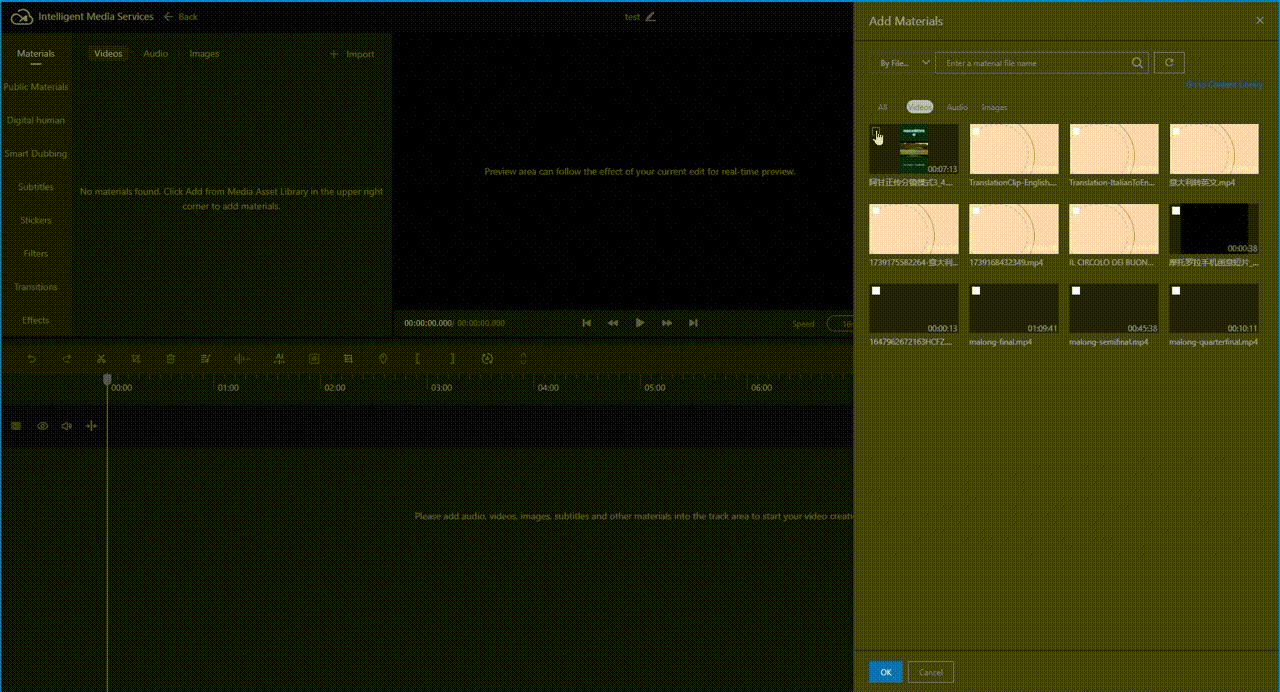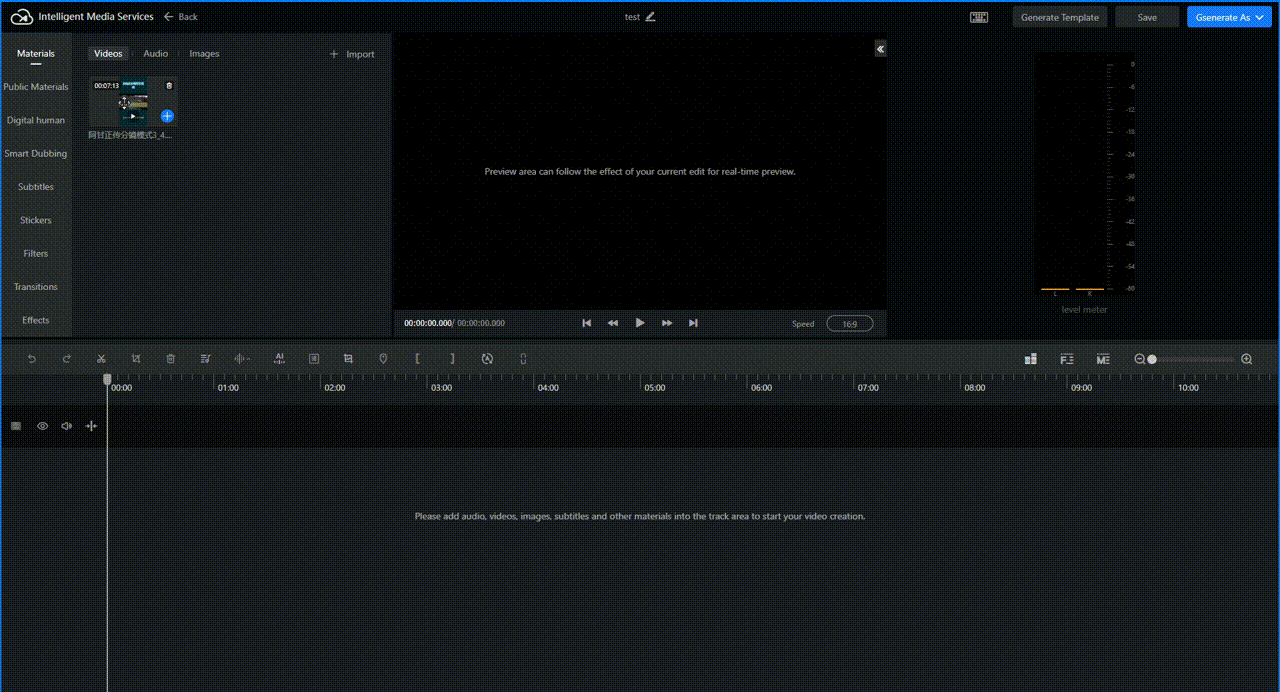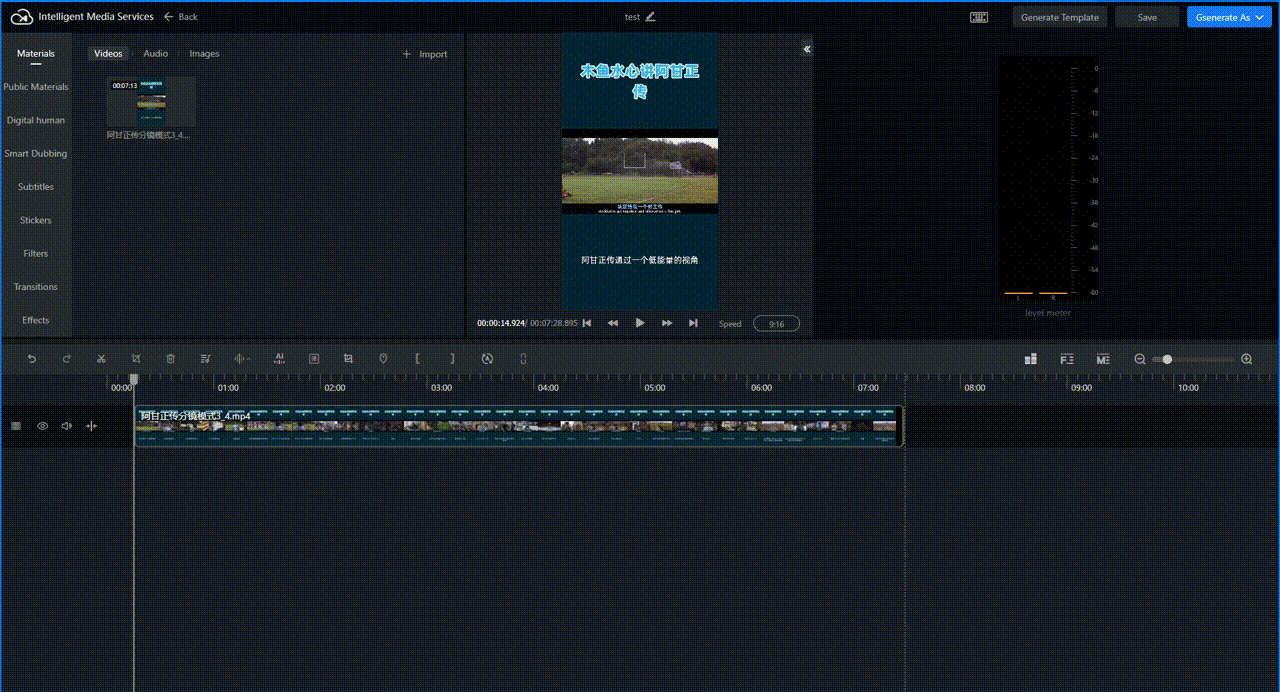
Select the audio or video that needs to be translated in the editing track, then click AI Translation. Configure the translation type, subtitle extraction, language, and subtitle erasure settings, and click Submit. The following image takes speech translation as an example.
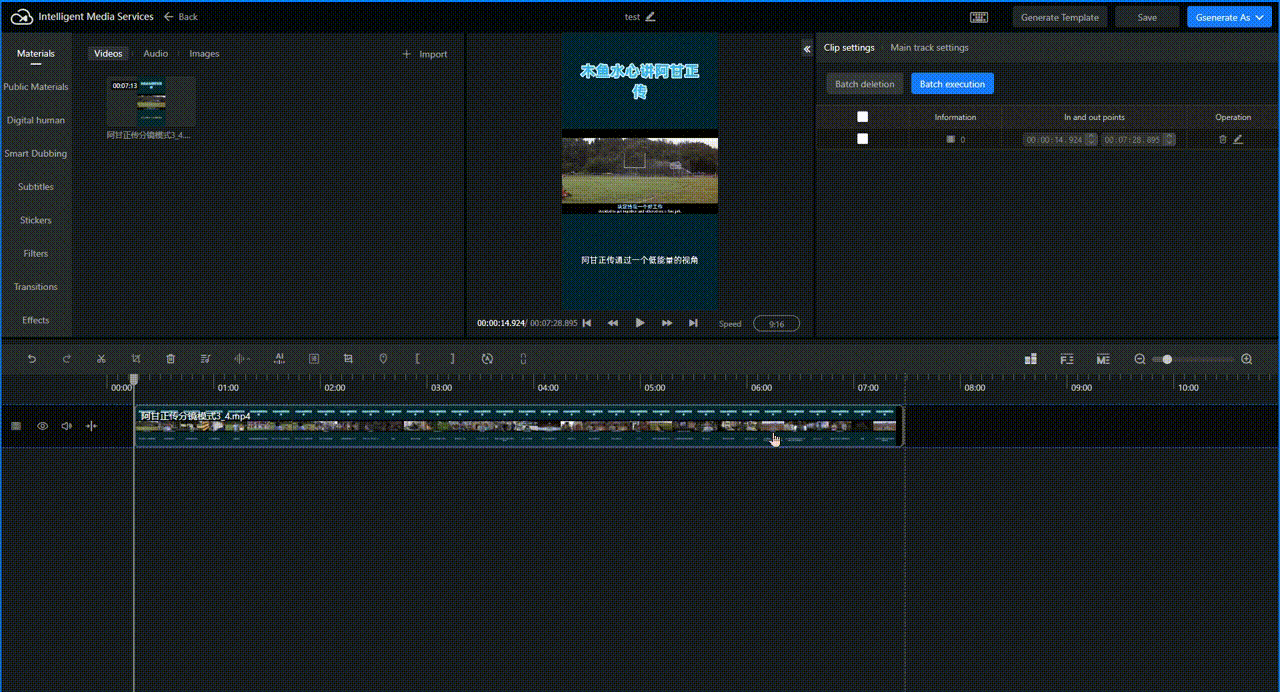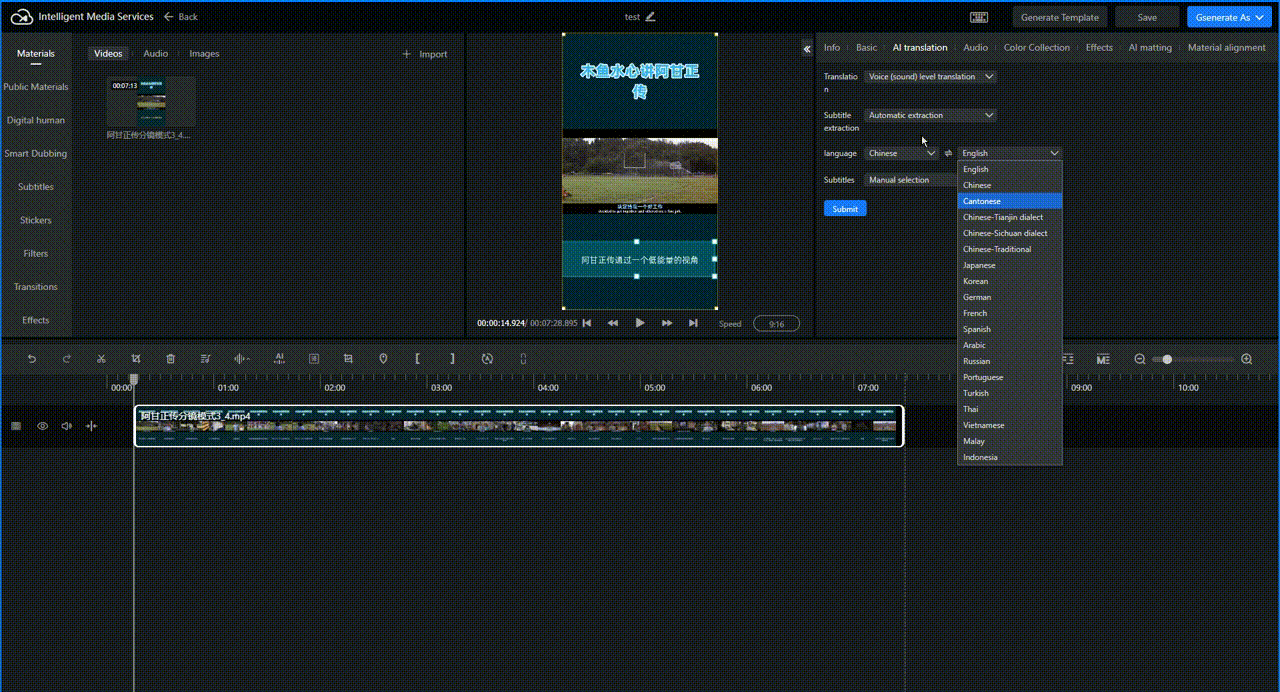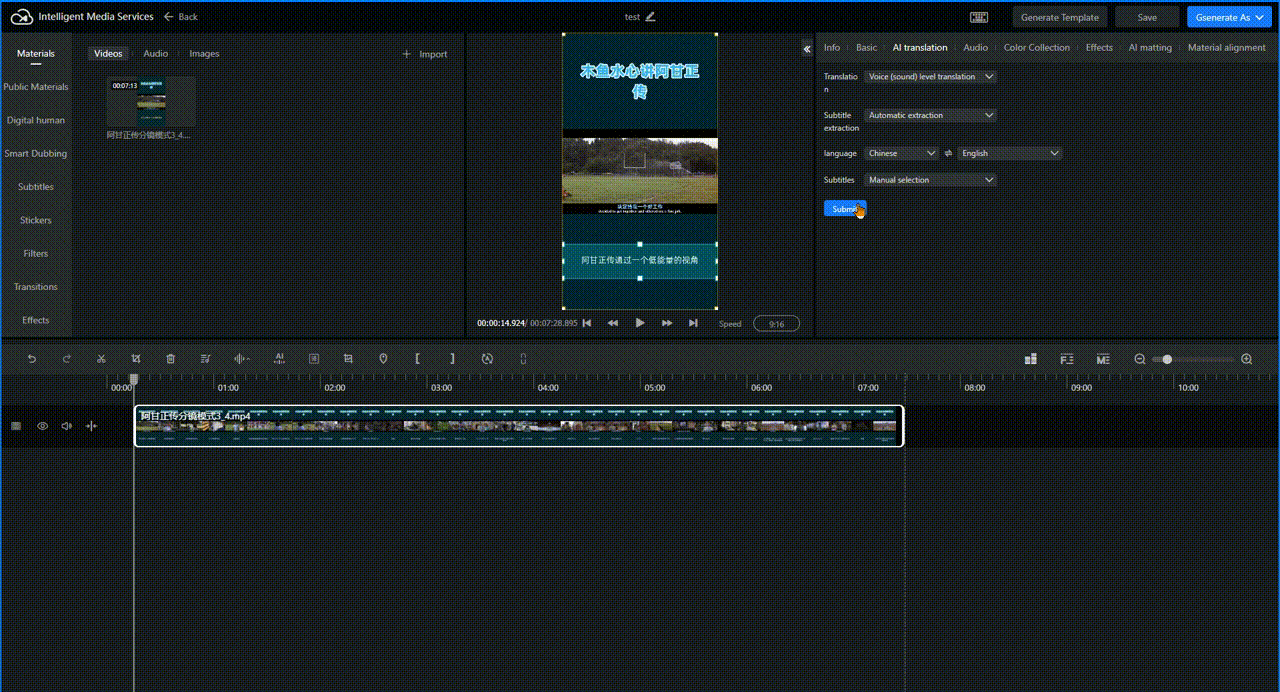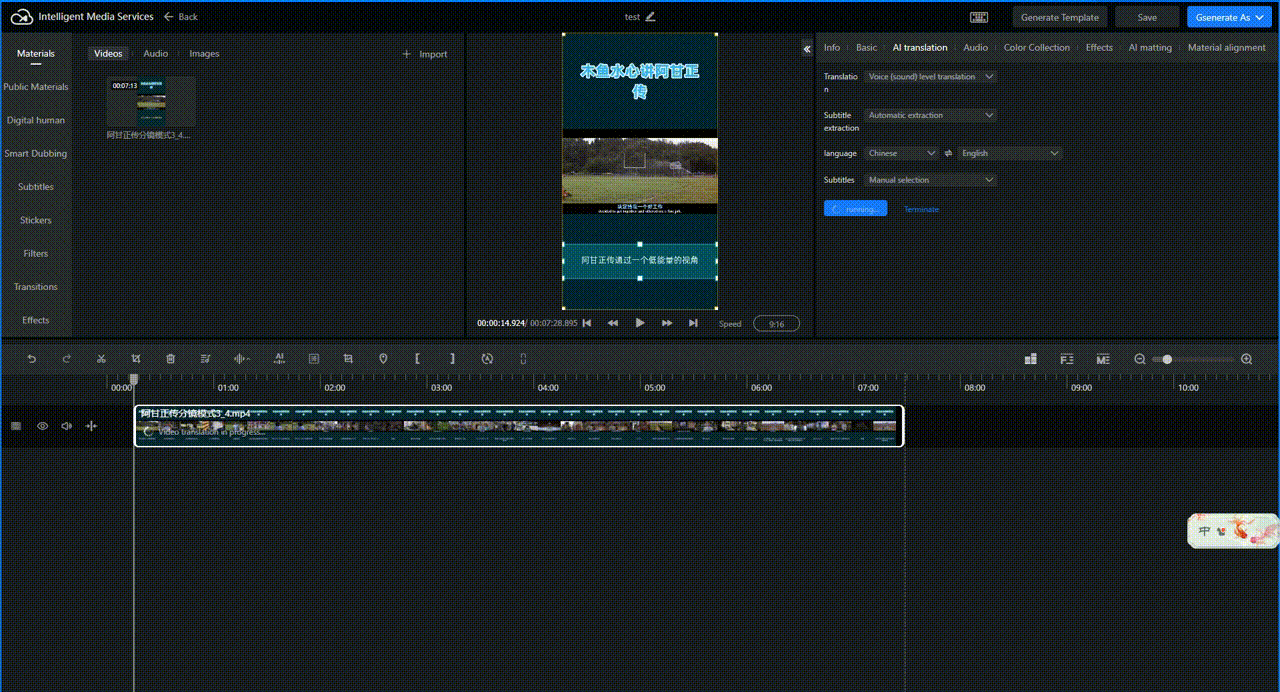
Wait a few minutes. The translated result is displayed in the track.

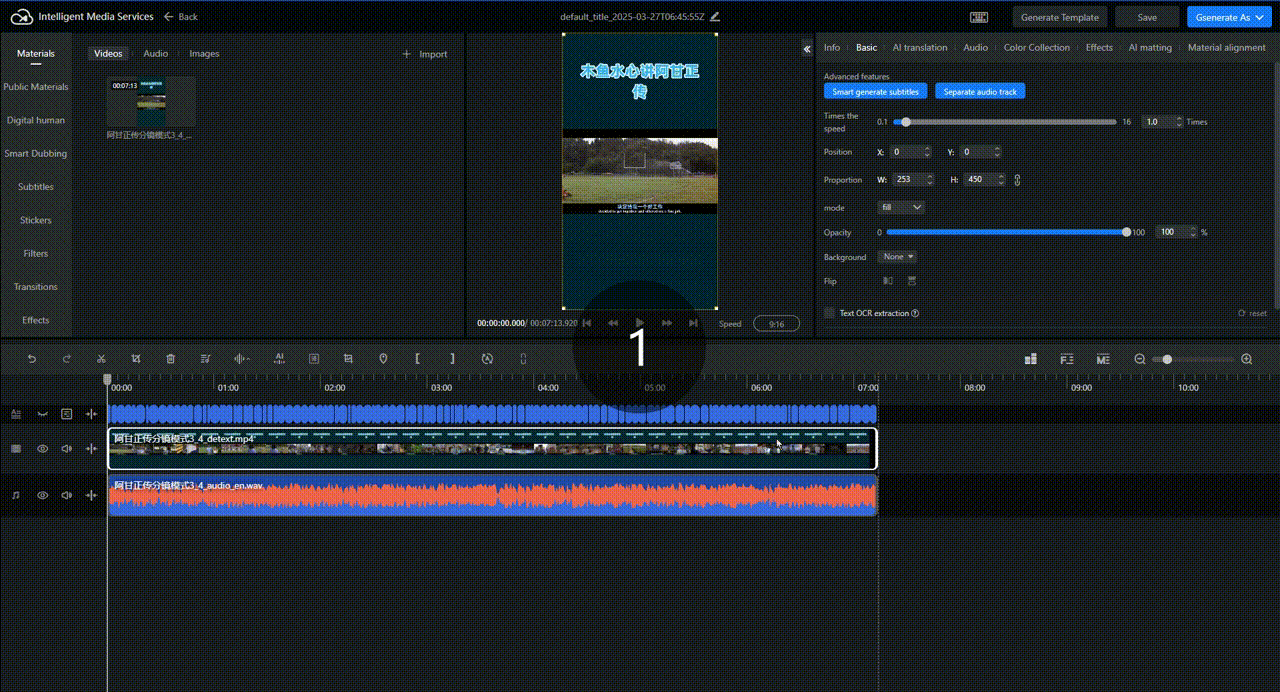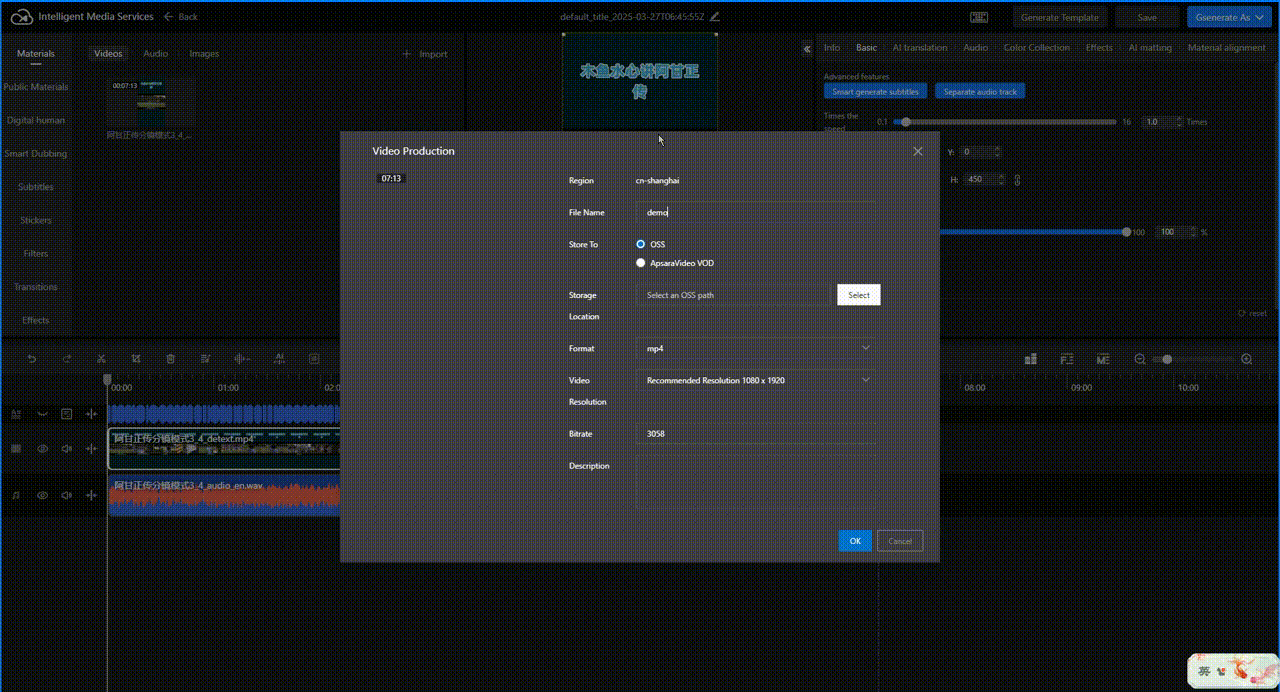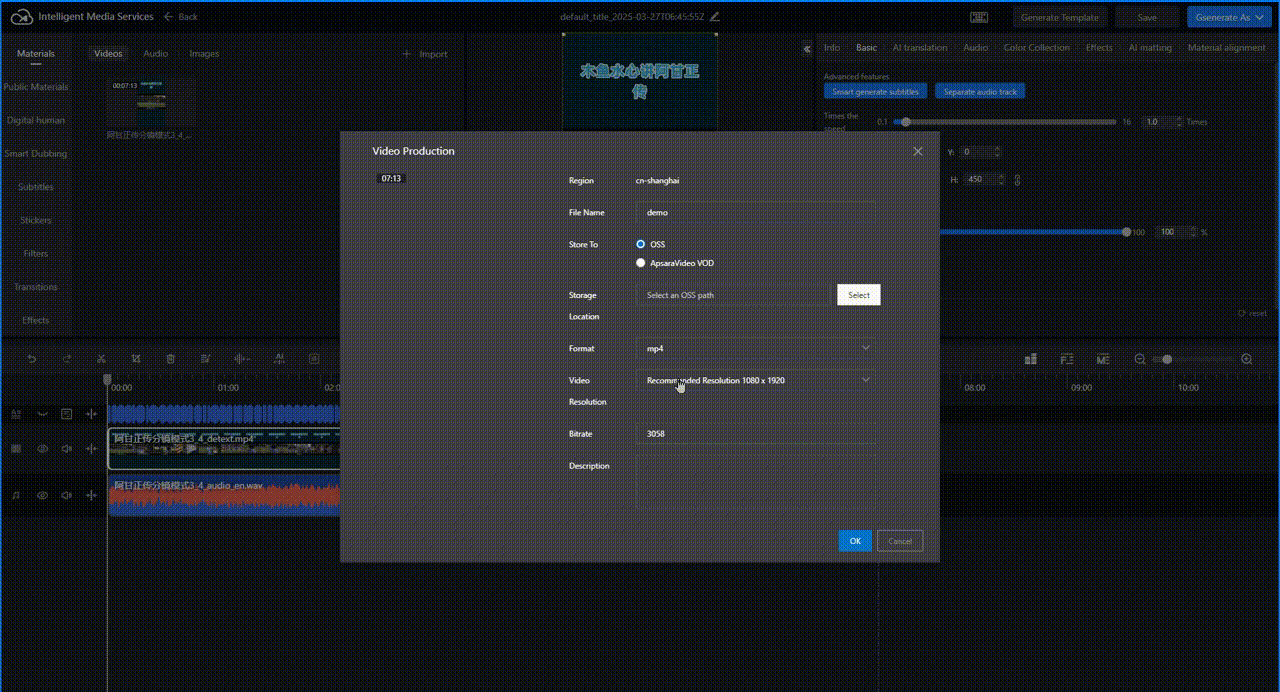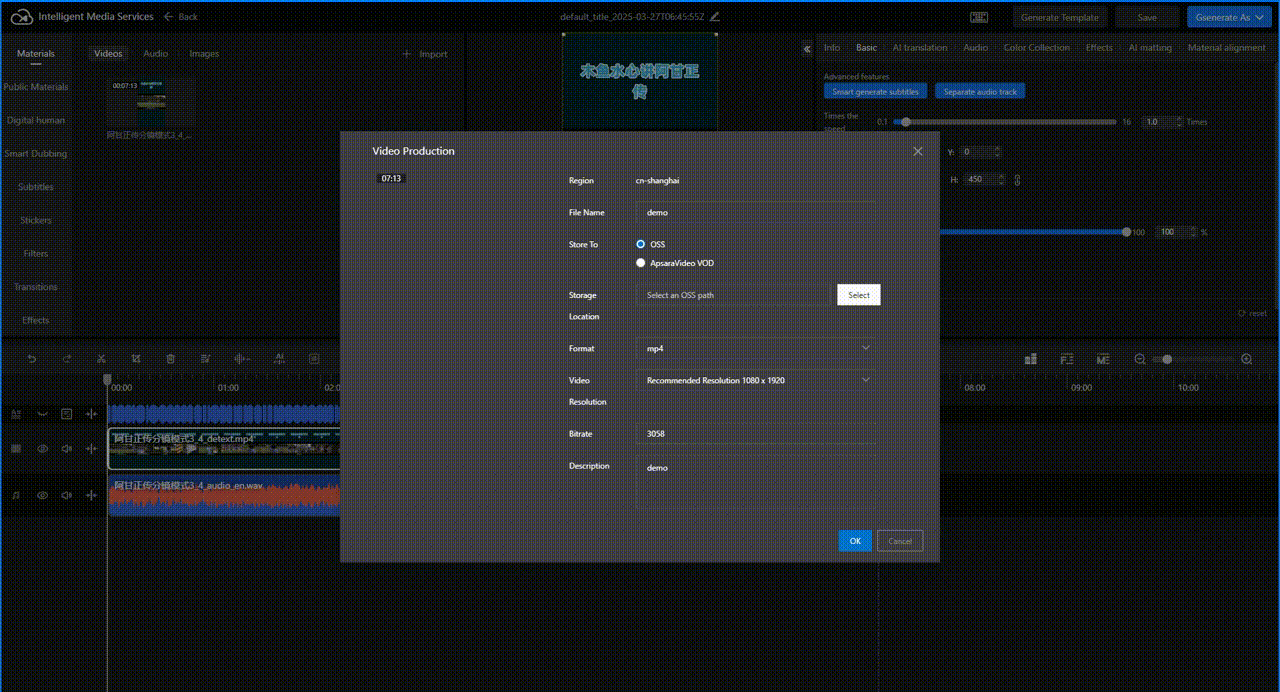
Click in the upper-right corner. Configure parameters for video production as prompted and click OK to generate and export the translated video.
Method 3: Creating through OpenAPI

Create a translation task
Call SubmitVideoTranslationJob to create a video translation task. For related parameters, see Video translation parameters and examples.
Query the result of a translation task
To get the status and result of a specific video translation task, call GetSmartHandleJob. The API returns processing progress, completion time, and URLs to final outputs.
Query translation task list
To view all ongoing or completed video translation tasks, call ListSmartJobs.
Delete a translation task
Call DeleteSmartJob to delete a completed task that no longer needs to be saved and release resources.
Perform post-editing (Optional)
If you are not satisfied with the translation results and want to make corrections, enable post-editing before submitting the translation task. This section introduces two methods to perform post-editing.
For lip-sync translation, post-editing only supports modifying the result of voice output. The lip movement cannot be modified.
Method 1: Use OpenAPI
For detailed API operations, see Speech translation - Manual correction.
Method 2: Use Online Editing (Web SDK)
Preparations
If you are not familiar with Online Editing, learn its basic operations.
Procedure
Go to the Video Translation page and select the task that needs modifications.
Click Edit in the Actions column to open the corresponding online editing project.
FAQ
How do I set the start and end times of a single line based on the audio waveform?
Example:
To split the translated subtitle "Great where are you" into two segments: "Great" and "where are you", align the start and end times of the segments with the troughs of the waveform. This optimizes the post-editing effect for speech translation.

Word count limit during post-editing
Ensure the word count of the adjusted content does not exceed 1.5 times the number before adjustment. Otherwise, it may cause the speech rate to be too fast after post-editing.
Example
Initial translation: Let's talk about this later. We need to go home now.
Inappropriate adjustment: Let's discuss this matter in more detail at a later time. Right now, we should focus on heading back home as it's important to ensure we get there safely and in good time. We can revisit this conversation when we are both more relaxed and have ample opportunity to explore all the aspects thoroughly.
Appropriate adjustment: Let's pick this up another time. We should be going home now.
Reference
To submit translation tasks through OpenAPI, learn about Video translation parameters and examples in advance.