Hologres V3.0 and later versions support the Query Queue feature. This feature enables ordered request processing, load balancing, and resource management. Under high concurrency, it ensures system stability and response efficiency.
Function Introduction
By default, requests submitted to an instance do not have concurrency control. The engine's Coordinator assigns resources and executes them immediately. When the Query Queue feature is enabled, Hologres matches incoming SQL requests against configured classifier rules and routes them to different query queues. Each query queue supports a maximum concurrency limit. When this limit is reached, new requests wait in the queue until compute resources become available.
Notes
-
Query Queue and optimizer settings apply at the instance level for general-purpose instances and at the compute group level for compute group instances. If an instance contains multiple databases, these settings affect all of them.
-
Only General-purpose and Virtual Warehouse instances of Hologres V3.0 and later versions support the query queue feature.
NoteIf your instance is running a version earlier than V3.0, you can upgrade your instance or join the Hologres DingTalk support group to request an upgrade. For more information about how to join the online support DingTalk group, see How do I get more online support?.
-
In Hologres V3.0.10 and later versions, you can configure a query queue to run all its SQL queries using Serverless Computing resources. Concurrency limits and queuing mechanisms apply only to local resources. Queries that use Serverless Computing are not affected by these settings.
-
Each General-purpose instance and each compute group in a Virtual Warehouse instance has a default query queue named
default_queue. This queue has no limits on the maximum number of concurrent queries or the maximum queue size.-
The
default_queuedoes not support classifiers. You can only configure its properties. -
The
default_queuehandles all requests that do not match any other query queue.
-
-
Each General-purpose instance and each compute group in a Virtual Warehouse instance supports a maximum of 10 query queues, including the
default_queue. Each query queue supports a maximum of 10 classifiers. -
You cannot enable the Query Queue feature on read-only replica instances independently. Read-only replica instances inherit the query queue rules from the primary instance.
-
Only queries whose engine_type is
HQE,PQE,SQE, orHiveQEcan be matched to query queues. The supported query types include SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE statements, and INSERT statements that are generated by COPY or CTAS commands. -
Queries that use Fixed Plan bypass query queues and are not subject to concurrency or queuing controls. For more information, see Accelerate SQL execution with Fixed Plan.
-
A classifier belongs to only one query queue, but a query queue can have multiple classifiers.
Procedure
Create a query queue
-
Syntax
-
General-purpose instance
CALL hg_create_query_queue (query_queue_name, max_concurrency, max_queue_size); -
Virtual Warehouse instance
CALL hg_create_query_queue (warehouse_name, query_queue_name, max_concurrency, max_queue_size);
-
-
Parameters
-
warehouse_name: Optional. The name of the compute group. If you do not specify this parameter, the query queue is created in the compute group to which you are currently connected.
NoteOnly Virtual Warehouse instances require this parameter.
-
query_queue_name: Required. The name of the query queue. The name must be unique within the instance or compute group.
-
max_concurrency: Optional. The maximum number of concurrent queries. The default value is -1, which indicates no limit. The value must be in the range of [-1, 2147483647).
-
max_queue_size: Optional. The maximum number of queued SQL queries. The default value is -1, which indicates no limit. The value must be in the range of [-1, 2147483647).
NoteWhen you create a query queue, you can configure only the max_concurrency and max_queue_size properties. To configure other properties, see Configure query queue properties.
-
-
Examples
-
General-purpose instance
-- Create a query queue named insert_queue with a maximum concurrency of 10. Do not add single quotes around the concurrency value. CALL hg_create_query_queue ('insert_queue', 10); -
Virtual Warehouse instance
-- In the init_warehouse compute group, create a query queue named insert_queue with a maximum concurrency of 10. CALL hg_create_query_queue ('init_warehouse', 'insert_queue', 10);
-
Create a classifier
-
Syntax
-
General-purpose instance
CALL hg_create_classifier (query_queue_name, classifier_name, priority); -
Virtual Warehouse instance
CALL hg_create_classifier (warehouse_name, query_queue_name, classifier_name, priority);
-
-
Parameters
-
warehouse_name: Optional. The name of the compute group. If you do not specify this parameter, the current compute group is used.
NoteOnly Virtual Warehouse instances require this parameter.
-
query_queue_name: Required. The name of the query queue to which the classifier belongs.
-
classifier_name: Required. The name of the classifier. The name must be unique within the instance or compute group.
-
priority: Optional. The matching priority. A larger value indicates a higher priority. The default value is 50. The value must be in the range of [1, 100]. If you do not specify this parameter when you create a classifier, you can configure it later. For more information, see Configure classifier properties.
Note-
Classifiers with higher priority values are matched first.
-
If multiple classifiers have the same priority, they are matched based on the lexicographical order of the query queue names and classifier names. For example, a query is matched to queue_a(classifier_1) before it is matched to queue_b(classifier_1).
-
-
-
Examples
-
General-purpose instance
-- In the insert_queue, create a classifier named classifier_insert with priority 20. Do not add single quotes around the priority value. CALL hg_create_classifier ('insert_queue', 'classifier_insert', 20); -
Virtual Warehouse instance
-- In the init_warehouse compute group's insert_queue, create a classifier named classifier_insert with priority 20. CALL hg_create_classifier ('init_warehouse', 'insert_queue', 'classifier_insert', 20);
-
Configure classifier matching rules
In the Query Queue feature, you can configure matching rules for classifiers to route SQL queries to the appropriate queues.
-
Syntax
-
General-purpose instance
CALL hg_set_classifier_rule_condition_value (query_queue_name, classifier_name, condition_name, condition_value); -
Virtual Warehouse instance
CALL hg_set_classifier_rule_condition_value (warehouse_name, query_queue_name, classifier_name, condition_name, condition_value);
-
-
Parameters
Name
Description
warehouse_name
Optional. The compute group name. If omitted, the current compute group is used.
NoteOnly Virtual Warehouse instances require this parameter.
query_queue_name
Required. The query queue name.
classifier_name
Required. The classifier name to configure.
condition_name and condition_value
Required. Supported condition attributes:
-
user_name: The UID of the current account.
-
command_tag: The request type. Values: INSERT, SELECT, UPDATE, DELETE.
Hologres implements COPY operations using INSERT for better efficiency. Therefore, limiting INSERT concurrency also affects COPY write concurrency.
-
db_name: The database name.
-
engine_type: The query engine. Values: HQE, PQE, SQE, HiveQE. Recommended for Hologres V3.1.18 and later.
-
digest: The SQL fingerprint. For details, see SQL fingerprint.
-
application_name: The application that initiated the query. Supported in V3.0.9 and later.
-
storage_mode: The storage mode. Values: hot, cold. Recommended for Hologres V3.1.18 or V3.1.8 and later.
-
write_table: The table written by the query. Format:
<db_name>.<schema_name>.<table_name>. Supported in V3.1 and later. -
read_table: The table read by the query. Supported in V3.1 and later.
A classifier can have multiple attributes, and each attribute can have multiple matching rules. In Hologres V3.1.18 and later versions, the relationship between attributes and rules is as follows:
-
If a classifier has rules for multiple attributes:
-
The rules for different attributes have an AND relationship. For example, if a classifier has rules for the user_name and command_tag attributes, a query must match both rules to be assigned to this classifier.
-
To define an OR relationship between attributes, where a query is matched if it meets the condition of any attribute, you can create multiple classifiers and assign them to the same query queue.
-
-
Within a classifier, matching rules for the same property have the following three types of relationships:
-
user_name/command_tag/db_name/digest/application_name:
-
The configured values form a set named set_a.
-
The attribute value of the query forms a set named set_b, which contains a single value.
-
The query is matched if
set_b ⊆ set_a.
-
-
storage_mode:
-
For the same property (currently limited to storage_mode), set_a is the collection of values configured in the matching rule.
-
The corresponding property collection for Query is set_b, which accepts the values 'hot', 'cold', or 'hot, cold'.
-
The query is matched only if
set_a == set_b.
-
-
engine_type/write_table/read_table:
-
The configured values form a set named set_a.
-
The tables involved in the query form a set named set_b, which can contain any number of tables.
-
The query is matched if
(set_a ∩ set_b) != ∅.
-
-
Note-
You can configure only one condition attribute at a time. If the condition value is case-sensitive, enclose it in double quotation marks ("").
-
To match multiple values for the same condition attribute, call the procedure multiple times. For example, to match both SELECT and INSERT for command_tag, execute two separate statements.
-
-
Examples
This example creates the query queue `test_queue` for the default compute group `init_warehouse` using a compute group instance. For general-purpose instances, omit the first input parameter.
CALL hg_create_query_queue ('init_warehouse', 'test_queue');-
Example 1: Assign queries that are initiated by the p4_123 or p4_456 user, or queries whose SQL fingerprints are xxx or yyy to the test_queue.
-- To define an OR relationship between user and digest attributes, create two classifiers. -- Create classifier_user and bind it to test_queue CALL hg_create_classifier ('init_warehouse', 'test_queue', 'classifier_user'); -- Set user-based matching rules for users "p4_123" or "p4_456" CALL hg_set_classifier_rule_condition_value ('init_warehouse','test_queue', 'classifier_user', 'user_name', 'p4_123'); CALL hg_set_classifier_rule_condition_value ('init_warehouse','test_queue', 'classifier_user', 'user_name', 'p4_456'); -- Create classifier_digest and bind it to test_queue CALL hg_create_classifier ('init_warehouse', 'test_queue', 'classifier_digest'); -- Set digest-based matching rules for fingerprints "xxx" or "yyy" CALL hg_set_classifier_rule_condition_value ('init_warehouse','test_queue', 'classifier_digest', 'digest', 'xxx'); CALL hg_set_classifier_rule_condition_value ('init_warehouse','test_queue', 'classifier_digest', 'digest', 'yyy'); -
Example 2: Assign queries that are initiated by the xx_bi application and access both hot and cold storage to the test_queue.
-- To define an AND relationship between application and storage mode, configure both attributes in one classifier. -- Create classifier_3 and bind it to test_queue CALL hg_create_classifier ('init_warehouse', 'test_queue', 'classifier_3'); -- Set application-based matching rule CALL hg_set_classifier_rule_condition_value ('init_warehouse','test_queue', 'classifier_3', 'application_name', 'xx_bi'); -- Set storage mode rules. Both "hot" and "cold" must be set so the query matches only if it accesses both. CALL hg_set_classifier_rule_condition_value ('init_warehouse','test_queue', 'classifier_3', 'storage_mode', 'hot'); CALL hg_set_classifier_rule_condition_value ('init_warehouse','test_queue', 'classifier_3', 'storage_mode', 'cold'); -
Example 3: Assign all queries that access cold storage to the test_queue.
-- Because storage_mode requires exact match, split "accessing cold storage" into two cases. -- Create classifier_cold_1 and bind it to test_queue CALL hg_create_classifier ('init_warehouse', 'test_queue', 'classifier_cold_1'); -- Queries with storage_mode = cold go here CALL hg_set_classifier_rule_condition_value ('init_warehouse','test_queue', 'classifier_cold_1', 'storage_mode', 'cold'); -- Create classifier_cold_2 and bind it to test_queue CALL hg_create_classifier ('init_warehouse', 'test_queue', 'classifier_cold_2'); -- Queries with storage_mode = hot,cold go here CALL hg_set_classifier_rule_condition_value ('init_warehouse','test_queue', 'classifier_cold_2', 'storage_mode', 'hot'); CALL hg_set_classifier_rule_condition_value ('init_warehouse','test_queue', 'classifier_cold_2', 'storage_mode', 'cold'); -
Example 4: Assign queries that read data from table a and write data to table b to the test_queue.
-- To define an AND relationship between read_table and write_table, configure both in one classifier. -- Create classifier_table and bind it to test_queue CALL hg_create_classifier ('init_warehouse', 'test_queue', 'classifier_table'); -- Set read_table rule. Queries reading table a match, regardless of other tables read. CALL hg_set_classifier_rule_condition_value ('init_warehouse','test_queue', 'classifier_table', 'read_table', 'db_name.schema_name.a'); -- Set write_table rule. Queries writing to table b match. CALL hg_set_classifier_rule_condition_value ('init_warehouse','test_queue', 'classifier_table', 'write_table', 'db_name.schema_name.b');
-
Additional operations
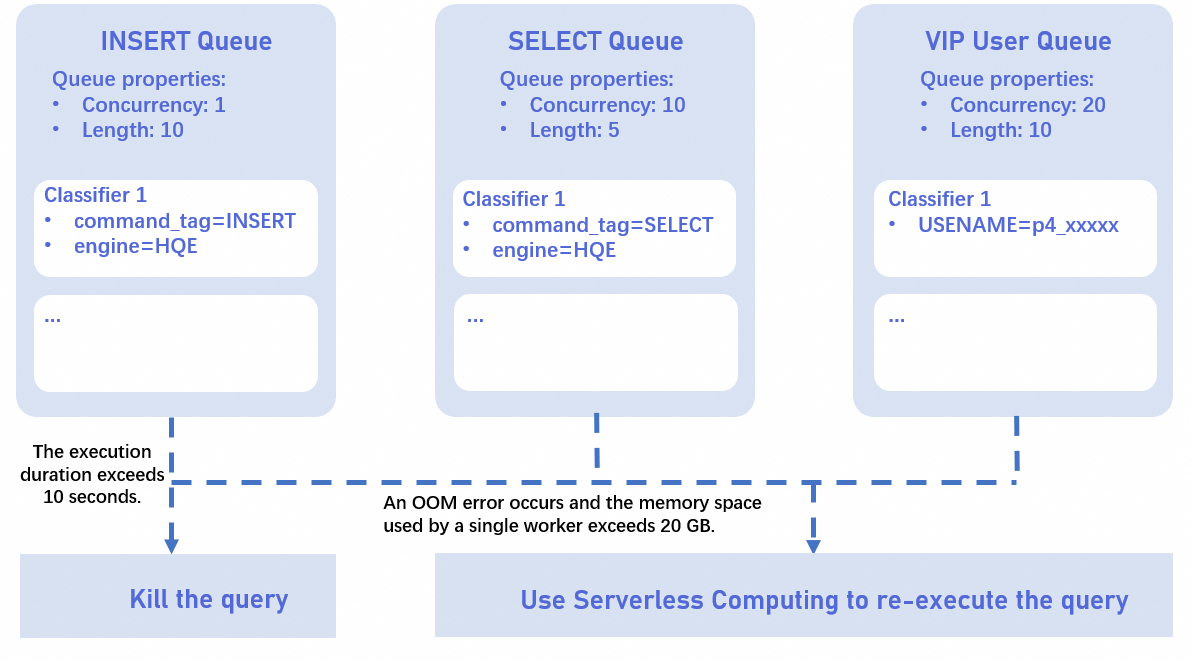
Large query control
To limit the impact of large queries, you can use the Query Queue feature to manage execution time and out-of-memory (OOM) conditions. For queries that exceed the configured thresholds, you can terminate them or rerun them using Serverless Computing resources.
-
Hologres V3.0 supports rerunning only SELECT queries. If you use FETCH to retrieve data, the query is rerun only if the FETCH operation returns no data. This ensures the accuracy of the results.
-
Query execution includes three phases: optimization_cost (generating the execution plan), start_query_cost (query startup), and get_next_cost (query execution). For more information, see View and analyze slow query logs. The large query control of the Query Queue feature considers only the get_next_cost phase. The queue wait time and lock wait time are not included.
-
Execution time control
You can set the big_query_execution_time_threshold_sec parameter. The unit is seconds. The default value is -1, which indicates no limit. The value must be in the range of [-1, 2147483647). The following examples show how to control the execution time:
-
Scenario 1: Terminate long-running queries
Queries in the select_queue run on local resources. If the execution time of a query exceeds 10 seconds, the query is terminated.
CALL hg_set_query_queue_property ('select_queue', 'big_query_execution_time_threshold_sec', '10'); -
Scenario 2: Rerun long-running queries
Queries in the select_queue run on local resources. If the execution time of a query exceeds 10 seconds, the query is terminated and then rerun using Serverless Computing.
CALL hg_set_query_queue_property ('select_queue', 'big_query_execution_time_threshold_sec', '10'); CALL hg_set_query_queue_property ('select_queue', 'enable_rerun_as_big_query_when_exceeded_execution_time_threshold', 'true'); CALL hg_set_query_queue_property ('select_queue', 'rerun_big_query_on_computing_resource', 'serverless');Note-
enable_rerun_as_big_query_when_exceeded_execution_time_threshold: Specifies whether to rerun a query using other resources after the query is terminated due to a timeout. The default value is false.
-
rerun_big_query_on_computing_resource: The name of the Serverless Computing resource that is used for rerunning the query.
-
-
-
OOM-based rerun
Queries in the select_queue run on local resources. If a query triggers an OOM error and uses more than 10 GB of memory on a single worker node, the query is rerun using Serverless Computing. The big_query_mem_threshold_when_oom_gb parameter sets the OOM memory threshold. The default value is -1, which indicates no limit. The value must be in the range of [-1, 64). The following example shows how to rerun a query based on OOM errors:
CALL hg_set_query_queue_property ('select_queue', 'big_query_mem_threshold_when_oom_gb', '10'); CALL hg_set_query_queue_property ('select_queue', 'enable_rerun_as_big_query_when_oom_exceeded_mem_threshold', 'true'); CALL hg_set_query_queue_property ('select_queue', 'rerun_big_query_on_computing_resource', 'serverless');
Query queue management
Delete a query queue
-
Syntax
-
General-purpose instance
CALL hg_drop_query_queue (query_queue_name); -
Virtual Warehouse instance
CALL hg_drop_query_queue (warehouse_name, query_queue_name);
-
-
Parameters
-
warehouse_name: Optional. The name of the compute group. If you do not specify this parameter, the current compute group is used.
NoteOnly Virtual Warehouse instances require this parameter.
-
query_queue_name: Required. The name of the query queue.
-
-
Examples
-
General-purpose instance
-- Delete the insert_queue query queue CALL hg_drop_query_queue ('insert_queue'); -
Virtual Warehouse instance
-- In the init_warehouse compute group, delete the insert_queue query queue CALL hg_drop_query_queue ('init_warehouse', 'insert_queue');
Delete query queue properties
-
Syntax
-
General-purpose instance
CALL hg_remove_query_queue_property (query_queue_name, property_key); -
Virtual Warehouse instance
CALL hg_remove_query_queue_property (warehouse_name, query_queue_name, property_key);
-
-
Parameters
-
warehouse_name: Optional. The name of the compute group. If you do not specify this parameter, the current compute group is used.
NoteOnly Virtual Warehouse instances require this parameter.
-
query_queue_name: Required. The name of the query queue.
-
property_key: Required. The name of the property. Valid values: max_concurrency, max_queue_size, and queue_timeout_ms. For more information, see Configure query queue properties.
-
-
Examples
-
General-purpose instance
-- Delete the max_concurrency property of insert_queue CALL hg_remove_query_queue_property('insert_queue', 'max_concurrency'); -- Delete the max_queue_size property of insert_queue CALL hg_remove_query_queue_property('insert_queue', 'max_queue_size'); -- Delete the queue_timeout_ms property of insert_queue CALL hg_remove_query_queue_property('insert_queue', 'queue_timeout_ms'); -
Virtual Warehouse instance
-- In the init_warehouse compute group, delete the max_concurrency property of insert_queue CALL hg_remove_query_queue_property('init_warehouse', 'insert_queue', 'max_concurrency'); -- In the init_warehouse compute group, delete the max_queue_size setting of insert_queue CALL hg_remove_query_queue_property('init_warehouse', 'insert_queue', 'max_queue_size'); -- In the init_warehouse compute group, delete the queue_timeout_ms property of insert_queue CALL hg_remove_query_queue_property('init_warehouse', 'insert_queue', 'queue_timeout_ms');
-
View query queue metadata
The metadata of query queues is stored in the hologres.hg_query_queues system table. The key fields are described in the following table.
|
Field name |
Data type |
Description |
|
warehouse_id |
INT |
The ID of the compute group. Note
For General-purpose instances, warehouse_id is 0. |
|
warehouse_name |
TEXT |
The compute group name. Note
For General-purpose instances, warehouse_name is empty. |
|
query_queue_name |
TEXT |
The name of the queue. |
|
property_key |
TEXT |
The property name. |
|
property_value |
TEXT |
The property value. |
Configure query queue properties
-
Syntax
-
General-purpose instance
CALL hg_set_query_queue_property (query_queue_name, property_key, property_value); -
Virtual Warehouse instance
CALL hg_set_query_queue_property (warehouse_name, query_queue_name, property_key, property_value);
-
-
Parameters
-
warehouse_name: Optional. The name of the compute group. If you do not specify this parameter, the current compute group is used.
NoteOnly Virtual Warehouse instances require this parameter.
-
query_queue_name: Required. The name of the query queue.
-
property_key and property_value: Required. The supported properties are described as follows:
-
max_concurrency: The maximum number of concurrent queries. The default value is -1, which indicates no limit. The value must be in the range of [-1, 2147483647).
-
max_queue_size: The maximum number of queued SQL queries. The default value is -1, which indicates no limit. The value must be in the range of [-1, 2147483647).
-
queue_timeout_ms: The maximum queue wait time. Unit: milliseconds (ms). Queries that exceed this time are terminated. The default value is -1, which indicates no limit. The value must be in the range of [-1, 2147483647).
-
-
-
Examples
-
General-purpose instance
-- Set max_concurrency of insert_queue to 15 CALL hg_set_query_queue_property('insert_queue', 'max_concurrency', '15'); -- Set max_queue_size of insert_queue to 15 CALL hg_set_query_queue_property('insert_queue', 'max_queue_size', '15'); -- Set queue_timeout_ms of insert_queue to 3000 ms CALL hg_set_query_queue_property('insert_queue', 'queue_timeout_ms', '3000'); -
Virtual Warehouse instance
-- In the init_warehouse compute group, set max_concurrency of insert_queue to 15 CALL hg_set_query_queue_property('init_warehouse', 'insert_queue', 'max_concurrency', '15'); -- In the init_warehouse compute group, set max_queue_size of insert_queue to 15 CALL hg_set_query_queue_property('init_warehouse', 'insert_queue', 'max_queue_size', '15'); -- In the init_warehouse compute group, set queue_timeout_ms of insert_queue to 3000 ms CALL hg_set_query_queue_property('init_warehouse', 'insert_queue', 'queue_timeout_ms', '3000');
-
Clear queued requests from a query queue
-
Syntax
-
General-purpose instance
CALL hg_clear_query_queue (query_queue_name); -
Virtual Warehouse instance
CALL hg_clear_query_queue (warehouse_name, query_queue_name);
-
-
Parameters
-
warehouse_name: Optional. The name of the compute group. If you do not specify this parameter, the current compute group is used.
NoteOnly Virtual Warehouse instances require this parameter.
-
query_queue_name: Required. The name of the query queue.
-
-
Examples
-
General-purpose instance
-- Clear all queued requests in select_queue CALL hg_clear_query_queue ('select_queue'); -
Virtual Warehouse instance
-- Clear all queued requests in select_queue in the init_warehouse compute group CALL hg_clear_query_queue ('init_warehouse', 'select_queue');
-
Classifier management
Delete a classifier
-
Syntax
-
General-purpose instance
CALL hg_drop_classifier (query_queue_name, classifier_name); -
Virtual Warehouse instance
CALL hg_drop_classifier (warehouse_name, query_queue_name, classifier_name);
-
-
Parameters
-
warehouse_name: Optional. The name of the compute group. If you do not specify this parameter, the current compute group is used.
NoteOnly Virtual Warehouse instances require this parameter.
-
query_queue_name: Required. The name of the query queue.
-
classifier_name: Required. The name of the classifier.
-
-
Examples
-
General-purpose instance
-- In insert_queue, delete the classifier_insert classifier CALL hg_drop_classifier ('insert_queue', 'classifier_insert'); -
Virtual Warehouse instance
-- In the init_warehouse compute group's insert_queue, delete the classifier_insert classifier CALL hg_drop_classifier ('init_warehouse', 'insert_queue', 'classifier_insert');
-
Delete classifier properties
-
Syntax
-
General-purpose instance
CALL hg_remove_classifier_property (query_queue_name, classifier_name, property_key); -
Virtual Warehouse instance
CALL hg_remove_classifier_property (warehouse_name, query_queue_name, classifier_name, property_key);
-
-
Parameters
-
warehouse_name: Optional. The name of the compute group. If you do not specify this parameter, the current compute group is used.
NoteOnly Virtual Warehouse instances require this parameter.
-
query_queue_name: Required. The name of the query queue.
-
classifier_name: Required. The name of the classifier.
-
property_key: Required. The supported property is priority. For more information, see Configure classifier properties.
-
-
Examples
-
General-purpose instance
-- In insert_queue, delete the priority property of classifier_insert CALL hg_remove_classifier_property ('insert_queue', 'classifier_insert', 'priority'); -
Virtual Warehouse instance
-- In the init_warehouse compute group's insert_queue, delete the priority property of classifier_insert CALL hg_remove_classifier_property ('init_warehouse', 'insert_queue', 'classifier_insert', 'priority');
-
Configure classifier properties
-
Syntax
-
General-purpose instance
CALL hg_set_classifier_property (query_queue_name, classifier_name, property_key, property_value); -
Virtual Warehouse instance
CALL hg_set_classifier_property (warehouse_name, query_queue_name, classifier_name, property_key, property_value);
-
-
Parameters
-
warehouse_name: Optional. The name of the compute group. If you do not specify this parameter, the current compute group is used.
NoteOnly Virtual Warehouse instances require this parameter.
-
query_queue_name: Required. The name of the query queue.
-
classifier_name: Required. The name of the classifier.
-
property_key and property_value: Required. The supported property is described as follows:
priority: The matching priority of the classifier. A larger value indicates a higher priority. The default value is 50. The value must be in the range of [1, 100].
Note-
Classifiers with higher priority values are matched first.
-
If multiple classifiers have the same priority, they are matched based on the lexicographical order of the query queue names and classifier names. For example, a query is matched to queue_a(classifier_1) before it is matched to queue_b(classifier_1).
-
-
-
Examples
-
General-purpose instance
-- In insert_queue, set the priority of classifier_insert to 30 CALL hg_set_classifier_property ('insert_queue', 'classifier_insert', 'priority', '30'); -
Virtual Warehouse instance
-- In the init_warehouse compute group's insert_queue, set the priority of classifier_insert to 30 CALL hg_set_classifier_property ('init_warehouse', 'insert_queue', 'classifier_insert','priority', '30');
-
Delete classifier matching rules
-
Delete a matching rule for a specific condition attribute (condition_name) in a classifier
-
Syntax
-
General-purpose instance
CALL hg_remove_classifier_rule_condition_value (query_queue_name, classifier_name, condition_name, condition_value); -
Virtual Warehouse instance
CALL hg_remove_classifier_rule_condition_value (warehouse_name, query_queue_name, classifier_name, condition_name, condition_value);
-
-
Parameters
-
warehouse_name: Optional. The name of the compute group. If you do not specify this parameter, the current compute group is used.
NoteOnly Virtual Warehouse instances require this parameter.
-
query_queue_name: Required. The name of the query queue.
-
classifier_name: Required. The name of the classifier.
-
condition_name and condition_value: Required. The condition attribute and its value that you want to delete. Valid values for condition_name: user_name, command_tag, db_name, engine_type, digest, and storage_mode. For more information, see Configure classifier matching rules.
-
-
Examples
-
General-purpose instance
-- In insert_queue, delete the command_tag = INSERT rule from classifier_insert CALL hg_remove_classifier_rule_condition_value ('insert_queue', 'classifier_insert', 'command_tag', 'INSERT'); -- In insert_queue, delete the user_name = p4_12345 rule from classifier_insert CALL hg_remove_classifier_rule_condition_value ('insert_queue', 'classifier_insert', 'user_name', 'p4_12345'); -- In insert_queue, delete the db_name = prd_db rule from classifier_insert CALL hg_remove_classifier_rule_condition_value ('insert_queue', 'classifier_insert', 'db_name', 'prd_db'); -- In insert_queue, delete the engine_type = HQE rule from classifier_insert CALL hg_remove_classifier_rule_condition_value ('insert_queue', 'classifier_insert', 'engine_type', 'HQE'); -- In insert_queue, delete the digest = md5edb3161000a003799a5d3f2656b70b4c rule from classifier_insert CALL hg_remove_classifier_rule_condition_value ('insert_queue', 'classifier_insert', 'digest', 'md5edb3161000a003799a5d3f2656b70b4c'); -- In insert_queue, delete the storage_mode = hot rule from classifier_insert CALL hg_remove_classifier_rule_condition_value ('insert_queue', 'classifier_insert', 'storage_mode', 'hot'); -
Virtual Warehouse instance
-- In init_warehouse's insert_queue, delete the command_tag = INSERT rule from classifier_insert CALL hg_remove_classifier_rule_condition_value ('init_warehouse', 'insert_queue', 'classifier_insert', 'command_tag', 'INSERT'); -- In init_warehouse's insert_queue, delete the user_name = p4_12345 rule from classifier_insert CALL hg_remove_classifier_rule_condition_value ('init_warehouse', 'insert_queue', 'classifier_insert', 'user_name', 'p4_12345'); -- In init_warehouse's insert_queue, delete the db_name = prd_db rule from classifier_insert CALL hg_remove_classifier_rule_condition_value ('init_warehouse', 'insert_queue', 'classifier_insert', 'db_name', 'prd_db'); -- In init_warehouse's insert_queue, delete the engine_type = HQE rule from classifier_insert CALL hg_remove_classifier_rule_condition_value ('init_warehouse', 'insert_queue', 'classifier_insert', 'engine_type', 'HQE'); -- In init_warehouse's insert_queue, delete the digest = md5edb3161000a003799a5d3f2656b70b4c rule from classifier_insert CALL hg_remove_classifier_rule_condition_value ('init_warehouse', 'insert_queue', 'classifier_insert', 'digest', 'md5edb3161000a003799a5d3f2656b70b4c'); -- In init_warehouse's insert_queue, delete the storage_mode = hot rule from classifier_insert CALL hg_remove_classifier_rule_condition_value ('init_warehouse', 'insert_queue', 'classifier_insert', 'storage_mode', 'hot');
-
-
-
Delete all matching rules for a specific condition attribute (condition_name) in a classifier
-
Syntax
-
General-purpose instance
CALL hg_remove_classifier_rule_condition (query_queue_name, classifier_name, condition_name); -
Virtual Warehouse instance
CALL hg_remove_classifier_rule_condition (warehouse_name, query_queue_name, classifier_name, condition_name);
-
-
Parameters
-
warehouse_name: Optional. The name of the compute group. If you do not specify this parameter, the current compute group is used.
NoteOnly Virtual Warehouse instances require this parameter.
-
query_queue_name: Required. The name of the query queue.
-
classifier_name: Required. The name of the classifier.
-
condition_name: Required. The condition attribute whose rules you want to delete. Valid values: user_name, command_tag, db_name, engine_type, digest, and storage_mode. For more information, see Configure classifier matching rules.
-
-
Examples
-
General-purpose instance
-- In insert_queue, delete all command_tag rules from classifier_insert CALL hg_remove_classifier_rule_condition ('insert_queue', 'classifier_insert', 'command_tag'); -- In insert_queue, delete all user_name rules from classifier_insert CALL hg_remove_classifier_rule_condition ('insert_queue', 'classifier_insert', 'user_name'); -- In insert_queue, delete all db_name rules from classifier_insert CALL hg_remove_classifier_rule_condition ('insert_queue', 'classifier_insert', 'db_name'); -- In insert_queue, delete all engine_type rules from classifier_insert CALL hg_remove_classifier_rule_condition ('insert_queue', 'classifier_insert', 'engine_type'); -- In insert_queue, delete all digest rules from classifier_insert CALL hg_remove_classifier_rule_condition ('insert_queue', 'classifier_insert', 'digest'); -- In insert_queue, delete all storage_mode rules from classifier_insert CALL hg_remove_classifier_rule_condition ('insert_queue', 'classifier_insert', 'storage_mode'); -
Virtual Warehouse instance
-- In init_warehouse's insert_queue, delete all command_tag rules from classifier_insert CALL hg_remove_classifier_rule_condition ('init_warehouse', 'insert_queue', 'classifier_insert', 'command_tag'); -- In init_warehouse's insert_queue, delete all user_name rules from classifier_insert CALL hg_remove_classifier_rule_condition ('init_warehouse', 'insert_queue', 'classifier_insert', 'user_name'); -- In init_warehouse's insert_queue, delete all db_name rules from classifier_insert CALL hg_remove_classifier_rule_condition ('init_warehouse', 'insert_queue', 'classifier_insert', 'db_name'); -- In init_warehouse's insert_queue, delete all engine_type rules from classifier_insert CALL hg_remove_classifier_rule_condition ('init_warehouse', 'insert_queue', 'classifier_insert', 'engine_type'); -- In init_warehouse's insert_queue, delete all digest rules from classifier_insert CALL hg_remove_classifier_rule_condition ('init_warehouse', 'insert_queue', 'classifier_insert', 'digest'); -- In init_warehouse's insert_queue, delete all storage_mode rules from classifier_insert CALL hg_remove_classifier_rule_condition ('init_warehouse', 'insert_queue', 'classifier_insert', 'storage_mode');
-
-
View classifier metadata
The metadata of classifiers is stored in the hologres.hg_classifiers system table. The key fields are described in the following table.
|
Field |
Data type |
Description |
|
warehouse_id |
INT |
The ID of the compute group. Note
For General-purpose instances, warehouse_id is 0. |
|
warehouse_name |
TEXT |
The compute group name. Note
For General-purpose instances, warehouse_name is empty. |
|
query_queue_name |
TEXT |
The name of the queue that you want to query. |
|
classifier_name |
TEXT |
The classifier name. |
|
property_key |
TEXT |
The property name. |
|
property_value |
TEXT |
The property value. |
Run query queue queries using Serverless Computing resources
In Hologres V3.0.10 and later versions, you can configure a query queue to run all its queries using Serverless Computing resources. After the configuration, queries in the queue request Serverless resources based on the submission order and priority. These queries are no longer affected by the concurrency limits or queuing mechanisms of the queue. For more information, see Serverless Computing User Guide.
If Serverless Computing is unavailable in the zone where the instance resides, queries run on local compute resources.
-
General-purpose instance
-
Syntax
-- Run all queries in the target queue using Serverless resources CALL hg_set_query_queue_property('<query_queue_name>', 'computing_resource', 'serverless'); -- (Optional) Set query priority when using Serverless resources. Values: 1-5. Default: 3 CALL hg_set_query_queue_property('<query_queue_name>', 'query_priority_when_using_serverless_computing', '<priority>'); -
Parameters
-
query_queue_name: Required. The name of the query queue.
-
priority: The priority. The default value is 3. The value must be in the range of
[1, 5].
-
-
Example
-- Run all queries in the target queue using Serverless resources CALL hg_set_query_queue_property('insert_queue', 'computing_resource', 'serverless'); -- Set Serverless query priority to 2 CALL hg_set_query_queue_property('insert_queue', 'query_priority_when_using_serverless_computing', '2');
-
-
Compute group instance
-
Syntax
-- Run all queries in the target queue using Serverless resources CALL hg_set_query_queue_property('<warehouse_name>', '<query_queue_name>', 'computing_resource', 'serverless'); -- (Optional) Set query priority when using Serverless resources. Values: 1-5. Default: 3 CALL hg_set_query_queue_property('<warehouse_name>', '<query_queue_name>', 'query_priority_when_using_serverless_computing', '<priority>'); -
Parameters
-
warehouse_name: Required. The name of the compute group.
-
query_queue_name: Required. The name of the query queue.
-
priority: Required. The priority. The default value is 3. The value must be in the range of
[1, 5].
-
-
Example
-- Run all queries in the target queue using Serverless resources CALL hg_set_query_queue_property('init_warehouse', 'insert_queue', 'computing_resource', 'serverless'); -- Set Serverless query priority to 2 CALL hg_set_query_queue_property('init_warehouse', 'insert_queue', 'query_priority_when_using_serverless_computing', '2');
-
Common scenarios
View the query queue used by a specific SQL statement
You can use the EXPLAIN statement to view the query queue. The Query Queue field in the result indicates the assigned queue. The following is an example:
-- Create a query queue with concurrency 10 and max queue size 20
CALL hg_create_query_queue ('select_queue', 10, 20);
-- Create a classifier and bind the command_tag attribute
CALL hg_create_classifier ('select_queue', 'classifier_1');
CALL hg_set_classifier_rule_condition_value ('select_queue', 'classifier_1', 'command_tag', 'select');
-- Use Explain Analyze to view the matched classifier and query queue
EXPLAIN ANALYZE SELECT * FROM hg_stat_activity;The following is the result.
QUERY PLAN
Gather (cost=0.00..14.96 rows=1000 width=408)
[4:1 id=100003 dop=1 time=16/16/16ms rows=142(142/142/142) mem=43/43/43KB open=0/0/0ms get_next=16/16/16ms]
-> Forward (cost=0.00..12.19 rows=1000 width=408)
[0:4 id=100002 dop=4 time=16/8/5ms rows=142(39/35/33) mem=6/6/6KB open=16/8/5ms get_next=0/0/0ms scan_rows=142(39/35/33)]
-> ExecuteExternalSQL on PQE (cost=0.00..10.04 rows=0 width=408)
" External SQL: SELECT "datid" AS c_d2adb610_0, "datname" AS c_d2adb760_1, "pid" AS c_d2adb8a0_2, "usesysid" AS c_d2adba10_3, "usename" AS c_d2adbb60_4, "application_name" AS c_d2adbd10_5, "client_addr" AS c_d2adbe80_6, "client_hostname" AS c_d2df1020_7, "client_port" AS c_d2df1190_8, "backend_start" AS c_d2df1300_9, "xact_start" AS c_d2df1470_10, "query_start" AS c_d2df15e0_11, "state_change" AS c_d2df1750_12, "wait_event_type" AS c_d2df18c0_13, "wait_event" AS c_d2df1a30_14, "state" AS c_d2df1b80_15, "backend_xid" AS c_d2df1cf0_16, "backend_xmin" AS c_d2df1e60_17, "query" AS c_d2df1fb0_18, "backend_type" AS c_d2df2120_19, "query_id" AS c_d2df2290_20, "transaction_id" AS c_d2df2400_21, "extend_info" AS c_d2df2570_22, "running_info" AS c_d2df26e0_23 FROM pg_catalog."hg_stat_activity""
Query id:[1001002491453065719]
Query Queue: init_warehouse.select_queue.classifier_1View the query queue for active queries
You can run the following SQL statement to view the query queue name, status, and queue time for active queries.
SELECT
running_info::json -> 'current_stage' ->> 'stage_name' AS stage_name,
running_info::json -> 'current_stage' ->> 'queue_time_ms' AS queue_time_ms,
running_info::json ->> 'query_queue' AS query_queue,
*
FROM
hg_stat_activity;View the query queue in Query Log
You can use the following SQL statement to view the query queue, status, and queue time in the Query Log. The query_detail field records information about the query queue. For more information about the hologres.hg_query_log system table, see View the query_log table.
SELECT * FROM hologres.hg_query_log WHERE query_detail like '%query_queue = <warehouse_name>.<queue_name>%';-- Only compute group instances require warehouse_nameThe extended_info field in the result includes the following information:
-
serverless_computing_source: Indicates the source of the SQL statement that is executed using Serverless Computing. Valid values:-
user_submit: The SQL statement is explicitly submitted to run on Serverless resources and is not related to the Query Queue feature. -
query_queue: The SQL statement is from a query queue that is configured to run entirely on Serverless resources. -
query_queue_rerun: The SQL statement is automatically rerun on Serverless resources using the large query control of the Query Queue feature.
-
-
query_id_of_triggered_rerun: This parameter is returned only when the value of serverless_computing_source is query_queue_rerun. It indicates the original query ID of the rerun SQL statement.
Create query queues with different matching rules
-
Example 1: Create a query queue for INSERT requests.
After the query queue is created, all INSERT SQL requests are matched by classifier_1 and assigned to the insert_queue.
-- Create a query queue with concurrency 10 and max queue size 20 CALL hg_create_query_queue ('insert_queue', 10, 20); -- Create a classifier and bind the command_tag attribute CALL hg_create_classifier ('insert_queue', 'classifier_1'); CALL hg_set_classifier_rule_condition_value ('insert_queue', 'classifier_1', 'command_tag', 'INSERT'); -
Create a query queue for users p4_123 and p4_345.
After the query queue is created, SQL requests that are initiated by the p4_123 and p4_345 users are matched by classifier_2 and assigned to the user_queue.
-- Create a query queue with concurrency 3 and unlimited queue size CALL hg_create_query_queue ('user_queue', 3); CALL hg_set_query_queue_property('user_queue','max_queue_size', -1); -- Create a classifier and set user_name matching rules CALL hg_create_classifier ('user_queue', 'classifier_2'); CALL hg_set_classifier_rule_condition_value ('user_queue', 'classifier_2', 'user_name', 'p4_123'); CALL hg_set_classifier_rule_condition_value ('user_queue', 'classifier_2', 'user_name', 'p4_345');NoteIf the user account is a custom account, enclose the account name in double quotation marks (""). Example:
CALL hg_set_classifier_rule_condition_value ('user_queue', 'classifier_2', 'user_name', '"BASIC$xxx"');. -
Create a query queue for databases test and postgres.
After the query queue is created, SQL requests for the test and postgres databases are matched by classifier_3 and assigned to the db_queue.
-- Create a query queue with concurrency 5 CALL hg_create_query_queue ('db_queue', 5); -- Set max queue time to 600000 ms. Queries exceeding this time fail. CALL hg_set_query_queue_property ('db_queue', 'queue_timeout_ms', '600000'); -- Create a classifier and bind the db_name attribute CALL hg_create_classifier ('db_queue', 'classifier_3'); CALL hg_set_classifier_rule_condition_value ('db_queue', 'classifier_3', 'db_name', 'test'); CALL hg_set_classifier_rule_condition_value ('db_queue', 'classifier_3', 'db_name', 'postgres'); -
Create a query queue for HQE engine requests.
After the query queue is created, SQL requests that are processed by the HQE engine are matched by classifier_4 and assigned to the hqe_queue.
-- Create a query queue with concurrency 10 CALL hg_create_query_queue ('hqe_queue', 10); -- Create a classifier and bind the engine_type attribute CALL hg_create_classifier ('hqe_queue', 'classifier_4'); CALL hg_set_classifier_rule_condition_value ('hqe_queue', 'classifier_4', 'engine_type', 'HQE');
Block all tasks (extreme scenario)
You can set the concurrency and queue size of the insert_queue to 0. The following is an example:
CALL hg_set_query_queue_property ('insert_queue', 'max_concurrency', '0');
CALL hg_set_query_queue_property ('insert_queue', 'max_queue_size', '0');