Hologres V4.0 and later supports multi-cluster and auto scaling for compute group instances. A compute group can be scaled out to multiple clusters, and the number of clusters automatically scales based on the load. This feature accommodates high-concurrency requests and provides resource isolation within the compute group.
Architecture
If the multi-cluster feature is disabled, all compute resources for a compute group are consolidated within a single cluster. All requests sent to this compute group share these compute resources. For more information about the architecture of a compute group instance when the multi-cluster feature is disabled, see Compute group instance architecture.
If the multi-cluster feature is enabled, a compute group can contain multiple clusters with physically isolated compute resources. A load-balancing frontend (FE) node automatically routes incoming requests to a specific cluster for execution.
If auto scaling is also enabled, the compute group automatically schedules elastic compute resources based on its load, such as resource usage and queue length. When the load is high, the feature launches a new cluster to handle higher concurrency. When the load is low, it automatically releases the elastic cluster to reduce costs.

Scenarios
Multi-cluster feature
This feature is ideal for scenarios with high-concurrency, small-to-medium queries. It uses cluster-level load isolation and FE load balancing to support higher concurrency and automatic request group isolation.
This feature is not suitable for scenarios with low-concurrency, large tasks. For example, Write compute group 2 in the Architecture section handles large-volume offline data writes and requires more compute resources in a single cluster. Therefore, the scaling capability of a compute group, such as manual scale-out or scheduled auto scaling, is a better fit for this scenario.
Auto scaling feature
The auto scaling feature is suitable for the following scenarios:
High-concurrency, small-to-medium queries: This is the same scenario as for the multi-cluster feature.
Unpredictable request peaks: If peaks are predictable, you can manually adjust the number of clusters or use scheduled auto scaling.
Definitions
For more information about the concepts of multi-cluster and the definitions of instance-level and compute group-level compute resources, see Overview of resource elasticity.
The following example shows the resource usage for an instance:
Instance
Instance reserved resources: 64 CU, which include the following:
Allocated resources: 32 CU. These are the reserved compute resources of the init_warehouse compute group.
Unallocated resources: 32 CU. These resources can be used to create new compute groups or increase the reserved compute resources of the init_warehouse compute group.
Instance elastic resources: 32 CU. These are the compute resources scaled out for the init_warehouse compute group by the auto scaling feature.
init_warehouse compute group:
Number of reserved clusters: 1.
Specifications of a single cluster: 32 CU.
Reserved resources: 32 CU (1 × 32).
Current number of clusters: 2, including 1 reserved cluster and 1 elastic cluster.
Elastic resources: 32 CU. These are the compute resources scaled out by the auto scaling feature.
Total compute resources: 64 CU, including 32 CU of reserved resources and 32 CU of elastic resources.
Billing
Instance reserved resources: These are the dedicated compute resources for a compute group instance. They are billed based on the instance's billing method (subscription or pay-as-you-go).
Auto scaling compute resources: These are the additional compute resources launched by the auto scaling feature for a compute group. The billing formula is as follows:
Cost = Actual elastic resources used by the instance (CU × hours) × Unit price. For more information about unit prices, see Billing overview.NoteThe system records the instance's current elastic resource usage every minute. Every hour, the system calculates the usage, converts the unit, generates the bill for that hour, and automatically deducts the fee from your account.
Instance elastic resources are independent of unallocated instance resources. The auto scaling feature launches additional elastic compute resources even if unallocated resources are available within the instance's reserved resources.
Limits
The multi-cluster and auto scaling features are supported only in Hologres V4.0 and later.
These features are supported only for compute group instances, not for serverless or general-purpose instances.
Supported regions
Multi-cluster feature: Supported in all regions.
Auto scaling feature:
Region
Auto scaling support
Description
China (Hangzhou), China (Shanghai), China (Beijing), China (Shenzhen)
Support
This feature is in public preview in these regions. To apply for a trial, use your Alibaba Cloud account to fill out this form.
China (Chengdu), China (Shanghai), China (Beijing), China (Shenzhen), China (Hong Kong), Singapore, Germany (Frankfurt), US (Silicon Valley), US (Virginia), UAE (Dubai), Japan (Tokyo), Malaysia (Kuala Lumpur), Indonesia (Jakarta), China (Shanghai) Finance Cloud, China (Beijing) Gov Cloud, China (Shenzhen) Finance Cloud
Not supported
You cannot apply for a trial.
Notes
Permissions required to use the multi-cluster and auto scaling features:
You must use an Alibaba Cloud account or a RAM user that has the AliyunHologresWarehouseFullAccess permission. This permission grants read-only access to the Hologres console and configuration permissions for the auto scaling feature. For more information about how to grant permissions, see Grant permissions to a RAM user.
The account must have Superuser permissions within the instance. For more information about how to grant permissions, see Grant development permissions on an instance to a RAM user.
Adding or removing clusters in a compute group may have an impact. For more information, see Manage compute groups.
Scheduled auto scaling and auto scaling cannot be used simultaneously for the same compute group.
For a compute group with auto scaling configured, you can still perform all compute group management operations in the console, such as scale-up, scale-in, start, stop, and delete.
Auto scaling resources are pay-as-you-go compute resources, and successful scale-out is not guaranteed. Configure CloudMonitor alerts for failed events as described in Monitoring and Alerts.
Guide to using Multi-cluster
You can use the multi-cluster feature by modifying the number of reserved clusters for a compute group. For more information, see Manage compute groups.
Guide to using auto scaling
You can enable the auto scaling feature for a compute group. This allows the system to automatically scale out elastic clusters in addition to the reserved clusters, based on the compute group's load, such as resource usage and queue length.
Entry point
Log on to the Hologres console. In the top menu bar, select the region where your instance is located.
In the navigation pane on the left, select Instances. Click the Instance ID/Name of the target instance to go to the Instance Details page.
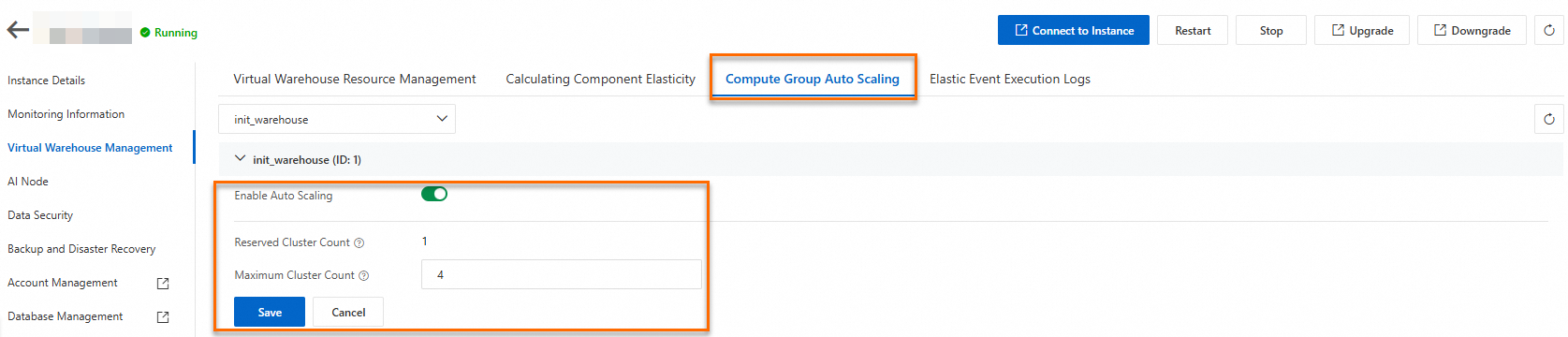
In the navigation pane on the left of the instance details page, click Virtual Warehouse Management. On the page that appears, click the Auto-scaling tab.
Click Enable Auto-scaling to turn on the switch. Configure Maximum Clusters and click Save.
Usage examples
After you enable auto scaling as described in the preceding section (with single cluster specifications of 32 CU, 1 reserved cluster, and a maximum of 4 clusters), you can follow these steps to verify the auto scaling capability. This example uses pgbench, a native performance stress testing tool for PostgreSQL.
Create test tables in Hologres and write data to them.
CREATE TABLE tbl_1 (col1 int, col2 int, col3 text); CREATE TABLE tbl_2 (col1 int, col2 int, col3 text); INSERT INTO tbl_1 SELECT i, i+1, md5(random()::text) FROM generate_series (0, 500000) AS i; INSERT INTO tbl_2 SELECT i, i+1, md5(random()::text) FROM generate_series (0, 500000) AS i;On the stress testing server, create a stress testing SQL file named
select.sqland add the following SQL statement:EXPLAIN ANALYZE SELECT * FROM tbl_1 LEFT JOIN tbl_2 ON tbl_1.col3 = tbl_2.col3 ORDER BY 1;On the stress testing server, set the password as an environment variable.
export PGPASSWORD='<AccessKey_Secret>'Run the following stress testing command. For more information about parameter settings, see Connect to and develop in Hologres.
pgbench -c 30 \ -j 30 \ -f select.sql \ -d <Database> \ -U <AccessKey_ID> \ -h <Endpoint> \ -p <Port> \ -T 1800During the stress test, the monitoring metrics for the compute group are shown in the following figures:
Cluster CPU usage:

The load on Cluster 1 remains high. This triggers auto scaling (Point 1) and adds a cluster.
After the stress test is complete, the load on both clusters is low. This triggers auto scaling (Point 2) and removes a cluster.
Compute group CPU usage:

Before auto scaling adds a cluster, the CPU usage of the compute group is continuously above 85%.
After the cluster is added, the overall CPU usage of the compute group drops to around 70%.
Monitoring and Alerts
Monitoring metrics
You can view the following metrics in the Hologres console. You can also configure alerting rules for these metrics if needed. For more information, see Monitoring metrics in the Hologres console.
Cluster CPU usage
Cluster memory usage
Number of cores scaled out by compute group auto scaling
Elastic event execution logs
Go to the Virtual Warehouse Management page and click the Elastic Event Execution Logs tab.
Select a time range to view the history of auto scaling events. The logs include the running time, compute group, execution status, event type, number of reserved clusters, and target number of clusters.
CloudMonitor events
Hologres auto scaling scale-out events are recorded in CloudMonitor.
Go to the CloudMonitor Event Center. On the System Events page, select Hologres in the Event Monitoring area to monitor auto scaling events. These include the following:
Instance:Warehouse:AutoElastic:Start: The start event of compute group auto scaling.Instance:Warehouse:AutoElastic:Finish: The completion event of compute group auto scaling.Instance:Warehouse:AutoElastic:Failed: The failure event of compute group auto scaling.
You can configure notifications, alerts, and other operations based on CloudMonitor events. For more information, see Use system events for alerting.
The following example shows the details of a CloudMonitor event for a failed auto scaling scale-out:
{
"status": "Failed",
"instanceName": "<instance_id>",
"resourceId": "<instance_resource_id>",
"content": {
"AutoElasticCPU": <cpu_num>,
"ScaleType": "ScaleOut",
"ScheduleId": "xxxxxx",
"WarehouseId": "<warehouse_id>",
"WarehouseName": "<warehouse_name>"
},
"product": "hologres",
"time": 1722852008000,
"level": "WARN",
"regionId": "<region>",
"id": "<event_id>",
"groupId": "0",
"name": "Instance:Warehouse:TimedElastic:Failed"
}ActionTrail
Operations performed in the Hologres console, such as editing auto scaling settings, and the actual cluster scale-out operations triggered by auto scaling are recorded in ActionTrail. For more information, see Event audit logs.