This topic describes the Paimon-based Hologres Serverless data lake solution, which enables flexible, on-demand acceleration of queries on Paimon data stored in Object Storage Service (OSS) without requiring reserved resources. You pay only for the data scanned by your SQL statements. The solution delivers a flexible and scalable data lake architecture to help you better manage and use your data, improve data-driven decision-making, and drive business innovation.
Background information
Apache Paimon is a unified lake storage format for streaming and batch processing that supports high-throughput writes and low-latency queries. Common compute engines on the Alibaba Cloud big data platform—such as Flink, Hologres, MaxCompute, and EMR Spark—are well integrated with Paimon. You can use Apache Paimon to quickly build your own data lake storage service on OSS and connect it to these compute engines for data analysis. For more information, see Apache Paimon.
Hologres shared clusters provide a serverless online query acceleration service designed for foreign tables in MaxCompute and OSS data lakes. Built on Hologres’ cloud-native architecture with separated storage and compute, shared clusters accelerate analysis of lake data in OSS. You can use them on demand and pay based on the amount of data scanned by your SQL statements. For more information, see Overview of shared clusters.
Architecture
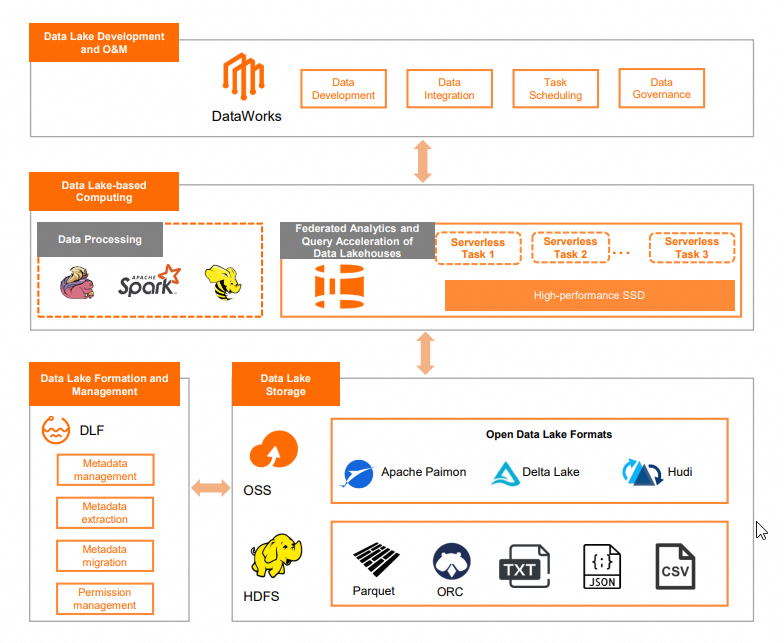
Prerequisites
-
You have purchased a Hologres shared cluster instance. For more information about how to purchase one, see Purchase a Hologres instance.
-
Activate the Data Lake Formation (DLF) metadata creation service. For more information, see DLF Quick Start.
-
(Optional) To use DLF’s custom data catalog feature, create a data catalog in DLF first. This catalog is used when you create a foreign server. For more information, see Create a data catalog.
-
You have activated OSS for data lake storage.
-
You have enabled the OSS-HDFS service. For more information, see Enable the OSS-HDFS service.
Hologres dedicated instances also support reading data from Paimon and other lake formats using the same procedures as shared cluster instances. This topic uses a shared cluster instance as an example.
Precautions
-
Only Hologres V2.1.6 and later support querying data from Paimon data lakes.
-
Hologres shared clusters support only reading data from OSS data lakes and do not support importing OSS data. To import OSS data into Hologres internal tables, use a dedicated instance.
Procedure
-
Purchase a new EMR data lake instance.
Log on to the EMR on ECS console and create an EMR cluster. For more information, see Create a cluster. The key parameter settings are as follows:
Configuration Item
Description
Business Scenario
Select Data Lake.
Optional Services
The required services are Spark, Hive, and Paimon. Select other services as needed.
Metadata
Select DLF Unified Metadata.
DLF Data Catalog
-
To use a custom DLF data catalog, select a created catalog, such as paimon_catalog. For more information, see Create a data catalog.
-
You can also select the default catalog. If you use the DLF default catalog, you do not need to specify the
dlf_catalogparameter when you create a foreign server in the Hologres shared cluster.
Cluster Storage Root Path
Select the path of a bucket for which the OSS-HDFS service is activated.
-
-
Build the data source.
This example uses 10 GB of TPC-H data. Use EMR Hive to build a data source in textfile format. For more information about building the data source, see Build data using EMR Spark.
ImportantWhen generating data, replace the
./dbgen -vf -s 100command with./dbgen -vf -s 10. -
Use Spark to create Paimon tables.
-
Log on to Spark SQL.
spark-sql --conf spark.sql.catalog.paimon=org.apache.paimon.spark.SparkCatalog --conf spark.sql.catalog.paimon.metastore=dlf -
Create a database.
-- Create a database. CREATE DATABASE paimon_db location 'oss://${oss-hdfs-bucket}/tpch_10G/paimon_tpch_10g/';${oss-hdfs-bucket}: The name of the bucket for which the OSS-HDFS service is activated. -
Create Paimon tables and import the textfile data prepared in the Build the data source step.
-- Switch to the database that you just created. use paimon_db; -- Create tables and import data. CREATE TABLE nation_paimon TBLPROPERTIES ( 'primary-key' = 'N_NATIONKEY' ) AS SELECT * from ${source}.nation_textfile; CREATE TABLE region_paimon TBLPROPERTIES ( 'primary-key' = 'R_REGIONKEY' ) AS SELECT * FROM ${source}.region_textfile; CREATE TABLE supplier_paimon TBLPROPERTIES ( 'primary-key' = 'S_SUPPKEY' ) AS SELECT * FROM ${source}.supplier_textfile; CREATE TABLE customer_paimon partitioned BY (c_mktsegment) TBLPROPERTIES ( 'primary-key' = 'C_CUSTKEY' ) AS SELECT * FROM ${source}.customer_textfile; CREATE TABLE part_paimon partitioned BY (p_brand) TBLPROPERTIES ( 'primary-key' = 'P_PARTKEY' ) AS SELECT * FROM ${source}.part_textfile; CREATE TABLE partsupp_paimon TBLPROPERTIES ( 'primary-key' = 'PS_PARTKEY,PS_SUPPKEY' ) AS SELECT * FROM ${source}.partsupp_textfile; CREATE TABLE orders_paimon partitioned BY (o_orderdate) TBLPROPERTIES ( 'primary-key' = 'O_ORDERKEY' ) AS SELECT * FROM ${source}.orders_textfile; CREATE TABLE lineitem_paimon partitioned BY (l_shipdate) TBLPROPERTIES ( 'primary-key' = 'L_ORDERKEY,L_LINENUMBER' ) AS SELECT * FROM ${source}.lineitem_textfile;${source}: The name of the database where the *_textfile tables are located in Hive.
-
-
Create a foreign server in the Hologres shared cluster.
NoteWhen creating the new EMR data lake instance:
-
If you set DLF Data Catalog to a custom data catalog, you must set the
dlf_catalogparameter to the custom catalog. -
If you set DLF Data Catalog to the default catalog, you do not need to configure the
dlf_catalogparameter. You can remove it before running the command.
-- Create a foreign server. CREATE SERVER IF NOT EXISTS dlf_server FOREIGN data wrapper dlf_fdw options ( dlf_catalog 'paimon_catalog', dlf_endpoint 'dlf-share.cn-shanghai.aliyuncs.com', oss_endpoint 'cn-shanghai.oss-dls.aliyuncs.com' ); -
-
Create foreign tables for the Paimon tables in the Hologres shared cluster.
IMPORT FOREIGN SCHEMA paimon_db LIMIT TO ( lineitem_paimon ) FROM SERVER dlf_server INTO public options (if_table_exist 'update'); -
Query data.
The following SQL statement is an example of Q1:
SELECT l_returnflag, l_linestatus, SUM(l_quantity) AS sum_qty, SUM(l_extendedprice) AS sum_base_price, SUM(l_extendedprice * (1 - l_discount)) AS sum_disc_price, SUM(l_extendedprice * (1 - l_discount) * (1 + l_tax)) AS sum_charge, AVG(l_quantity) AS avg_qty, AVG(l_extendedprice) AS avg_price, AVG(l_discount) AS avg_disc, COUNT(*) AS count_order FROM lineitem_paimon WHERE l_shipdate <= date '1998-12-01' - interval '120' DAY GROUP BY l_returnflag, l_linestatus ORDER BY l_returnflag, l_linestatus;NoteFor the other 21 SQL statements, see 22 TPC-H query statements.