Hologres V3.1 and later supports remote calls to user-defined functions (UDFs) in Function Compute (FC). You can use these functions to process complex business logic or perform advanced data operations. This topic describes how to use UDFs in Hologres.
Function overview
Remote functions allow you to extend data processing and analysis capabilities by integrating external functions into Hologres. In Hologres V3.1, remote functions support calls to the Alibaba Cloud Function Compute (FC) service. This feature lets you dynamically call FC to process complex business logic or perform advanced data operations while you query Hologres data.
Remote functions support the following three scenarios:
-
Real-time data processing: Call external functions in real time during data queries to perform data cleaning, format conversion, or complex calculations.
-
Third-party service integration: Use Function Compute to interact with other Alibaba Cloud services or third-party APIs using Hologres data.
-
Advanced analytics: Use Function Compute to implement advanced analytics algorithms, such as model inference or machine learning, and write the results directly to Hologres.
Prerequisites
-
You have a Hologres instance that is V3.1 or later. For more information, see Purchase a Hologres instance.
-
You have activated Function Compute, and your FC instance is V3.0. To do this, log on to the Function Compute console.
-
You have granted the
AliyunServiceRoleForHologresRemoteUDFservice-linked role.-
Log on to the Hologres console. In the navigation pane on the left, click Create a Service-linked Role.
-
Select
AliyunServiceRoleForHologresRemoteUDFand click Authorize Now. The following figure shows an example.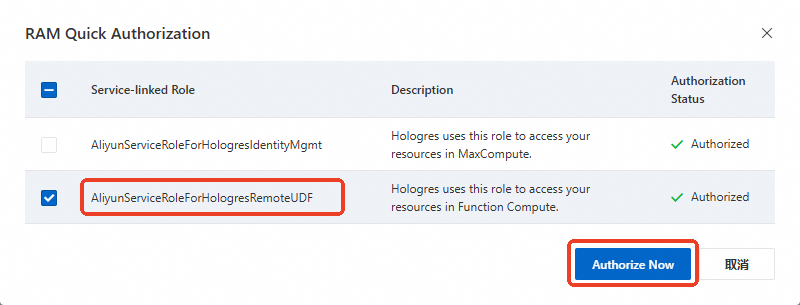
-
-
The Hologres instance and the Function Compute service must be in the same region.
-
You must activate the Alibaba Cloud Function Compute service, and then develop and deploy the function that Hologres calls. For more information, see Code development.
Precautions
-
Only scalar user-defined functions (UDFs) and user-defined table-valued functions (UDTFs) are supported. User-defined aggregate functions (UDAFs) are not supported.
-
Only the following data types and their corresponding array types are supported:
BOOLEAN,INTEGER,BIGINT,REAL,DOUBLE PRECISION, andTEXT. -
Remote functions do not support constants as input parameters.
-
This feature incurs fees in Function Compute (FC). For more information, see Billing.
-
This feature does not incur extra fees in Hologres.
Manage user-defined functions
Create an extension
Before you can use this feature for the first time, you must create an extension. The command is as follows:
CREATE EXTENSION [ IF NOT EXISTS ] function_compute;Create a function
Syntax
CREATE [ OR REPLACE ] FUNCTION <function_name>
( [ [ argmode ] [ argname ] <argtype> [ { DEFAULT | = } default_expr ] [, ...] ] )
[ RETURNS [SETOF] rettype | RETURNS TABLE ( column_name column_type) ]
LANGUAGE function_compute
AS '<fc_endpoint>/<func_name>'
{
{ CALLED ON NULL INPUT | RETURNS NULL ON NULL INPUT | STRICT }
| SET function_compute.qualifier TO <qualifier>
| SET function_compute.compression TO <compression>
| SET function_compute.max_batch_size TO <max_batch_size>
} ...Parameters
|
Parameter category |
Parameter |
Required |
Description |
|
Function name |
function_name |
Yes |
The name of the function.
|
|
Function parameters |
argtype |
Yes |
The data type of the parameter. |
|
argmode |
No |
The mode can be IN, OUT, or INOUT. The default is IN. To avoid ambiguity, do not use INOUT. A function can have only one OUT or INOUT parameter. |
|
|
argname |
No |
The name of the parameter.
|
|
|
default_expr |
No |
The default value. This applies only to input parameters. If a parameter has a default value, all subsequent parameters must also have default values. |
|
|
FC Endpoint |
LANGUAGE function_compute |
Yes |
A fixed value that declares the use of the Function Compute service. |
|
fc_endpoint |
Yes |
The internal network endpoint of FC. For more information, see Service endpoints. |
|
|
func_name |
Yes |
The name of the target function. You must create this function in the FC console beforehand. |
|
|
Return type |
rettype |
No |
The return value type. If the function has an OUT or INOUT parameter, you can omit the RETURNS clause. If the clause is present, it must match the result type implied by the output parameters. |
|
column_name |
No |
The name of an output column in the RETURNS TABLE syntax. This is another way to declare a named OUT parameter. The difference is that RETURNS TABLE also implies RETURNS SETOF, which means the function returns a set. |
|
|
column_type |
No |
The data type of an output column in the RETURNS TABLE syntax. |
|
|
Null-handling policy |
CALLED ON NULL INPUT |
No |
The default behavior. The function is called even if some of its arguments are null. The function must handle null values. |
|
RETURNS NULL ON NULL INPUT |
No |
The function automatically returns null if any of its arguments are null. |
|
|
STRICT |
No |
An alias for RETURNS NULL ON NULL INPUT. |
|
|
Function versioning |
qualifier |
No |
Specifies the function version or alias to call. The default value is |
|
Request compression algorithm |
compression |
No |
Specifies the compression algorithm for the request and response when calling the function. Valid values:
|
|
Maximum batch size per request |
max_batch_size |
No |
Specifies the maximum number of rows to send to FC in each batch. The main purpose is to set an upper limit on the number of rows for batch processing for FC functions that have memory limits or other constraints. If you do not specify this parameter, Hologres automatically calculates and uses the optimal batch size. Manual intervention is usually not required. |
Examples
-
Create a scalar UDF.
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION rf_add ( a INTEGER, b INTEGER DEFAULT 1 ) RETURNS BIGINT LANGUAGE function_compute AS 'xxxxxxxxxxxxx.cn-shanghai-internal.fc.aliyuncs.com/add' ; -
Create a UDTF.
-- Form 1 CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION rf_unnest(TEXT []) RETURNS TABLE (item TEXT ) LANGUAGE function_compute AS 'xxxxxxxxxxxxxx.cn-hangzhou-internal.fc.aliyuncs.com/unnest' STRICT SET function_compute.max_batch_size TO 1024; -- Form 2 CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION rf_unnest(TEXT []) RETURNS SETOF TEXT LANGUAGE function_compute AS 'xxxxxxxxxxxxxx.cn-hangzhou-internal.fc.aliyuncs.com/unnest' STRICT SET function_compute.max_batch_size TO 1024;
View a function
You can view the remote functions that you created.
SELECT
CASE
WHEN p.proretset = 'f' THEN 'scalar UDF'
WHEN p.proretset = 't' THEN 'UDTF'
END AS function_type,
n.nspname AS schema_name,
p.proname AS function_name,
pg_get_function_arguments(p.oid) AS arguments,
pg_get_function_result(p.oid) AS return_type,
p.proisstrict AS is_strict,
p.proconfig AS config,
pg_get_functiondef(p.oid) AS definition
FROM
pg_proc p
JOIN pg_language l ON p.prolang = l.oid
JOIN pg_namespace n ON p.pronamespace = n.oid
WHERE
l.lanname = 'function_compute'
AND p.prokind != 'p'
ORDER BY
function_type,
schema_name,
function_name;Delete a function
Syntax
DROP FUNCTION [ IF EXISTS ] <function_name> [ ( [ [ argmode ] [ argname ] <argtype> [, ...] ] ) ] [, ...]Parameters
|
Parameter |
Required |
Description |
|
function_name |
Yes |
The name of the function to delete. |
|
argtype |
Yes |
The data type of the parameter. |
|
argmode |
No |
The mode can be IN, OUT, or INOUT. The default is IN. To avoid ambiguity, do not use INOUT. A function can have only one OUT or INOUT parameter. |
|
argname |
No |
The name of the parameter. For input parameters, the name is for documentation purposes only. For output parameters, the name determines the column name in the result set. If omitted, the system generates a default name. |
Example
DROP FUNCTION rf_add(INTEGER, INTEGER);Data interaction format
Request format from Hologres to FC
Hologres calls the FC InvokeFunction API with a POST request. The request body is a JSON object containing a data key, which holds a two-dimensional array. Each element in the array represents a row of data from the batch and contains the parameters for the function call.
Data serialization rules
-
BOOLEANis serialized to the JSON boolean type. -
INTEGERandBIGINTare serialized to the JSON number type. -
REALandDOUBLE PRECISIONare serialized to the JSON number type. -
TEXTis serialized to the JSON string type. -
NULLis serialized to JSONnull.
Example
The following code provides an example of a serialized request for a remote function with the signature rf_demo(TEXT, INTEGER, BOOLEAN).
{
"data": [
["foo", 100, true],
[null, null, false],
["bar", 200, false]
]
} Response format from FC to Hologres
After FC finishes processing a batch of data, it must return the results to Hologres in a JSON format that adheres to the following specifications:
-
Scalar UDFs
-
The top-level object must contain a
resultsfield. The value of this field is an array, and each element corresponds to the result for one row of input data. -
Each result must be an array. The results must be in the same order as the input data. The Nth element in the results array corresponds to the Nth row of the input data.
The following code provides an example of the return value for a batch of four rows:
{ "results": [ ["Beijing"], ["Shanghai"], ["Shenzhen"], ["Guangzhou"] ] } -
-
UDTFs: A UDTF can generate multiple output rows from a single input row. The row number (row_num) is used to associate the output with the original input row.
-
The top-level object must contain a
resultsfield. The value of this field is an array, and each element corresponds to one row of output data. -
Each element in the results array must be an array that contains two elements:
-
row_num (first element): The 0-based index of the original input row. This number is used to associate the output with the input. The row_num values must be returned in ascending order.
-
result (second element): A row of the processed return value.
-
Here is an example:
{ "results": [ [0, "Beijing"], [1, "Shanghai"], [3, "Shenzhen"], [3, "Guangzhou"], ] } -
Example of a user-defined function
This example uses the unnest function.
-
Activate Function Compute.
Log on to the Function Compute console. You can also claim a free resource plan with a specific quota based on the on-screen instructions. For more information, see Trial quotas.
-
Create an FC event-triggered function.
-
In the navigation pane on the left, click Functions. Switch to the region where your Hologres instance resides.
-
On the Functions page, click Create Function. You are then redirected to the Create Function page.
-
Select Event Function and configure the following parameters. You can keep the default values for the other parameters. For more information, see Create an event-triggered function.
Parameter
Description
Function Name
Enter a custom name. For example,
unnest.Runtime
Select Built-in Runtimes / Python / Python 3.10.
Code Upload Method
Select Upload Code via ZIP Package.
Code Package
Upload the code package that you have written and packaged.
Save the following code to a file named unnest.py and compress it into unnest.zip.
import json def unnest(event, context): evt = json.loads(event) data = evt.get('data', None) if data is None: raise ValueError('no "data" key in event.') if not isinstance(data, list): raise ValueError('data is not a list.') res = list() for i in range(len(data)): if len(data[i]) != 1 or not isinstance(data[i], list): raise ValueError('the item in data is not a list.') for item in data[i][0]: res.append([i, item]) return json.dumps({'results': res})Handler
Enter
unnest.unnest.
-
-
Create a Hologres remote function.
NoteYou can complete the following steps on the HoloWeb platform. For more information, see Connect to HoloWeb.
CREATE EXTENSION IF NOT EXISTS function_compute; CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION rf_unnest(INTEGER []) RETURNS SETOF INTEGER STRICT LANGUAGE function_compute AS 'xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx.cn-shanghai-internal.fc.aliyuncs.com/unnest'; -
Prepare test data.
CREATE TABLE test_array ( numbers INTEGER[] ); INSERT INTO test_array (numbers) VALUES (ARRAY[1, 3]), (ARRAY[2, 4]), ('{}'), (ARRAY[]::INTEGER[]), (NULL); -
Call the remote function.
SELECT numbers, rf_unnest(numbers) FROM test_array; numbers | rf_unnest ---------+----------- {2,4} | 2 {2,4} | 4 {1,3} | 1 {1,3} | 3 (4 rows)