Global Accelerator (GA) accelerates access to the backend services of a specific domain name, reducing latency and improving user experience.
Scenario
A company headquartered in the US (Silicon Valley) deploys a web service on a self-managed server. The web service is accessible through the domain name www.example.com on port 80. Employees in the China (Shenzhen) office experience latency, jitter, and packet loss due to unstable cross-border networks.

GA directs traffic from the China (Shenzhen) office to the server in the US (Silicon Valley). Traffic enters the Alibaba Cloud acceleration network from an access point in China (Shenzhen) through an accelerated IP address. Intelligent routing then forwards client requests to the endpoint, reducing latency for the China (Shenzhen) office.
Prerequisites
An A record has been added to map the domain name www.example.com to the public IP address of the backend server.
This tutorial uses a pay-as-you-go standard GA instance as an example. Before creating a pay-as-you-go standard GA instance, note the following:
Pay-as-you-go GA instances use the Pay-by-data-transfer bandwidth billing method and do not need to be associated with a bandwidth plan. Data transfer fees over the GA network are settled and billed by Cloud Data Transfer (CDT). For more information, see Data transfer fee.
The first time you use a pay-as-you-go GA instance, go to the Activate Service page to activate the pay-as-you-go Global Accelerator service.
Step 1: Configure basic information about an instance
Log on to the GA console.
On the Instances page, click Create Standard Pay-as-you-go Instance.
In the Basic Instance Configuration step, configure the parameters based on the following table and click Next.
Parameter
Description
GA Instance Name
Enter a name for the GA instance.
Instance Billing Method
Pay-As-You-Go is selected by default.
You are charged instance fees, Capacity Unit (CU) fees, and data transfer fees for pay-as-you-go standard Global Accelerator instances.
For more information about instance fees and CU fees, see Billing of pay-as-you-go GA instances.
For more information about data transfer fees, see Traffic billing.
Resource Group
Select the resource group to which the standard Global Accelerator instance belongs.
The resource group must be created by the current Alibaba Cloud account in Resource Management. For more information, see Create a resource group.
Step 2: Configure an acceleration area
Specify the regions where users are located and allocate bandwidth for acceleration.
On the Configure Acceleration Areas page, specify an acceleration area and click Next.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Acceleration Area | From the drop-down list, select one or more regions to accelerate and click Add. In this example, China (Shenzhen) is selected. |
Note If the acceleration area is in the Chinese mainland and you use HTTP or HTTPS, apply for an ICP filing for the domain name. For more information, see Domain name management. | |
| Assign Bandwidth | |
| Maximum Bandwidth | Specify the maximum bandwidth for the acceleration area. Each acceleration area supports a bandwidth range of 2 to 10,000 Mbit/s. The maximum bandwidth is used for bandwidth throttling. Data transfer fees are managed by CDT. In this example, the default value 200 Mbit/s is used. |
Important A small maximum bandwidth value may cause throttling and packet drops. Specify a maximum bandwidth based on your business requirements. | |
| IP Protocol | Select the IP version used to access the GA service. In this example, IPv4 is selected. |
| ISP Line Type | Select the network type for accessing the GA service. In this example, BGP (Multi-ISP) is selected. |
Step 3: Configure a listener
A listener monitors connection requests and distributes them to endpoints based on the specified port and protocol. Each listener is associated with an endpoint group. Associate an endpoint group with a listener by specifying the region to which network traffic is distributed. Traffic is then distributed to the optimal endpoint in the endpoint group.
On the Configure listeners page, configure the listener and click Next.
The following table describes only the parameters relevant to this example. For other parameters, use the default values or adjust as needed. For more information, see other listener parameters.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Listener Name | Enter a name for the listener. |
| Routing Type | Select a routing type. In this example, Intelligent Routing is selected. |
| Protocol | Select a protocol for the listener. In this example, HTTP is selected. |
| Port | Specify the listener port for receiving and forwarding requests. Valid values: 1 to 65499. In this example, enter 80. |
Step 4: Configure an endpoint group and endpoints
On the Configure an endpoint group page, configure the endpoint group and its endpoints. The following table describes only the parameters relevant to this example. For other parameters, use the default values or adjust as needed. For more information, see other endpoint group parameters.
Parameter Description Region Select the region where the endpoint group is deployed. In this example, US (Silicon Valley) is selected. Endpoint Configuration Configure the endpoints: - Backend Service Type: Select Custom Domain Name. - Backend Service: Enter the domain name of the backend service. In this example, enter www.example.com.- Weight: Enter a weight for the endpoint. Valid values: 0 to 255. GA routes traffic to endpoints based on weights. In this example, the default value 255 is used. WarningSetting the weight of an endpoint to 0 stops traffic distribution to that endpoint. Proceed with caution.
Read the Compliance Commitments Regarding Cross-border Data Transfers, select Agree to the Preceding Compliance Agreement, and click Next. This scenario involves acceleration from China (Shenzhen) to the US (Silicon Valley). Agree to the Compliance Commitments Regarding Cross-border Data Transfers to enable this feature. After an instance is created, the Transmission Network Type is set to or Premium Bandwidth for Cross-domain Acceleration by default. This enables network acceleration between the Chinese mainland and other regions, such as Hong Kong (China), Macao (China), and Taiwan (China), without additional configuration. For more information, see Data transfer billing.
On the Configuration Review wizard page, confirm the information and click Submit.
NoteCreating a GA instance takes 3 to 5 minutes.
(Optional) After the instance is created, click Go to Instance Details below the task list. On the instance details page, click the Instance Information, Listeners, or Acceleration Areas tabs to view the instance configuration.
Step 5: Configure a CNAME record
To enable the acceleration service, map the accelerated domain name to the canonical name (CNAME) assigned to the GA instance:
Change the default DNS record of the existing A record to a region-specific DNS record. In this example, the DNS record is changed to North America_United States to handle requests from outside the Chinese mainland.
Add a CNAME record. In this example, a CNAME record maps the domain name
www.example.comto the CNAME assigned to the GA instance.

By default, the Free Edition of Alibaba Cloud DNS is used. Upgrade Alibaba Cloud DNS to the Standard or Ultimate Edition to return intelligent DNS query results to end users in different regions. For more information about how to upgrade, see Renewal.
On the Authoritative DNS Resolution page, find the domain name and click DNS Settings in the Actions column.
NoteFor a domain name not registered with Alibaba Cloud, add the domain name to the Alibaba Cloud DNS console before configuring DNS records.
On the DNS Settings page, modify the existing A record and click OK.
Find the A record and click Modify.
In the Modify DNS Record panel, select Outside Chinese Mainland, North America, and United States from the DNS Request Source drop-down list.
On the DNS Settings page, click Add DNS Record, configure the CNAME record parameters, and click OK.
Parameter Description Record Type Select CNAME. Hostname Enter the prefix of the accelerated domain name. In this example, enter www.DNS Request Source Use the default value. TTL The duration that a DNS record is cached on a DNS server. A smaller value means record modifications take effect faster. In this example, the default value of 10 minutes is used. Record Value Enter the CNAME assigned to the GA instance. View the CNAME on the Instances page.
Step 6: Test the acceleration performance
This example uses Alibaba Cloud Linux 3. Test commands vary by operating system. Refer to the user guide for your operating system.
For UDP listeners, verify acceleration performance using UDPing. For more information, see Verify the acceleration performance of a UDP listener.
Open the command-line interface (CLI) on a computer in the acceleration area. In this example, the acceleration area is China (Shenzhen).
Run the following command to verify that the CNAME record has taken effect: If the resolved CNAME matches the CNAME of the GA instance, the CNAME record has taken effect.
ping <Accelerated domain name>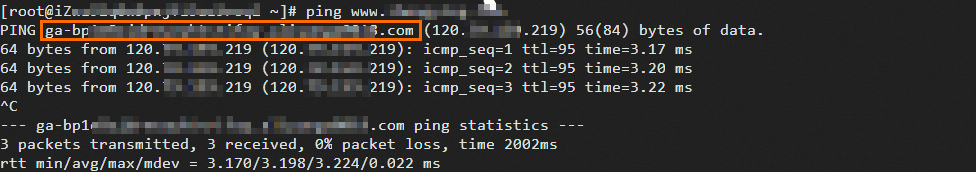
Run the following command to measure packet latency: The command output includes the following metrics: After GA is enabled, the total connection time from the client in China (Shenzhen) to the web service in the US (Silicon Valley) is reduced, indicating lower latency for the China (Shenzhen) office. Figure 1. Access latency before acceleration Figure 2. Access latency after acceleration
time_connect: Time to establish a TCP connection. Unit: seconds.
time_starttransfer: Time from when the client sends a request to when the first byte is received. Unit: seconds.
time_total: Total time from when the client sends a request to when the last byte is received. Unit: seconds.
NoteActual acceleration performance depends on your specific business environment and test results.
curl -o /dev/null -s -w "time_connect: %{time_connect}\ntime_starttransfer: %{time_starttransfer}\ntime_total: %{time_total}\n" "http[s]://<Accelerated domain name>"
