This document lists key alert metrics, recommended configurations, and best practices to help you effectively monitor job performance and diagnose issues.
Prerequisites
See Configure alert rules and choose the appropriate configuration method based on your workspace's monitoring service.
Unless explicitly specified, configure alert rules in the Cloud Monitor console.
To monitor multiple metrics using Prometheus, you must use a custom PromQL statement to create an alert rule. For a simpler setup, configure alert rules with Cloud Monitor.
Recommended alert rules
Use case | Metric(s)/event(s) | Rule configuration | Severity level | Recommended actions |
System event: | Upon event occurrence | P0 | 1. Check the configured restart policy. | |
Overview > |
| P0 | 1. Identify the cause.
2. Recover the job from the latest savepoint or checkpoint. | |
Checkpoint > |
| P0 | 1. See System checkpoints to troubleshoot the cause of checkpoint failures. 2. Identify the issue.
3. Dynamically update the configuration or restore the job from the latest checkpoint. | |
Overview > |
| P1 | 1. See Metric description to investigate the cause of the latency.
2. Take action based on the cause.
| |
Overview > |
| P1 | 1. Check 2. Take action based on the cause.
| |
Overview > |
| P1 | 1. Verify if data is reaching the sink operator.
2. Verify the sink operator sends data to the destination.
3. Temporarily enable dual-write to a backup system. | |
CPU > |
| P2 | 1. Use the flame graph or Flink UI to identify the hotspot operator.
2. Increase the parallelism for the bottleneck operator or allocate more vCPUs to TaskManagers. | |
Memory > |
| P2 | 1. Analyze GC logs to identify the problem.
2. Take action based on the cause: increase the heap size or increase the parallelism. |
Job availability
Create alert rules for job failures
Prometheus
Log on to Realtime Compute for Apache Flink's Management Console. Click Console in the Actions column of your workspace.
In the Development Console, navigate to , and click the name of your job deployment.
Click the Alarm tab. Switch to the Alarm Rules subtab, and click . In the Create Rule panel, for Content, select Job Failed from the Metric dropdown list.

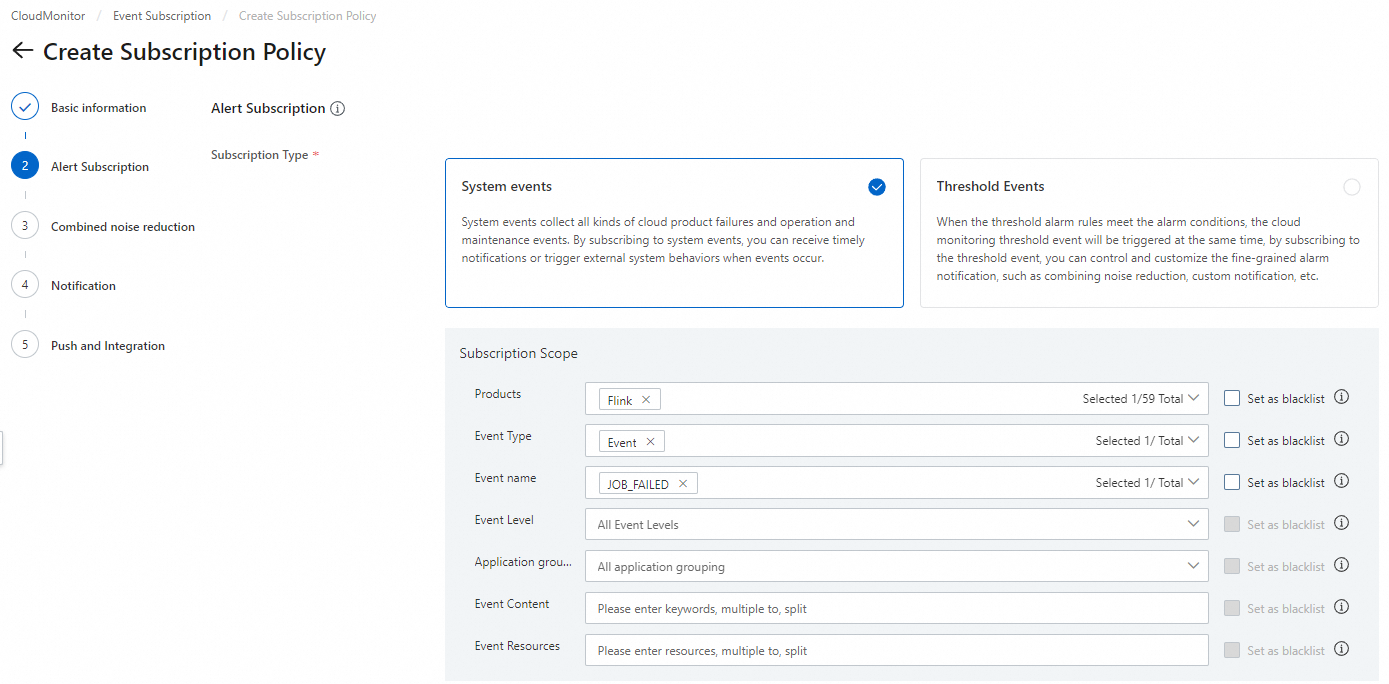
Cloud Monitor
Log on to the Cloud Monitor console.
In the left navigation pane, choose .
On the Subscription Policy tab, click Create Subscription Policy.
On the Create Subscription Policy page, configure the policy. For more information, see Manage event subscription policies (recommended).
Job stability
Frequent restarts
Metric:
NumOfRestartRule description: Alert if the job restarts one or more times within a minute.
Recommended configuration:
NumOfRestartMetric Value >= 1
Period: 1 Consecutive Cycle (1 Cycle = 1 Minute)
Notification: Phone Call + SMS Message + Email + Webhook (Critical)
Consecutive checkpoint failures
Metric:
NumOfCheckpointsRule description: Alert if no checkpoint succeeds for 5 minutes.
Recommended configuration:
NumOfCheckpointsMetric Value < 0
Period: 5 Consecutive Cycles (1 Cycle = 1 Minute)
Notification: Email + SMS + Phone + Webhook (Critical)
Data timeliness
Latency
Metrics:
CurrentEmitEventTimeLagNumOfRecordsInFromSourcePerSecond
Rule description: Alert if data is coming in and business latency exceeds 5 minutes. Choose a threshold and alert level as needed.
Recommended configuration:
CurrentEmitEventTimeLagMaximum Value >= 300000
NumOfRecordsInFromSourcePerSecondMetric Value > 0
Period: 5 Consecutive Cycles (1 Cycle = 1 Minute)
Upstream data flow interruptions
Metrics:
NumOfRecordsInFromSourcePerSecondSourceIdleTime
Rule description: Alert if data is coming in but not handled by the source for over 5 minutes. Choose a threshold and alert level as needed.
Recommended configuration:
NumOfRecordsInFromSourcePerSecondMetric Value <= 0
SourceIdleTimeMaximum Value > 60000
Period: 5 Consecutive Cycles (1 Cycle = 1 Minute)
Output issues
Metric:
NumOfRecordsOutToSinkPerSecondRule: Alert if there is no data output for more than 5 minutes. Choose a threshold and alert level as needed.
Recommended configuration:
NumOfRecordsOutToSinkPerSecondMetric Value <= 0
Period: 5 Consecutive Cycles (1 Cycle = 1 Minute)
Resource performance bottlenecks
CPU performance bottlenecks
Metric:
TMCPUUsageRule: Alert if CPU utilization exceeds 85% for more than 10 minutes.
Recommended configuration:
TMCPUUsageMaximum Value >= 85
Period: 10 Consecutive Cycles (1 Cycle = 1 Minute)
Memory performance bottlenecks
Metric:
TMHeapMemoryUsedRule: Alert if heap memory usage exceeds 90% for more than 10 minutes.
Recommended configuration:
TMHeapMemoryUsedMaximum Value >= Threshold (90%)
Determine this threshold based on JVM Heap on the page. For example, if usage is 194 MB / 413 MB, set the threshold to 372 MB (90% of 413 MB).

Period: 10 Consecutive Cycles (1 Cycle = 1 Minute)