When your Elasticsearch cluster experiences high CPU, memory, or disk utilization, or when query and write performance can't meet business needs, you can upgrade the cluster configuration to restore service stability.
When to upgrade
Consider upgrading your cluster if you experience any of these issues:
CPU utilization consistently above 70%
Memory pressure warnings or high heap usage
Disk usage above 80%
Slow query or write performance affecting business operations
If you meet these conditions, review the Before you start section to ensure your cluster is ready for upgrade.
Before you start
Cluster upgrades can cause temporary service latency, configuration conflicts, and billing changes. Review these prerequisites carefully before proceeding.
Prepare your environment
Complete these preparation steps before upgrading:
Create a snapshot: Back up your cluster to enable recovery if needed. Mandatory for production clusters. See Back up data.
Test in non-production: If possible, test the upgrade on a staging cluster that mirrors your production environment.
Schedule maintenance window: Plan upgrade during off-peak hours and notify your team.
Prepare client applications: Configure retry logic and error handling to manage transient connection failures during upgrade.
Service stability requirements
Cluster condition | Service impact | Recommended action |
Normal load + Replicas exist Normal load: CPU ≤ 60%, heap memory ≤ 50%, load < number of cores | Service continues with slight performance decrease | No extra action required |
High load + No replicas High load: CPU > 60%, heap memory > 50%, high concurrency | Occasional access timeouts |
|
High load + Abnormal status | Access timeouts or jitter | Fix cluster status before upgrading |
Pre-upgrade checks
Complete these checks to avoid cluster crashes, data loss, or service unavailability:
Cluster health: Run
GET _cluster/healthto ensure status is GREEN.Load safety: Run
GET _cat/nodes?vto verify CPU utilization ≤ 60%.Index readiness:
Check for closed indices:
GET /_cat/indices?v.If found, open them temporarily:
POST /<index_name>/_open.Ensure each index has at least 1 replica.
Shard balance: Run
GET _cat/shards?vto check for unbalanced shards.
Additional considerations
Capacity planning: Evaluate required cluster capacity.
Configuration constraints:
Upgrades don't support engine version changes.
Only one node type can be changed at a time.
Cost impact: Billing changes based on new configuration. See Pay-as-you-go and Subscription billing documentation.
Upgrade cluster configuration
Console
Go to the Instances page and click Upgrade Configuration.
Alternatively, go to your instance's Basic Information page and choose Configuration Change > Cluster Upgrade.
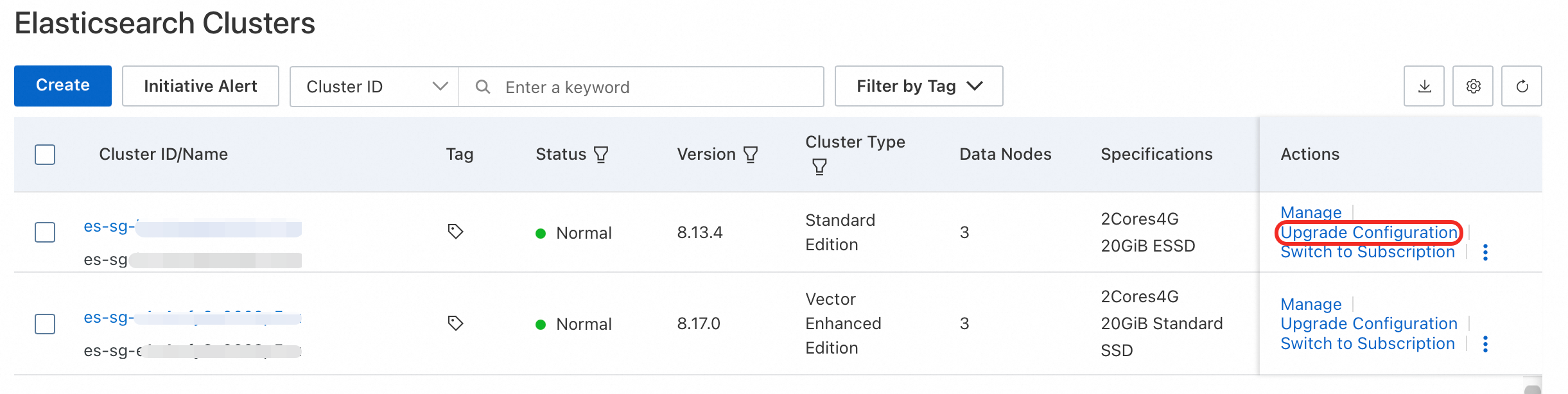
On the Upgrade/Downgrade page, adjust cluster node settings.
See Configure nodes for an Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch cluster for details.
NoteAvailable settings may vary based on your cluster type and engine version. The console takes precedence.
Choose an upgrade method.
Forced Update: Suits emergent upgrade needs, such as restoration from unavailability.
Intelligent Update (Defaults to Enable): Automatically chooses the optimal upgrade mechanism, or manually specify Blue-green Update or In-place Update after disabling this option.
For details, see Cluster update methods.
Review and agree to Terms of Service and click Buy Now.
When cluster status updates from Initializing to to Normal, the upgrade is complete.
API
Use the UpdateInstance API.
Verify the upgrade
After initiating the upgrade, your cluster status will change to Ini. Depending on the upgrade method selected, the process typically completes within 15-60 minutes. Do not make additional configuration changes during this time.
Monitor progress
Track upgrade progress in the console:
Go to your cluster's Basic Information page.
View the progress.
Next steps
After a successful upgrade, complete these post-upgrade tasks:
Adjust shard allocation (if you scaled out): Consider rebalancing shards across new nodes to optimize performance. Run
GET _cat/allocation?vto check current distribution. For details, see Unbalanced loads on a cluster.Monitor cluster performance: Track key metrics for 24-48 hours to ensure stability. Focus on:
CPU utilization
Heap memory usage
Query and write response times
Plan for future capacity: Review instance type and capacity assessment to anticipate future scaling needs.
Clean up old snapshots (optional): If the upgrade was successful and cluster is stable, you can remove the pre-upgrade snapshot to save storage costs.
Troubleshooting
Upgrade failure
If your upgrade does not complete successfully:
Cluster state is preserved (no data loss if replicas are configured).
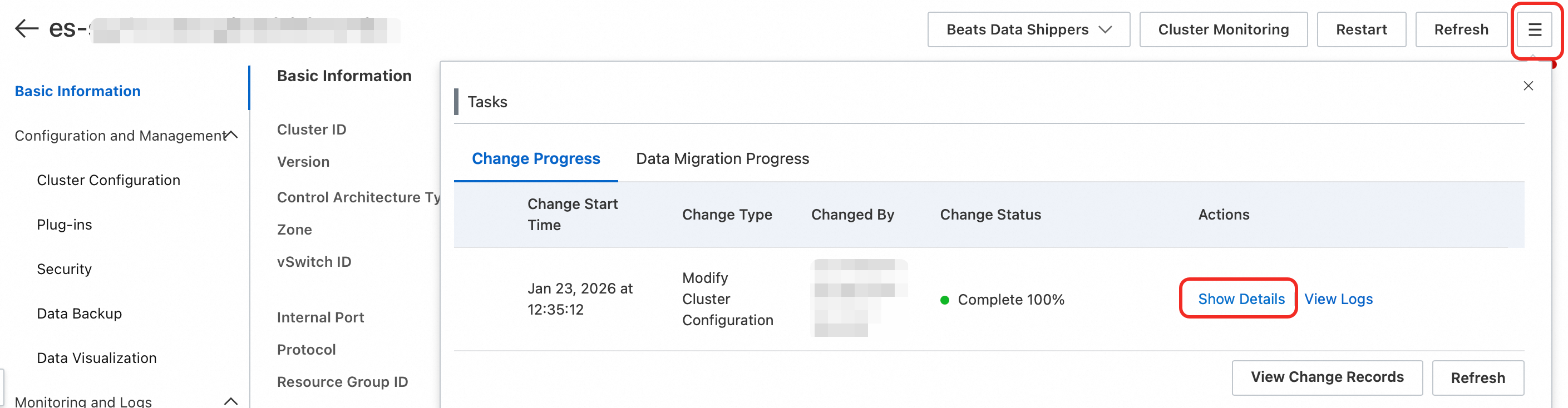
Check error logs in the console: Go to your instance's Basic Information page >
 > Show Details > Review error messages.
> Show Details > Review error messages.Contact support with error details and cluster information.
If necessary, restore from the snapshot you created before upgrade.
FAQ
Does changing the cluster configuration affect the ES service?
When upgrading a cluster, a "UpgradeVersionMustFromConsole" prompt appears. What should I do?
An error or timeout occurs when upgrading a cluster. What should I do?
Will changing the disk type of an ES instance cause existing data to be lost?