This guide walks you through the essential steps to create, configure, and connect to a PolarDB for MySQL on ENS cluster.
Supported regions
Currently, PolarDB for MySQL on ENS is supported only in Haikou Telecom, Türkiye (Istanbul)-1, Macao (China)-2, and Vietnam (Hanoi)-3.
1. Create an ENS network
Your PolarDB cluster must reside within an Edge Node Service (ENS) network.
If you have not used ENS before, you will need to complete the activation process first.
Go to the ENS console.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose .
Click Create Network.
On the Create Network page, configure the VPCs and vSwitches for the edge region where you plan to deploy your cluster.
2. Create a PolarDB on ENS cluster
Go to the PolarDB edge cluster purchase page.
Configure the following key parameters. You can leave other settings at their default values for this quick start.
Parameter | Description |
Billing Method | Edge clusters support only the subscription (Pre-paid) billing method. Note This is ideal for stable, long-term workloads. |
Edge Data Center | Select the edge region where the cluster resides. Note This must be the same region as the ENS network you created in Step 1 to ensure private network connectivity. |
Compatibility | Choose the MySQL-compatible version for the cluster.
|
Edition | Choose between Dedicated and General-purpose:
For a detailed comparison of the two editions, see How to choose between General-purpose and Dedicated specifications. |
Network | Select the VPC and vSwitch you created in Step 1. |
Specifications | Select the node specifications (CPU and memory) that meets your performance needs. |
Number Of Nodes | The default is two nodes (one read/write node and one read-only node). You can configure the number of nodes as needed. Note
|
Storage Type | Select the performance level for your underlying storage.
|
Storage Space | Configure the amount of storage space to purchase. The default is 100 GB. |
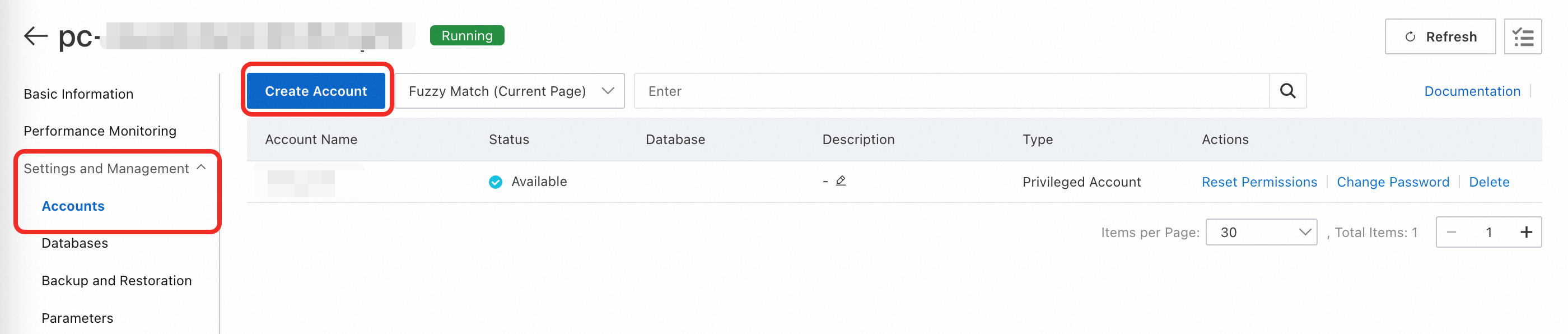
3. Create a database account
Go to the PolarDB console for edge clusters and select your newly created edge cluster.
From the left-side menu, click .
Click Create Account. You can create a Privileged Account or Standard Account based on your security needs. For more details, see Account permissions.
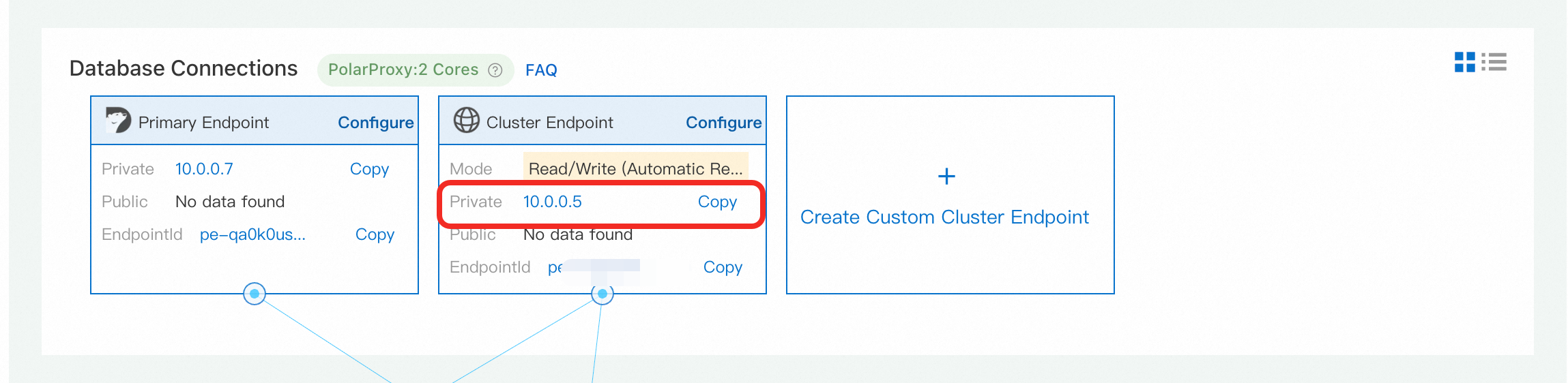
4. Get the cluster endpoint address
You will need the cluster's endpoint address to connect to it.
In the PolarDB console for edge clusters, navigate to your cluster's details page.
From the left-side menu, click Database Connection.
Copy the Cluster Endpoint address. This address load-balances connections across all nodes in your cluster. The default port is
3306.
5. Connect to your database
You can select a connection method based on your business requirements. See the following examples of connecting to a cluster:
Use a client to connect to a cluster
You can use a MySQL client to connect to a PolarDB cluster. MySQL Workbench 8.0.29 is used in this example. The operations by using other types of clients are similar.
Install MySQL Workbench. For more information, visit the MySQL Workbench download page.
Start MySQL Workbench and choose .
Enter the connection information and click OK.
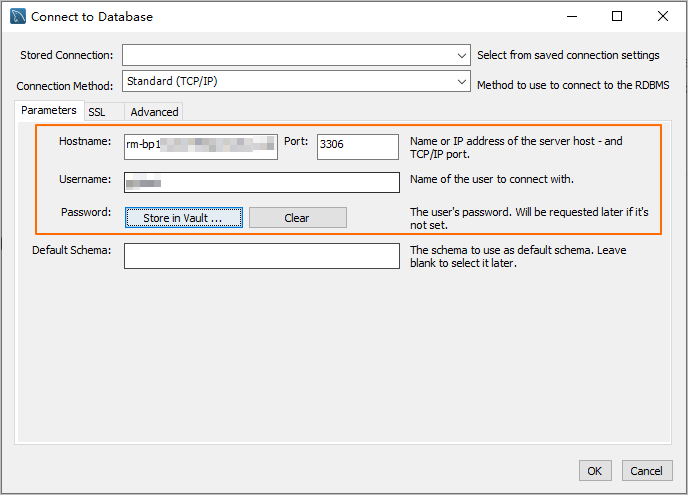
Parameter
Description
Example
Hostname
The database endpoint. For more information, see Database connection.
pc-2***.rwlb.rds.aliyuncs.com
Port
The port number that corresponds to the database endpoint.
NoteThe default port number is 3306.
3306
Username
The database account. For more information, see Create a database account.
polardb_mysql_user
Password
The password of the database account.
Pass***233
Use the CLI to connect to a cluster
If MySQL client is installed on your server, you can run commands in the CLI to connect to a PolarDB for MySQL cluster.
Syntax:
mysql -h <Endpoint> -P <Port> -u <Account> -p <Password>Example:
mysql -h pc-2***.rwlb.rds.aliyuncs.com -P3306 -upolardb_mysql_user -pPass***233Parameter | Description | Example |
-h | The database endpoint. For more information, see Database connection. | pc-2***.rwlb.rds.aliyuncs.com |
-P | The port number that corresponds to the database endpoint. Note
| 3306 |
-u | The database account. For more information, see Create a database account. | polardb_mysql_user |
-p | The password of the database account. Note This parameter is required.
| Pass***233 |
Use an application to connect to a cluster
Connecting to a PolarDB for MySQL cluster is similar to connecting to regular MySQL databases. You only need to replace the endpoint, port, account, and password of the database. The following examples show how to use applications to access a PolarDB database in some development languages:
Java
In this example, a Maven project is used to connect to the PolarDB for MySQL cluster by using the MySQL JDBC driver.
First, add the dependency of the MySQL JDBC driver to the pom.xml file. Sample code:
<dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <version>8.0.27</version> </dependency>Connect to the cluster. Replace the
<HOST>, port number,<USER>,<PASSWORD>,<DATABASE>,<YOUR_TABLE_NAME>, and<YOUR_TABLE_COLUMN_NAME>with the information of your database.import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.DriverManager; import java.sql.ResultSet; import java.sql.Statement; public class DatabaseConnection { public DatabaseConnection() { } public static void main(String[] args) { // The endpoint, port, and database name of the PolarDB cluster to be connected. String url = "jdbc:mysql://<HOST>:3306/<DATABASE>?useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC"; // The database account. String user = "<USER>"; // The password of the database account. String password = "<PASSWORD>"; try { Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password); Statement stmt = conn.createStatement(); // The name of the data table to be queried. ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery("SELECT * FROM `<YOUR_TABLE_NAME>`"); while(rs.next()) { // The column name of the data table to be queried. System.out.println(rs.getString("<YOUR_TABLE_COLUMN_NAME>")); } rs.close(); stmt.close(); conn.close(); } catch (Exception var7) { var7.printStackTrace(); } } }
Python
In this example, Python3 is used to connect to the PolarDB for MySQL cluster by using the PyMySQL library.
First, install the PyMySQL library. You can run the following command to install it:
pip3 install PyMySQLConnect to the cluster. Replace the
<HOST>, port number,<USER>,<PASSWORD>,<DATABASE>, and<YOUR_TABLE_NAME>with the information of your database.import pymysql # The database connection parameters. host = '<HOST>' # The endpoint of the PolarDB cluster. port = 3306 # The default port 3306 user = '<USER>' # The database account. password = '<PASSWORD>' # The password of the database account. database = '<DATABASE>' # The name of the database to be connected. try: # Establish a database connection. connection = pymysql.connect( host=host, port=port, user=user, passwd=password, db=database ) # Obtain the cursor. with connection.cursor() as cursor: # Execute an SQL query. sql = "SELECT * FROM '<YOUR_TABLE_NAME>'" # The name of the table to be queried. cursor.execute(sql) # Obtain the query result. results = cursor.fetchall() for row in results: print(row) finally: # Close the database connection. if 'connection' in locals() and connection.open: connection.close()
Go
In this example, go1.23.0 is used to connect to the PolarDB for MySQL cluster by using the database/sql package and go-sql-driver/mysql driver.
First, install the
go-sql-driver/mysqldriver. You can run the following command to install the driver:go get -u github.com/go-sql-driver/mysqlConnect to the cluster. Replace the
<HOST>, port number,<USER>,<PASSWORD>,<DATABASE>, and<YOUR_TABLE_NAME>with the information of your database.package main import ( "database/sql" "fmt" "log" _ "github.com/go-sql-driver/mysql" ) func main() { // Database connection parameters. dbHost := "<HOST>" // The endpoint of the PolarDB cluster. dbPort := "3306" // The default port 3306. dbUser := "<USER>" // The database account. dbPass := "<PASSWORD>" // The password of the database account. dbName := "<DATABASE>" // The name of the database to be connected. // Build DSN (Data Source Name) dsn := fmt.Sprintf("%s:%s@tcp(%s:%s)/%s?charset=utf8mb4&parseTime=True&loc=Local", dbUser, dbPass, dbHost, dbPort, dbName) // Create a database connection. db, err := sql.Open("mysql", dsn) if err != nil { log.Fatalf("Failed to connect to database: %v", err) } defer db.Close() // Test the connection. err = db.Ping() if err != nil { log.Fatalf("Failed to ping database: %v", err) } // Create a cursor. var result string err = db.QueryRow("SELECT VERSION()").Scan(&result) if err != nil { log.Fatalf("Failed to execute query: %v", err) } // Print the database version. fmt.Printf("Connected to database, version: %s\n", result) // Execute an SQL query. rows, err := db.Query("SELECT * FROM '<YOUR_TABLE_NAME>'") // The name of the data table that is queried. if err != nil { log.Fatalf("Failed to execute query: %v", err) } defer rows.Close()