When you use a notebook in Alibaba Cloud E-MapReduce (EMR) Serverless Spark, you can run Hadoop commands to access Object Storage Service (OSS) or OSS-HDFS. This topic describes how to run Hadoop commands in an EMR Serverless Spark notebook to perform OSS- or OSS-HDFS-related operations.
Prerequisites
EMR Serverless Spark:
A notebook session is created. In this example, a notebook whose engine version is esr-4.1.1 is used. For more information, see Manage notebook sessions.
A notebook is developed. For more information, see Develop a notebook.
OSS:
OSS is activated and a bucket is created. For more information, see Activate OSS and Create a bucket.
OSS-HDFS is activated. For more information, see Enable OSS-HDFS.
Permission configuration:
Required permissions are configured to access OSS or OSS-HDFS resources across accounts. For more information, see How do I implement cross-account access to OSS resources?
NoteIn this example, the read and write permissions on OSS are configured in the OSS console. You can configure the permissions based on your business requirements.
Limits
The operations described in this topic are supported only in the following engine versions:
esr-4.x: esr-4.1.1 or later.
esr-3.x: esr-3.1.1 or later.
esr-2.x: esr-2.5.1 or later.
Supported operations
Here are some of the operations you can perform in a notebook with the engine version esr-4.1.1:
ls: lists the files and directories in a specific OSS or OSS-HDFS path.mv: moves files or directories.cp: copies files or directories.stat: obtains the metadata of a specific file or directory.
You can run the !hadoop fs -help command to view the help information.
Currently, all FS commands supported by Jindo CLI can be used in Notebook. For detailed commands, examples, and applicable scenarios, see Jindo CLI user guide. When using the examples in Notebook, replace jindo with !hadoop.
Access path formats
This section describes the access path format of OSS or OSS-HDFS:
OSS:
oss://<bucketName>/<object-path>OSS-HDFS:
oss://<bucketName>.<region>.oss-dls.aliyuncs.com/<object-path>
Parameters in the paths:
<bucketName>: the name of the OSS bucket. Example:my-bucket.region: the ID of the region in which the OSS bucket resides. Example:cn-hangzhou.<object-path>: the path of the object in an OSS bucket. Example:spark/file.txtorlogs/.
Command usage
When you develop a notebook, run the !hadoop fs command to perform the following operations:
List the files and directories in a specific path (ls)
Run the following command to list the files and directories in a specific path:
!hadoop fs -ls oss://<bucketName>/<object-path>Example 1: List the files and directories in the spark path.
!hadoop fs -ls oss://my-bucket/spark/The following figure shows the output.

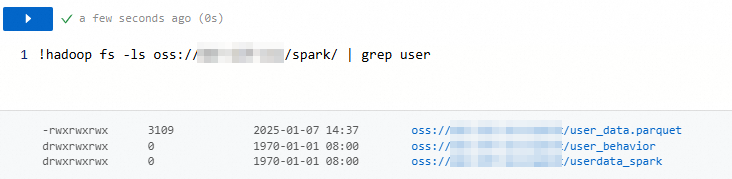
Example 2: Run the commands
-lsandgreptogether to query the files and directories whose name includes user:!hadoop fs -ls oss://my-bucket/spark/ | grep userThe following figure shows the output.
Move a file or directory (mv)
Run the following command to move a file or directory to a specific path:
!hadoop fs -mv oss://<bucketName>/<object-path>/source oss://<bucketName>/<object-path>/destinationFor example, run the following command to move the file.txt file in the sr path to the user path. If the file.txt file already exists in the destination path, the file will be overwritten.
!hadoop fs -mv oss://my-bucket/sr/file.txt oss://my-bucket/user/file.txtCopy a file or directory (cp)
Run the following command to copy a file or directory from the source path to the destination path:
!hadoop fs -cp oss://<bucketName>/<object-path>/source oss://<bucketName>/<object-path>/destinationFor example, run the following command to copy the file.txt file from the spark path to the spark2 path. If the file.txt file already exists in the destination path, the file will be overwritten.
!hadoop fs -cp oss://my-bucket/spark/file.txt oss://my-bucket/spark2/file.txtView the metadata of a file or directory (stat)
Run the following command to view the details of a specific file or directory:
!hadoop fs -stat oss://<bucketName>/<object-path>/to/fileFor example, run the following command to view the metadata of the file.txt file:
!hadoop fs -stat oss://my-bucket/spark/file.txt