The node label feature allows YARN to isolate different types of jobs at the physical layer when the jobs are scheduled to run on YARN. This topic describes how to add node labels based on your business type and node type.
Background information
YARN provides queues and node labels that you can use to manage resources and schedule jobs. Queues and node labels assume different roles and play unique roles in managing resources in a cluster.
Queues are used to allocate logical resources. You can use queues to allocate the computing resources of a cluster to different user groups or applications based on a preset ratio. This ensures that resources are evenly allocated to different teams or different types of workloads in a shared cluster environment.
You can use node labels to mark specific nodes in a cluster and allocate resources in a fine-grained manner based on the labels. Node labels are important for applications that have specific requirements on hardware, such as applications that have high requirements on GPUs and memory size.
Queues are used to allocate resources and schedule jobs, and node labels are used to group nodes and isolate jobs. You can use queues together with node labels to manage resources and schedule jobs in a flexible and efficient manner.
You can use node labels to group your nodes based on your business requirements and cluster status. This way, you can manage and schedule cluster resources in an efficient manner. You can add node labels to group different types of jobs, such as data synchronization jobs, batch jobs, and real-time jobs. You can also add node labels to group different types of instances, such as instances that belong to the CPU-optimized, memory-optimized, and GPU-accelerated compute-optimized instance families.
Prerequisites
An E-MapReduce (EMR) cluster that contains the YARN service is created. For more information, see Create a cluster.
Capacity Scheduler is used for YARN. Only Capacity Scheduler supports the node label feature.
Example
Background information
An enterprise requires two child queues named warehouse and analysis, and two partitions named batch and streaming. The warehouse queue requires 60% of resources to process batch jobs and 70% of resources to process streaming jobs. The analysis queue requires 30% of resources to process batch jobs and 20% of resources to process streaming jobs. The default partition of YARN is DEFAULT_PARTITION. The partition allocates 60% of resources to the warehouse queue and 30% of resources to the analysis queue, and reserves 10% of resources for other business requirements. For more information, see the following figure.

In this example, queues are used together with node labels to flexibly manage resources and physically isolate offline jobs from other jobs. This ensures that the performance and stability of other jobs are not affected. In this example, a DataLake cluster of EMR V5.16.0 is used. The procedure for resource management by using queues and node labels for other types of EMR clusters of other versions is basically the same as that for the DataLake cluster of EMR V5.16.0.
Step 1: Edit resource queues
Log on to the EMR console. On the EMR on ECS page, find the desired cluster and click Services in the Actions column. On the Services tab, click YARN.
On the YARN service page, click the Edit Resource Queue tab. On the tab, click Manage Queues.
In the Manage Child Queues dialog box, click Add Queue to add the two queues named warehouse and analysis.
Enter 60, 30, and 10 in the Queue Capacity column of the warehouse, analysis, and default queues correspondingly. Then, select Started from the drop-down list of the queues in the Status column.

The following figure shows the configurations.
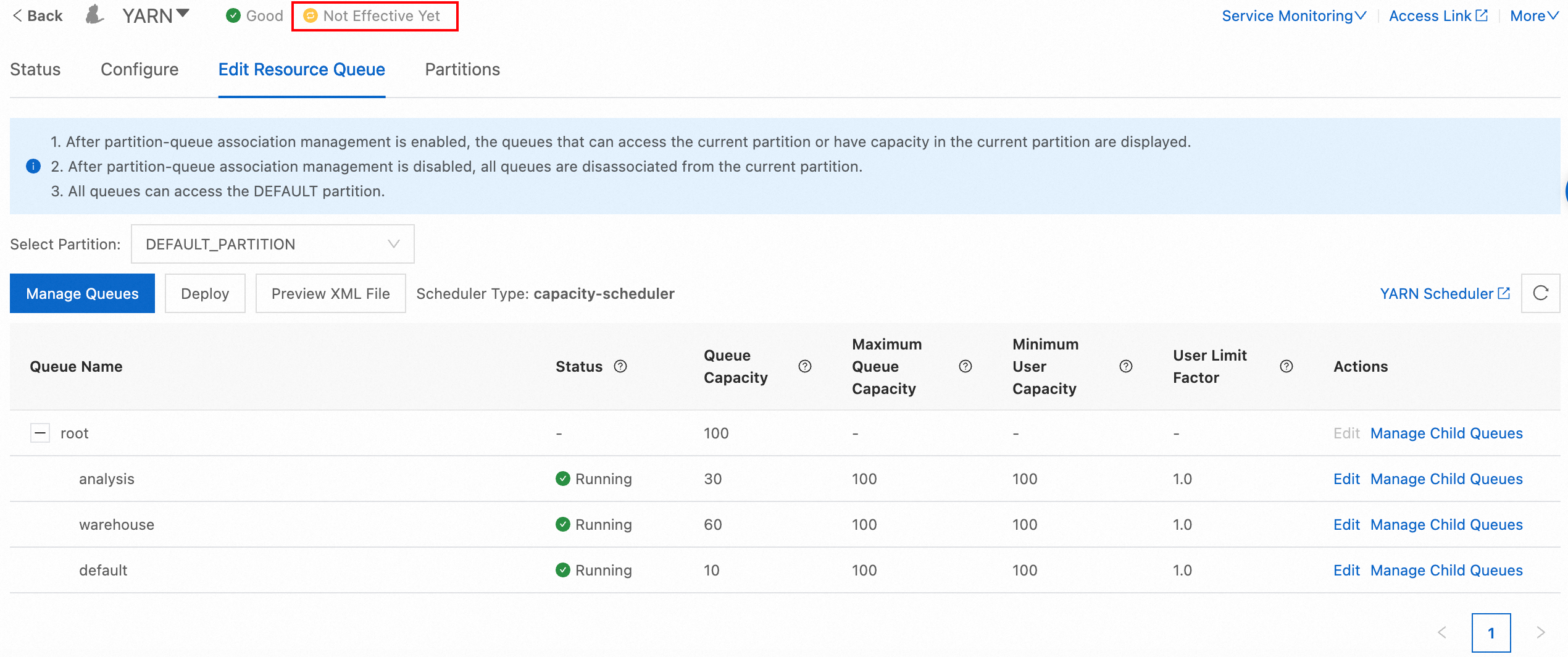
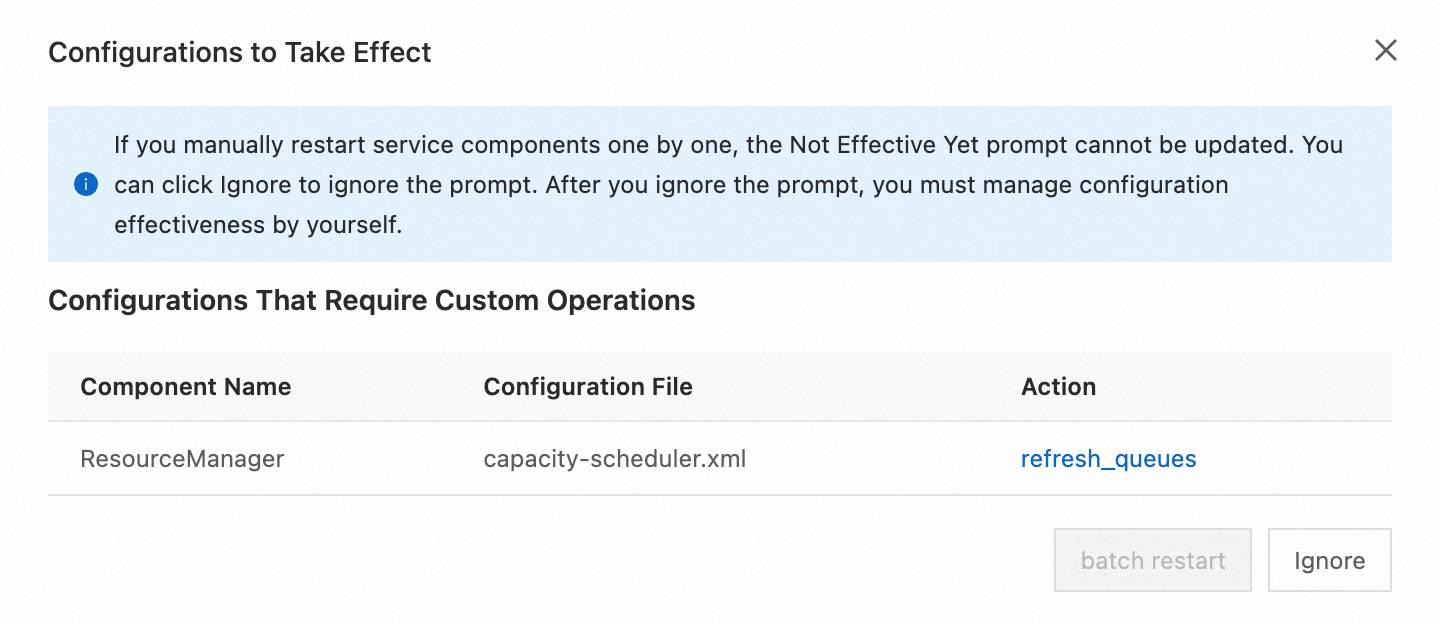
Click Not Effective Yet. In the Configurations to Take Effect dialog box, click refresh_queues in the Actions column.
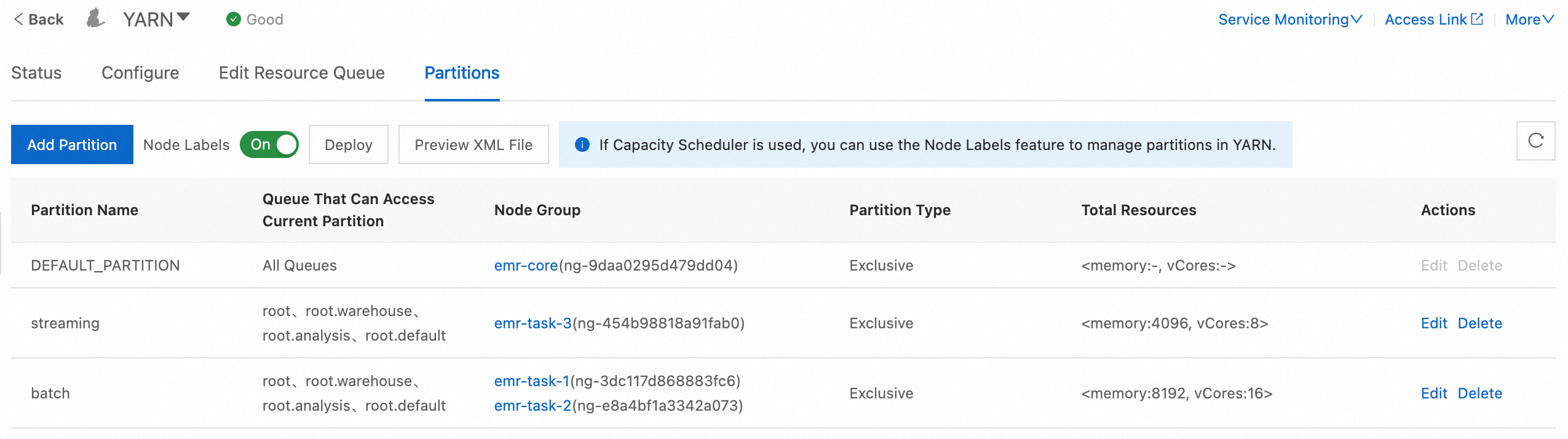
Step 2: Add partitions and associate nodes with the partitions
Click the Partitions tab. On the tab, click Add Partition to add a partition named streaming.
In the Add Partition dialog box, configure the Partition Name, Partition Type, and Associated Node Groups parameters.
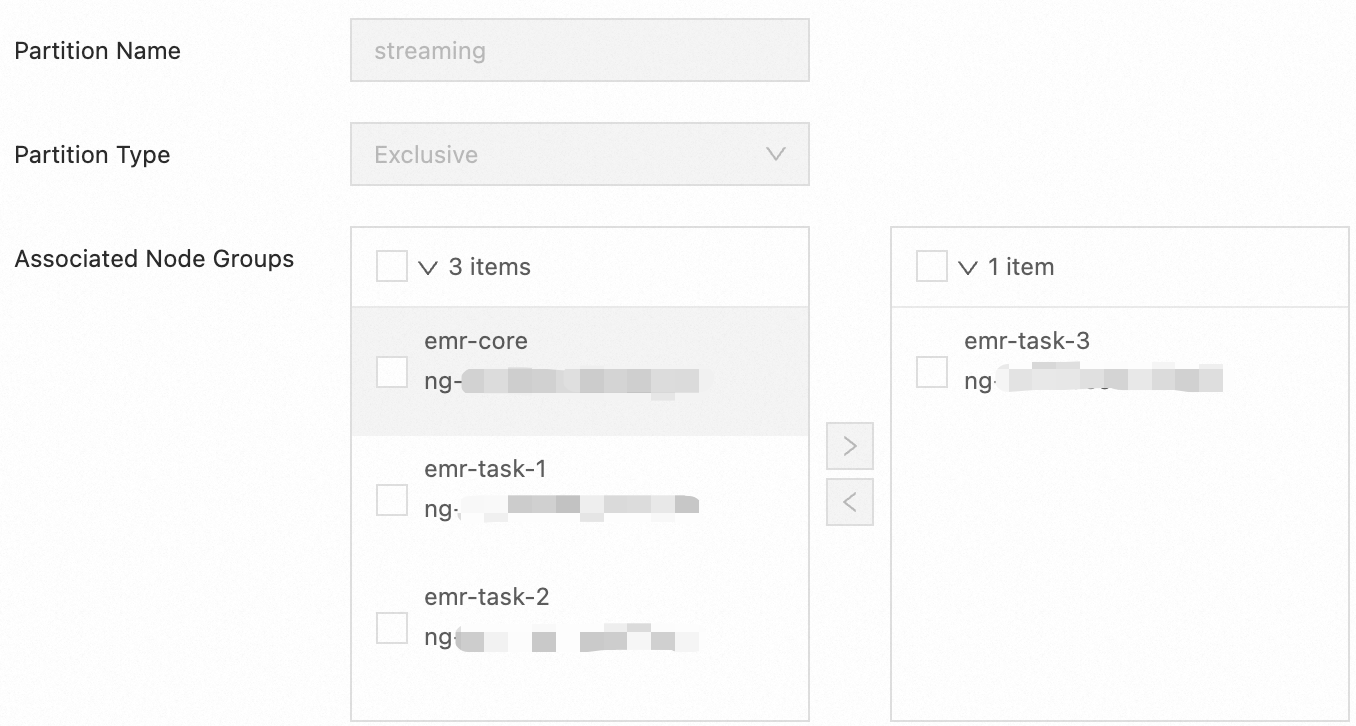
Partition Name: Enter streaming.
Partition Type: Select Exclusive from the drop-down list. This indicates that containers can be allocated to a node of an exclusive partition only if the partition is exactly matched.
Associated Node Groups: Select the node group that you want to associate with the partition. In this example, emr-task-3 is selected. The emr-task-3 node group contains memory-optimized instances that are suitable for running real-time jobs that store a large amount of intermediate data and require low latency. You can associate a node group with a partition based on your business requirements and instance type.
Repeat the preceding operations to add a partition named batch.
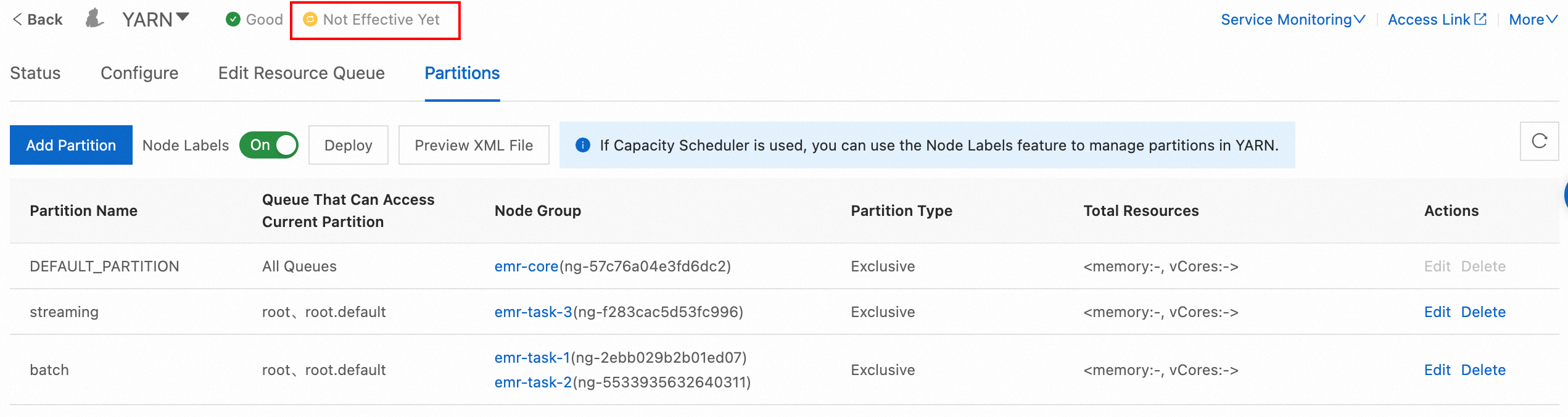
Click Not Effective Yet. In the Configurations to Take Effect dialog box, click refresh_labels in the Actions column.

View the total resources of each partition in the Total Resources column after the configuration takes effect.
Step 3: Enable partition-queue association management
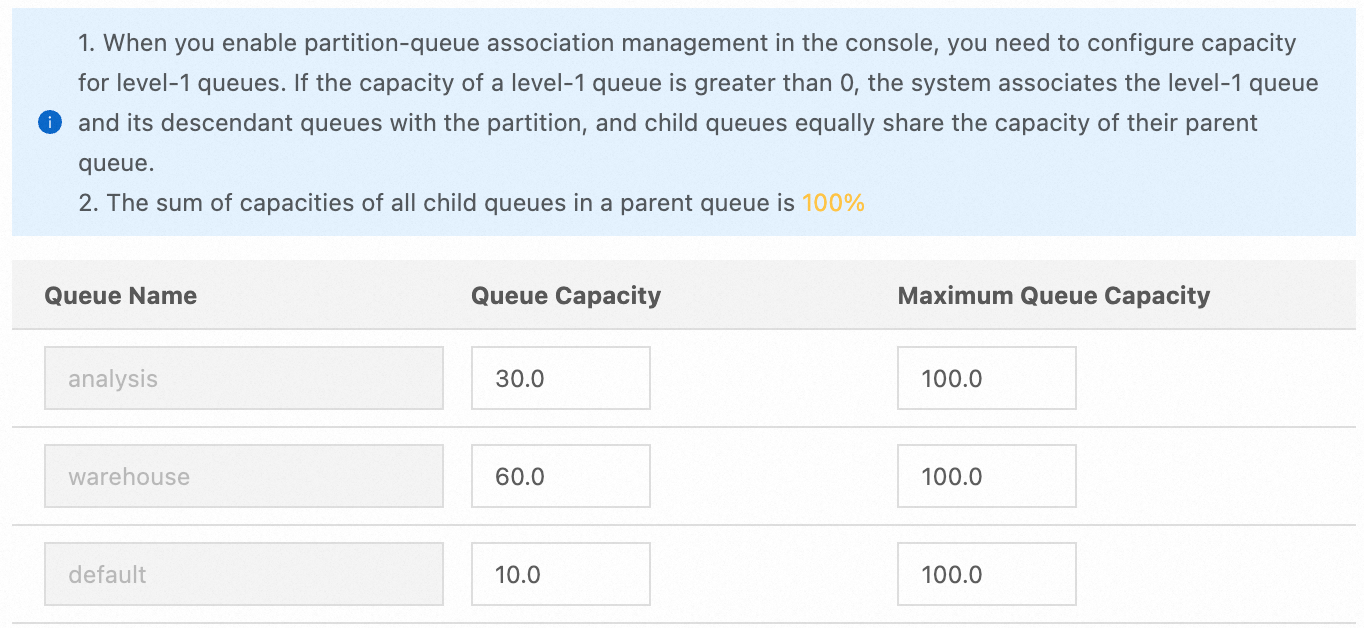
On the Edit Resource Queue tab, select the batch and streaming partitions from the Select Partition drop-down list in sequence and turn on Enable Partition-queue Association Management.
In the Enable Partition-queue Association Management dialog box, specify the queue capacity for each partition in the Queue Capacity column and click OK.
batch: In the Queue Capacity column, enter 30 for the analysis queue, 60 for the warehouse queue, and 10 for the default queue.
streaming: In the Queue Capacity column, enter 20 for the analysis queue, 70 for the warehouse queue, and 10 for the default queue.
 Note
NoteIn this example, all queues have permissions to run in each partition. If you want a specific partition to run only the jobs submitted by specific queues, you can specify the capacity of a queue to 0.
Click Not Effective Yet. In the Configurations to Take Effect dialog box, click refresh_queues in the Actions column.
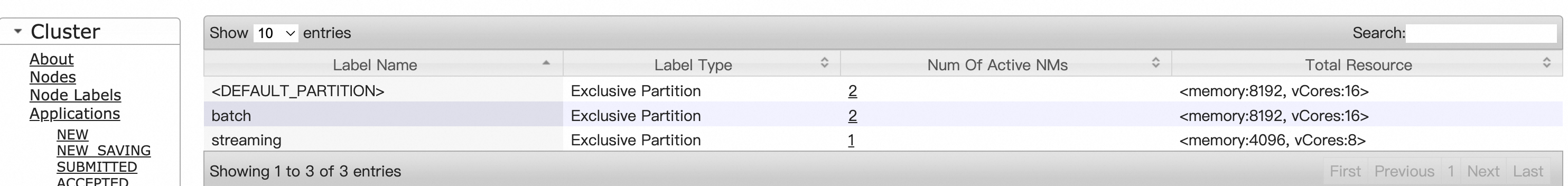
Check whether the node labels take effect on the web UI of YARN.
Result on the Node Labels page
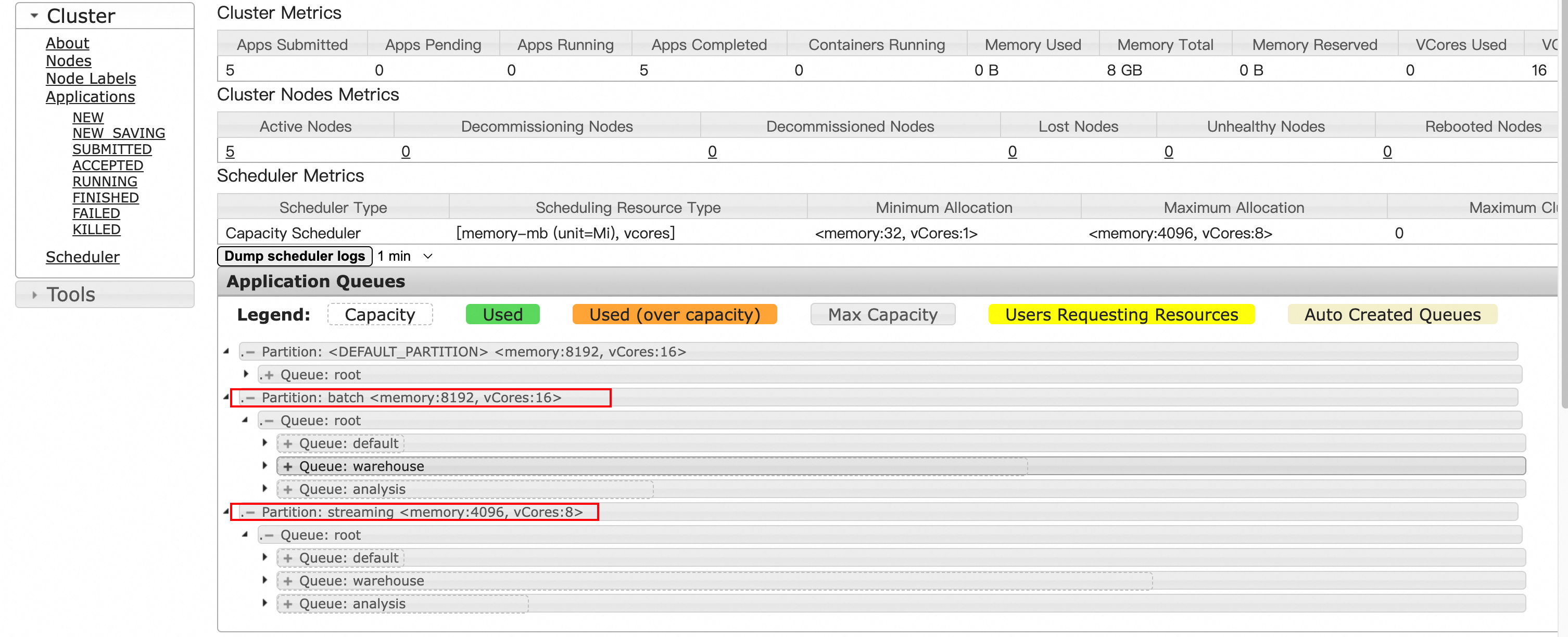
Result on the Scheduler page
Step 4: Submit jobs to specific partitions
After you configure the queues and node labels for your cluster, you can submit jobs to specific queues and nodes to run.
Log on to the master node of your cluster and go to the installation directory of Spark. In this example, the directory is /opt/apps/SPARK3/spark-3.3.1-hadoop3.2-1.1.1.
cd /opt/apps/SPARK3/spark-3.3.1-hadoop3.2-1.1.1Upload the JAR package that is required to submit Spark jobs. This section describes how to use spark-submit to submit Spark jobs.
./bin/spark-submit --class org.apache.spark.examples.SparkLR --master yarn --deploy-mode cluster --driver-memory 1g --executor-memory 2g --conf spark.yarn.am.nodeLabelExpression=batch --conf spark.yarn.executor.nodeLabelExpression=batch --queue=warehouse examples/jars/spark-examples_2.12-3.3.1.jarParameter
Description
class
The main class of an application. Example: org.apache.spark.examples.SparkLR.
master
The location where submitted jobs are run. Set the value to YARN.
deploy-mode
The location where the driver starts. Set the value to cluster.
driver-memory
The memory size of the driver. Set the value to 1g.
executor-memory
The memory size of each executor. Set the value to 2g.
spark.yarn.am.nodeLabelExpression
The label of the node on which the ApplicationMaster (AM) runs. Set the value to batch.
spark.yarn.executor.nodeLabelExpression
The label of the node on which the executor runs. Set the value to batch.
queue
The queue to which the jobs are submitted. Set the value to warehouse.
NoteIf you specify only a queue before you submit jobs, the jobs are submitted to the default partition of the queue. You can click Edit in the Actions column of a queue on the Edit Resource Queue tab to change the default partition of the queue based on your business requirements.
On the web UI of YARN, check whether SparkLR jobs are submitted to the warehouse queue and run on the batch partition.
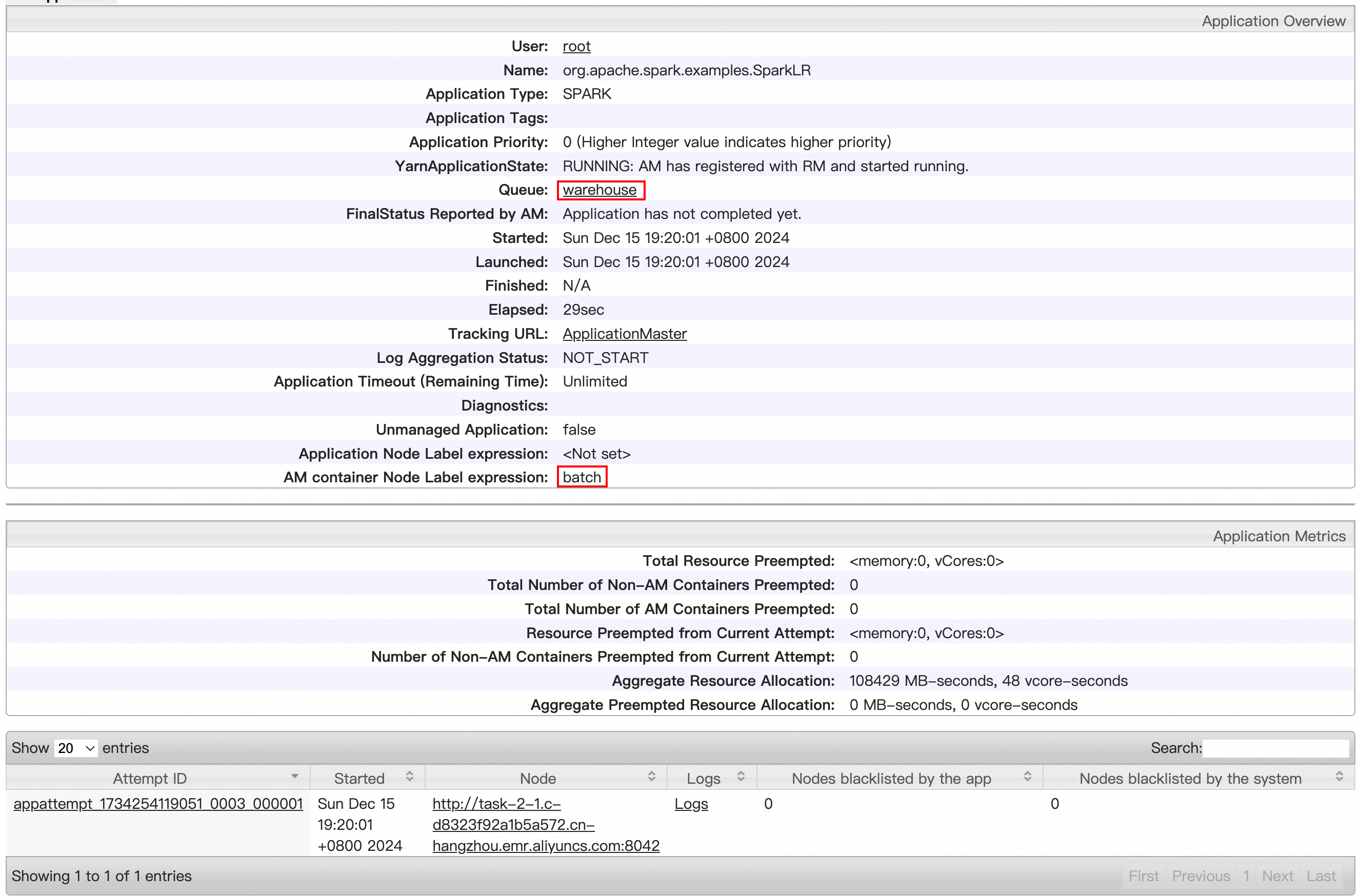
You can use queues together with node labels of YARN to implement logical and physical isolation of resources for your jobs. This prevents mutual interference among different jobs to ensure the performance and stability of the jobs.
FAQ
What do I do if specific jobs do not run on a specific partition when I use spark-submit to submit jobs?
Check whether the spark.yarn.executor.nodeLabelExpression parameter is added to the command that is used to submit jobs.
Check whether the configurations of the queues and partitions take effect.
What do I do if the status of jobs is always displayed as ACCEPTED when I use spark-submit to submit jobs?
Check whether the queue to which jobs are submitted has sufficient resources. If the queue has insufficient resources, wait until other jobs are complete and resources are released before you submit the jobs.
If the queue has sufficient resources, click the specific job ID on the web UI of YARN and check the description of the Diagnostics parameter. If the description contains the message "Queue's AM resource limit exceeded", the queue has sufficient resources but the AM resources are insufficient. The resources of a queue are allocated to the AM and executors. The AM resources are used to submit the main application, and the executor resources are used to process jobs. In this case, you must adjust the resource ratio of the queue. You can appropriately increase the ratio of AM resources to ensure that Spark jobs are successfully submitted.

To adjust the resource ratio of the queue, find the capacity_scheduler.xml file on the Configure tab of the YARN service page and change the value of the yarn.scheduler.capacity.maximum-am-resource-percent configuration item. For example, you can change the value of the configuration item from 0.25 to 0.5.

NoteYou can adjust the default resource ratio of the AM based on your business requirements. For example, if a large number of small jobs exist in your cluster, you can appropriately increase the resource ratio of the AM.
References
For more information about YARN schedulers, see YARN schedulers.
For more information about the node label feature of YARN, see Node labels.