If the system checks that a zone where your Elasticsearch cluster resides has insufficient resources when you upgrade the configuration of your Elasticsearch cluster, you can migrate the nodes in the zone to another zone. This ensures that the zones where the cluster resides provide sufficient resources for the upgrade. If your single-zone Elasticsearch cluster cannot meet the requirements of high-concurrency queries or large-volume data writes due to business expansion, you can upgrade the cluster to a multi-zone cluster to avoid single points of failure (SPOFs) and implement high availability for the cluster. This topic describes how to migrate nodes in a zone and how to upgrade the deployment mode of a cluster.
Background information
Zone: In most cases, a data center corresponds to a zone. In some cases, a data center corresponds to multiple zones. For example, the AM5 data center corresponds to the cn-hangzhou-d and cn-hangzhou-finance-d zones. To facilitate Elasticsearch management, if a data center is removed, the related zones are removed.
Node migration across zones: You can migrate Elasticsearch nodes from a zone to another zone that has sufficient resources. This operation helps resolve resource bottlenecks and implement load balancing to avoid configuration upgrade failures due to insufficient resources. Elasticsearch provides standardized capabilities to allow you to migrate nodes for a cluster across zones. The migration is implemented based on the blue-green deployment capability of Elasticsearch. This enables smooth, graceful cluster changes.
Deployment mode upgrade: You can upgrade your cluster from a single-zone cluster to multi-zone cluster. Multi-zone deployment improves the disaster recovery capabilities of a cluster. This operation helps prevent SPOFs and enhance cluster availability and stability.
Billing
You are charged based on the number of nodes that you use. The actual bills prevail. For more information, see Elasticsearch billing.
Precautions
Node migration across zones
You can migrate the nodes only in a single zone to another zone at a time. If you want to migrate the nodes in multiple zones, you need to perform migration multiple times.
After you migrate the nodes in a zone to another zone, the system performs a rolling restart for your cluster. The time required for the migration depends on the size, data volume, and load of your cluster. We recommend that you perform migration during off-peak hours.
In most cases, if the indexes of your cluster have replica shards and the load of your cluster is normal, your cluster can still provide services during migration. The following items indicate that the load of a cluster is normal: The CPU utilization of each node in the cluster is about 60%, the heap memory usage of each node in the cluster is about 50%, and the value of NodeLoad_1m for each node is less than the number of vCPUs for the node.
If the indexes of your cluster do not have replica shards, the load of the cluster is excessively high, and large amounts of data are written to or queried in your cluster, access timeouts may occur during migration. We recommend that you configure an access retry mechanism for your client before you migrate nodes in a zone. This reduces the impact on your business.
Deployment mode upgrade
You can upgrade a cluster deployed in a single zone to a cluster deployed across two or three zones. You cannot upgrade a cluster deployed across two zones to a cluster deployed across three zones.
To ensure cluster stability, the system enables dedicated master nodes by default during the upgrade.
During the upgrade, the existing nodes of the cluster are restarted, and the system automatically adjusts the number of data nodes to ensure that data is evenly distributed across multiple zones.
Formula for calculating the number of data nodes:
Total number of data nodes = Number of data nodes in a single zone after the upgrade × Number of zonesFor example, a cluster is deployed in a single zone and has six data nodes. After the cluster is upgraded to a cluster deployed across three zones, the number of data nodes in each zone of the cluster is
2.NoteIf a cluster is deployed in a single zone but has fewer data nodes, you cannot make sure that at least one data node is assigned to each zone after you upgrade the cluster to a cluster deployed across multiple zones. In this case, the system automatically adds data nodes as needed. For example, a cluster deployed in a single zone has only two data nodes in total. When you upgrade the cluster to a cluster deployed across three zones, the system automatically adds one data node (that is, a total of three data nodes) to ensure that one data node is assigned to each zone.
Prerequisites
Node migration across zones
Make sure that your Elasticsearch cluster is in a normal state.
You can run the
GET _cat/health?vcommand to view the status of the cluster.In the Kibana console of your cluster, check whether your cluster stores indexes in the close state. If your cluster stores such indexes, you must open the indexes. Otherwise, the upgrade fails.
Run the following command to view the statuses of indexes:
GET /_cat/indices?v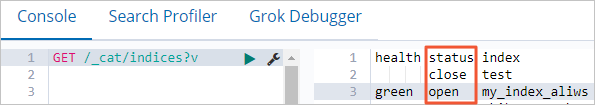
Run the following command to open an index in the close state:
POST /<index_name>/_openReplace <index_name> with the name of the index in the close state.
Make sure that a zone with sufficient resources exists within the current account.
We recommend that you select the destination zone from bottom to top in alphabetical order because the zone may have sufficient resources. For example, if both cn-hangzhou-e and cn-hangzhou-h are available, select cn-hangzhou-h. After you migrate nodes to another zone, you must manually upgrade the configuration of your Elasticsearch cluster.
Make sure that the
cluster.routing.allocation.enableconfiguration items is set toall, indicating that automatic shard allocation is allowed. Otherwise, the change process may be blocked.You can run the
GET _cluster/settingscommand to view the configuration. If the value ofcluster.routing.allocation.enableis notall, run the following command:PUT _cluster/settings { "transient": { "cluster.routing.allocation.enable": "all" } }
Deployment mode upgrade
Make sure that your Elasticsearch cluster is in a normal state.
You can run the
GET _cat/health?vcommand to view the status of the cluster.Make sure that the connection distribution of your client is optimized to avoid uneven distribution of persistent connections.
If the persistent connections between your client and an Elasticsearch cluster are concentrated on nodes in a specific zone (for example, Zone A) while nodes in other zones have few connections, the nodes in Zone A may experience high load and resource exhaustion due to too many connections, while other nodes remain idle. You can optimize connection distribution by configuring a connection validity period, concurrently restarting clients, or using separate client nodes. For more information, see Multi-zone architecture.
Make sure that the
cluster.routing.allocation.enableconfiguration items is set toall, indicating that automatic shard allocation is allowed. Otherwise, the change process may be blocked.You can run the
GET _cluster/settingscommand to view the configuration. If the value ofcluster.routing.allocation.enableis notall, run the following command:PUT _cluster/settings { "transient": { "cluster.routing.allocation.enable": "all" } }
Migrate nodes in a zone
To migrate nodes in a zone, perform the following steps:
Node migration triggers a cluster restart. During the restart, the cluster can still provide services, but the services may be unstable. Therefore, we recommend that you migrate nodes during off-peak hours.
Go to the details page of your cluster.
Log on to the Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch console.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Elasticsearch Clusters.
In the top navigation bar, select the desired resource group and region. In the cluster list, find your cluster and click its ID.
In the Node Visualization section of the Basic Information page, move the pointer over the zone whose nodes you want to migrate. Then, click Migrate.
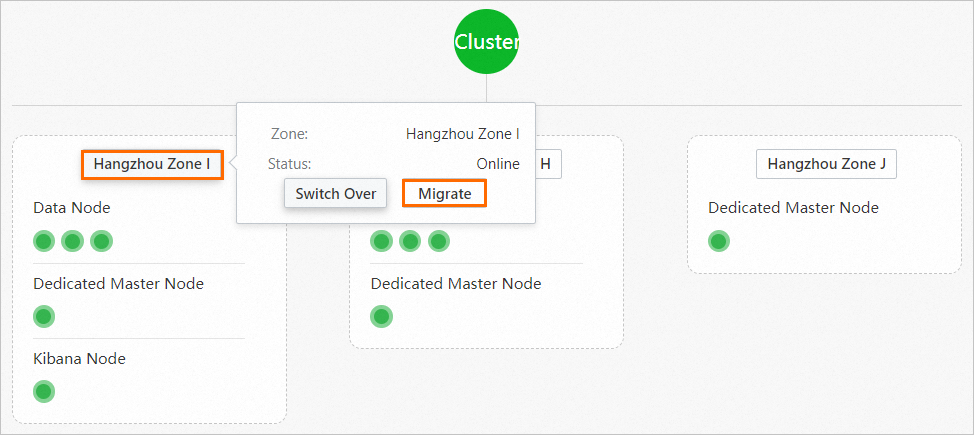
In the Migrate Nodes dialog box, configure Destination Zone and vSwitch.
Parameter
Description
Destination Zone
Select the zone to which you want to migrate nodes.
The selected zone may also have insufficient resources or may be unavailable. In this case, select another zone.
To ensure high availability of nodes, you cannot select other zones where nodes for the Elasticsearch cluster are deployed.
vSwitch
If your cluster is a single-zone cluster, you must select a new vSwitch for node migration. In most cases, the vSwitch that is provided by default is used.
NoteIf your cluster is a multi-zone cluster or a cluster deployed on the Alibaba Finance Cloud, you do not need to select a new vSwitch.
If no vSwitch is available, create a vSwitch. For more information, see Create and manage vSwitches.
Read the terms of data migration, select the check box, and then click OK.
Then, the system restarts the cluster. After the cluster is restarted, the nodes are migrated to the destination zone.
ImportantDuring the migration, you need to purchase dedicated master nodes in the destination zone. In this case, the original zone and destination zone coexist.
After the migration, the original zone may still be displayed on the Basic Information and Upgrade/Downgrade pages in the Elasticsearch console due to delayed information updates. This does not affect the use of the cluster in the new zone. You can view the actual zones where the cluster resides in the Node Visualization section of the Basic Information page.
After the nodes in the zone are migrated, the IP addresses of the nodes change. If you specified the IP addresses in the configuration of your cluster, you must update the IP addresses after the migration.
Upgrade the deployment mode of a cluster to multi-zone deployment
To upgrade the deployment mode of a cluster to multi-zone deployment, perform the following steps:
Load imbalance may occur during the upgrade. For information about how to resolve this issue, see Unbalanced loads on a cluster.
Go to the details page of your cluster.
Log on to the Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch console.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Elasticsearch Clusters.
In the top navigation bar, select the desired resource group and region.
On the page that appears, find the cluster for which you want to upgrade the deployment mode and click Upgrade Configuration in the Actions column.
On the Upgrade/Downgrade page, set Number of Zones to 2-AZ or 3-AZ (recommended). Then, follow the instructions to complete the purchase.
NoteYou can configure other parameters based on your business requirements or retain default values for them. You are charged based on the number of nodes that you use. The actual bills prevail. For more information, see Elasticsearch billing.
What to do next
After the migration or upgrade is complete, you can go to the cluster details page to view the details of the changed zones.