This topic describes how to associate an elastic IP address (EIP) with an elastic network interface (ENI). If you associate EIPs with ENIs and associate the ENIs with an Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance, the ECS instance can use multiple EIPs. This improves the service availability, flexibility, and scalability.
Background information
Each ENI is assigned a private IP address. After you associate an EIP with an ENI, the ENI is capable of sending and receiving network traffic through both a private IP address and a public IP address. If you migrate an ENI that is associated with an EIP from an ECS instance to another ECS instance, both the private and public IP addresses of the ENI are migrated. This ensures the reliability and availability of your service.
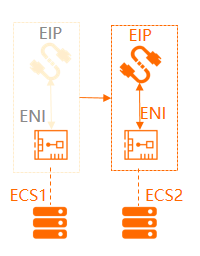
You can associate multiple ENIs with an ECS instance. You can associate each ENI with an EIP. This way, the ECS instance has multiple public IP addresses. The ECS instance can use the EIPs to provide Internet-facing services. You can configure security group rules for the ECS instance to control access from the Internet.
Association modes
You can associate an EIP with an ENI in one of the following EIP modes:
NAT mode
Cut-through mode
Multi-EIP-to-ENI mode
NoteAlibaba Cloud no longer accepts new applications for using the multi-EIP-to-ENI mode.
We recommend that you expose an EIP by adding a secondary CIDR block to a virtual private cloud (VPC). For more information, see Expose an EIP on an NIC by adding a secondary CIDR block to a VPC.
The following table describes the differences among these modes.
Item | NAT mode | Cut-through mode | Multi-EIP-to-ENI mode |
Whether the EIP is displayed on the ENI in the operating system | No | Yes Note You can run the ifconfig or ipconfig command to query the public IP address of the ENI. | Yes Note After you configure a static IP address in the operating system, you can run the ifconfig or ipconfig command to query the public IP address of the ENI. |
Types of ENIs that can be associated with EIPs | Primary ENI and secondary ENI Note After you associate an EIP with an ECS instance, the EIP is associated with the primary ENI of the ECS instance. For more information, see Associate an EIP with an ECS instance. | Secondary ENI | Secondary ENI |
The maximum number of EIPs that can be associated with a primary ENI | 1 | EIPs cannot be associated with primary ENIs | EIPs cannot be associated with primary ENIs |
The maximum number of EIPs that can be associated with a secondary ENI | Based on the number of private IP addresses of the secondary ENI Note Each EIP can be mapped to a private IP address of a secondary ENI. If a secondary ENI is assigned 10 private IP addresses, at most 10 EIPs can be associated with the secondary ENI. | 1 Note You can associate an EIP with only the primary private IP address of a secondary ENI in cut-through mode. | 10 |
Whether the private network feature of a secondary ENI is available after an EIP is associated with the secondary ENI | Yes | No | Yes |
Supported protocols | EIPs do not support protocols that are managed by NAT application layer gateways (ALGs), such as H.323, Session Initiation Protocol (SIP), Domain Network System (DNS), and Real Time Streaming Protocol (RTSP). | EIPs support all IP protocols, such as FTP, H.323, SIP, DNS, RTSP, and Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) | EIPs support all IP protocols, such as FTP, H.323, SIP, DNS, RTSP, and TFTP |
Supported regions | All regions | China (Hangzhou), China (Shanghai), China (Qingdao), China (Beijing), China (Zhangjiakou), China (Hohhot), China (Shenzhen), China (Guangzhou), China (Chengdu), Singapore, Indonesia (Jakarta), Germany (Frankfurt), UK (London), and US (Virginia) | China (Shenzhen), China (Shanghai), China (Beijing), China (Zhangjiakou), China (Chengdu), Singapore, Germany (Frankfurt), US (Virginia), and UK (London) |
Prerequisites
A secondary ENI is created in a VPC. The secondary ENI and the EIP are created in the same region. For more information, see Create an ENI.
Associate an EIP with a secondary ENI in NAT mode
If you associate an EIP with a secondary ENI in NAT mode, the public and private IP addresses of the ENI are available at the same time. In this case, the EIP is not displayed on the secondary ENI.
Before or after a secondary ENI is associated with an ECS instance, EIPs can be associated with the secondary ENI in NAT mode. However, the number of ENIs supported by an ECS instance and the number of private IP addresses supported by an ENI are limited. We recommend that you associate a secondary ENI with an ECS instance before you associate EIPs with the secondary ENI in NAT mode. Before you perform the operations, take note of the following information:
The number of secondary ENIs that can be associated with an ECS instance varies with the ECS instance family. For more information, see Overview of instance families.
If you associate a secondary ENI with an ECS instance, some images cannot automatically identify the IP address of the secondary ENI or add routes. You must configure the secondary ENI on the ECS instance to identify the IP address of the ENI and add routes. For more information, see Configure a secondary ENI.
If an IPv4 gateway is activated in the VPC to which the ECS instance belongs, you must configure routes for the IPv4 gateway to allow instances in the VPC to access the Internet. For more information about how to configure routes for an IPv4 gateway, see Create and manage an IPv4 gateway.
Log on to the Elastic IP Address console.
In the top navigation bar, select the region where the EIP is created.
On the Elastic IP Addresses page, find the EIP that you created and click Associate with Resource in the Actions column.
In the Associate EIP with Resource dialog box, set the following parameters and click OK.
Parameter
Description
Instance Type
Select ENI.
Resource Group
Select the resource group to which the secondary ENI belongs.
Mode
Select NAT Mode.
In NAT mode:
The number of EIPs that can be associated with a secondary ENI depends on the number of private IP addresses that are assigned to the secondary ENI.
The EIP is associated with the ENI in NAT mode. Both the private IP addresses and public IP addresses of the ENI are available.
You cannot query the EIP in the operating system. To query the EIP, call the DescribeEipAddresses operation. For more information, see DescribeEipAddresses.
EIPs do not support protocols that are managed by NAT application layer gateways (ALGs), such as H.323, Session Initiation Protocol (SIP), Domain Network System (DNS), and Real Time Streaming Protocol (RTSP).
Select an instance to associate
Select the secondary ENI with which you want to associate the EIP.
If Allocated is displayed in the IP Status column and the ID of the secondary ENI is displayed in the Associated Instance Type/ID column, the EIP is associated with the secondary ENI.
After you complete the preceding operations, you may need to configure routes for the secondary ENI. For more information, see Configure routes.
Associate an EIP with a secondary ENI in cut-through mode (not recommended)
If you associate an EIP with a secondary ENI in cut-through mode, the EIP replaces the private IP address of the secondary ENI. The secondary ENI serves as a public network interface controller (NIC). In this case, you can query the EIP in the operating system.
Before you perform the operations, make sure that the following requirements are met:
The region to which the EIP and secondary ENI belong supports the cut-through mode.
The secondary ENI is not associated with an ECS instance. If the secondary ENI is associated with an ECS instance, you must disassociate the secondary ENI from the ECS instance. Then, associate the EIP with the secondary ENI in cut-through mode and associate the secondary ENI with the ECS instance. For more information, see Disassociate a secondary ENI.
No IPv4 gateway exists in the VPC to which the secondary ENI belongs.
If you use a subscription EIP and the EIP is associated with a secondary ENI in cut-through mode, and the secondary ENI is associated with an ECS instance, the private network feature of the secondary ENI is unavailable after the EIP is released.EIP To use the private network feature of the secondary ENI in this scenario, you must disassociate the secondary ENI from the ECS instance, and associate the secondary ENI with the ECS instance again.
Log on to the Elastic IP Address console.
In the top navigation bar, select the region where the EIP is created.
On the Elastic IP Addresses page, find the EIP that you created and click Associate with Resource in the Actions column.
In the Associate EIP with Resource dialog box, configure the following parameters and click OK.
Parameter
Description
Instance Type
Select ENI.
Resource Group
Select the resource group to which the secondary ENI belongs.
Mode
Select Cut-through Mode.
Select an instance to associate
Select the secondary ENI with which you want to associate the EIP.
If Allocated is displayed in the IP Status column and the ID of the secondary ENI is displayed in the Associated Instance Type/ID column, the EIP is associated with the secondary ENI.
In the Associated Instance Type/ID column, click the ID of the secondary ENI.
In the upper-right corner of the details page, click Bind to Instance and select an ECS instance.
NoteThe number of ENIs supports by an ECS instance varies based on the instance family. For more information, see the Overview of instance families.
If you associate a secondary ENI with an ECS instance, some images cannot automatically identify the IP address of the secondary ENI or add routes. You must configure the secondary ENI on the ECS instance to identify the IP address of the ENI and add routes. For more information, see Configure a secondary ENI.
If you associate an EIP in cut-through mode, the ECS instance automatically generates a route that uses the secondary ENI as the egress interface. The route priority is lower than that of the primary ENI. You can modify the priorities of the routes based on your business requirements. For more information, see Configure routes.
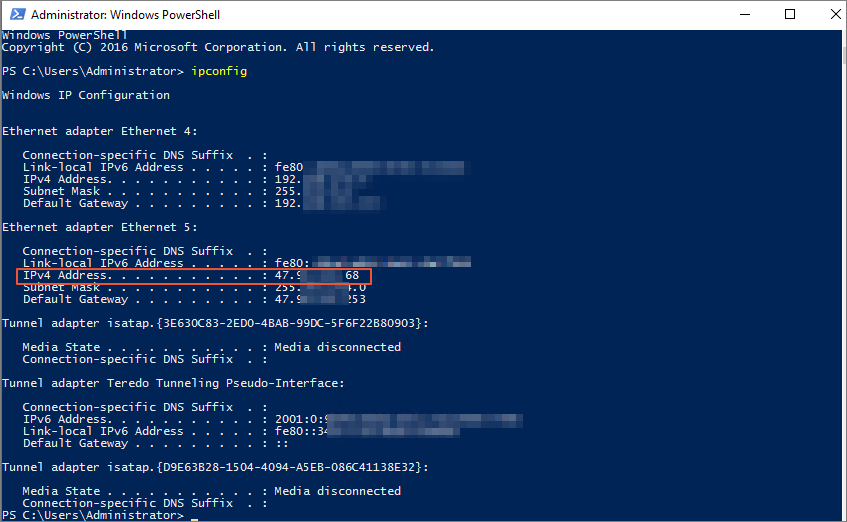
Log on to the ECS instance by using the associated EIP and run the
ipconfigcommand to view the network configuration of the ECS instance.NoteMake sure that the security group rules of the ECS instance allow remote access.
The following figure shows that the private IP address of the ECS instance is replaced by the EIP.
Associate EIPs with a secondary ENI in multi-EIP-to-ENI mode (application no longer accepted)
If you associate multiple EIPs with a secondary ENI in multi-EIP-to-ENI mode, the private and public IP addresses are available at the same time. You can query the EIPs in the operating system.
Log on to the Elastic IP Address console.
In the top navigation bar, select the region where the EIP is created.
On the Elastic IP Addresses page, find the EIP that you created and click Associate with Resource in the Actions column.
In the Associate EIP with Resource dialog box, configure the following parameters and click OK.
Parameter
Description
Instance Type
Select ENI.
Resource Group
Select the resource group to which the secondary ENI belongs.
Mode
Select Multi-EIP-to-ENI Mode.
Select an instance to associate
Select the secondary ENI with which you want to associate the EIP.
If Allocated is displayed in the IP Status column and the ID of the secondary ENI is displayed in the Associated Instance Type/ID column, the EIP is associated with the secondary ENI.
To associate more EIPs with the secondary ENI, repeat the preceding steps.
In the Associated Instance Type/ID column, click the ID of the secondary ENI.
In the upper-right corner of the details page, click Bind to Instance and select an ECS instance.
NoteIf a secondary ENI is associated with EIPs in multi-EIP-to-ENI mode and you want to associate the secondary ENI with an ECS instance, the ECS instance must belong to one of the following instance families: ecs.d1ne, ecs.ebmc4, ecs.ebmg5, ecs.ebmhfg5, ecs.f1, ecs.gn5i, ecs.gn6v, ecs.i2, ecs.r1, ecs.re4, ecs.re4e, ecs.sccg5, ecs.sccgn6, ecs.scch5, ecs.g5, ecs.c5, ecs.r5, ecs.t5, ecs.sn2ne, ecs.se1ne, and ecs.sn1ne. For more information, see Instance families.
After you associate EIPs with a secondary ENI in multi-EIP-to-ENI mode and associate the secondary ENI with an ECS instance, you must enable Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) for the ECS instance. Otherwise, the multi-EIP-to-ENI mode does not take effect.
Call the DescribeEipGatewayInfo operation to query the gateways and subnet masks of the EIPs. For more information, see DescribeEipGatewayInfo.
Log on to the ECS instance and configure the EIPs for the ECS instance. For more information, see Configure EIPs for an ECS instance that runs Windows and Configure EIPs for an ECS instance that runs Linux.
ImportantThe preceding topics describe how to configure secondary private IP addresses for ECS instances. You can follow the same procedure to configure EIPs for ECS instances. However, you must specify the gateways and subnet masks of EIPs instead of the gateways and subnet masks of secondary private IP addresses.
After you configure the EIPs for the ECS instance, you can run the ifconfig or ipconfig command to query the EIPs.
FAQ
Am I charged an EIP configuration fee (public IP retention fee) after I associate an EIP with a secondary ENI?
You are not charged an EIP configuration fee (public IP retention fee) for subscription EIPs.
You are charged an EIP configuration fee (public IP retention fee) if you associate a pay-as-you-go EIP with a secondary ENI.
Do I need to perform additional configurations after I associate an EIP with an ENI and associate the ENI with an ECS instance?
If applications that provide services, such as websites, are deployed on the ECS instance, you do not need to configure routes on the ECS instance or in the VPC. The EIP associated with the secondary ENI can be used to provide services.
If you want the ECS instance to access the Internet, you must configure the default route of the ECS instance or create specific routes for the ECS instance. By default the primary ENI is used to forward packets to the Internet. You can adjust route priorities to use the secondary ENI to forward packets. You can also create specific routes to forward packets to the Internet from multiple ENIs or a random ENI to implement load balancing.
For more information, see Configure routes.
References
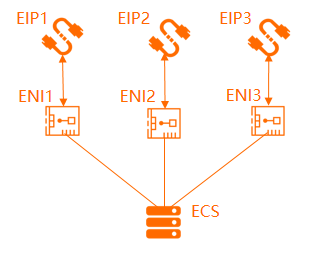
Associate multiple EIPs with an ECS instance in NAT mode: If multiple applications are hosted on an ECS instance and each application needs to use an independent public IP address, you can associate multiple EIPs with an ECS instance by using a secondary ENI in NAT mode. This way, the ECS instance is associated with multiple EIPs.
Expose an EIP on an NIC by adding a secondary CIDR block to a VPC: We recommend that you use the secondary CIDR block feature to expose an EIP on an NIC.
AssociateEipAddress: associates an EIP with an instance in the same region.