Tair (Redis OSS-compatible) is a database service that is compatible with the open-source Redis protocol and provides hybrid storage of memory and disks. It is built on a highly reliable active-active architecture and a smoothly scalable cluster architecture to meet business requirements for high throughput, low latency, and flexible configuration changes. You can use Data Transmission Service (DTS) to synchronize a Codis cluster to a Tair (Redis OSS-compatible) instance.
Prerequisites
You have created a target Tair (Redis OSS-compatible) instance (version 4.0, 5.0, or 6.0). For more information, see Create a Redis instance.
The available storage space on the target Tair (Redis OSS-compatible) instance must be greater than the storage space used by the source Codis database.
Each master node in the source Codis cluster must be able to execute the
psynccommand.The repl-timeout parameter specifies the replication timeout period between the slave and master nodes of the source Redis instance. The default value is 60 seconds. We recommend that you run the
config set repl-timeout 600command to set the value to 600 seconds. If the source database has a large data volume, you can increase the value of the repl-timeout parameter.
Synchronization principles
DTS synchronizes an entire Codis cluster by synchronizing each of its Codis-Groups. You must create a separate data synchronization task for each Codis-Group.
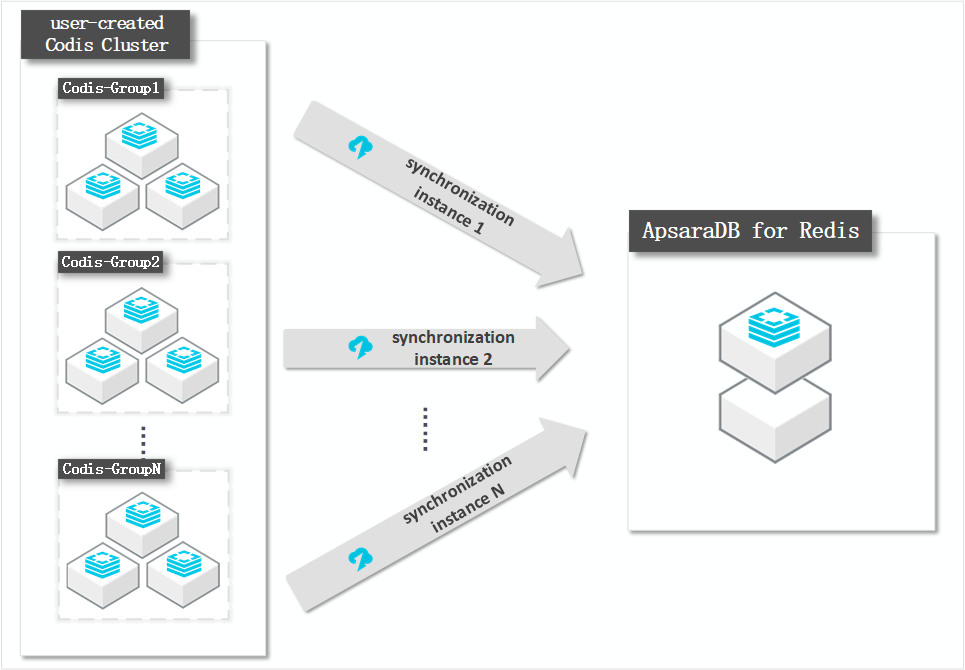
Architecture of the Codis cluster
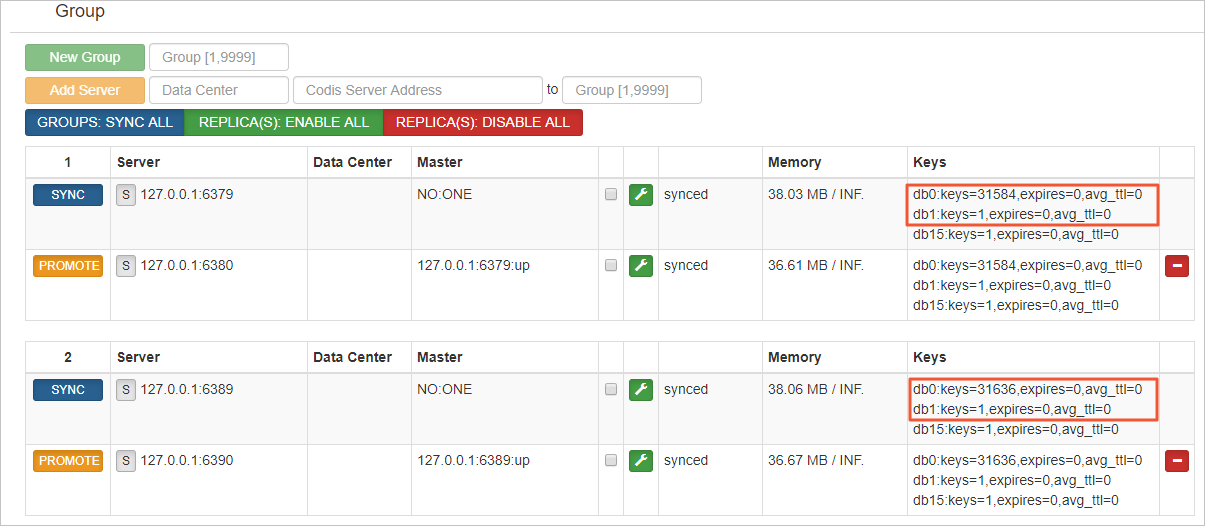
In this example, the Codis cluster has two Codis-Groups. Each Codis-Group uses a master-replica architecture, as shown in the following figure.
Precautions
DTS uses the resources of the source and destination instances during initial full data synchronization. This may increase the loads on the database servers. If you synchronize a large volume of data or if the server specifications cannot meet your requirements, database services may become unavailable. Before you synchronize data, evaluate the impact of data synchronization on the performance of the source and destination instances. We recommend that you synchronize data during off-peak hours.
If the
bindparameter is configured in the redis.conf file of the source Redis database, you must set the value of this parameter to the internal IP address of the ECS instance. The setting ensures that DTS can connect to the source database.To ensure the stability of the synchronization link, increase the value of the
repl-backlog-sizeparameter in the redis.conf file of the source cluster.To ensure synchronization quality, DTS inserts a key named
DTS_REDIS_TIMESTAMP_HEARTBEATinto the source cluster. This key is used to record the update timestamp.Do not run the
FLUSHDBorFLUSHALLcommands on the source cluster. If you do, data inconsistency occurs between the source and destination databases.By default, the maxmemory-policy parameter that specifies how data is evicted is set to volatile-lru for Tair (Redis OSS-compatible) instances. If the destination instance has insufficient memory, data inconsistency may occur between the source and destination instances due to data eviction. In this case, the data synchronization task does not stop running.
To prevent data inconsistency, we recommend that you set maxmemory-policy to noeviction for the destination instance. This way, the data synchronization task fails if the destination instance has insufficient memory, but data loss can be prevented for the destination instance.
NoteFor more information about data eviction policies, see What is the default eviction policy?
If an expiration policy is enabled for specific keys in the source database, these keys may not be deleted at the earliest opportunity after they expire. Therefore, the number of keys in the destination database may be less than that in the source database. You can run the INFO command to view the number of keys in the destination database.
NoteThe number of keys that do not have the expiration policy enabled or have not expired is the same between the source and destination databases.
The target Tair (Redis OSS-compatible) instance must be version 4.0, 5.0, or 6.0. If you want to synchronize data across versions, you can only synchronize from a lower version to a higher version. You must confirm compatibility in advance. For example, you can create a pay-as-you-go Redis instance for testing. After the test is complete, you can release the instance or convert it to a subscription instance.
If the destination instance is a cluster instance and a shard reaches its memory limit, or if the destination instance has insufficient storage space, the DTS task fails with an out of memory (OOM) error.
You cannot use DTS to synchronize data if Transparent Data Encryption (TDE) is enabled on the destination instance.
Billing
| Synchronization type | Task configuration fee |
| Schema synchronization and full data synchronization | Free of charge. |
| Incremental data synchronization | Charged. For more information, see Billing overview. |
Supported synchronization topologies
One-way one-to-one synchronization
One-way one-to-many synchronization
One-way cascade synchronization
For more information, see Synchronization topologies.
Supported synchronization commands
APPEND
BITOP, BLPOP, BRPOP, BRPOPLPUSH
DECR, DECRBY, DEL
EVAL, EVALSHA, EXEC, EXPIRE, EXPIREAT
GEOADD, GETSET
HDEL, HINCRBY, HINCRBYFLOAT, HMSET, HSET, HSETNX
INCR, INCRBY, INCRBYFLOAT
LINSERT, LPOP, LPUSH, LPUSHX, LREM, LSET, LTRIM
MOVE, MSET, MSETNX, MULTI
PERSIST, PEXPIRE, PEXPIREAT, PFADD, PFMERGE, PSETEX, PUBLISH
RENAME, RENAMENX, RESTORE, RPOP, RPOPLPUSH, RPUSH, RPUSHX
SADD, SDIFFSTORE, SELECT, SET, SETBIT, SETEX, SETNX, SETRANGE, SINTERSTORE, SMOVE, SPOP, SREM, SUNIONSTORE
ZADD, ZINCRBY, ZINTERSTORE, ZREM, ZREMRANGEBYLEX, ZUNIONSTORE, ZREMRANGEBYRANK, ZREMRANGEBYSCORE
PUBLISH operations cannot be synchronized.
If you run the EVAL or EVALSHA command to call Lua scripts, DTS cannot identify whether these Lua scripts are executed on the destination instance. This is because the destination instance does not explicitly return the execution results of Lua scripts during incremental data synchronization.
When DTS runs the SYNC or PSYNC command to transfer data of the LIST type, DTS does not clear the existing data in the destination instance. As a result, the destination instance may contain duplicate data records.
Procedure
Create a migration job.
Log on to the Data Transmission Service console.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose Data Synchronization.
In the top navigation bar, select the region where the ECS instance is located.
On the page that appears, click Create Task.
Configure the source and destination databases.
Category
Configuration
Description
Task
Task Name
The name of the DTS sync task.
Source Database
Database Type
On the NoSQL database tab, select Tair/Redis.
Access Method
Select Self-managed Database on ECS.
Instance Region
Select the region where the ECS instance was created.
Replicate Data Across Alibaba Cloud Accounts
DTS supports data synchronization between instances that belong to different Alibaba Cloud accounts. In this example, the instances are under the same account.
ECS Instance ID
Select the ID of the ECS instance that hosts the master node of the Codis-Group.
NoteDTS synchronizes the entire cluster by synchronizing each Codis-Group. First, enter the ECS instance ID for the master node of the first Codis-Group. When you configure the sync task for the second Codis-Group, enter the ECS instance ID for its master node, and so on, until you configure sync tasks for all Codis-Groups.
Instance Mode
Basic Edition.
NoteBecause of the special architecture of a Codis cluster, you cannot synchronize the entire cluster at once. DTS synchronizes the cluster by synchronizing each Codis-Group. Therefore, you must select Standalone.
Port Number
The database port.
Authentication Method
Password Login.
Database Password
Enter the database password of the master node.
NoteThis parameter is optional. If no password is set, you can leave this empty.
Encryption
The connection method. You can select Non-encrypted connection or SSL-encrypted connection. In this example, select Non-encrypted.
Destination Database
Database Type
Tair/Redis is automatically selected.
Access Method
Select Alibaba Cloud Instance.
Instance Region
Select the region where the destination cloud instance was created.
Replicate Data Across Alibaba Cloud Accounts
DTS supports data synchronization between instances that belong to different Alibaba Cloud accounts. In this example, the instances are under the same account.
Instance Type
Select the instance type.
Instance ID
Select the target Tair (Redis OSS-compatible) instance ID.
Authentication Method
Password Login.
Database Password
Enter the database password that you set for the cloud instance.
NoteThe database password must be in the <user>:<password> format. For example, if the custom username of the Redis instance is admin and the password is Rp829dlwa, enter admin:Rp829dlwa.
Encryption
The connection method. You can select Non-encrypted connection or SSL-encrypted connection. In this example, select Non-encrypted.
Click Test Connectivity and Proceed.
In the CIDR Blocks of DTS Servers dialog box, click Conform authorization and test link.
Configure task objects.
Configure objects:
For Synchronization Types, Full Data Synchronization + Incremental Data Synchronization is checked by default and cannot be modified.
For Processing Mode of Conflicting Tables, select Precheck and Report Errors.
In the Source Objects box, select the database to migrate, check Select All, and then click
 to move it to the Selected Objects box. Then, click Next Advanced Settings.
to move it to the Selected Objects box. Then, click Next Advanced Settings.
Advanced configurations: Keep the default settings and click Next Data Verification.
Data verification: check Full Data Verification, and then click Next: Save Task Settings and Precheck.
Configure objects:
For Synchronization Types, Full Data Synchronization + Incremental Data Synchronization is checked by default and cannot be modified.
For Processing Mode of Conflicting Tables, select Precheck and Report Errors.
In the Source Objects box, select the database to migrate, check Select All, and then click
 to move it to the Selected Objects box. Then, click Next Advanced Settings.
to move it to the Selected Objects box. Then, click Next Advanced Settings.
After the Precheck Success Rate reaches 100%, click Next: Purchase Instance.
On the Pay-As-You-Go tab, select the Instance Class for the data migration instance (this example uses micro). Select Data Transmission Service (Pay-as-you-go) Service Terms, and click Buy and Start.
The migration task begins.
Click the migration task ID to go to the task details page. On the details page, click Task Management in the navigation pane on the left to view the progress. When full migration is complete and incremental synchronization is running, verify the data in Tair.
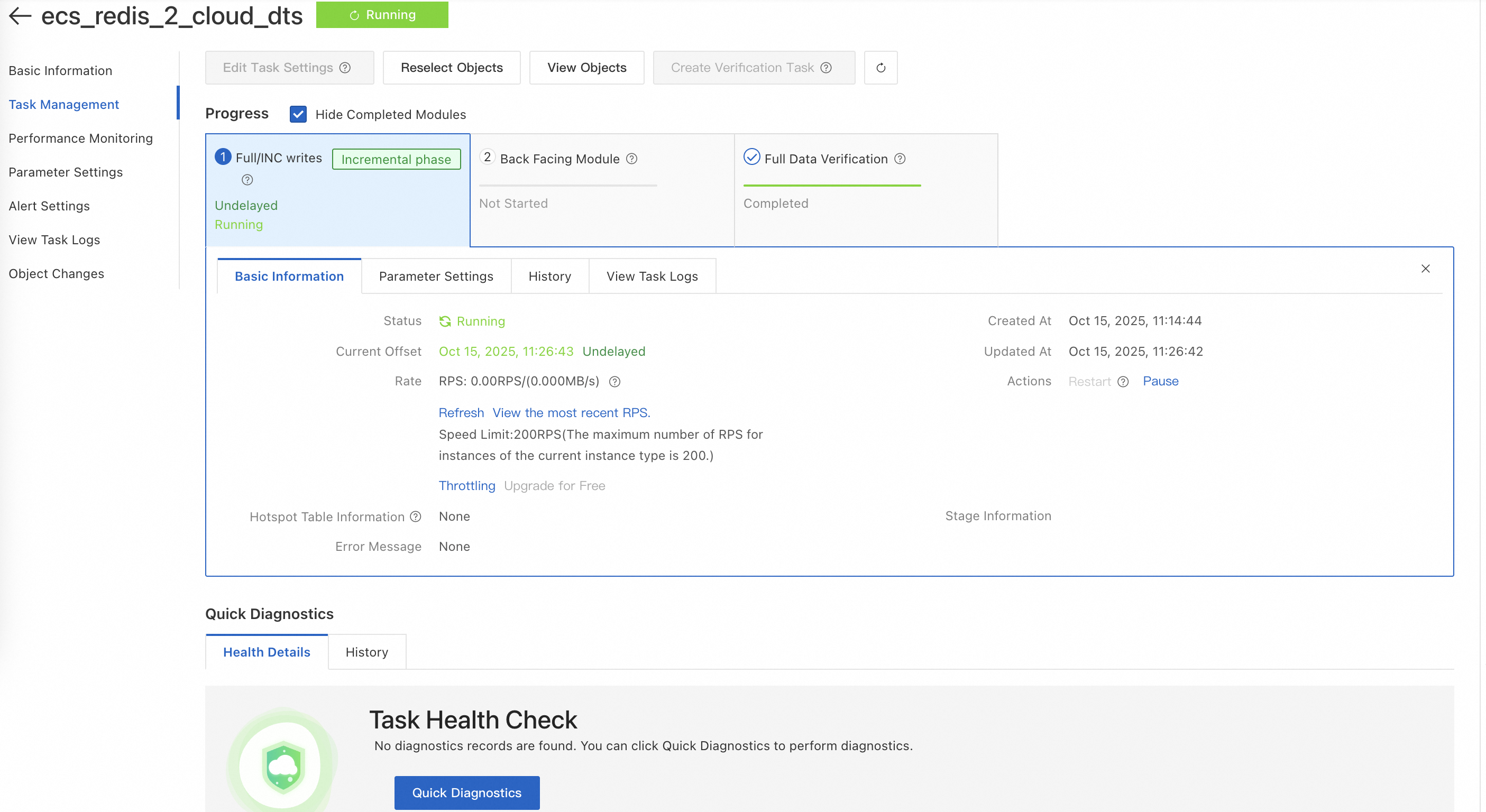 Note
NoteDTS synchronization tasks support cross-region data synchronization and migration. This solution uses data synchronization within the same region and VPC as an example to demonstrate how to achieve data consistency. For more information, see Synchronization solution overview.
Repeat Step 1 to Step 8 to create data synchronization tasks for the remaining Codis-Groups.
Result
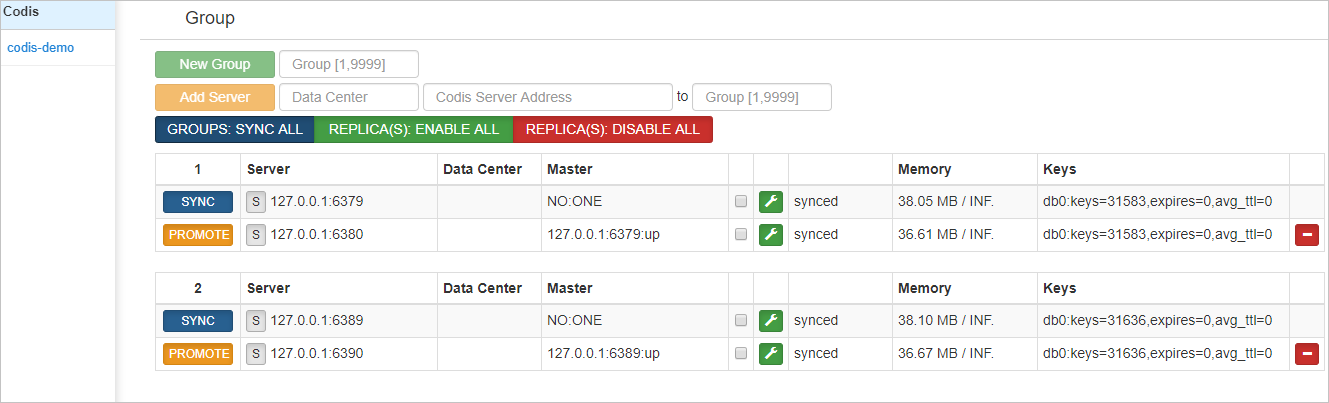
In this example, the Codis cluster has two Codis-Groups, so two data synchronization tasks are created. As shown in the following figure, after the initial synchronization is complete, both tasks are in the Synchronizing state.
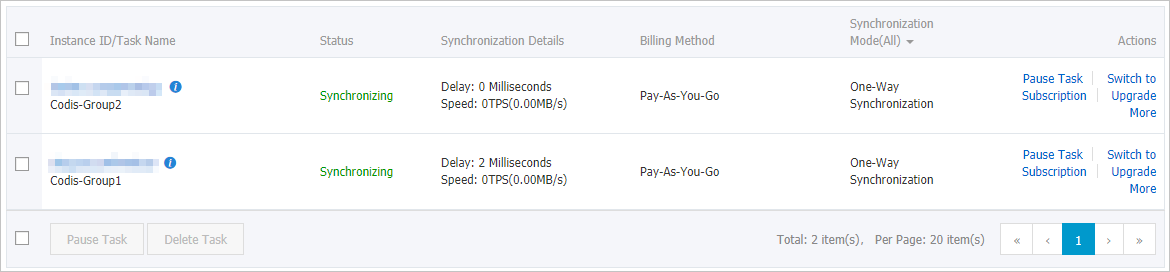
In this example, databases DB0 and DB1 are synchronized. After you log on to the Redis instance using DMS, you can see that the total number of keys is the same as that in the source Codis cluster.
Figure 1. Tair (Redis OSS-compatible) instance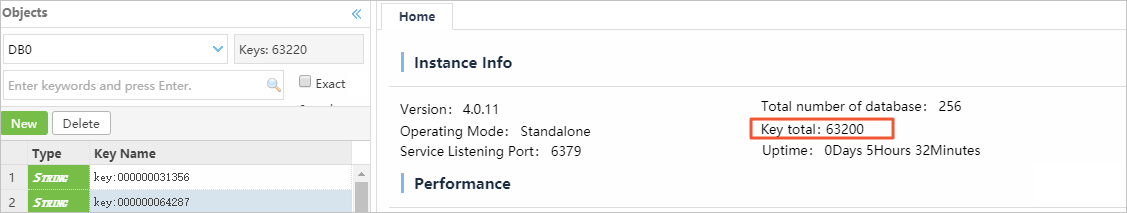
Figure 2. Source Codis cluster