This topic describes how to configure two-way data synchronization between Tair (Redis OSS-Compatible) Enhanced Edition instances by using Data Transmission Service (DTS). This feature is applicable to scenarios such as active geo-redundancy and geo-disaster recovery.
Prerequisites
The source and destination instances are Tair (Redis OSS-Compatible) Enhanced Edition instances that run Redis 5.0.
An ESSD/SSD-based instance of Tair (Redis OSS-Compatible) Enhanced Edition cannot be configured as the source instance.
If a persistent memory-optimized instance of Tair (Redis OSS-Compatible) Enhanced Edition is configured as the source instance, you must set the appendonly parameter to yes.
Tair (Redis OSS-Compatible) Enhanced Edition supports the cluster, standard, and read/write splitting architectures.
Precautions
During two-way data synchronization, the data synchronization task in the forward direction performs full data synchronization and incremental data synchronization. The data synchronization task in the reverse direction performs only incremental data synchronization.
WarningTo ensure data consistency, do not modify or write data to the same key in the source and destination databases when the two-way data synchronization tasks are running.
DTS uses the resources of the source and destination databases during full data synchronization. This may increase the loads of the database servers. If you synchronize large amounts of data or the server specifications cannot meet your requirements, the database services may become unavailable. Before you synchronize data, evaluate the impacts of data synchronization on the performance of the source and destination instances. We recommend that you synchronize data during off-peak hours.
We recommend that you do not run the
FLUSHDBorFLUSHALLcommand in the source instance during data synchronization. If you run one of the commands, data inconsistency may occur between the source and destination instances.By default, the maxmemory-policy parameter that specifies how data is evicted is set to volatile-lru for Tair (Redis OSS-compatible) instances. If the destination instance has insufficient memory, data inconsistency may occur between the source and destination instances due to data eviction. In this case, the data synchronization task does not stop running.
To prevent data inconsistency, we recommend that you set maxmemory-policy to noeviction for the destination instance. This way, the data synchronization task fails if the destination instance has insufficient memory, but data loss can be prevented for the destination instance.
NoteFor more information about data eviction policies, see What is the default eviction policy of Tair?
If an expiration policy is enabled for specific keys in the source database, these keys may not be deleted at the earliest opportunity after they expire. Therefore, the number of keys in the destination database may be less than that in the source database. You can run the INFO command to view the number of keys in the destination database.
NoteThe number of keys that do not have the expiration policy enabled or have not expired is the same between the source and destination databases.
If the direct connection mode is disabled for the destination Tair (Redis OSS-Compatible) instance, DTS uses the proxy mode to write data to the destination instance.
NoteFor more information about how to enable the direct connection mode for an instance, see Enable the direct connection mode.
During data synchronization, if the number of shards in the source or destination Tair (Redis OSS-Compatible) instance is increased or decreased, or if you change the specifications of the source or destination instance, such as scaling up the memory capacity, you must reconfigure the data synchronization task. To ensure data consistency, we recommend that you clear the data that has been synchronized to the source and destination Tair (Redis OSS-Compatible) instances before you reconfigure the data synchronization task.
During data synchronization, the endpoint of the source or destination Tair (Redis OSS-Compatible) instance may be changed. For example, the endpoint of the source or destination instance is changed if the zone of the instance is changed or the network type is changed from classic network to Virtual Private Cloud (VPC). In this case, you must reconfigure the data synchronization task.
Limits on synchronizing data from a standalone Tair (Redis OSS-Compatible) instance to an Tair (Redis OSS-Compatible) cluster instance: Each command can be run only on a single slot in an Tair (Redis OSS-Compatible) cluster instance. If you perform operations on multiple keys in the source database and the keys belong to different slots, the following error occurs:
CROSSSLOT Keys in request don't hash to the same slotWe recommend that you perform operations on only one key during data synchronization. Otherwise, the data synchronization task is interrupted.
If the destination instance is deployed in a cluster architecture and the amount of memory used by a shard in the destination instance reaches the upper limit, or if the available storage space of the destination instance is insufficient, the data synchronization task fails due to out of memory (OOM).
If the transparent data encryption (TDE) feature is enabled for the source or destination instance, you cannot use DTS to synchronize data.
A two-way data synchronization instance contains a forward synchronization task and a reverse synchronization task. If an object is to be synchronized in both the forward and reverse synchronization tasks when you configure or reset the instance, the following rules apply:
Only one of the tasks can synchronize both the full data and incremental data of the object. The other task synchronizes only the incremental data of the object.
The source data of the current task can be synchronized only to the destination of the task. The synchronized data is not used as the source data of the other task.
Billing
| Synchronization type | Task configuration fee |
| Schema synchronization and full data synchronization | Free of charge. |
| Incremental data synchronization | Charged. For more information, see Billing overview. |
Commands that can be synchronized
APPEND
BITOP, BLPOP, BRPOP, and BRPOPLPUSH
DECR, DECRBY, and DEL
EVAL, EVALSHA, EXEC, EXPIRE, and EXPIREAT
GEOADD and GETSET
HDEL, HINCRBY, HINCRBYFLOAT, HMSET, HSET, and HSETNX
INCR, INCRBY, and INCRBYFLOAT
LINSERT, LPOP, LPUSH, LPUSHX, LREM, LSET, and LTRIM
MOVE, MSET, MSETNX, and MULTI
PERSIST, PEXPIRE, PEXPIREAT, PFADD, PFMERGE, and PSETEX
RENAME, RENAMENX, RPOP, RPOPLPUSH, RPUSH, and RPUSHX
SADD, SDIFFSTORE, SELECT, SET, SETBIT, SETEX, SETNX, SETRANGE, SINTERSTORE, SMOVE, SPOP, SREM, and SUNIONSTORE
UNLINK, ZADD, ZINCRBY, ZINTERSTORE, ZREM, ZREMRANGEBYLEX, ZUNIONSTORE, ZREMRANGEBYRANK, and ZREMRANGEBYSCORE
SWAPDB (This command cannot be synchronized if the source or destination instance is deployed in the cluster architecture.)
The PUBLISH command cannot be synchronized.
If you run the EVAL or EVALSHA command to call Lua scripts, DTS cannot identify whether these Lua scripts are executed on the destination database. This is because the destination database does not explicitly return the execution results of Lua scripts during incremental data synchronization.
When DTS runs the SYNC or PSYNC command to transfer data of the LIST type, DTS does not clear the existing data. As a result, the destination database may contain duplicate data records.
Permissions required for database accounts
Instance | Permissions and authorization method |
Source Tair (Redis OSS-Compatible) instance | The database accounts of the source and destination instances must have read and write permissions. For more information about how to grant permissions to an account, see Create and manage database accounts. |
Destination Tair (Redis OSS-Compatible) instance |
Procedure
Purchase a data synchronization instance. For more information, see Purchase a DTS instance.
ImportantOn the buy page, set the Source Instance parameter to Redis, the Destination Instance parameter to Redis, and the Synchronization Topology parameter to Two-way Synchronization.
Log on to the DTS console.
NoteIf you are redirected to the Data Management (DMS) console, you can click the
 icon in the
icon in the  to go to the previous version of the DTS console.
to go to the previous version of the DTS console.In the left-side navigation pane, click Data Synchronization.
In the upper part of the Synchronization Tasks page, select the region in which the destination instance resides.
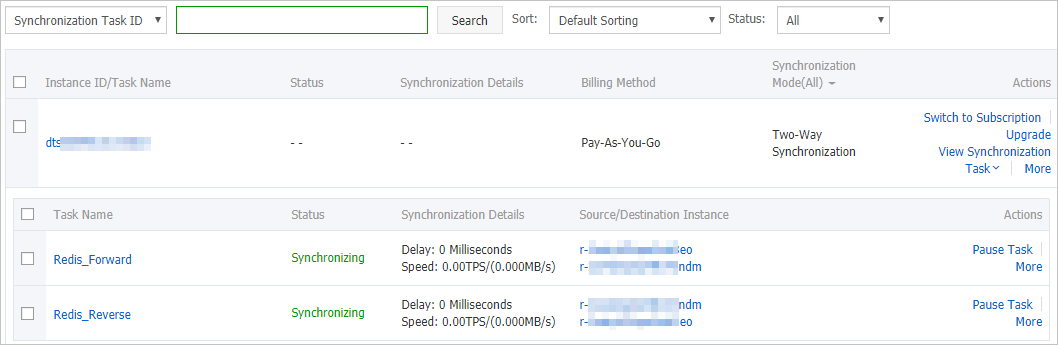
Configure the data synchronization task in the forward direction.
Find the data synchronization instance, and click Configure Task in the Actions column of the first data synchronization task.
ImportantA two-way data synchronization instance contains two data synchronization tasks. You must set parameters for each task. When you configure the second data synchronization task, find the task and click Configure Task in the Actions column.
Configure the source and destination instances.
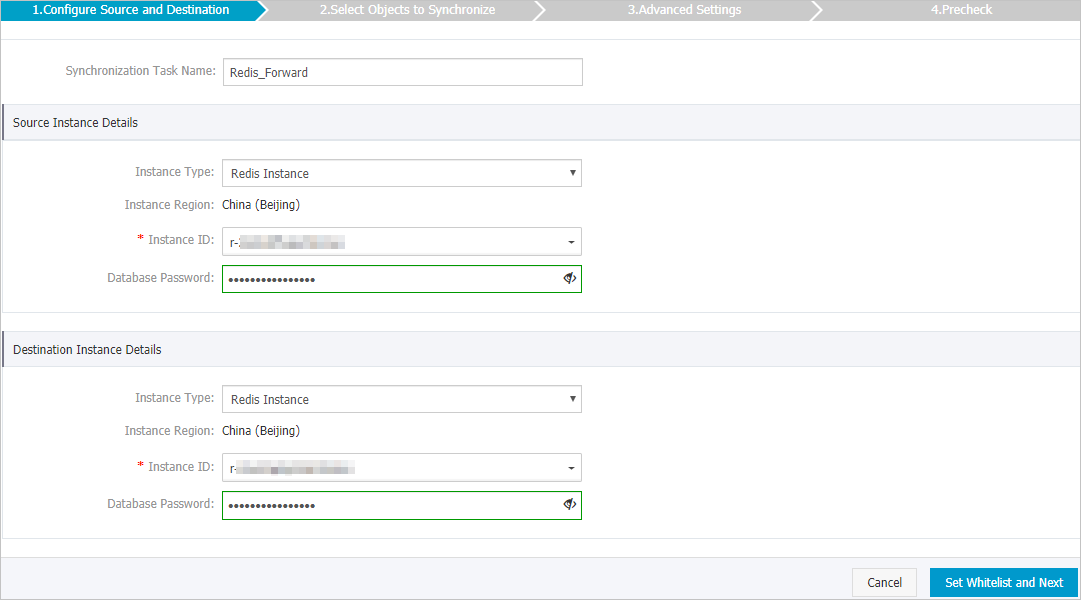
Section
Parameter
Description
N/A
Synchronization Task Name
The task name that DTS automatically generates. We recommend that you specify a name that can help you identify the task. You do not need to specify a unique task name.
Source Instance Details
Instance Type
The type of the source instance. Select Redis Instance.
Instance Region
The region of the source instance that you selected on the buy page. The value of this parameter cannot be changed.
Instance ID
The ID of the source Tair (Redis OSS-Compatible) instance.
ImportantWhen you configure the data synchronization task in the reverse direction, select the ID of the destination Tair (Redis OSS-Compatible) instance.
Database Password
The password of the database account of the source Tair (Redis OSS-Compatible) instance. For information about the permissions required for the database account, see Permissions required for database accounts.
ImportantThe database password is in the <user>:<password> format. For example, if the username of the account that you use to log on to the instance is admin and the password is Rp829dlwa, the database password is admin:Rp829dlwa.
Destination Instance Details
Instance Type
The type of the destination instance. Select Redis Instance.
Instance Region
The region of the destination instance that you selected on the buy page. The value of this parameter cannot be changed.
Instance ID
The ID of the destination Tair (Redis OSS-Compatible) instance.
ImportantWhen you configure the data synchronization task in the reverse direction, select the ID of the source Tair (Redis OSS-Compatible) instance.
Database Password
The password of the database account of the destination Tair (Redis OSS-Compatible) instance. For information about the permissions required for the database account, see Permissions required for database accounts.
ImportantThe database password is in the <user>:<password> format. For example, if the username of the account that you use to log on to the instance is admin and the password is Rp829dlwa, the database password is admin:Rp829dlwa.
In the lower-right corner of the page, click Set Whitelist and Next.
NoteYou do not need to modify the security settings of ApsaraDB instances, such as ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL and ApsaraDB for MongoDB instances, or self-managed databases that are hosted on Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instances. DTS automatically adds the CIDR blocks of DTS servers to the whitelists of ApsaraDB instances or the security group rules of ECS instances. For more information, see Add the CIDR blocks of DTS servers to the security settings of on-premises databases.
After data synchronization is complete, you can remove the CIDR blocks of DTS servers from the whitelists or security groups.
Select the synchronization policy and the objects to be synchronized.
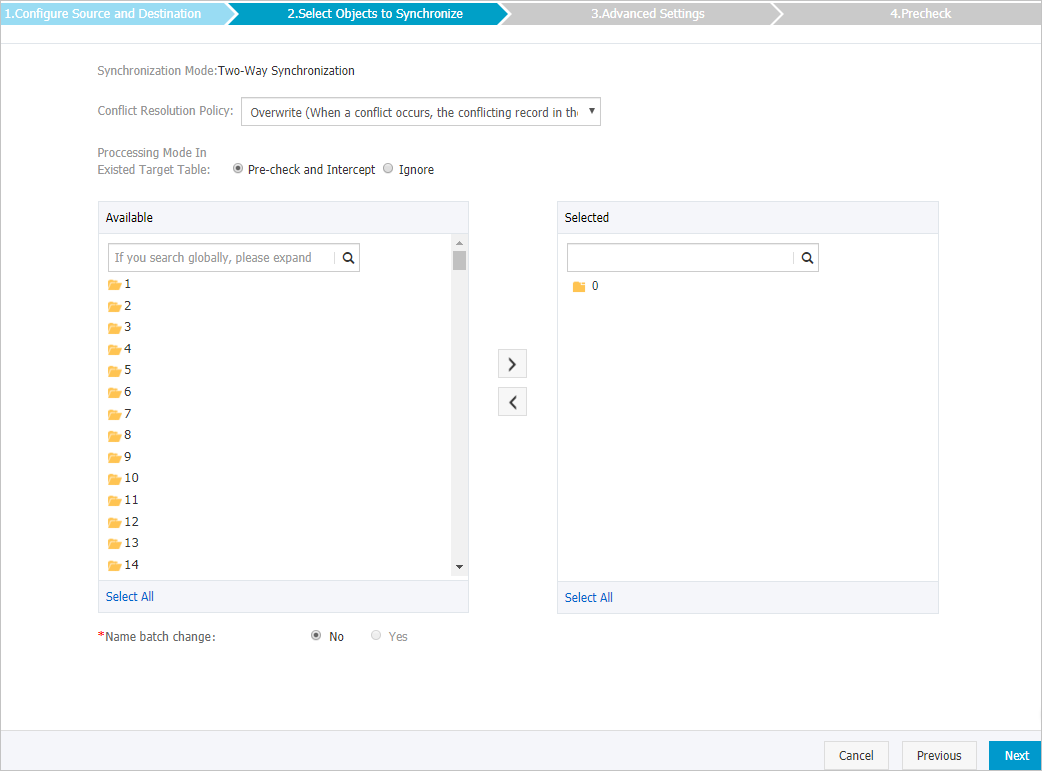
Setting
Parameter
Description
Select the synchronization policy
Conflict Resolution Policy
Overwrite (When a conflict occurs, the conflicting record in the destination instance is overwritten)
During data synchronization, if data records have the same key but different values, the data record with the latest key value overwrites the conflicting records.
Processing Mode In Existed Target Table
Pre-check and Intercept: checks whether the destination instance is empty. If the destination instance is empty, the precheck is passed. If the destination instance is not empty, an error is returned during the precheck and the data synchronization task cannot be started.
Ignore: skips the check for empty destination databases.
WarningIf you select Ignore, the data records in the source database overwrite the data records with the same keys in the destination database. Proceed with caution.
Select the objects to be synchronized
N/A
Select one or more databases from the Available section and click the
 icon to move the databases to the Selected section.
icon to move the databases to the Selected section. You can select only databases as the objects to be synchronized. Keys cannot be selected as the objects to be synchronized.
Rename databases and tables
N/A
In this scenario, you cannot rename the objects.
Specify whether to copy temporary tables to the destination database when DMS performs online DDL operations on the source tables
N/A
If you use DMS to perform online DDL operations on the source database, you can specify whether to synchronize temporary tables generated by online DDL operations.
Yes: DTS synchronizes the data of temporary tables generated by online DDL operations.
NoteIf online DDL operations generate a large amount of data, the data synchronization task may be delayed.
No: DTS does not synchronize the data of temporary tables generated by online DDL operations. Only the original DDL data of the source database is synchronized.
NoteIf you select No, the tables in the destination database may be locked.
Configure Retry Time for Failed Connections
N/A
By default, if DTS fails to connect to the source or destination database, DTS retries within the next 720 minutes (12 hours). You can specify the retry time based on your needs. If DTS reconnects to the source and destination databases within the specified time, DTS resumes the data synchronization task. Otherwise, the data synchronization task fails.
NoteWhen DTS retries a connection, you are charged for the DTS instance. We recommend that you specify the retry time based on your business needs. You can also release the DTS instance at your earliest opportunity after the source and destination instances are released.
In the lower-right corner of the page, click Next.
Select the initial synchronization types.
The value is set to Include full data + incremental data and cannot be changed. DTS synchronizes historical data from the source Tair (Redis OSS-Compatible) instance to the destination Tair (Redis OSS-Compatible) instance. Then, DTS synchronizes incremental data.
ImportantIf all the required objects have been synchronized from the source instance to the destination instance, the data synchronization task in the reverse direction synchronizes only incremental data.
If a version-related error message appears, you can upgrade the source Tair (Redis OSS-Compatible) instance to a specified version. For more information, see Upgrade the major version and Update the minor version of an instance.
In the lower-right corner of the page, click Precheck.
NoteBefore you can start the data synchronization task, DTS performs a precheck. You can start the data synchronization task only after the task passes the precheck.
If the task fails to pass the precheck, you can click the
 icon next to each failed item to view details.
icon next to each failed item to view details. After you troubleshoot the issues based on the details, initiate a new precheck.
If you do not need to troubleshoot the issues, ignore the failed items and initiate a new precheck.
Close the Precheck dialog box after the following message is displayed: Precheck Passed. Then, the data synchronization task in the forward direction starts.
Wait until initial forward synchronization is completed and the data synchronization task is in the Synchronizing state.
You can view the status of the data synchronization task on the Synchronization Tasks page.
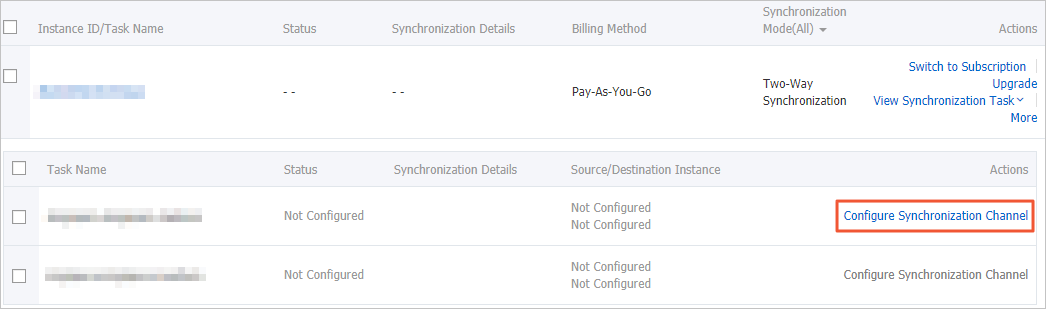
Configure the data synchronization task in the reverse direction.
Find the second data synchronization task and click Configure Synchronization Channel in the Actions column.
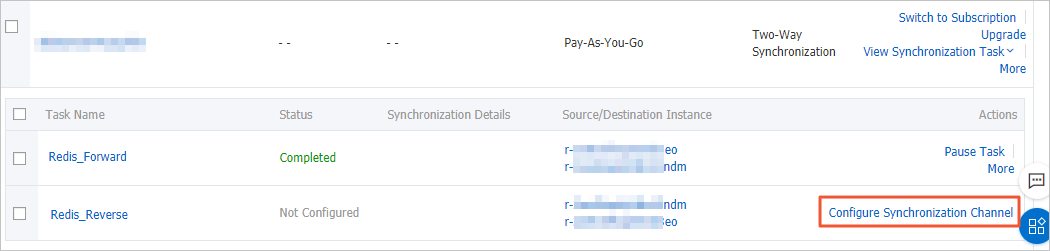
Repeat the substeps in Step 5.
Result
After a period of time, both data synchronization tasks are in the Synchronizing state.