This topic answers frequently asked questions (FAQs) about configuring DNS records.
FAQ
How do I point a domain name to a website server address?
Pointing a domain name to a website server is a process called domain name resolution. This process allows users to access a website service at an IP address using an easy-to-remember domain name. For more information, see Add a DNS record.
What record types does Alibaba Cloud DNS support?
Alibaba Cloud DNS supports the following record types:
Record type | Description and scenarios | Commonness score |
A record | Points a domain name to a specified IPv4 address. Often used for website domain name resolution. | 5 points. This is the most basic record type. Almost every domain name requires an A record. |
CNAME record | Points a domain name to another domain name. Often used for website resolution, CDN acceleration, enterprise email, and Global Traffic Manager. | 5 points. Alias pointing is common and versatile. Frequently used for CDN and cloud services. |
MX record | Specifies the mail server for a domain name and sorts servers by priority. | 4 points. Required for email-related services, but not needed otherwise. |
AAAA record | Points a domain name to a specified IPv6 address. Often used when a website needs to be accessed over an IPv6 address. | 4 points. IPv6 adoption is accelerating. In recent years, most cloud services have added default support for IPv6. |
TXT record | Used to identify and describe a domain name. Often used for domain ownership verification, digital certificates, SPF records (for anti-spam), and domain name retrieval. | 5 points. Commonly used for various verifications, such as SSL, SPF, email, and DNS. |
Explicit URL Forwarding, Implicit URL Forwarding | Points a domain name to an existing site. | 2 points. Supported by only some DNS providers. Mainly used for domain name redirection. |
NS record | Specifies the DNS servers that manage the DNS configuration for a domain name. Often used to delegate a subdomain to another DNS provider. | 3 points. Common for subdomain-level settings. Not changed frequently. |
SRV record | Identifies which server is running a specific service. Common in Microsoft's directory management systems. | 2 points. Required for instant messaging and enterprise service protocols. Rare for regular websites. |
CAA record | Specifies the authorized certification authorities (CAs) that can issue HTTPS certificates for a domain name. Used to prevent incorrect issuance of HTTPS certificates and improve website security. | 2 points. Enhances security for certificate (SSL/TLS) management. Common in specific scenarios. |
PTR record | Maps an IP address to a domain name. A PTR record can be used to verify whether an IP address corresponds to a specific domain name. | 1 point. Mainly used for reverse DNS lookups, such as for mail servers. Rarely used for regular websites. |
SVCB record | Aims to improve service discovery by providing protocol and endpoint information. This optimizes client connection decisions and improves performance and security. | 1 point. An emerging protocol used by HTTP/3, QUIC, and others. Currently uncommon. |
HTTPS record | A specialized version of the SVCB record, specifically for describing HTTPS services. | 1 point. A new standard for HTTPS optimization. Browser support is gradually being added. Not yet common for regular websites. |
For more information, see Add a DNS record.
Does Alibaba Cloud DNS support port resolution?
No, it does not. Common record types such as A, AAAA, and CNAME only map domain names to IP addresses and do not include port information. This means api.example.com can resolve only to 1.1.x.x. To access the service, you must specify the port in the client URL, such as http://api.example.com:8080/. If you do not want to display the port in the domain name, you can hide it by setting up an Nginx reverse proxy for HTTPS forwarding and port hiding.
Use URL forwarding
The URL forwarding record type supports forwarding domain name requests to another URL, which can be in the format of domain name + port number. This method also works as a reverse proxy and is not covered by a Service-Level Agreement (SLA). We recommend that you set up an Nginx reverse proxy for HTTPS forwarding and port hiding.
Scenario: You have a domain name cloud-example.com. The service IP address is 1.1.x.x, and the service port is 8888. You have already configured a DNS record, and the service can be accessed at http://demo.cloud-example.com:8888. Or, you have not configured a DNS record, and the service can only be accessed at http://1.1.x.x:8888.
Goal: You want to access the service at http://www.cloud-example.com without the port number appearing in the URL.
Solution:
If the service can only be accessed at
http://1.1.x.x:8888, you must first configure a DNS record. For more information, see A record.Record Type
A
Host
demo.cloud-example.com
Record Value
1.1.x.x
After the DNS record takes effect, you can access the service at
http://demo.cloud-example.com:8888.Configure an Implicit URL Forwarding forwarding record. For more information, see URL forwarding.
Record Type
Implicit URL Forwarding
Host
www.cloud-example.com
Record Value
http://demo.cloud-example.com:8888
NoteQ: Why not enter
http://1.1.x.x:8888directly as the record value?A: URL forwarding does not support URLs with IP addresses as record values.
This lets you access the service at
http://demo.cloud-example.com:8888by visitinghttp://www.cloud-example.com.
Does Alibaba Cloud DNS provide website building services?
Alibaba Cloud DNS provides domain name resolution services, which point your domain name to the IP address of your website server. If you need website building services, see Build a website on an ECS instance.
How do I configure DNS resolution for a domain name not registered with Alibaba Cloud?
If your domain name is not registered with Alibaba Cloud and you want to use Alibaba Cloud DNS for resolution, consider the following scenarios:
If your domain name is registered with another provider but has no DNS configuration, see Configure DNS for a domain name not registered with Alibaba Cloud.
If your domain name, registered with either Alibaba Cloud or another provider, is configured for DNS resolution with another provider and you want to migrate it to Alibaba Cloud DNS, see Smoothly migrate domain name resolution to Alibaba Cloud DNS.
How do I point a domain name to another site?
First, determine your requirement:
If you want users who visit domain name A to be redirected to domain name B, use URL forwarding.
If domain name A is an alias for domain name B and you want visiting domain name A to have the same effect as visiting domain name B, use a CNAME record.
For more information about adding a CNAME or URL record, see Add a DNS record.
What do 'host' and 'record value' mean?
Host: The host is the domain prefix that you add when you create a subdomain. To add a DNS record for the primary domain name, enter an at sign (@) for the host. For example, if your primary domain name is
example.comand you want visitors to usewww.example.com, enterwwwas the host.Record value: The record value is the specific value associated with the host. Its meaning depends on the record type. The following are examples of record values for common record types:
A record: The record value is an IPv4 address, such as
192.0.2.0.AAAA record: The record value is an IPv6 address, such as
2001:db8::.CNAME record: The record value is a domain name, such as
www.example.com.MX record: The record value is the domain name of a mail server, such as
mail.example.com. It usually includes a priority value, such as10 mail.example.com.NS record: The record value is the domain name of an authoritative DNS server, such as
ns1.example.com.
For more information about record types, see Add a DNS record.
Does Alibaba Cloud DNS support weighted round-robin?
Yes. When a domain name resolves to multiple IP addresses, you can use weighted round-robin to configure different weights for each IP address. This lets you distribute access traffic among the IP addresses in different proportions. You might use this feature to perform A/B testing by sending a small portion of traffic to a server with software changes. For instructions, see Configure weights.
Does Alibaba Cloud DNS support anycast networks?
Yes. Alibaba Cloud DNS uses a global anycast network of DNS servers to respond to user queries from the server closest to the user's geographic location. This provides users with lower query latency and allows changes to DNS records to take effect in seconds.
Does Alibaba Cloud DNS support Dynamic Domain Name System (DDNS)?
Dynamic Domain Name System (DDNS) is a service that binds a frequently changing public IP address to a fixed domain name in real time. This allows external networks to access your home or company network devices through the domain name at any time. Alibaba Cloud DNS does not currently support DDNS.
What is the default TTL for different DNS record types? Can I change these values?
The default Time to Live (TTL) for all DNS record types in Alibaba Cloud DNS is 10 minutes (600 seconds). You can change the TTL value. The minimum allowed TTL value varies by Alibaba Cloud DNS edition:
Free Edition/Personal Edition: The minimum TTL is 10 minutes (600 seconds).
Ultimate Edition: The minimum TTL is 1 second.
To modify the TTL value, see Configure TTL.
Are there limits on the number of hosted domain names and DNS records in Alibaba Cloud DNS?
Alibaba Cloud DNS does not limit the number of hosted primary domain names. The limits on DNS records are as follows:
A maximum of 100,000 DNS records can be added for a single primary domain name, including records for all its subdomains.
For the same host or subdomain on the same resolution line and with the same record type, the Free Edition of DNS allows a maximum of 10 DNS records, while the paid editions allow a maximum of 100 DNS records.
For explicit/implicit URL forwarding records, the Free Edition supports 2 records, the Personal Edition supports 5 records, and the Enterprise Edition supports 10 records.
The Premium Edition can exceed the preceding limits. For more information, see Version Comparison.
Does Alibaba Cloud DNS support wildcard entries (wildcard DNS)? If so, what types are supported?
For information about wildcard DNS support and how it takes effect, see Wildcard DNS.
What should I do if the DNS settings interface shows that the traffic limit for this period has been exceeded?
This occurs because the number of invocations during this period is high, which triggers global throttling. We recommend that you use a term query to avoid this issue.
A/AAAA records
What is IPv6? Does Alibaba Cloud DNS support IPv6?
IPv6 stands for Internet Protocol Version 6. It is the next-generation IP protocol designed by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) to replace IPv4. Because IPv4 has a limited number of network addresses, which severely restricts the application and development of the Internet, IPv6 not only solves the problem of network address scarcity but also removes barriers for various access devices to connect to the Internet.
Alibaba Cloud DNS supports IPv6. You can add an AAAA record in the DNS settings to allow visitors to access your website using an IPv6 address. In addition, the DNS servers in the Alibaba Cloud DNS server cluster fully support IPv6.
For more information, see Add a DNS record.
Can a subdomain point to multiple IP addresses?
Yes, you can point a subdomain to multiple IP addresses. This is often used to evenly distribute DNS query requests across multiple servers to reduce server load. Alibaba Cloud DNS lets you add multiple IP addresses for A/AAAA records. During a DNS query, Alibaba Cloud DNS returns a list of all configured IP addresses to the user's local DNS server. The local DNS server then decides which IP address to return to the visitor. To return addresses based on weights, see Configure weights.
Can one ECS instance resolve more than two domain names?
Yes. The IP address of an ECS server can support the resolution of multiple domain names. This means that different primary domain names or subdomains can all point to the same IP address. For more information about the configuration, see:
Are there any restrictions on the IP addresses that DNS records can point to?
No. The IP address can be any public or internal IP address. However, in real-world business scenarios, an internal IP address is not meaningful and is typically used only for testing.
Can I enter an IP address outside China for a DNS record?
You can directly enter an IP address from outside the Chinese mainland in the Record Value field. Alibaba Cloud DNS does not restrict whether the server IP address is inside or outside the Chinese mainland.
If a subdomain is configured with both an IPv6 address and an IPv4 address, how does DNS resolve it?
The DNS query result returns an IPv6 address only if the visitor's client machine supports the IPv6 protocol stack.
1. Example DNS record configuration:
Record Type | Host | Resolution Line | Record Value |
AAAA | www | Default | ff03:0:0:0:0:0:x:x |
A | www | Default | 1.1.x.x |
Resolution effect:
The visitor's client machine supports both IPv6 and IPv4: The client sends two resolution requests to the local DNS (one for the IPv6 address and one for the IPv4 address). The local DNS then sends two resolution requests to Alibaba Cloud DNS. Alibaba Cloud DNS returns the IPv6 and IPv4 addresses that the domain name points to. The client ultimately decides which address to return to the visitor. Typically, the IPv6 address is returned with priority.
The visitor's client machine supports only IPv6: The client sends a request for the IPv6 address to the local DNS. The local DNS then requests the IPv6 address from Alibaba Cloud DNS. Alibaba Cloud DNS returns the IPv6 address, and the client returns it to the visitor.
The visitor's client machine supports only IPv4: The client sends a request for the IPv4 address to the local DNS. The local DNS then requests the IPv4 address from Alibaba Cloud DNS. Alibaba Cloud DNS returns 1.1.x.x, and the client returns the resolved address 1.1.x.x to the visitor.
2. Example DNS record configuration:
Record Type | Host | Line parsing | Record Value |
AAAA | www | Outside China | ff03:0:0:0:0:0:x:x |
A | www | Default | 1.1.x.x |
The visitor's client machine supports both IPv6 and IPv4, and the visitor is from outside the Chinese mainland: The client sends two resolution requests to the local DNS (one for the IPv6 address and one for the IPv4 address). The local DNS also sends two resolution requests to Alibaba Cloud DNS. Alibaba Cloud DNS returns the IPv6 and IPv4 addresses that the domain name points to. The client ultimately decides which address to return to the visitor. Typically, the IPv6 address is returned with priority.
The visitor's client machine supports only IPv4, and the visitor is from outside the Chinese mainland: The client sends a request for the IPv4 address to the local DNS. The local DNS then requests the IPv4 address from Alibaba Cloud DNS. However, no IPv4 address is configured for the "Outside China" line in Alibaba Cloud DNS, so the resolution request cannot be completed.
The visitor's client machine supports only IPv4, and the visitor is from the Chinese mainland: The client sends a request for the IPv4 address to the local DNS. The local DNS then requests the IPv4 address from Alibaba Cloud DNS. Alibaba Cloud DNS returns the IPv4 address, and the client returns the resolved address 1.1.x.x to the visitor.
The visitor's client machine supports both IPv6 and IPv4, and the visitor is from the Chinese mainland: The client sends two resolution requests to the local DNS (one for the IPv6 address and one for the IPv4 address). The local DNS also sends two resolution requests to Alibaba Cloud DNS. However, only an IPv4 address is configured for the default line in Alibaba Cloud DNS. No IPv6 address is configured. Therefore, Alibaba Cloud DNS can only respond with the IPv4 address to the local DNS. The client then returns the resolved address 1.1.x.x to the visitor.
If a domain name resolves to multiple servers, can this achieve DNS load balancing?
Yes. When a domain name resolves to multiple server IP addresses, you can use weighted round-robin to configure different weights for each IP address. This lets you distribute access traffic among the IP addresses in different proportions. You can achieve a DNS load balancing effect by setting the weights to a 1:1 ratio. For instructions, see Configure weights.
How do I use an SDK to add an A record and set its weight?
Use addDomainRecord to add a DNS record. By default, A records use the polling mode.
Use SetDNSSLBStatus to enable or disable weighted round-robin. Set
Open=trueto enable weighted round-robin forAorAAAArecords.Obtain the
RecordIdof the DNS record and call UpdateDNSSLBWeight to modify the weight of the record.If you just added the DNS record in the first step, you can retrieve the
RecordIdfrom the return value.If the DNS record already exists, you can call DescribeDomainRecords to query the
RecordIdfrom the list of DNS records.
CNAME records
What is the difference between a CNAME record and URL forwarding?
A CNAME record is a type of DNS record that lets you point a domain name (an alias) to another domain name. URL forwarding redirects access requests for one domain name to another URL. This can be an internal redirect (implicit forwarding, usually implemented with an iframe) or an external redirect (explicit forwarding, usually using a 301 or 302 redirect) to the target address. The differences are as follows:
A CNAME record keeps the accessed domain name unchanged, while explicit URL forwarding changes the URL that is displayed in the address bar.
A CNAME record is suitable for situations where you need to map one domain name to another for a long time. URL forwarding is more suitable for temporary redirection, website migration, or scenarios where you want to hide the actual access address.
Why do I see a conflict error between A and CNAME records when adding a record?
A records and CNAME records cannot be added for the same host and the same request source line. We recommend that you use different hosts or different request source lines to create the A and CNAME records. For more information about other types of conflicts, see DNS record conflict rules.
Why do I see a conflict error between MX and CNAME records when adding a record?
In the DNS resolution process, different record types have different priorities. Therefore, for the same host and the same resolution line, some record types cannot coexist. This can create configuration risks and cause service unavailability. For more information, see DNS record conflict rules.
Can a CNAME record resolve to a specific path?
No. CNAME records are designed to map one domain name to another, not to a specific file path or directory.
Do I need to add a dot (.) at the end of a domain name when configuring DNS resolution?
No. The dot at the end of a domain name represents the root domain. Alibaba Cloud DNS automatically adds it on the backend, so you do not need to add it.
Why can't a CNAME record point to Baidu?
Most large websites, including Baidu, do not allow external domain names to point directly to their domains using CNAME records for security and abuse prevention reasons. To direct traffic to Baidu, we recommend that you use URL redirection (301 or 302) instead of a CNAME record.
Can I configure multiple CNAME records for a single domain name on a single line? How do DNS queries respond?
Yes, you can configure multiple CNAME records at the same time. They are returned based on their weights. For more information, see Configure weights.
TXT records
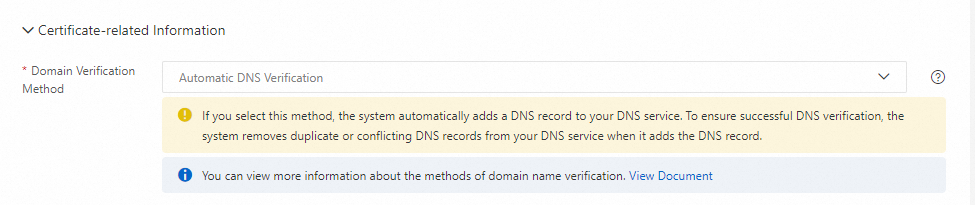
Why is there an extra TXT record in my DNS records?
When you use certain Alibaba Cloud products, a TXT record may be added for domain ownership verification. For example, if you are on the Alibaba Cloud SSL Certificates purchase page and select Automatic DNS Validation for the Domain Validation Method under Certificate Associated Information, the system automatically adds a TXT record for you. For more information, see How do I select a domain validation method?
MX records
What does the priority of an MX record mean?
If you have only one MX record, its priority is meaningless. Priority is relevant only when you have multiple MX records for your domain name. The sending mail server first tries to deliver the email to the server with the lowest MX priority number. If that server fails to receive the email, the sending server automatically tries the next server with the lowest priority, and so on, until the email is delivered successfully or all servers fail, which results in a delivery error.
Can I use a foreign trade mailbox for MX resolution?
Yes. For more information, see Configure mailbox resolution.
Why do I see a conflict error between MX and CNAME records when adding a record?
In the DNS resolution process, different record types have different priorities. Therefore, for the same host and the same resolution line, some record types cannot coexist. This can create configuration risks and cause service unavailability. For more information, see DNS record conflict rules.
How do I configure DNS resolution for a mailbox not hosted by Alibaba Cloud?
To configure DNS resolution for a mailbox not hosted by Alibaba Cloud, consider the following scenarios:
The domain name is registered with Alibaba Cloud, uses Alibaba Cloud DNS, and uses a non-Alibaba Cloud mailbox product.
Contact your mailbox provider to obtain a checklist of the DNS records that you need to configure. Then, see Configure mailbox resolution to configure them.
The domain name is registered with Alibaba Cloud, does not use Alibaba Cloud DNS, and uses a non-Alibaba Cloud mailbox product.
Contact your mailbox provider to obtain a checklist of the DNS records that you need to configure. Then, contact your DNS provider to configure them.
The domain name is not registered with Alibaba Cloud, uses Alibaba Cloud DNS, and uses a non-Alibaba Cloud mailbox product.
Contact your mailbox provider to obtain a checklist of the DNS records that you need to configure. Then, see Configure mailbox resolution to configure them.
NS records
When adding a subdomain, I need to add an NS record under the primary domain, but I get an 'NS record conflicts with subdomain' error. What should I do?
The 'NS record conflicts with subdomain' error usually occurs because multiple different types of DNS records exist at the same level. You can resolve this by carefully checking the existing DNS records, deleting the conflicting ones, and then adding the NS record. However, this operation may affect the resolution of other DNS records under the subdomain. For more information, see DNS record conflict rules.
URL forwarding
What is the difference between 301 and 302 redirection?
301 redirect: 301 means Permanently Moved.
302 redirect: 302 means Temporarily Moved.
Similarity: Both 301 and 302 status codes indicate a redirection. When a browser receives a 301 or 302 status code from the server, it redirects to a new URL. This new URL is obtained from the Location header in the response. The user sees their entered address A instantly change to another address B.
Difference: A 301 redirect indicates that the resource at the old address A has been permanently removed and is no longer accessible. Search engines crawl the new content and replace the old URL with the new one. A 302 redirect indicates that the resource at the old address A still exists and is accessible. The redirection from A to B is temporary. Search engines crawl the new content but keep the old URL.
After I add a URL forwarding record, the resolution result from a `dig` command does not match the console settings. Why?
When you add a URL forwarding record, Alibaba Cloud DNS automatically adds an A record for you. The A record points to the URL forwarding server address provided by Alibaba Cloud DNS. Therefore, if the record value that you added in the console is a URL, but the `dig` command returns an A record with an IP address such as 203.107.XX.XX, this is normal.
After I add a URL forwarding record, accessing the domain name displays an HTTP ERROR 502. Why?
If you receive a message that an ICP filing is required when you add the URL forwarding record, check whether both the source domain name and the target domain name have completed their ICP filings. If not, complete the ICP filing process.
If you have already added a URL forwarding record and encounter a 502 error, it may be because the ICP filing has become invalid.
When I add a URL forwarding record for a domain name, why do I get an error about an abnormal ICP filing?
When you add a URL forwarding record, the source domain name is resolved to an Alibaba Cloud forwarding server, which then handles the forwarding proxy. The Alibaba Cloud URL forwarding servers are deployed in the Chinese mainland. Therefore, the source domain name must have a valid ICP filing. The ICP filing does not have to be completed through Alibaba Cloud.
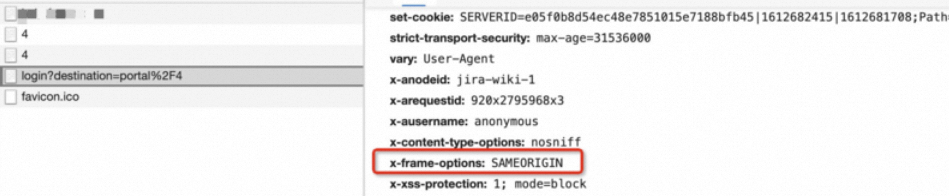
After I add an implicit URL forwarding record, accessing the domain name displays a blank page. Why?
You can see an error message in your browser, such as Chrome. This is because the X-Frame-Options header is set on the target site, which prevents it from being nested in a frame. Contact your website technician to remove the X-Frame-Options configuration from the target site.
After I add an implicit URL forwarding record, the page opens correctly, but the browser's address bar shows the target URL. Why?
Check the JavaScript code on the target URL page. If you find the code marked in the image below, remove it.

After I add a URL forwarding record, refreshing the page redirects to an incorrect address. Why?
This usually happens if the target page (the site at the forwarded URL) contains JavaScript code that sets up a redirect. Contact your website technician to investigate.
I added a URL forwarding record in Alibaba Cloud DNS, but a `dig` test does not return the corresponding A record and value. Why?
If a `dig` command for the source domain name does not return an IP address related to 203.107.XX.XX, submit a ticket for Alibaba Cloud DNS, and our technical staff will handle it for you.
After I add a URL forwarding record, opening the page displays an ERR_EMPTY_RESPONSE error. Why?
This usually occurs during a CC attack. Because the queries per second (QPS) for the domain name is too high, the URL forwarding server stops the forwarding service for that domain name. We recommend that you use another method to implement the forwarding service.
After I add a URL forwarding record, opening the page displays a 'Connection refused' error. Why?
Symptom: No interception information is displayed in the console.
Cause: The connection is blocked by a same-origin policy. Check the network path for the header of the last 200 OK response. It may contain a same-origin restriction.
Solution: This issue is usually caused by the security policy settings of your website. We recommend that you check your configuration or use only explicit URL forwarding.
How many URL forwarding records can I set?
The number of supported URL forwarding records varies by Alibaba Cloud DNS edition:
Free Edition: 2
Personal Edition: 5
Ultimate Edition: 10
Premium Edition: Unlimited
For more information about the differences between editions, see the URL Forwarding (Single Domain) comparison in Version Comparison.
Does URL forwarding support HTTPS configuration?
The source domain name for URL forwarding supports HTTP but not HTTPS. The target address supports both HTTP and HTTPS. To redirect HTTPS requests, you must install an SSL certificate on an intermediate server or use a service that supports automatic issuance of universal certificates. Due to certificate management, security, and other considerations, this feature is not supported. If you want to forward HTTPS requests, you must configure an HTTPS redirect on your source server. The following is an example configuration for Nginx:
server {
listen 443 ssl;
server_name yourdomain.com;
ssl_certificate /path/to/cert.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /path/to/cert.key;
return 301 https://targetsite.com$request_uri;
}Does URL forwarding support redirection with path parameters?
Explicit and implicit URL forwarding do not support configuration with parameters.
